Patents
Literature
83 results about "Indole-3-acetic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
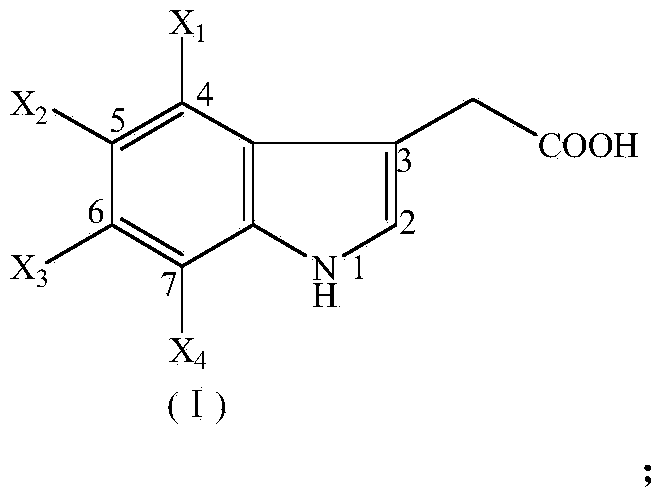
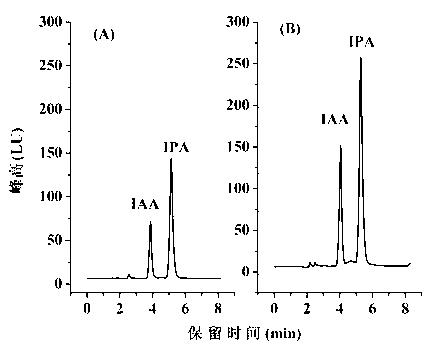
Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA, 3-IAA) is the most common, naturally occurring, plant hormone of the auxin class. It is the best known of the auxins, and has been the subject of extensive studies by plant physiologists. IAA is a derivative of indole, containing a carboxymethyl substituent. It is a colorless solid that is soluble in polar organic solvents.
Personal care compositions and methods for the beautification of mammalian skin and hair
Personal care composition comprising from about 0.05% to about 5% of at least one aquaporin-stimulating compound selected from the group consisting of xanthine, caffeine; 2-amino-6-methyl-mercaptopurine; 1-methyl xanthine; 2-aminopurine; theophylline; theobromine; adenine; adenosine; kinetin; p-chlorophenoxyacetic acid; 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid; indole-3-butyric acid; indole-3-acetic acid methyl ester; beta-naphthoxyacetic acid; 2,3,5-triiodobenzoic acid; adenine hemisulfate; n-benzyl-9-(2-tetrahydropyranyl)adenine; 1,3-diphenylurea; 1-phenyl-3-(1,2,3-thiadiazol-5-yl)urea; zeatin; indole-3-acetic acid; 6-benzylaminopurine; alpha-napthaleneacetic acid; 6-2-furoylaminopurine; green tea extract; white tea extract; menthol; tea tree oil; ginsenoside-RB1; ginsenoside-RB3; ginsenoside-RC; ginsenoside-RD; ginsenoside-RE; ginsenoside-RG1; ginseng root extract; ginseng flower extract; pomegranate extract, extracts from Ajuga turkestanica; extracts from viola tricolor and combinations thereof; an additional ingredient selected from the group consisting of niacinamide, glycerin and mixtures thereof, and a dermatologically-acceptable carrier.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Plasmid encoding IAA and a method thereof
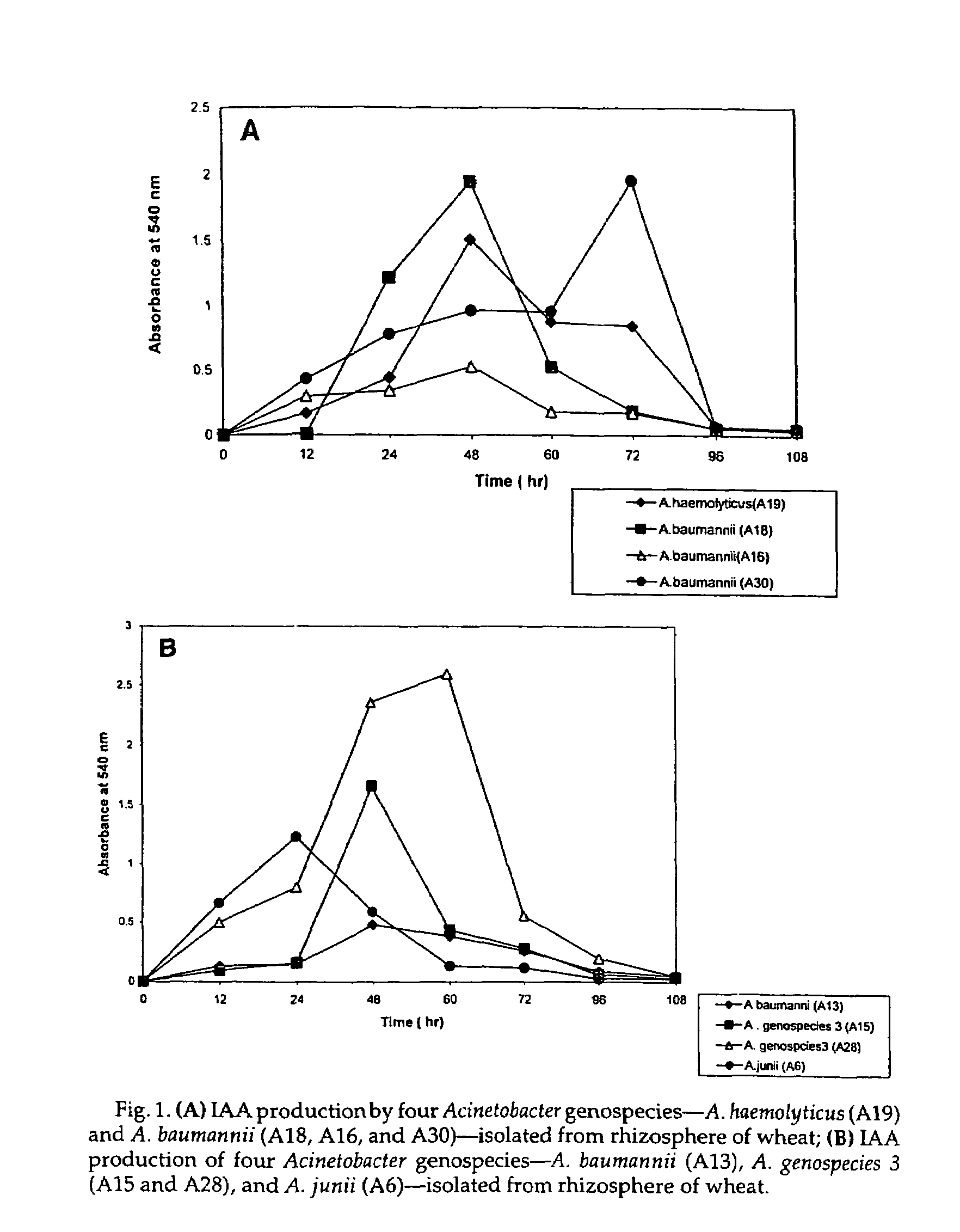
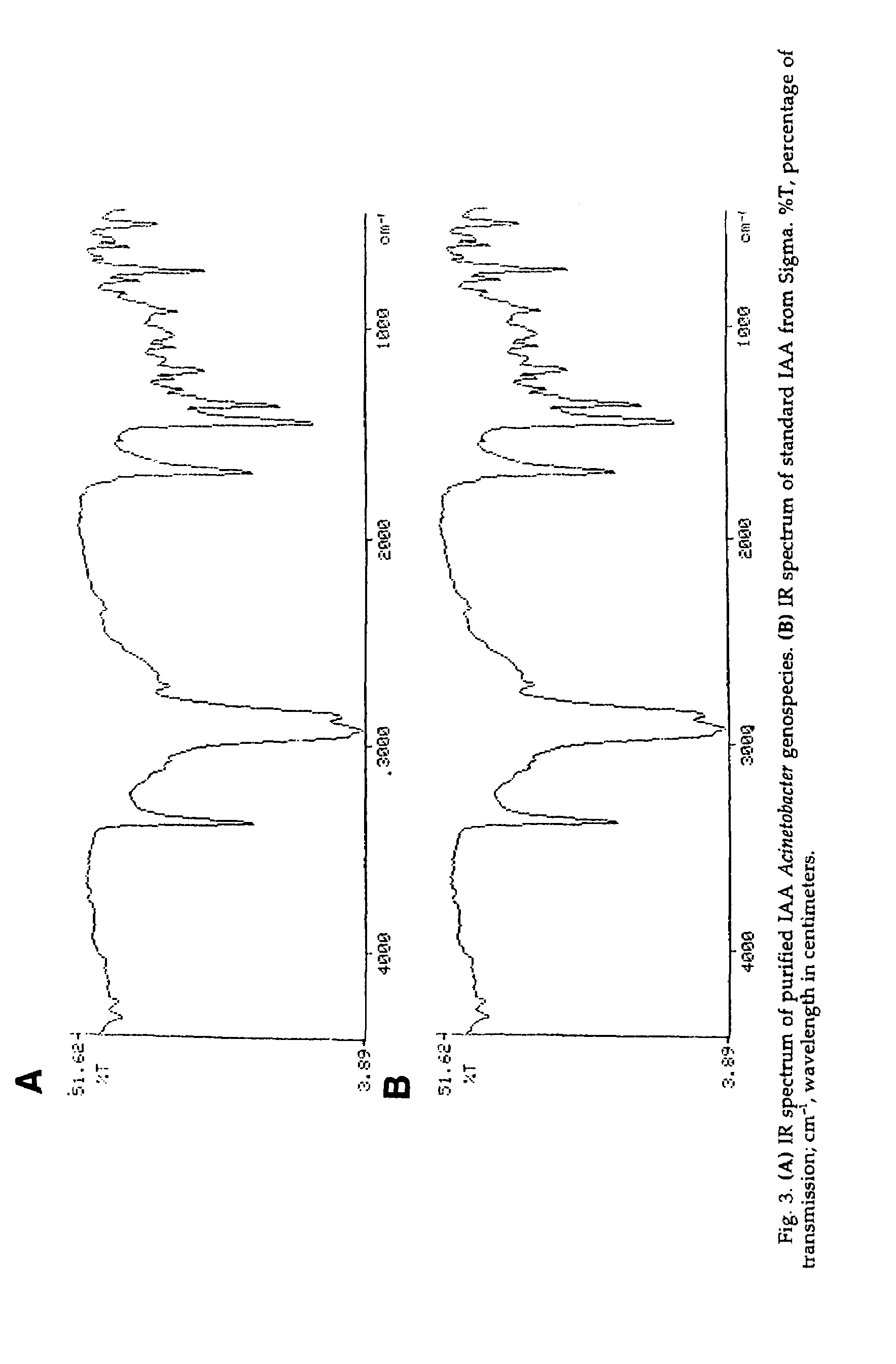
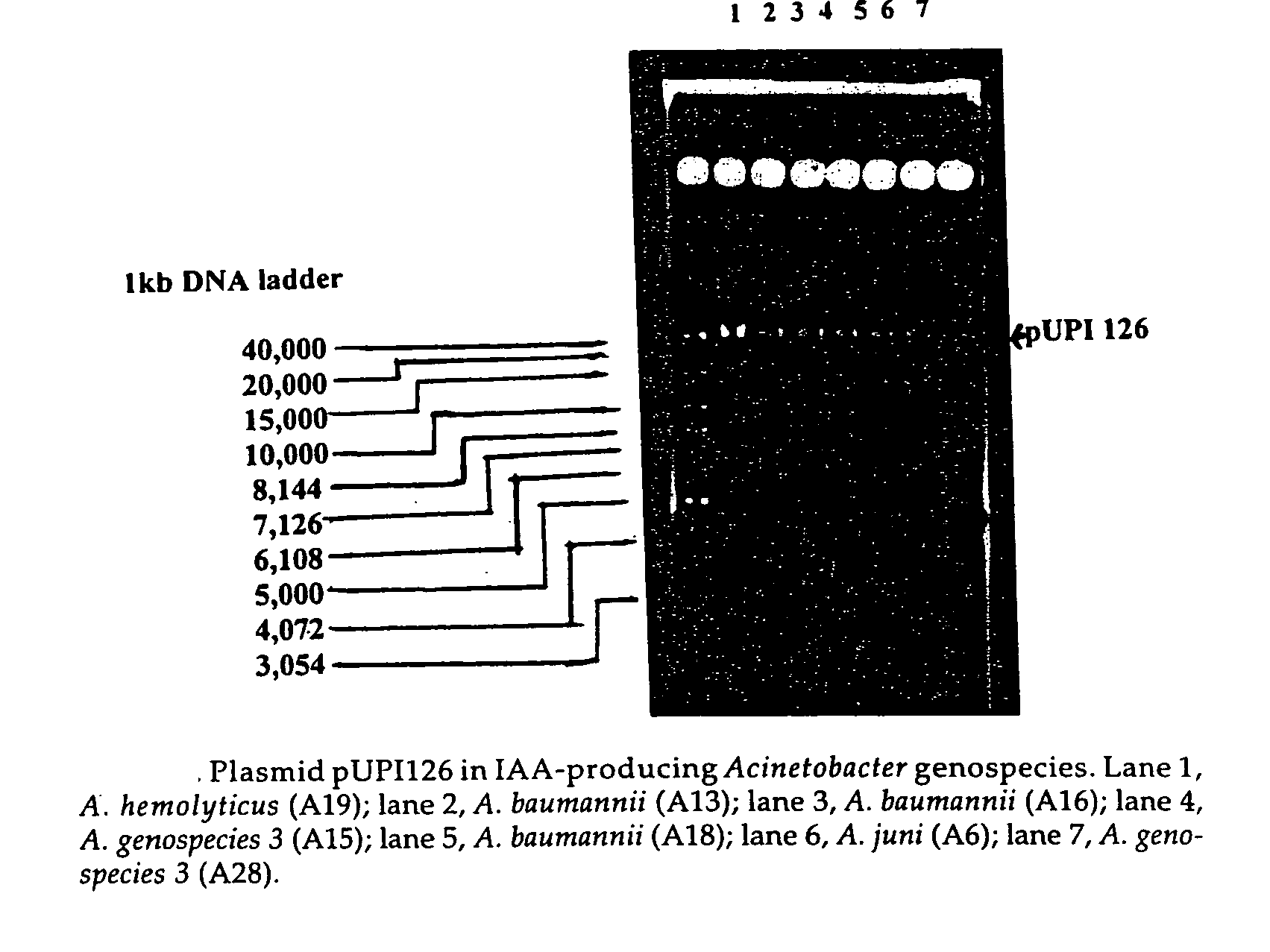
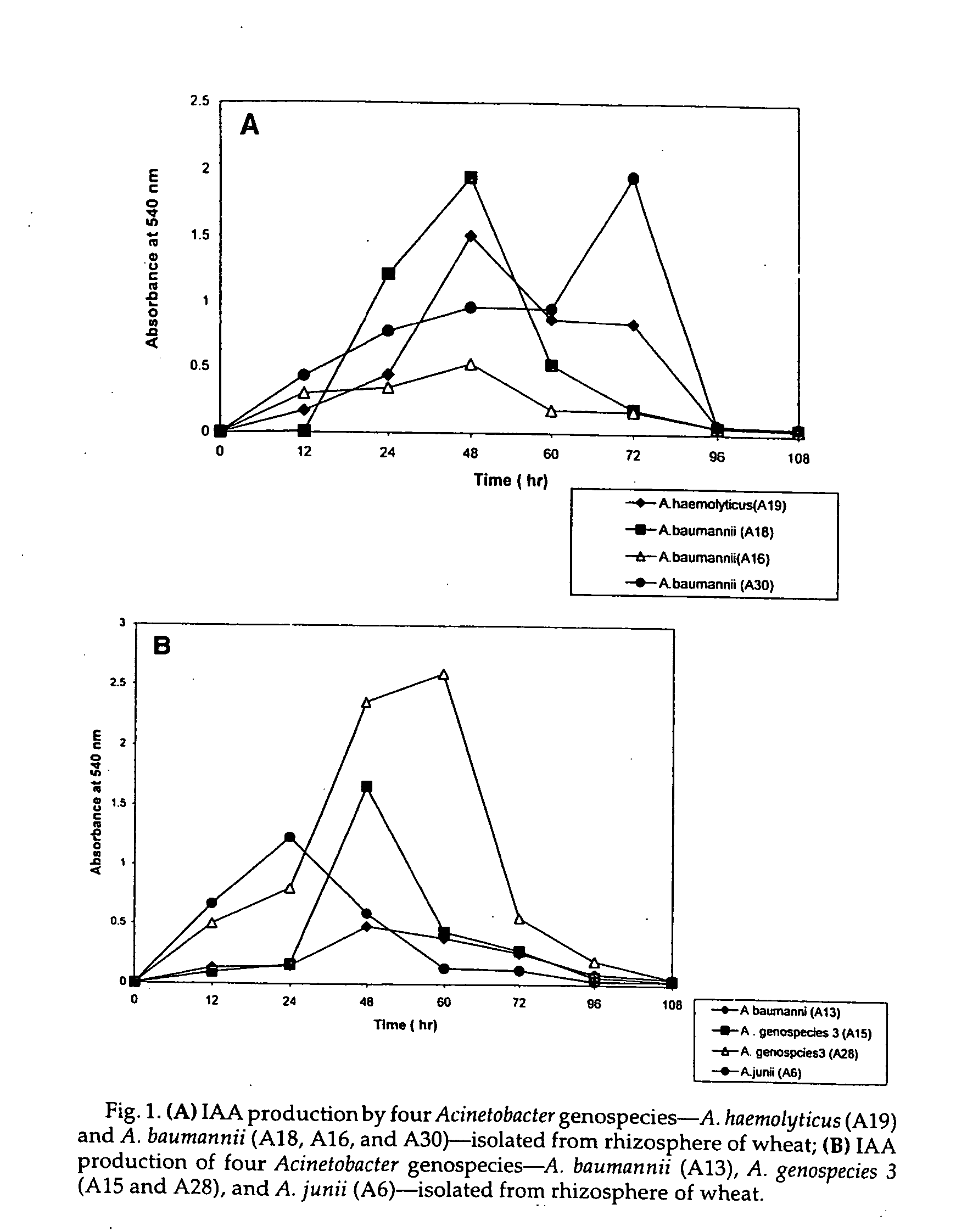
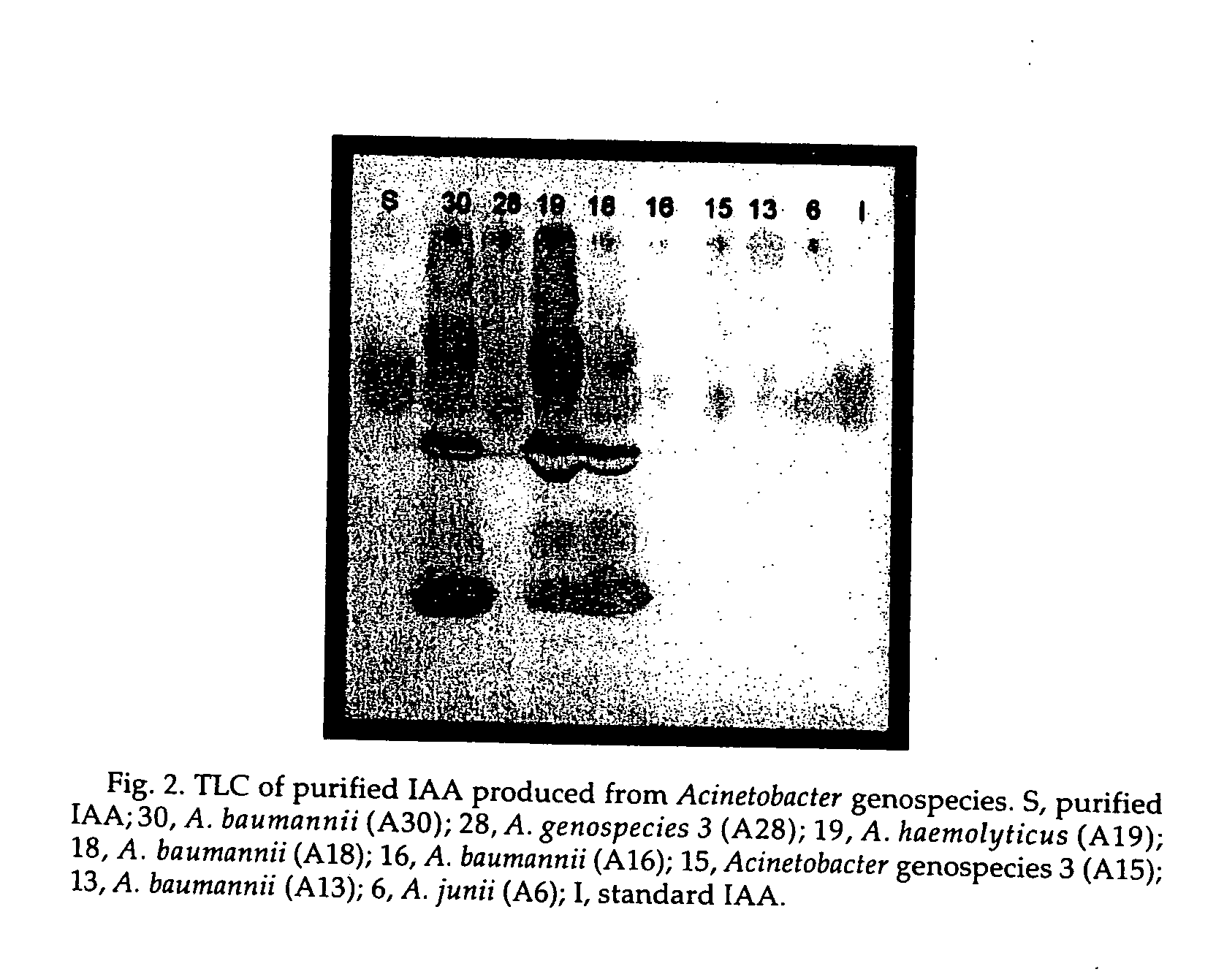
