Low-beryllium copper alloy metallographic corrosive agent and display method of metallographic structure of low-beryllium copper alloy
A technology of beryllium copper alloy and metallographic structure, which is applied in the field of metallographic sample preparation, can solve the problems of low beryllium copper alloy metallographic structure inspection, etc., and achieve the effect of simple process and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
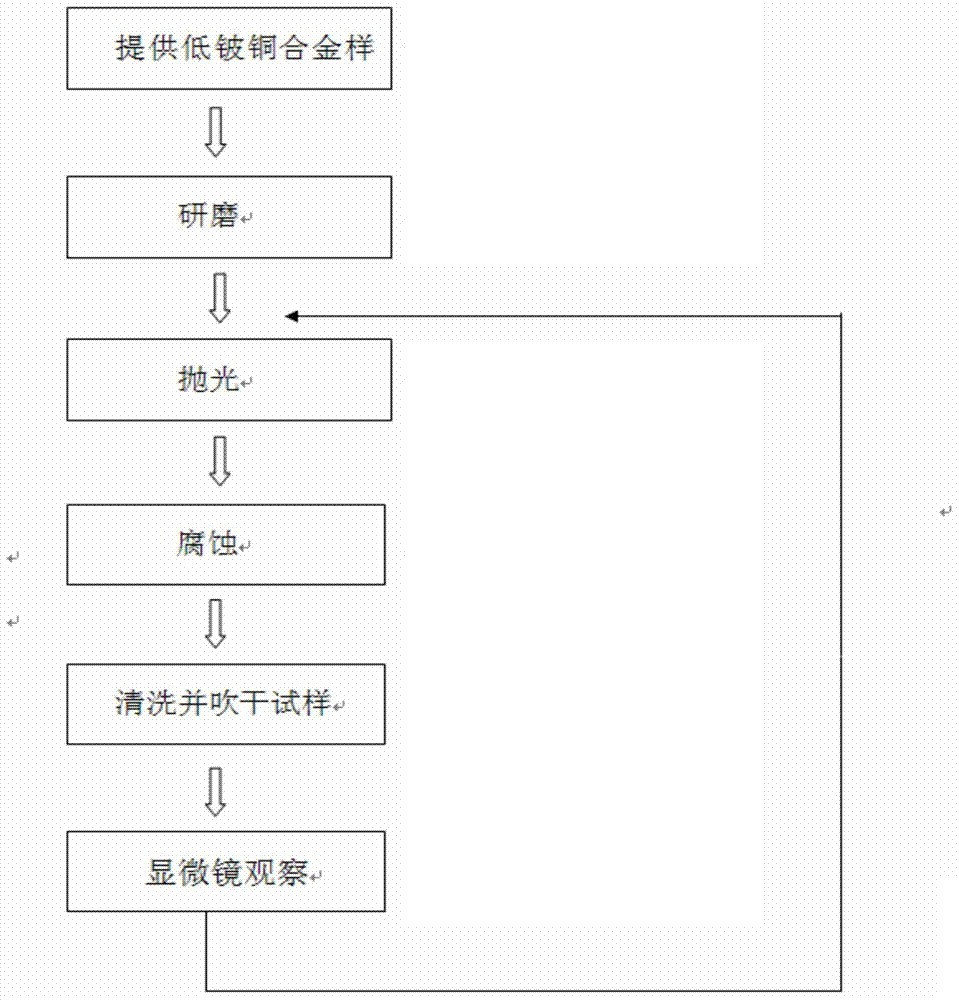
[0041] 1) Sampling
[0042] Provide a low beryllium copper alloy sample with a beryllium content of less than 1%, cut or cut a part of it as a sample, the length of the sample is less than 20mm, the width is less than 15mm, and the cross-sectional area of the circular cross section is less than 300mm 2 .
[0043] 2) grinding
[0044] Use silicon carbide water sandpaper or aluminum oxide water sandpaper, use water as a wetting agent, and use mesh numbers No.180, No.400, No.800 and No.1500 for grinding in turn, and rotate the sample after each change of sandpaper Grinding at 90 degrees until the rough scratches from the previous process are removed.
[0045] 3) polishing
[0046] Sprinkle or spray the polishing solution on the flannelette attached to the polishing machine for mechanical polishing. Use two polishing, that is, use 3 micron and 1 micron alumina polishing liquid (pure water and alumina suspension) to polish on the flannelette, or use other particle size polish...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Sampling, grinding, polishing and sample cleaning observation are the same as in Example 1.
