Spent mushroom substrate high-temperature decomposition composite bacterial agent and preparation method thereof
A compound bacterial agent, pyrolysis technology, used in biochemical equipment and methods, microorganism-based methods, bacteria, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0030] (1) The 8 strains of bacteria were cultured separately, and the culture methods were as follows:
[0031] Strain preservation number ATCC51176, the culture of DSM3670Aeribacillus pallidus, will be composed of glucose 1.0g, peptone 7.5g, beef extract 5.0g, yeast powder 2.5g, casamino acids 2.5g, sodium chloride 5.0g, distilled water 1000.0ml composition medium, pH The value was adjusted to 8.5; 60 ℃ protected from light static culture for 48h.
[0032] For the cultivation of strain preservation number DSM2027, ATCC7954 Geobacillus stearothermophilus, a culture medium consisting of 5.0g of sodium chloride, 10.0g of beef extract, 10.0g of peptone, and 1000.0mL of distilled water was adjusted to a pH value of 7.2; statically cultured at 60°C in the dark for 48 hours.
[0033] For the cultivation of strain preservation number DSM7064 Brevibacillus thermoruber, adjust the pH value to 7.0 in a culture medium consisting of 15.0 g of glucose, 5.0 g of yeast powder, 0.2 g of calc...
example 2
[0050] Example 2, same as Example 1, the difference is,
[0051] (1) The mixed fermentation ratio of the 8 strains of bacteria is: Aeribacillus pallidus (strain preservation number ATCC51176, DSM3670), Geobacillus stearothermophilus (strain preservation number DSM2027, ATCC7954), Brevibacillus thermoruber (strain preservation number DSM7064), Clostridium stercorarium subsp.thermolacticum (strain collection number ATCC43739, DSM2910), Clostridium thermocellum (strain collection number NCIB10682, ATCC27405), Desulfotomaculum nigrificans (strain collection number DSM574, ATCC19858), Geobacillus thermoglucosidasius (strain collection number DSM21625), Symbiophilum8 the The cell number content in the strain is specifically 12%, 14%, 3%, 14%, 17%, 10%, 14% and 16%.
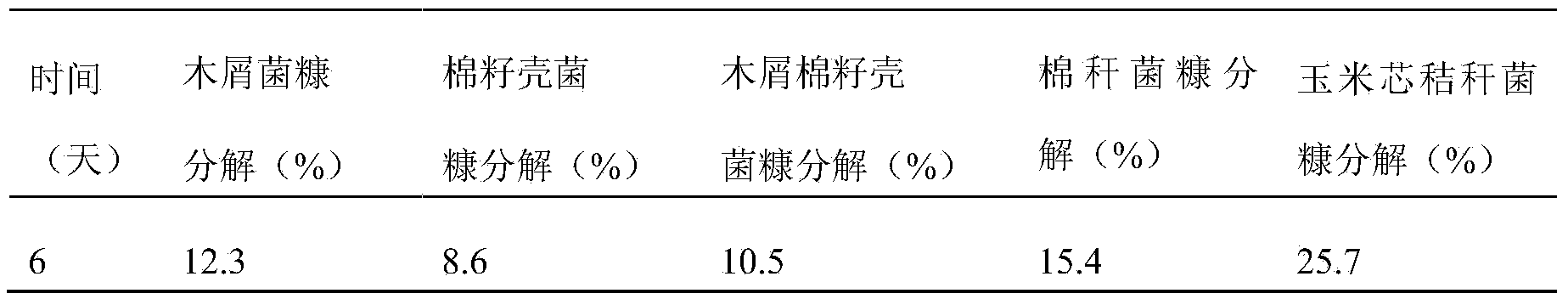
[0052] The composite bacterial agent prepared in this example is shown in Table 2 for its ability to decompose different bacterial chaff.