The present invention relates to a plasmid pUPI126 encoding indole-3 acetic acid (IAA) production, Acinetobacter strains having plasmid pUPI126, a bioinoculum for promoting growth of wheat plant, and a method of promoting wheat plant growth, the method comprising treating wheat seeds with the bioinoculum.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Pseudomonas Bacterium
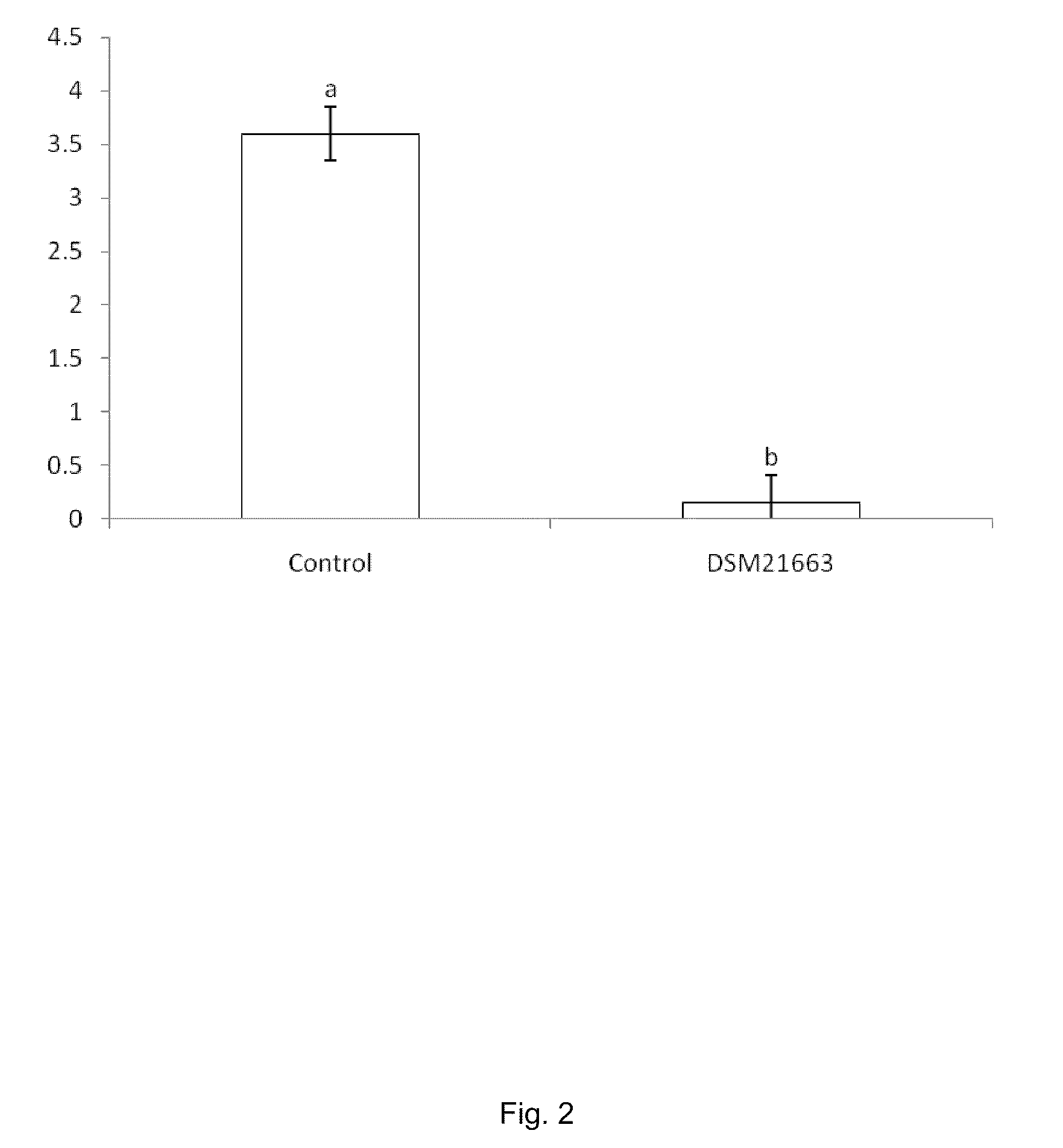
According to the present invention a new isolate of a Pseudomonas spp, DSM 21663, has been shown to possess unique properties. This Pseudomonas is a plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium (PGPR). Among its modes of action involved in plant growth-promotion are anti-biotic production (2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol, (DAPG); pyrrolnitrin, PRN and others), indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) production and phosphate solubilization, and production of unique volatiles. The strain is fluorescent, oxidase-positive, and has the ability to suppress soil-borne root and foliar pathogens of both fungal and bacterial origin.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Plasmid encoding IAA and a method thereof
The present invention relates to a plasmid pUPI126 encoding indole-3 acetic acid (IAA) production; it also relates to a Acinetobacter strains having plasmid pUPI126; a bioinoculum for promoting growth of wheat plant, and lastly, it relates to a method of promoting wheat plant growth, said method comprising treating wheat seeds with the bioinoculum.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Camellia chrysantha culture medium for tissue culture and quick breeding
The present invention uses improved MS culture medium as basis, and adds the active carbon, indole-3-acetic acid, 3-indolebutyric acid and 6-benzylaminopurine as auxiliary agent to make tissue cultivation of two key stages of induced growth of bunch bud and seedling-strengthening and rooting of camllia chrysantha. The invention can be used for implementing industrial quick seedling cultivation.
Owner:GUANGXI FUXIN SCI & TECH
