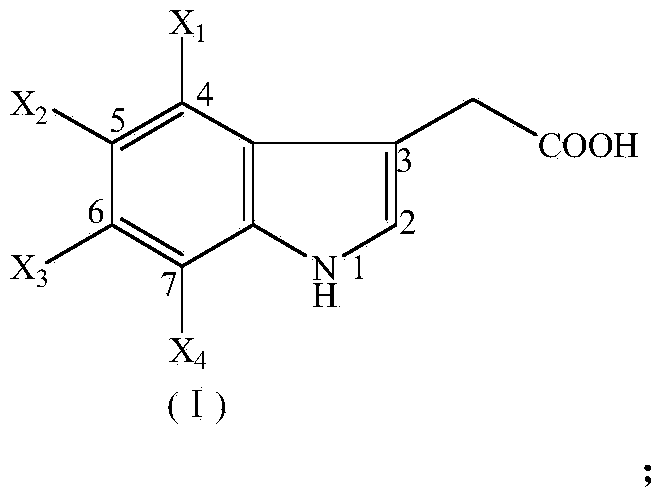
Application of halogenated indole-3-acetic acid as herbicide
A halogenated indole, herbicide technology, applied in the field of pesticide chemistry, can solve the problem of unmentioned herbicides, etc., and achieve the effects of low toxicity, good environmental compatibility, and high-efficiency herbicidal activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] The preparation of embodiment 1 halogenated indole-3-acetic acid
[0027] The present invention utilizes the involved compound halogenated indole-3-acetic acid, which can be realized by the following methods.
[0028] Option One:
[0029]Halogenated indole-3-acetic acids can be prepared by Fischer indole ring method, specifically:
[0030] (1) React glutamic acid with NaClO under acidic conditions to obtain 3-formyl propionic acid;
[0031] (2) Diazotize the corresponding substituted aniline compound with sodium nitrite under acidic conditions, and then reduce the product to obtain the corresponding halophenylhydrazine;
[0032] (3) Reaction of the corresponding halophenylhydrazine with 3-formylpropionic acid to generate the corresponding halophenylhydrazone, and the corresponding halophenylhydrazone is rearranged to generate the corresponding haloindole-3-acetic acid.
[0033] This process is described in: Fox SW and Bullock MW, Journal of the American Chemical Soci...
preparation example 14
[0046] Preparation 14-fluoroindole-3-acetic acid
[0047] Slowly add 8.8g of 37% formaldehyde solution (0.11mol) dropwise to a solution of 16.5g of 33% dimethylamine solution (0.12mol) and 25mL of glacial acetic acid, and keep it at 0-5°C for 1 hour. At 0-5°C, 10 g of 4-fluoroindole (0.074 mol) was added dropwise and reacted for 1 hour. Rise to room temperature, keep stirring for 24 hours, take samples and control until the reaction is completed, the reaction mixture is acidified with 4N hydrochloric acid solution, and extracted three times with ethyl acetate. The aqueous layer was washed with 4N sodium hydroxide solution and extracted three times with ethyl acetate, and the ethyl acetate layers were combined. The ethyl acetate layer was washed successively with water, washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, concentrated ethyl acetate in vacuo, and finally recrystallized from ethyl acetate and n-hexane to obtain 4-fluoro-3-N,N-dimethylaminomethyl ba...
preparation example 25
[0050] Preparation 25,7-Difluoroindoleacetic acid
[0051] At 0°C, add 100.0g of 2,4-difluoroaniline (0.78mol) to 400mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid, and after stirring for 30 minutes, slowly drop a solution consisting of 84.0g of sodium nitrite (1.21mol) and 120mL of water into the above In the reactants, the reaction system was stirred for 1 hour. A solution consisting of 360 g of stannous chloride (1.90 mol) dissolved in 400 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid was added to the above system, the entire reaction system was stirred for 1.5 hours, and the pH was adjusted to 10 with 4N sodium hydroxide solution. Extracted three times with ethyl acetate, combined the ethyl acetate layers, washed the organic layer with water and saturated brine successively, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, concentrated ethyl acetate in vacuo, and finally recrystallized with ethyl acetate and n-hexane to obtain 2,4- Difluorophenylhydrazine.
[0052] With 800mL of benzene and 200mL of w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com