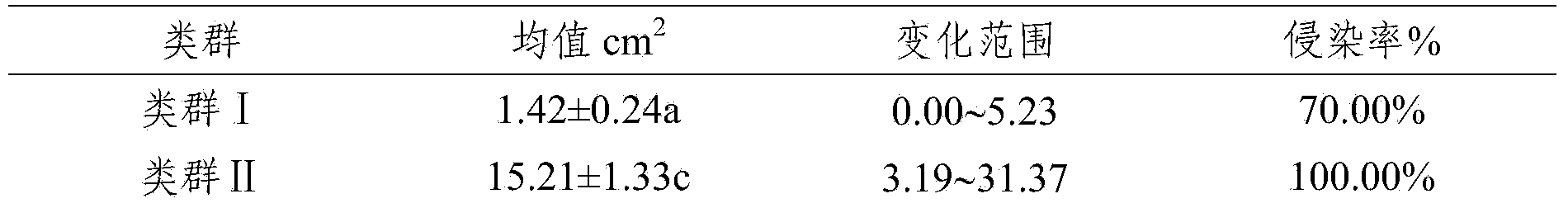Artificial feeding method of fragrant pear euzophera pyriella
A technology for the superior spot borer and the superior spot borer pupa, which is applied in the direction of animal husbandry and the like, and achieves the effects of consistent development, neat insect age and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] The artificial rearing method of embodiment 1 fragrant pear leaf borer
[0046] (1) screening the bacterial strain of pear tree rot pathogen
[0047]The samples of fragrant pear disease were mainly collected from Aksu and Bayingolengzhou in Xinjiang. Indoor separation and purification, observed and recorded the colony characteristics of 60 pear rot pathogen strains on PDA. The 60 strains of P. pear rot were classified into 3 groups. Among them: group Ⅰ (representing strain XJxl5) gray-green easy sporulation group; 32 (53%), group II (representing strain XJxl9 (CGMCC No.8507) yellow easy sporulation group; 25 (42%), group III (representative strain XJxl4), gray-white dystocia group, and its pathogenicity was determined.
[0048] Table 1 Results of analysis of variance of lesion expansion area of different strains
[0049]
[0050]
[0051] Note: 1. Mean values are listed as mean ± standard error; 2. Different letters in the same column indicate extremely si...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The artificial rearing method of embodiment 2 Fragrant pear leaf borer
[0059] The 3 types of bacterial strains screened in Example 1 are prepared into mushroom cakes according to the method of the present invention for subsequent use.
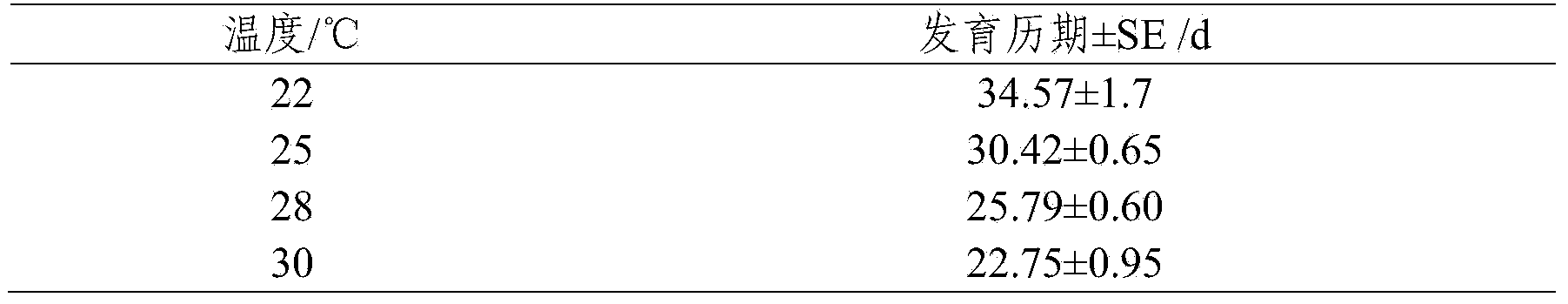
[0060] Mature larvae of Eustoma chinensis were collected in the fragrant pear orchard of the Forestry Institute Extension Station in Aksu Prefecture, and pupated and emerged indoors. Referring to the method of Example 1, 502 newly hatched larvae were obtained, which were respectively placed in petri dishes of three types of bacterial strains. The petri dish was moved to an artificial climate box with a temperature range of 22° C. and a humidity of 60% RH.
[0061] Table 3 Survival rate of Ceratocystis spp. under the conditions of different types of strains
[0062]
[0063] Table 4 Oviposition and hatching rate of females in different population types
[0064]
Embodiment 3
[0065] The artificial rearing method of embodiment 3 Fragrant pear leaf borer
[0066] The type II bacterial strain screened in Example 1 was prepared into mushroom cake according to the method of the present invention for subsequent use. Mature larvae of Eustoma chinensis were collected in the fragrant pear orchard of the Forestry Institute Extension Station in Aksu Prefecture, and pupated and emerged indoors. With reference to the method of Example 1, 750 newly hatched larvae were obtained and placed in a petri dish of pear tree rot fungus. The petri dish was moved to an artificial climate box with a temperature range of 25° C. and a humidity of 60% RH for raising. The results showed that the survival rate of 3rd instar larvae was 90%, the pupation rate was 82.35%, the adult eclosion rate was 76.19%, and the average egg production per head was 25.48.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com