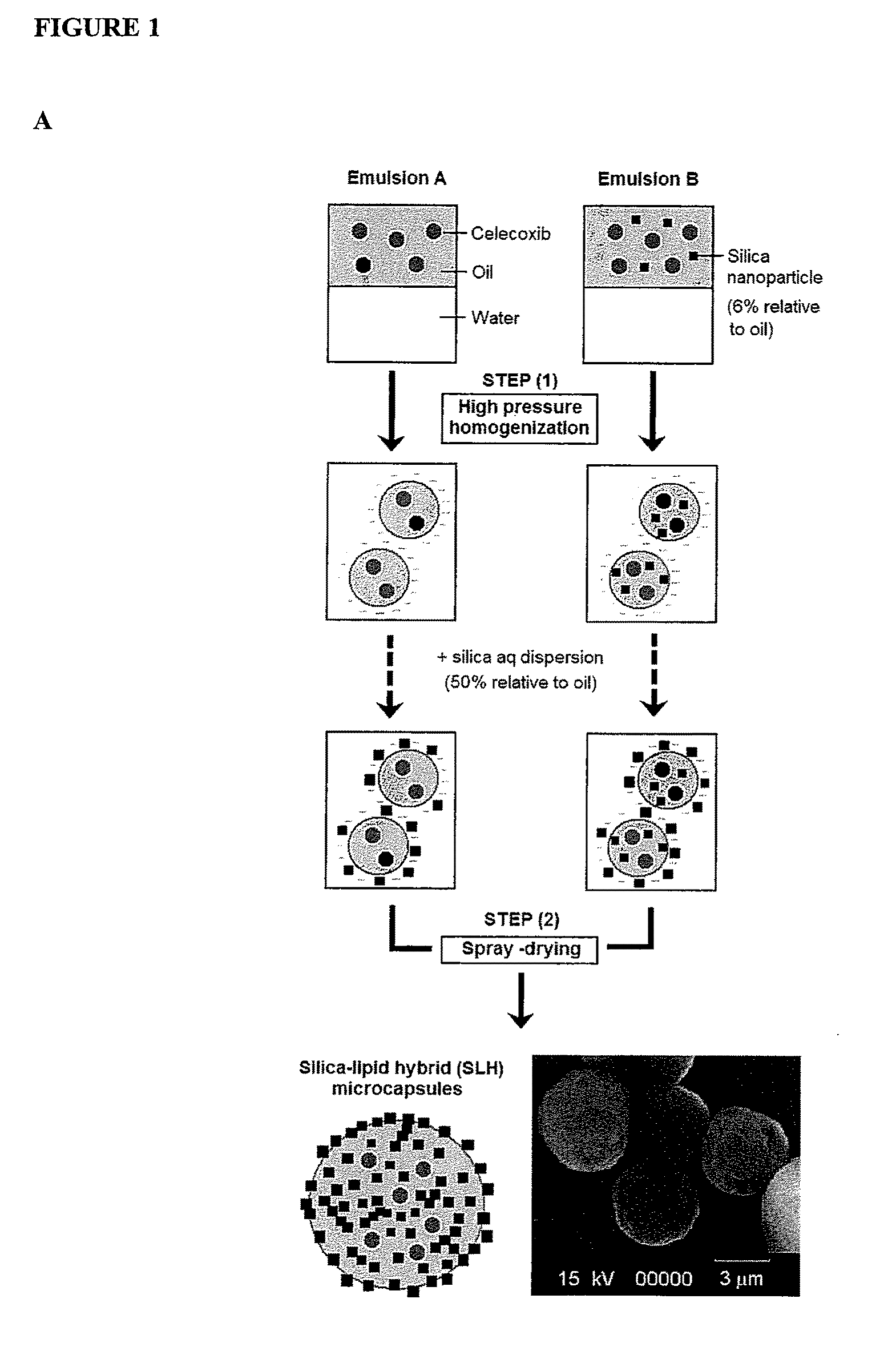
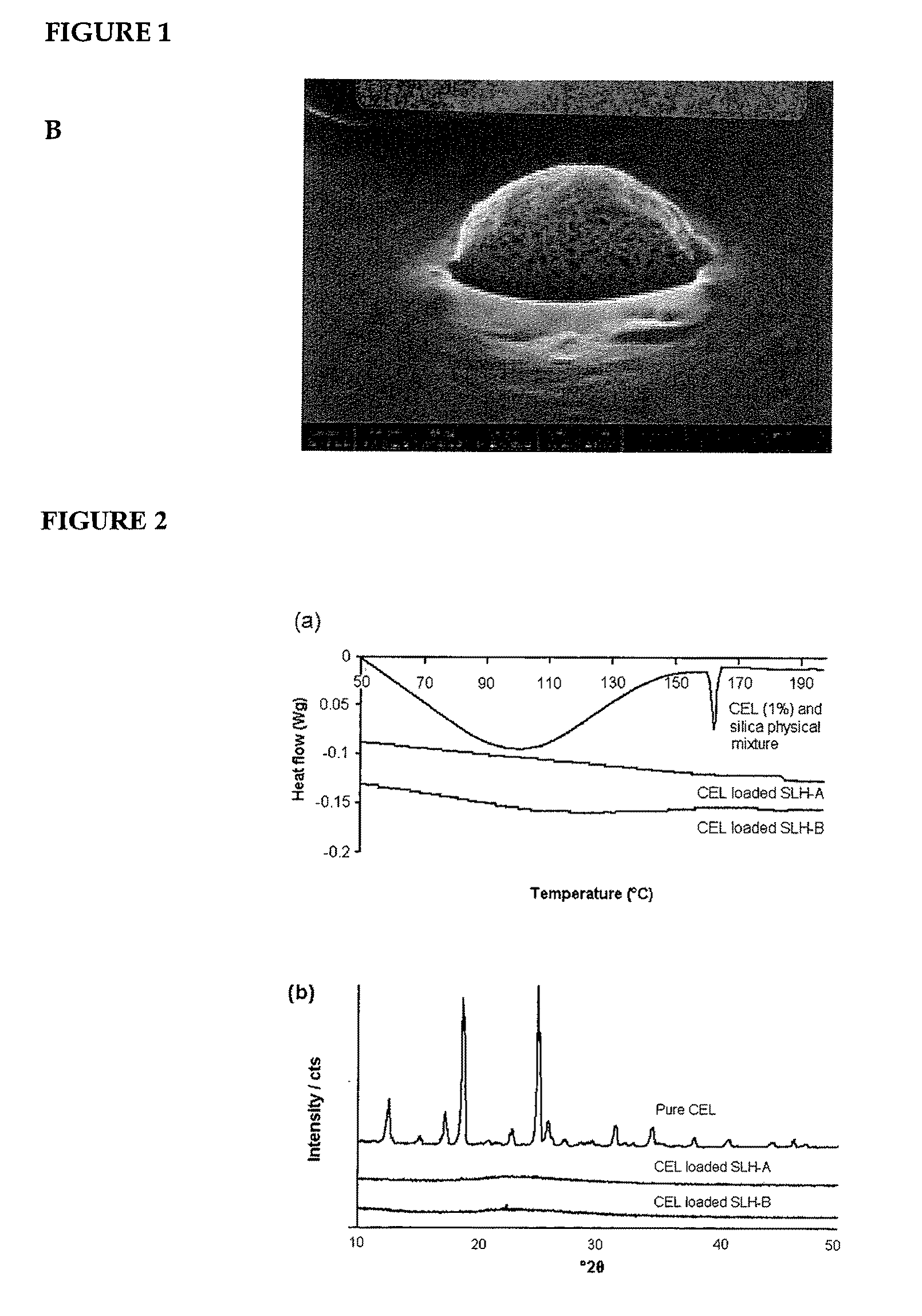
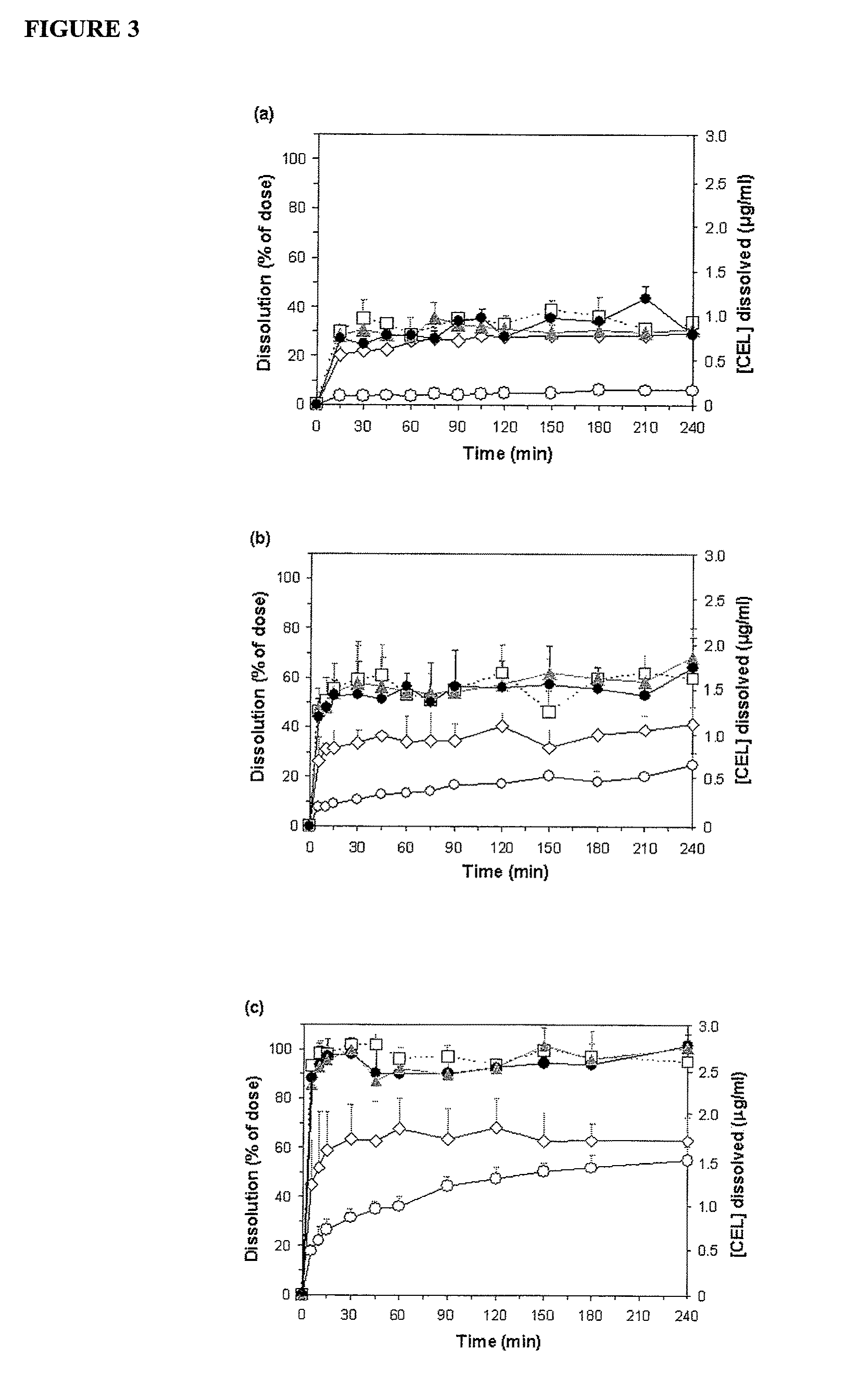
Nanoparticle-stabilized capsule formulation for treatment of inflammation
ActiveUS20090263486A1Quick releaseImprove bioavailabilityPowder deliveryBiocideAcetic acidAqueous droplet
A formulation for the delivery of an anti-inflammatory agent to a subject is described. In one particular application of the invention, the formulation comprises oil-based or aqueous droplets comprising indomethacin (1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1-H-indole-3-acetic acid) or celecoxib (4-[5-(4-methylphenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl) pyrazol-1-yl] benzenesulfonamide) stabilised by nanoparticles, particularly silica nanoparticles.
Owner:REFORMPHARM PTY LTD
Rooting induction method of test-tube plantlet of cunninghamia lanceolata
ActiveCN103229723AHair root unificationFast rootingPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSocial benefitsEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a rooting induction method of a test-tube plantlet of cunninghamia lanceolata. The rooting induction method comprises the steps of: cutting a 1-2cm multiplication subculture plantlet, inoculating in a pre-rooting culture medium for culturing, wherein the pre-rooting culture medium uses 1 / 2MS-MS as a base culture medium, and also comprises 0.02-0.08mg / L of NAA (Naphthalene Acetic Acid), 2.5 percent of cane sugar and 0.7 percent of agar; carrying out rooting culture after pre-rooting and culturing for 15-25 days, wherein a rooting culture medium uses improved 1 / 2 MS as a basic culture medium, and also comprises 0.10-0.25mg / L, 0.05-0.08mg / L of IAA (Indole-3-Acetic Acid), 2.5 percent of cane sugar and 0.7 percent of agar; and placing in a proper environment for culturing to obtain a rooted test-tube plantlet. After the cunninghamia lanceolata is rooted and cultured by adopting the rooting induction method, the rooting rate, the root system quantity and the root system germination uniformity of the test-tube plantlet of the cunninghamia lanceolata can be increased, more excellent rooted test-tube plantlets are provided for production and application, and good economic benefit and social benefit are obtained.