[0057] In the corrosion process, first prepare the etchant according to the following ratio:
[0058] 9 water ferric nitrate 5.0g±0.1,
[0059] Chromium trioxide 0.5g±0.1,
[0060] Ethanol 75.0mL±5.0, analytically pure,
[0061] 27.5%-30% hydrogen peroxide 5.0mL±0.5,
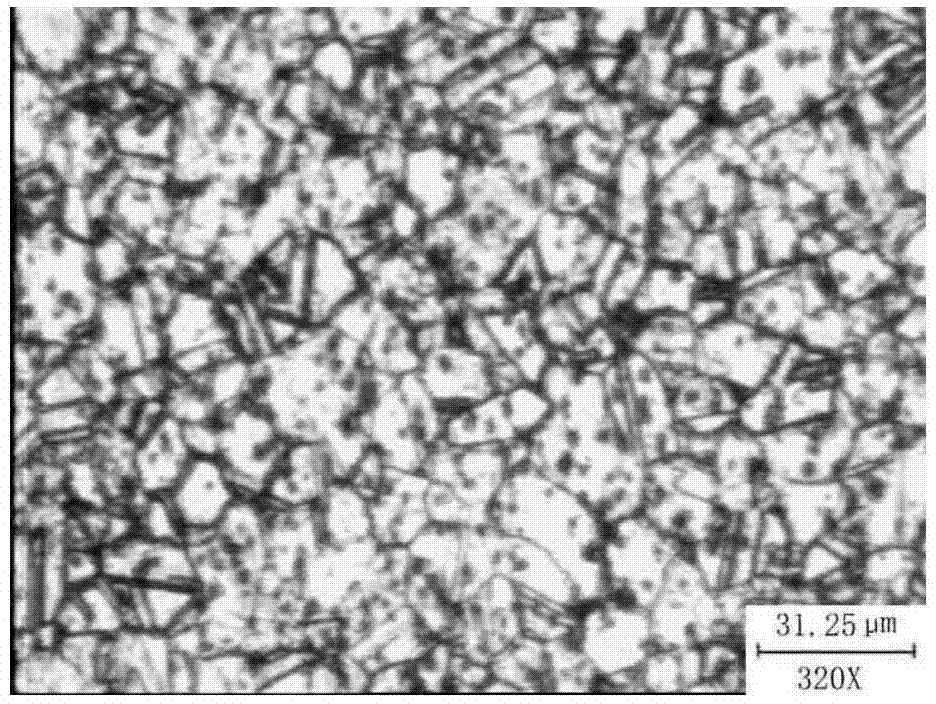
[0062] First weigh ferric nitrate and chromium trioxide, add ethanol and hydrogen peroxide successively, and stir with a glass rod until ferric nitrate and chromium trioxide are completely dissolved. After preparing the corrosive agent, use tweezers to hold the cotton wool and dip it into the corrosive agent, and wipe the surface of the polished sample. image 3 Microstructure picture of low beryllium copper alloy after quenching + aging shown for this method.
Embodiment 3
[0064] Sampling, grinding, polishing and sample cleaning observation are the same as in Example 1.
[0065] In the corrosion process, first prepare the etchant according to the following ratio:
[0066] Corrosive 1:
[0067] Ferric chloride 10g±0.1,
[0068] Potassium dichromate 0.5g±0.1,
[0069] 36%-38% hydrochloric acid 3ml±0.5,
[0070] Water 130-330mL±5,
[0071] First weigh ferric chloride and potassium dichromate, then add water and hydrochloric acid with a mass concentration of 36%-38% successively, and stir with a glass rod until the ferric chloride and potassium dichromate are completely dissolved.
[0072] Corrosive 2:
[0073] 25%-28% ammonia water 25.0mL±2.0,
[0074] 27.5%-30% hydrogen peroxide 5.0mL±0.5,
[0075] Water 25.0mL±2.0,
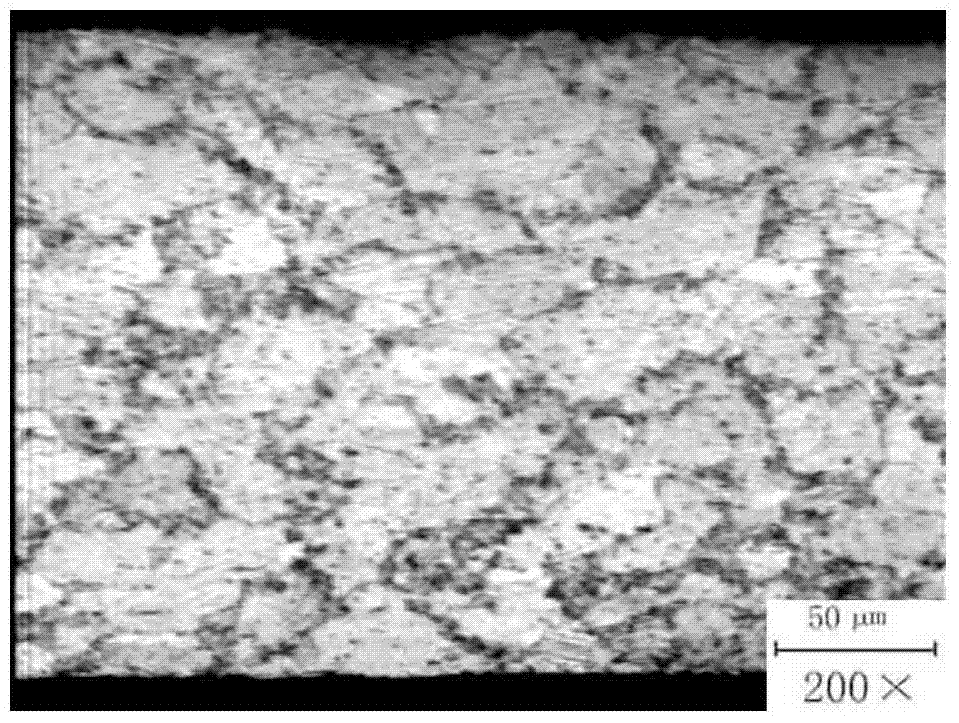
[0076] First use tweezers to hold the cotton wool and dip it in corrosive agent 1, wipe the surface of the polished sample for 15S-30s, rinse it with clean water, and then immerse it in corrosive agent 2 for 3-5s. Figure 4 It...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com