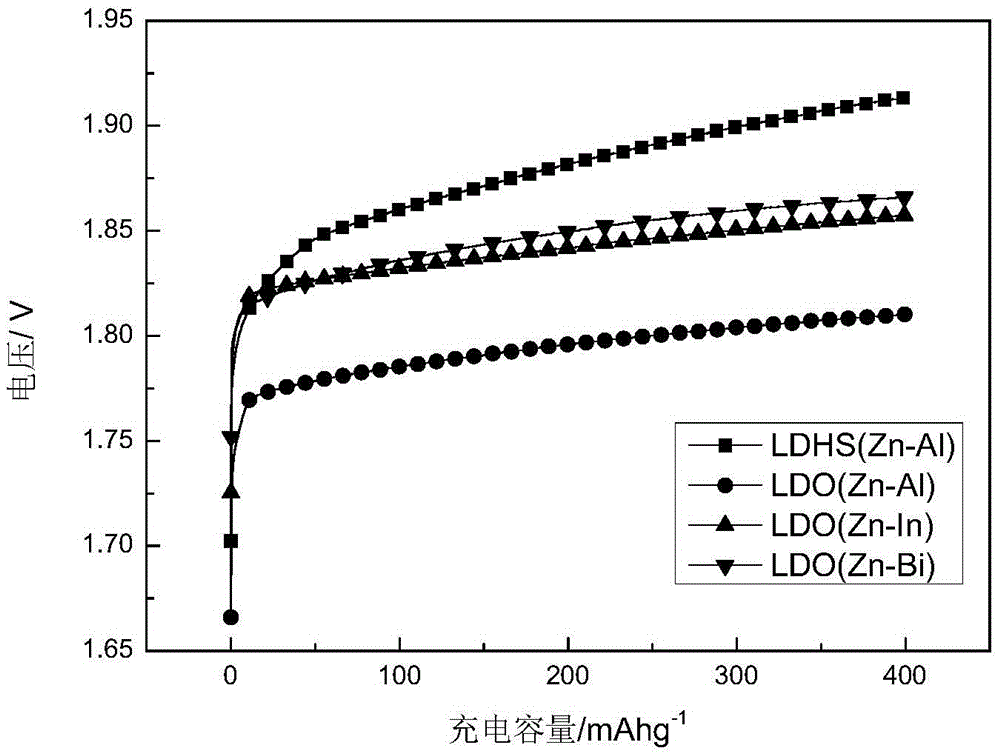
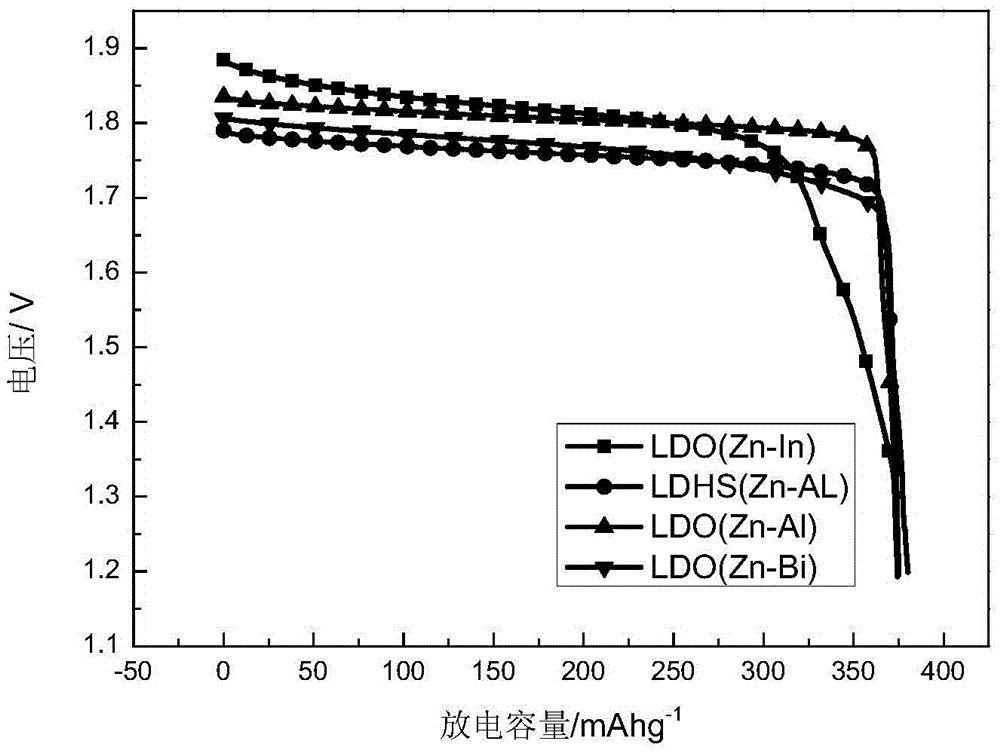
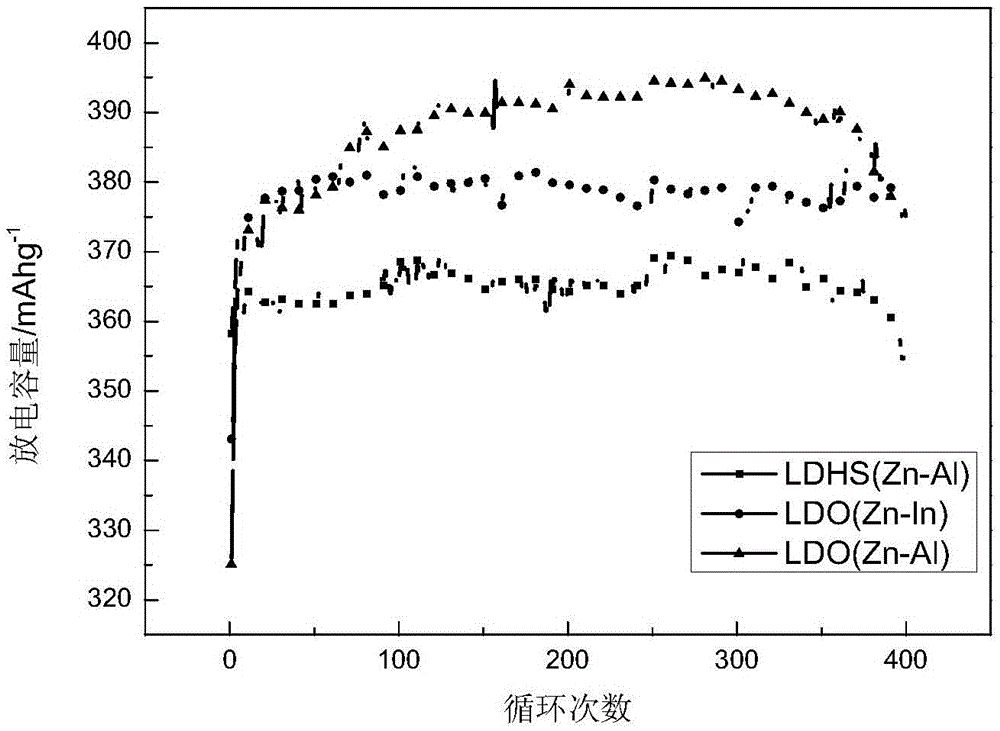
Application of a zinc-based binary layered composite oxide as an electrode material for a zinc-nickel battery
A composite oxide and zinc-based binary layer technology, applied in battery electrodes, alkaline battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the capacity of zinc oxide, and achieve improved electrochemical performance, dendrite improvement, and discharge specific capacity high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Dissolve 8.95 parts by weight of analytically pure zinc nitrate in 100 parts by weight of deionized water, dissolve 2.25 parts by weight of analytically pure aluminum nitrate in 100 parts by weight of deionized water, and mix the above two solutions evenly to form a salt solution. 3.4 parts by weight of sodium hydroxide and 2.10 parts by weight of sodium carbonate were dissolved in 50 parts by weight of deionized water to form an alkaline solution. Under strong mechanical stirring, slowly add the salt solution and alkali solution dropwise into 50 parts by weight of deionized water, control the pH of the solution to 10.0, continue to stir for 80 minutes, age for 20 hours, and finally filter, wash and remove the precipitate. Dry at 60°C for 4 hours to obtain a carbonate-type zinc-aluminum hydrotalcite sample. The hydrotalcite is placed in a muffle furnace and calcined at a high temperature of 500° C. for 5 hours to obtain a zinc-aluminum layered composite oxide. Add 0.8...
Embodiment 2