Owner:GUANGXI FORESTRY RES INST
Stress-resistance and health-care mycorhiza microbial inoculum of Pinus massoniana and application method of stress-resistance and health-care mycorhiza microbial inoculum
The invention discloses a stress-resistance and health-care mycorhiza microbial inoculum of Pinus massoniana and an application method of the stress-resistance and health-care mycorhiza microbial inoculum. The stress-resistance and health-care mycorhiza microbial inoculum is prepared by compounding a mycorhiza microbial inoculum and plant hormone naphthylacetic acid or benzpyrole-3-acetic acid; and the mycorhiza microbial inoculum is formed by fermenting Lactarius akahatsu or Lactarius hatsudake through a solid fermentation culture medium. The stress-resistance and health-care mycorhiza microbial inoculum is used for carrying out slurry dipping treatment on seedling root systems or is buried into Pinus massoniana forest soil in a forestation process, so that not only can root-taking and growth of the Pinus massoniana be increased, but also the tree vigor is enhanced and the stress resistance is improved; and therefore Pinus massoniana defoliation, seedling damping-off and Pestalotiopsis apiculatus are prevented from happening.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Natural skin whitener: 4-hydroxy-oxindole-3-acetic acid
InactiveUS20100158842A1Potent anti-irritantPotent anti-oxidantBiocideCosmetic preparationsWhitening AgentsHyperpigmentation disorder
A cosmetic and dermatological composition comprises 2, 3-dihydro-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1-H-indole-3-acetic acid (4-hydroxy-1-oxindole-3-acetic acid) as an active ingredient for use as a melanin inhibitor and as an anti-tyrosinase enzyme inhibitor. This composition is excellent as a skin whitening agent. Since it also has potent antioxidant and anti-irritant activities it is useful in a cosmetic composition for improving hyperpigmentation disorders of the skin.