[0053] Table 2 Composite bacteria agent's ability to decompose different bacte...
example 3
[0055] Example 3, the same as Example 1, the difference is,
[0056] (1) Among the complex bacteria, Aeribacillus pallidus (strain preservation number ATCC51176, DSM3670), Geobacillus stearothermophilus (strain preservation number DSM2027, ATCC7954), Brevibacillus thermoruber (strain preservation number DSM7064), Clostridium stercorarium subsp. , DSM2910), Clostridium thermocellum (strain collection number NCIB10682, ATCC27405), Desulfotomaculum nigrificans (strain collection number DSM574, ATCC19858), Geobacillus thermoglucosidasius (strain collection number DSM21625), Symbiobacterium thermophilum (strain collection number DSM21625), and Symbiobacterium thermophilum (strain collection number 28) with specific content of 16 cells %, 15%, 4%, 11%, 18%, 7%, 11%, and 18%.
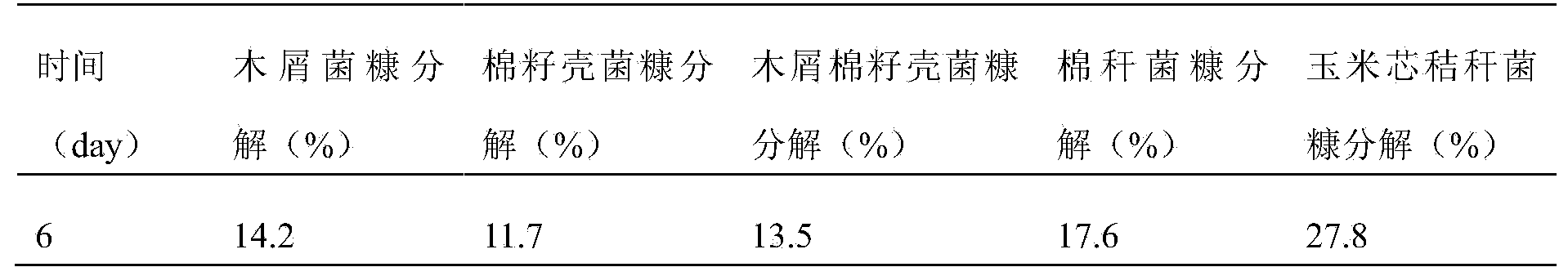
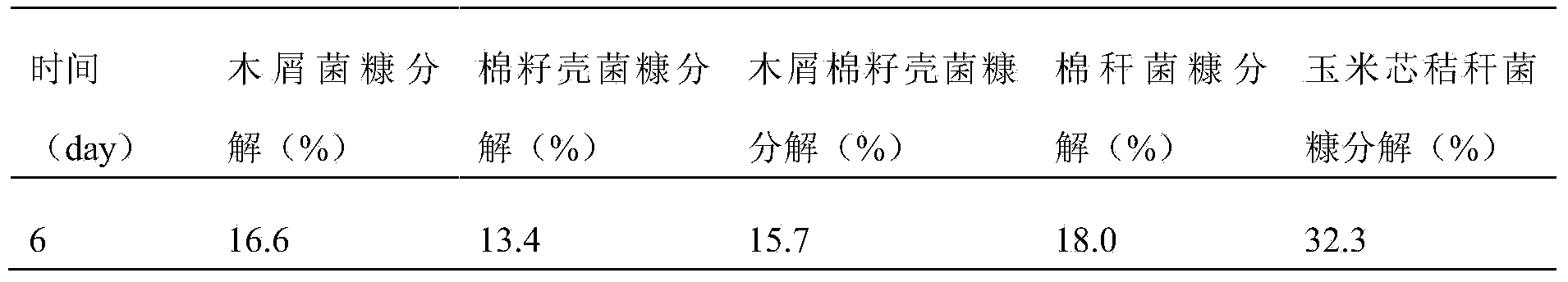
[0057] The composite bacterial agent prepared in this example is shown in Table 3 for its ability to decompose different bacterial chaff.
[0058] Table 3 Decomposition ability of compound microbial agent to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com