[0031]Dissolve 8.95 parts by weight of analytically pure zinc nitrate in 100 parts by weight of deionized water, dissolve 2.25 parts by weight of analytically pure indium nitrate in 100 parts by weight of deionized water, and mix the above two solutions evenly to form a salt solution . 3.4 parts by weight of potassium hydroxide and 2.1 parts by weight of potassium carbonate were dissolved in 50 parts by weight of deionized water to form an alkaline solution. Under strong mechanical stirring, slowly add salt solution and alkali solution dropwise into 50 parts by weight of deionized water, control the pH of the solution to 10.0, continue to stir for 100 minutes, age for 20 hours, and finally filter, wash and remove the precipitate. Dry at 60°C for 4 hours to obtain a carbonate-type zinc indium hydrotalcite sample. The hydrotalcite is placed in a muffle furnace and calcined at a high temperature of 500° C. for 5 hours to obtain a zinc-indium layered composite oxide. Add 0.86g o...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Dissolve 8.95 parts by weight of analytically pure zinc nitrate in 100 parts by weight of deionized water, dissolve 2.25 parts by weight of analytically pure bismuth nitrate in 100 parts by weight of deionized water, and mix the above two solutions evenly to form a salt solution . 3.4 parts by weight of potassium hydroxide and 2.1 parts by weight of potassium carbonate were dissolved in 50 parts by weight of deionized water to form an alkaline solution. Under strong mechanical stirring, slowly add the alkali solution and the alkali solution dropwise into 50 parts by weight of deionized water, control the pH of the solution to 10.0, continue to stir for 120 minutes, age for 20 hours, and finally filter, wash, and remove the precipitate. Dry at 60°C for 4 hours to obtain a carbonate-type zinc-bismuth hydrotalcite sample. The hydrotalcite is placed in a muffle furnace and calcined at a high temperature of 500° C. for 5 hours to obtain a zinc-bismuth layered composite oxid...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com