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS LLC
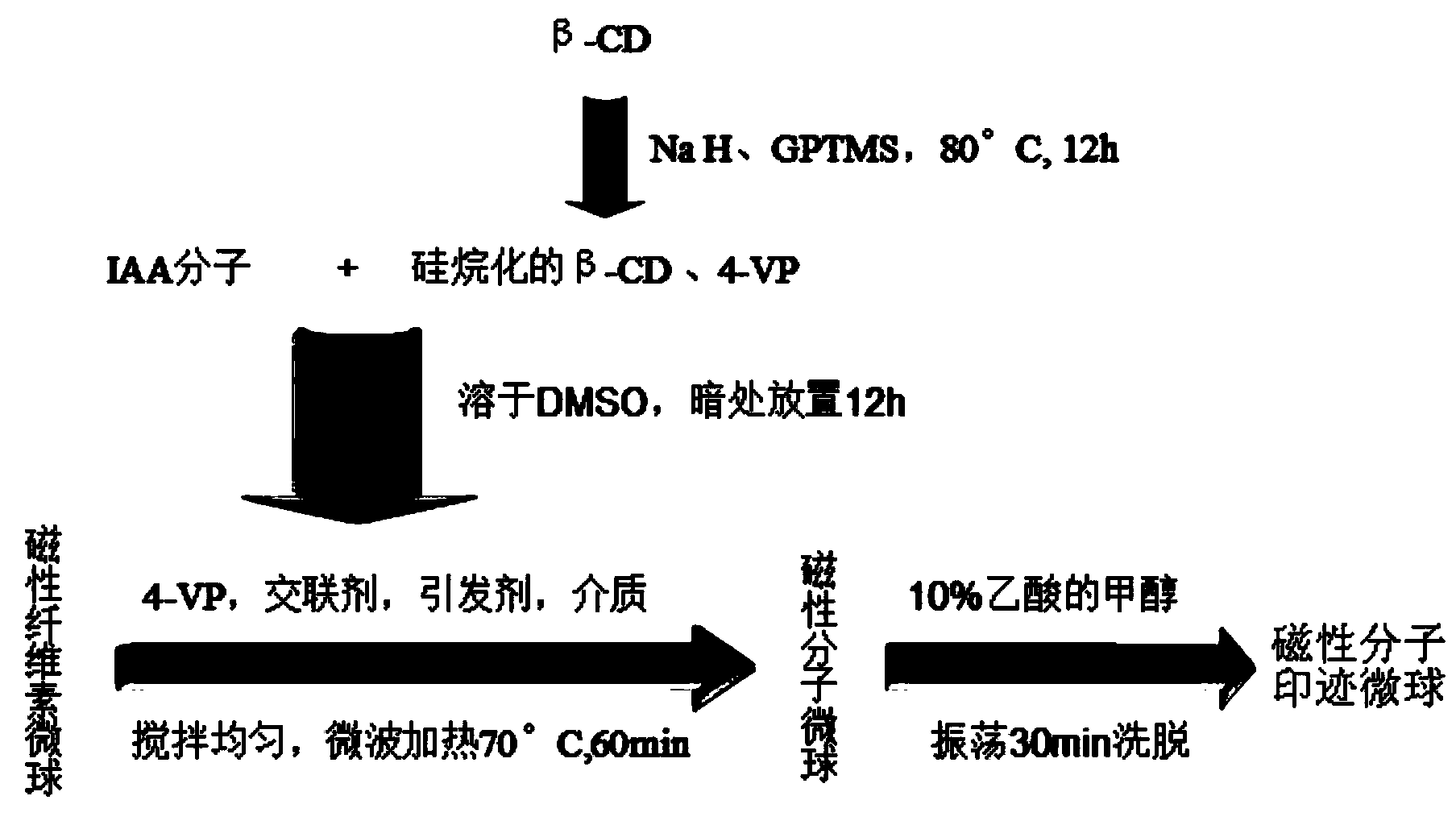
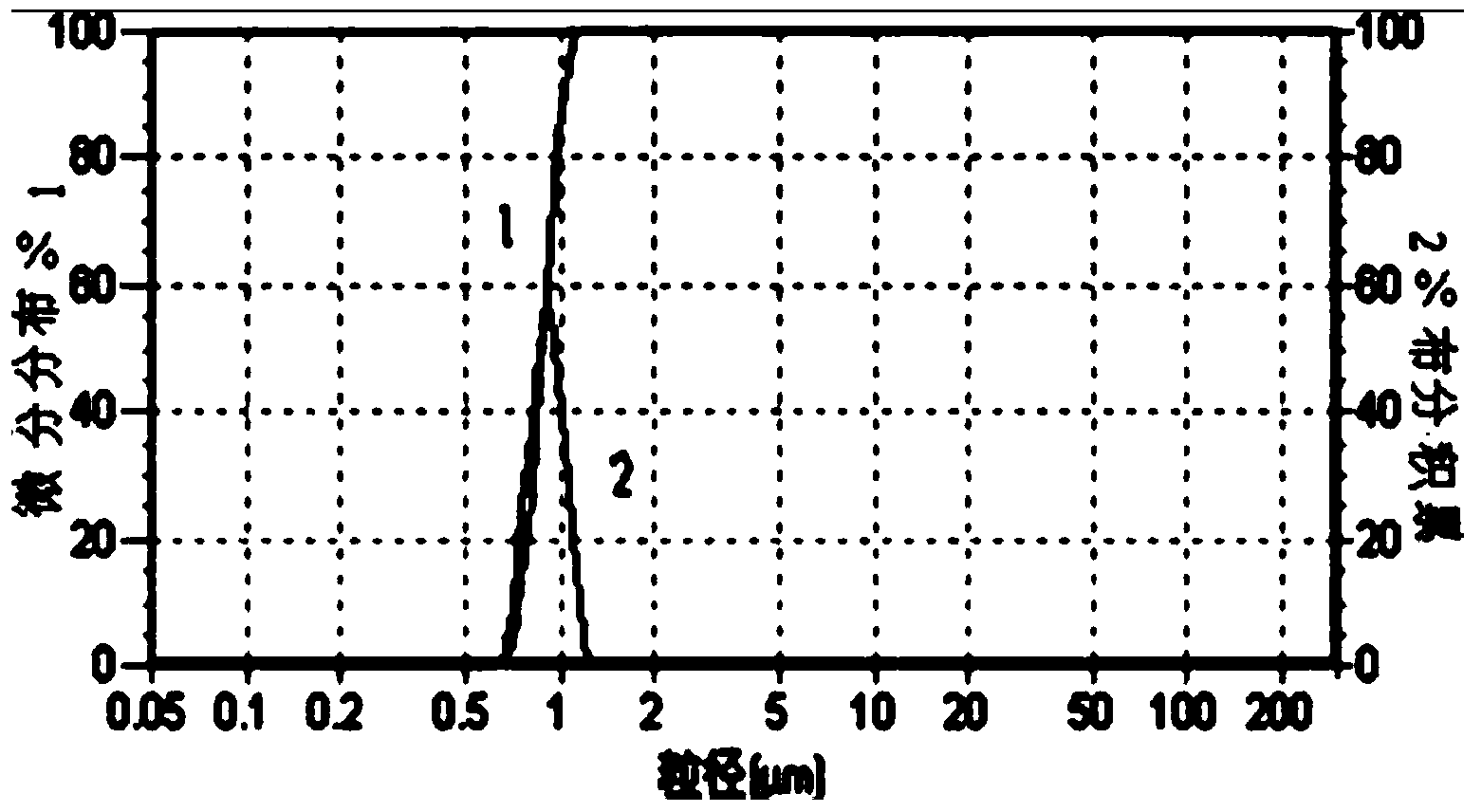
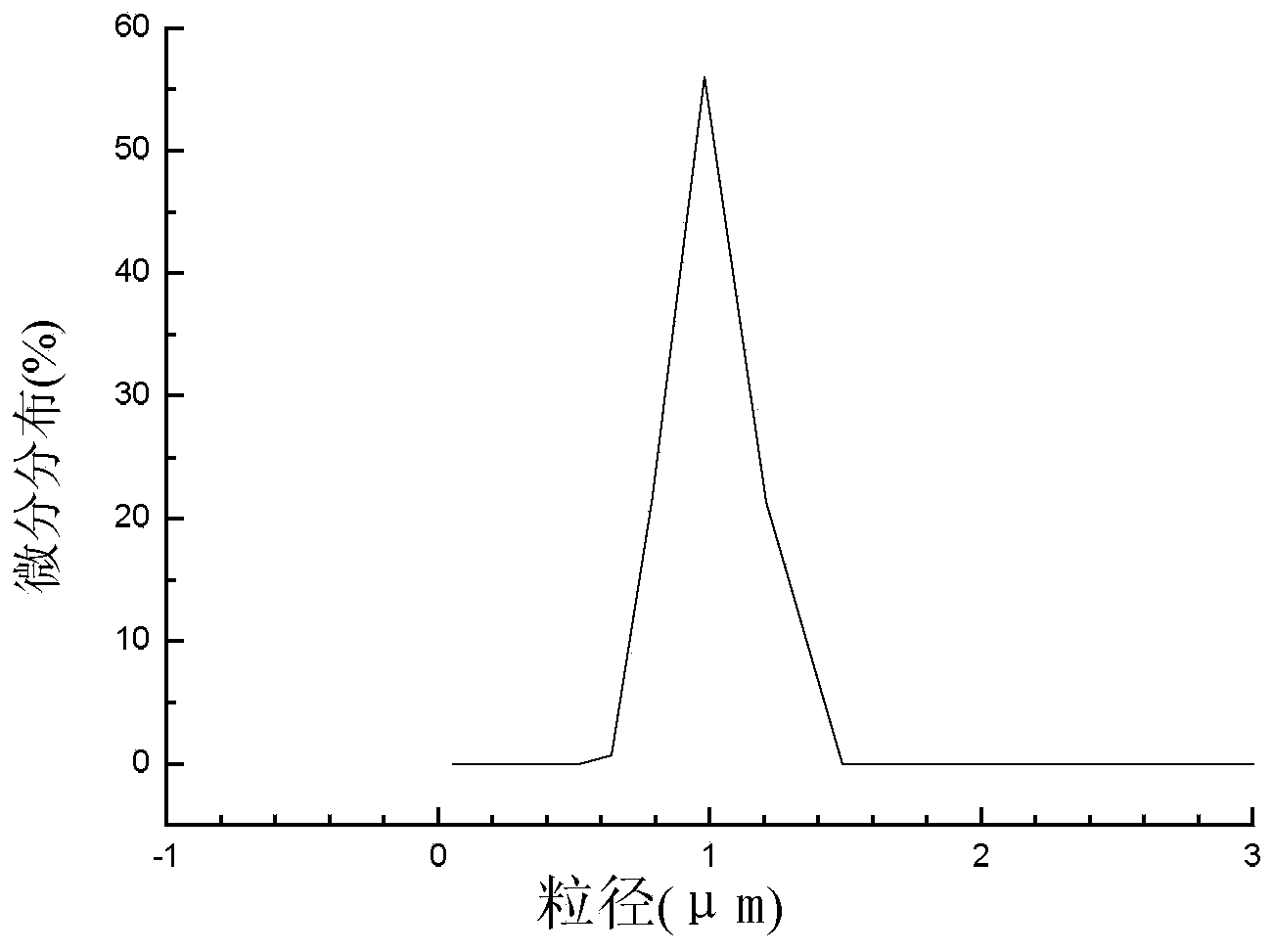
Indole-3-acetic acid molecularly imprinted magnetic cellulose microsphere and preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN103626920ASuperparamagneticSafe and non-toxicOther chemical processesComponent separationAcetic acidCellulose
The invention discloses an indole-3-acetic acid molecularly imprinted magnetic cellulose microsphere and a preparation method and applications thereof, which relate to a nano magnetic cellulose molecularly imprinted microsphere and a preparation method and applications thereof. The invention is designed for solving the problem that an existing IAA (indole-3-acetic acid) detection method is complicated in step, time-consuming, quantitative in jamming and high in cost. The indole-3-acetic acid molecularly imprinted magnetic cellulose microsphere disclosed by the invention is prepared from an IAA, 4-VP, silanized beta-CD (beta-cyclodextrin), DMSO (dimethylsulfoxide), nano magnetic cellulose microsphere particles, a crosslinking agent, styrene, an initiator and water. The method comprises the following steps: 1, activating cellulose; 2, dissolving the cellulose; 3, preparing nano Fe3O4 magnetic liquid; 4, preparing nano magnetic cellulose microsphere particles; 5, silanizing beta-cyclodextrin; and 6, preparing the IAA molecularly imprinted magnetic cellulose microsphere. The indole-3-acetic acid molecularly imprinted magnetic cellulose microsphere disclosed by the invention, as an adsorbent, is used for quantitatively detecting the content of an indole-3-acetic acid in plant tissues.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Lycium exsertum tissue culture and rapid propagation method
ActiveCN103843664AReduce the impactLow costCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureCulture mediumsIndole-3-acetic acid
The invention discloses a lycium exsertum tissue culture and rapid propagation method, aiming at solving the propagation problem of introduced lycium exsertum. The method comprises the following steps: explant culturing, primary culturing, subculturing, rooting culturing, seedling hardening and transplanting. The lycium exsertum tissue culture and rapid propagation method has the advantages that only is 6-Benzylaminopurine blended with indole-3-acetic acid when subculturing is performed on the lycium exsertum, so that the influence of hormone accumulation on multiple subculturing is reduced, and the cost is also lowered; no hormone is added in the adopted culture medium when rooting culturing is performed on subcultured seedlings of lycium exsertum, so that the preparation of the culture medium is simplified, the cost is lowered, and the effect is good; peat, vermiculite and perlite in the transplanting medium are mixed according to the ratio of 1:1:1, so that water retaining and heat preservation effects can be achieved in the transplanting process, and the survival rate of transplanting can be increased.
Owner:甘肃鼎鑫农业科技有限公司
Application of halogenated indole-3-acetic acid as herbicide
InactiveCN103621505AImprove herbicidal activityBroad herbicidal spectrumBiocideAnimal repellantsAcetic acidIndole-3-acetic acid
The invention provides an application of halogenated indole-3-acetic acid as herbicide and further provides novel herbicide. According to the invention, halogenated indole-3-acetic acid has efficient herbicidal activity and wide herbicide controlling spectrum. Meanwhile, halogenated indole-3-acetic acid is free of harmful effect to afterreap crops. In addition, halogenated indole-3-acetic acid stays in soil for a short period of time and is low in toxicity, good in environmental compatibility and high in safety.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Tissue culture and rapid propagation method of solanaceae lycium brevipes
ActiveCN104094841AReduce the impact of multiple passagesReduce the impactPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsLycium brevipesPeat
The invention discloses a tissue culture and rapid propagation method of solanaceae lycium brevipes, and aims to solve the problem of propagation of introduced lycium barbarum. The method comprises the following steps: explant treatment, primary culture, subculture, rooting culture, hardening seedling and transplanting, the advantages of the method are as follows: A, only 6-benzyl amino adenine and indole-3-acetic acid are used for mixing during subculture of the solanaceae lycium brevipes, the effect of hormone accumulation on multi times of subculture can be greatly reduced, the cost is also reduced; B, peat and vermiculite in the ratio of 1:1 are used as a hardening seedling and transplanting matrix, the matrix is simple in ratio, light in mass, good in performance in transplanting test, and higher in transplanting survival rate; and C, the tissue culture and rapid propagation method plays a great role on late improvement and application of local Chinese wolfberry.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Selenium-enriched tomato liquid fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104447042APromote absorptionPromote growthAnimal corpse fertilisersFertilisers by pryogenic processesPhosphateImpurity
The invention discloses a selenium-enriched tomato liquid fertilizer which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 5-8 parts of potassium nitrate, 4-6 parts of nostoc sphaeroids kutz, 4-7 parts of funaria hygrometrica, 4-6 parts of potassium chloride, 5-7 parts of ammonium bicarbonate, 4-8 parts of urea, 1-3 parts of klockmannite, 3-5 parts of mulberry fruits, 2-3 parts of ground phosphate rock, 3-5 parts of plant ash, and 6-9 parts of auxiliaries. The tomato liquid fertilizer is uniform and free from impurity and is simple to prepare, the contents of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium as well as medium trace elements can all meet the growth requirement of tomatoes, due to the adding of klockmannite, mulberry fruit, nostoc sphaeroids kutz and other raw materials, the content of selenium in the fertilizer can be greatly increased, and crushed funaria hygrometrica contains promoters such as kinetin and benzpyrole-3-acetic acid capable of promoting tomatoes to absorb nutrients and grow, and thus the fertilizer is a tomato liquid fertilizer with a remarkable effect.
Owner:TAIHU SHIKE AGRI TECH
Bacillus megatherium T317, microbial agent and preparation method of microbial agent
ActiveCN106011002AHigh sporulationGood qualityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAcetic acidMicroorganism
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial agents, in particular to bacillus megatherium T317, a microbial agent and a preparation method of the microbial agent. The bacillus megatherium T317 is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the collection number is CCTCCM 2015753. The preparation method of the microbial agent comprises the following steps of (1) separating and sieving; (2) purifying and storing; (3) solid fermenting and culturing; (4) preparation of microbial agent, so as to obtain the microbial agent of the bacillus megatherium T317. The microbial agent has the advantages that the bacillus megatherium T317 is used as an original strain, and the nitrogenase activity and the auxin secreting capability are measured; the bacillus megatherium T317 has higher nitrogenase activity and IAA (indole acetic acid) secreting capability, the nitrogenase activity of bacillus megatherium T317 is 800-900nmol / (mL h), and the IAA secreting amount is 300-400mg / L in the growth and metabolism process.
Owner:DONGGUAN BAODE BIOLOGICAL ENG
Cutting propagation method for kmeria septentrionalis
InactiveCN106561425AIncrease rooting rate of cuttingsHigh rooting rateBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAspirinAcetic acid
The invention discloses a cutting propagation method for kmeria septentrionalis. The method includes the following steps that firstly, half-lignified branches are collected at September to October of every year and are trimmed into cutting slips, after the stem bases of the cutting slips are sterilized, soaking is performed in a rooting inductive agent for 2 h, taking out and drying are performed, and the rooting inductive agent is mainly a mixed aqueous solution of naphthyl acetic acid, indole acetic acid, aspirin and saccharose, wherein the concentration of the naphthyl acetic acid is 100-300 mg / L, the concentration of the indole acetic acid is 500-800 mg / L, the concentration of the aspirin is 50-100 mg / L and the concentration of the saccharose is 15-30 g / L; secondly, the cutting slips are inserted into a seedling bed medium and are immediately irrigated with the rooting inductive agent; and thirdly, a shade frame is erected on a seedling bed, the relative humidity in the seedling bed is controlled at 70-80%, the temperature is 26-28 DEG C, and the light shading rate is 50-60%. The cutting propagation method for the kmeria septentrionalis has the beneficial effects of being high in cutting rooting rate and survival rate, easy and convenient to operate, and the like.
Owner:GUANGXI BOTANICAL GARDEN OF MEDICINAL PLANTS
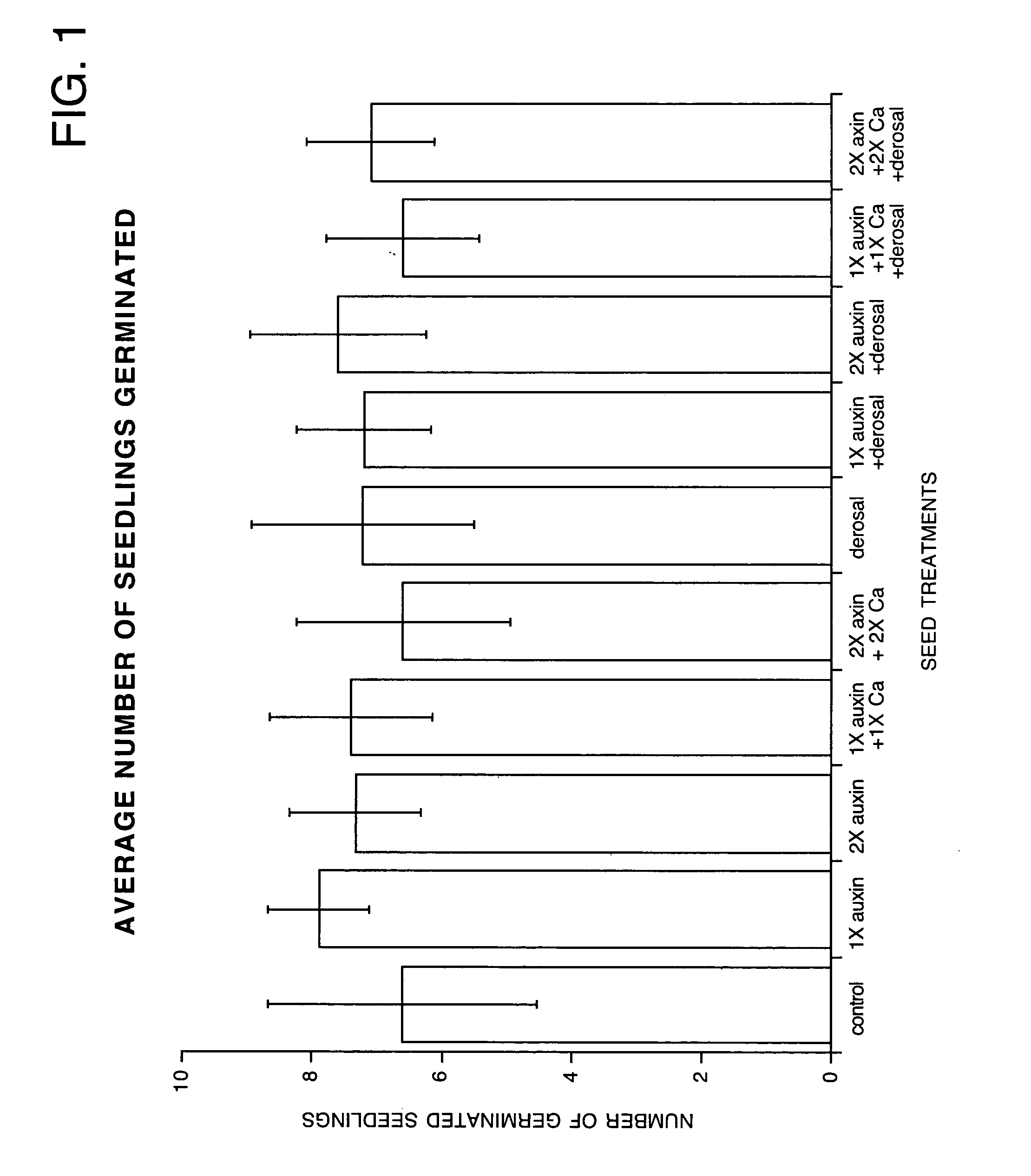
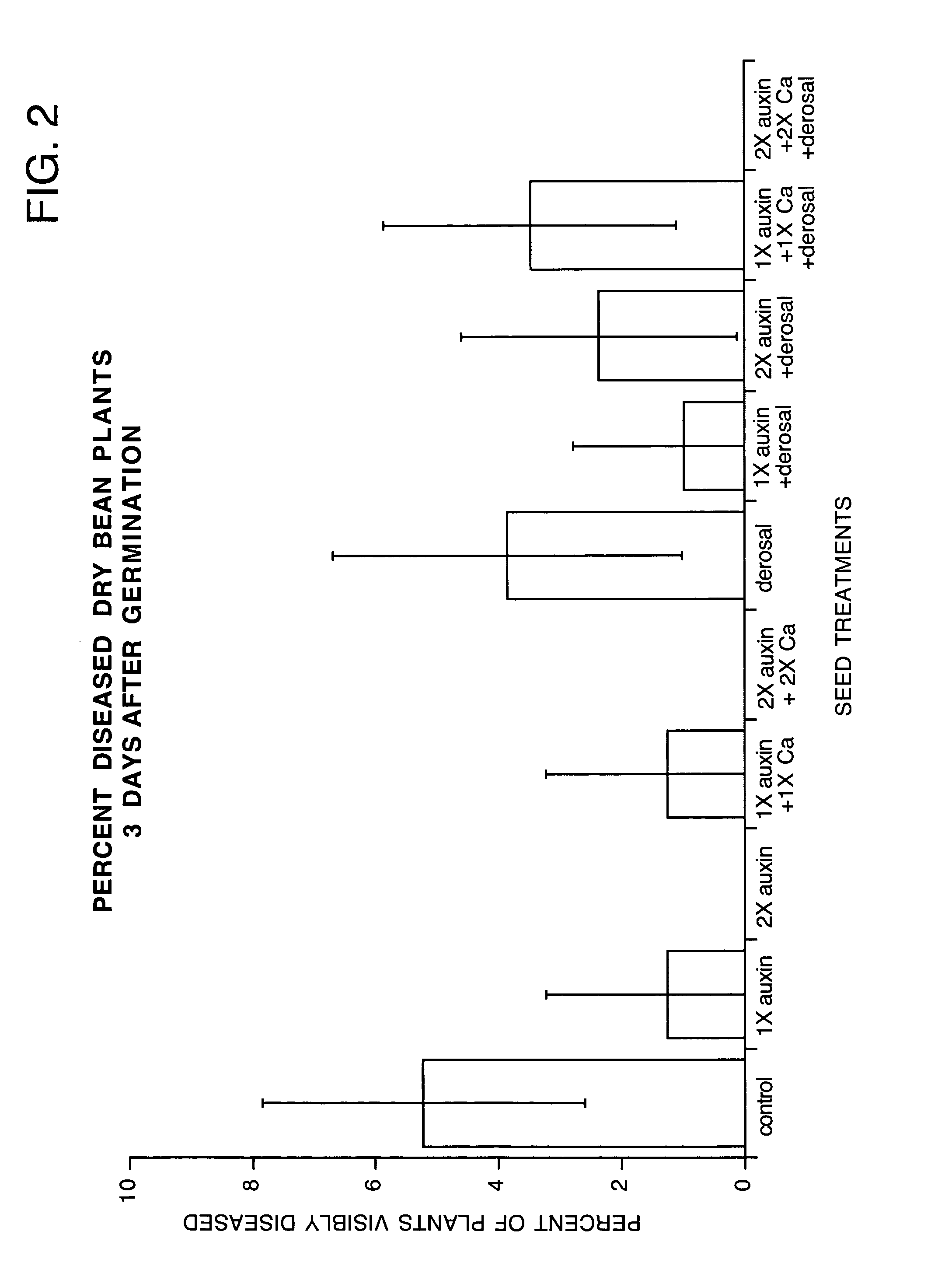
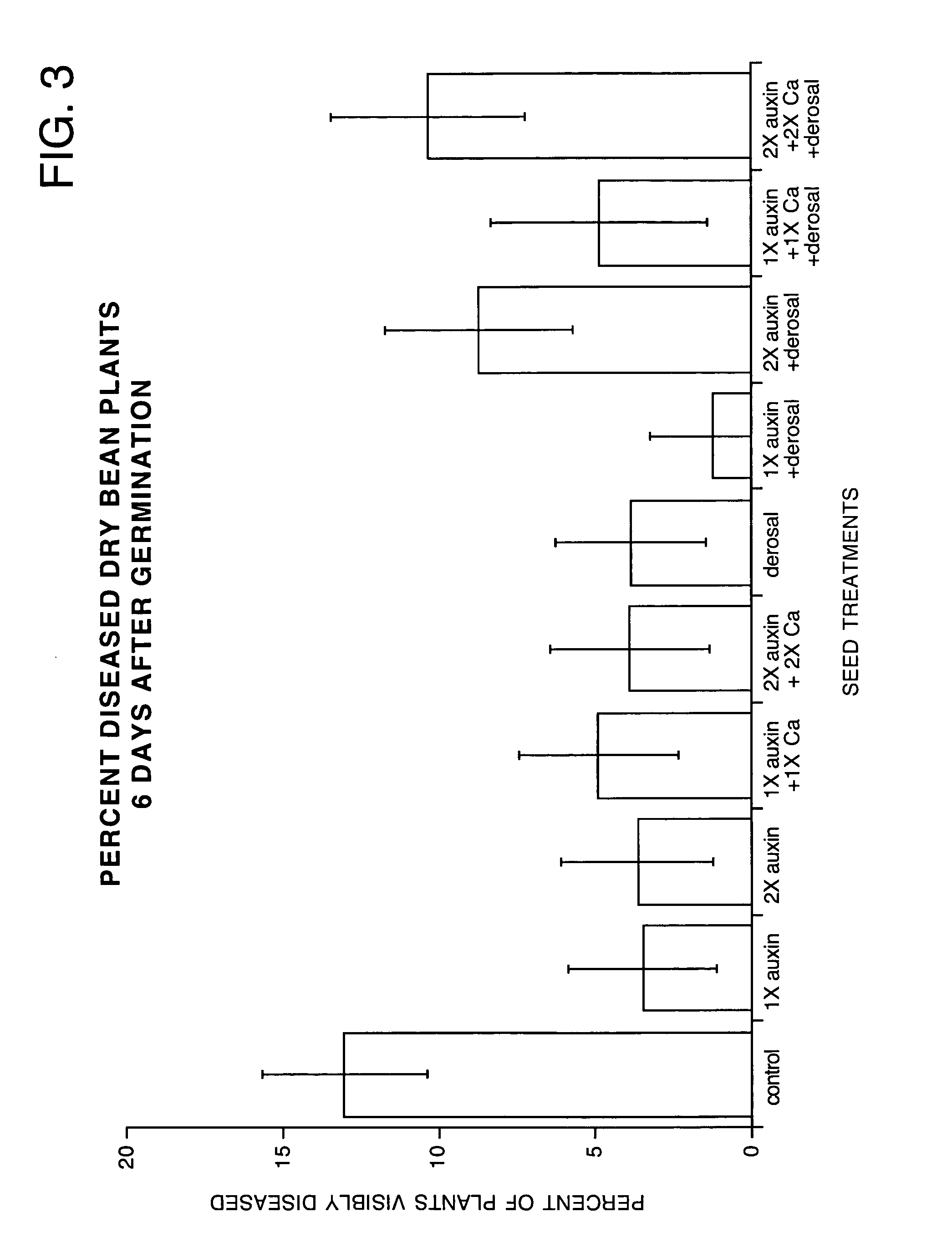
Controlling plant pathogens and pests with applied or induced auxins
InactiveUS20050043177A1Inhibit growth of harmfulNegative effectBiocideAnimal repellantsMetaboliteFungal microorganisms
The present invention is directed to methods for inhibiting the growth of disease organisms, particularly fungi and bacteria, on plant tissues. The present invention is also directed to methods for inhibiting the infestation of plants by insects and larva, particularly sucking and chewing insects. These methods are achieved by applying an auxin or a plant growth regulator (PGR) which will effect the level of auxin in the plant tissue to the seeds or tubers of the plant prior to planting or to the roots, foliage, flowers or fruit of the plant after planting. The auxin or PGR is applied in an amount effective to inhibit growth of the disease organisms or insects, but in an amount insufficient to negatively effect growth of the plant tissues. The auxin may be applied as a natural auxin, synthetic auxin, auxin metabolite, auxin precursor, auxin derivative or a mixture thereof. The presently preferred auxin is indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). The auxin or PGR may be applied to the seeds, tubers or plant tissues. Seeds or tubers may be sprayed with or immersed in an aqueous solution containing the auxin or PGR. Conventional spraying and drip irrigation systems may be used to apply an aqueous solution containing an auxin or PGR to plant tissues. The auxin or PGR may also be applied to the plant tissues as a powder or may be encapsulated within a biologically compatible material to provide slow release to the roots of the plant. The plant tissues may be dusted with a powder, including the auxin or PGR. The encapsulated auxin may be placed in the root zone for uptake of the auxin or PGR by the roots.
Owner:STOLLER ENTERPRISES INC
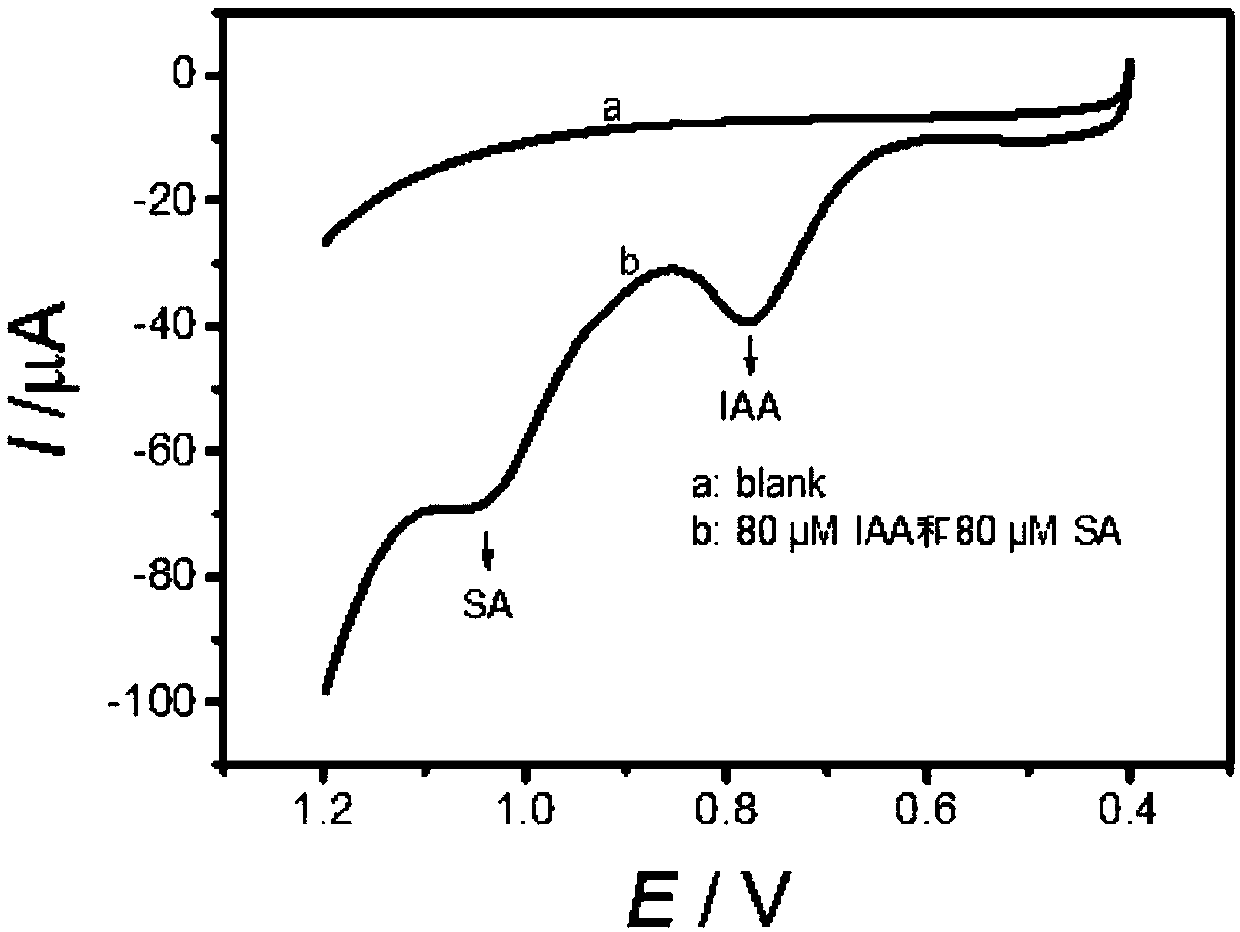
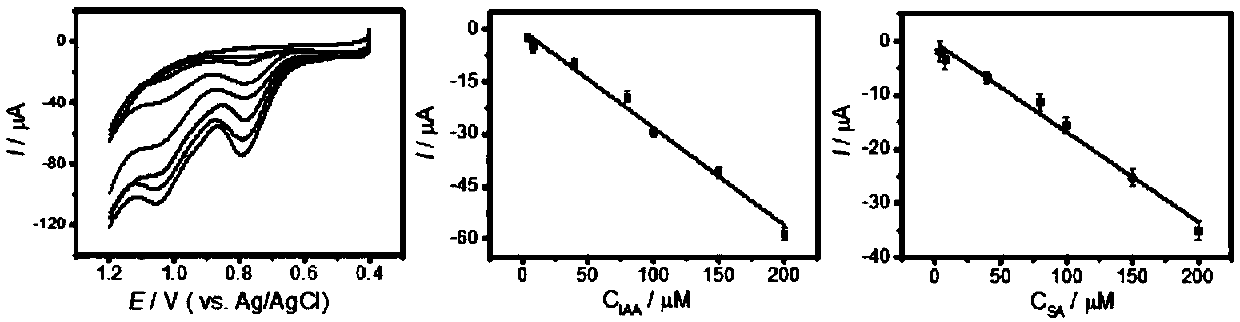
Method for detecting indoleacetic acid and salicylic acid and electrochemical sensor used in method
InactiveCN109521072AImprove adsorption capacityFlexible designMaterial electrochemical variablesPlatinumAcetic acid
The invention discloses a method for detecting indoleacetic acid and salicylic acid and an electrochemical sensor used in the method. The electrochemical sensor comprises a three-electrode system anda detection pool, wherein the three-electrode system comprises a working electrode, an Ag / AgCl reference electrode and a platinum wire counter electrode; the working electrode is a modified glassy carbon electrode; and the detection pool is internally filled with a detection base solution of a buffer solution. Electrochemical detection is carried out on IAA (Indole-3-Acetic Acid) and SA (SalicylicAcid) by utilizing a graphene hydrogel modified electrode; the problems that a general chromatographic method and an immunological detection method are complicated to operate, expensive in cost, highin sample size, high in time consumption, and the like, are solved; the real-time detection on the IAA and the SA is realized; the electrochemical sensor has the advantages of being convenient and quick, being high in detection sensitivity, having the detection limit of the IAA being as low as 0.677 mug / ml and the detection limit of the SA being as low as 0.569 mug / ml, and being low in needed sample amount, extremely low in detection cost, little in interference, and the like, and can be used for realizing the fast, simple, convenient and accurate quantitative detection on the IAA and the SA.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
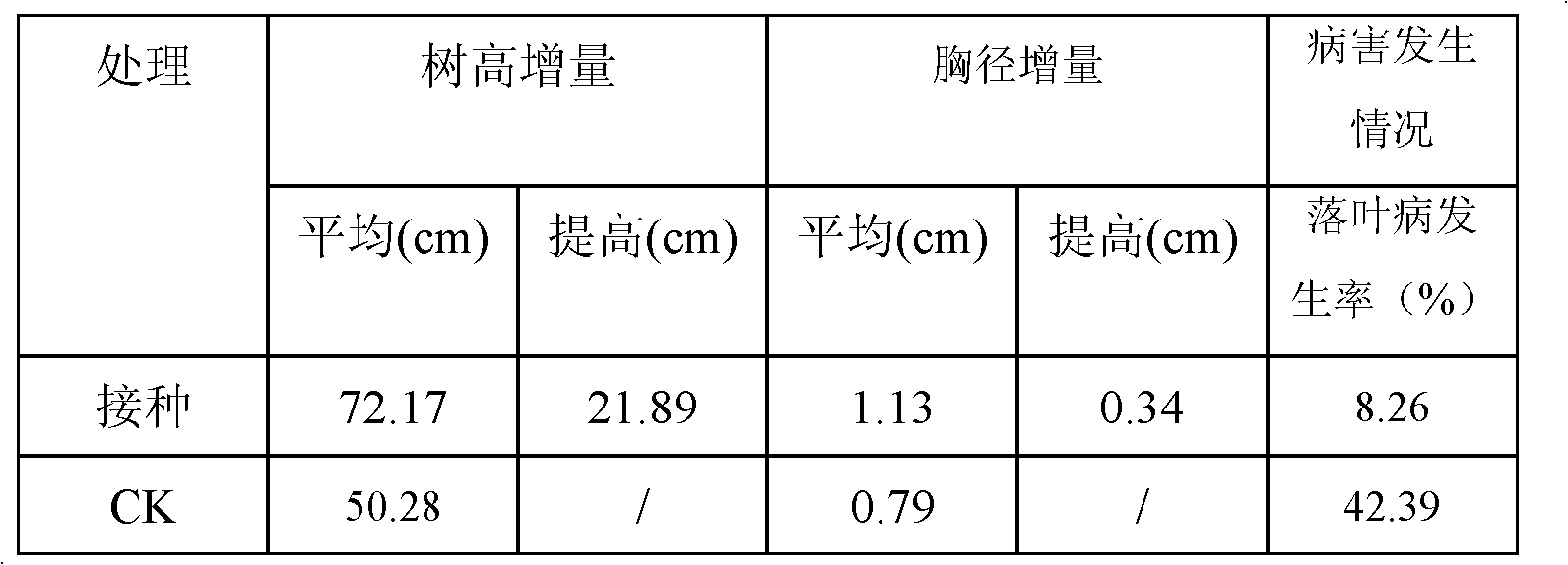
Fertilizing method for improving stress tolerance and productivity of masson pine forest
InactiveCN102612914APromote rootingPromote growthFertilising methodsHorticultureFermentationLactarius akahatsu
The invention discloses a fertilizing method for improving stress tolerance and productivity of a masson pine forest. The method includes the following steps: when the masson pines are arrayed in a matrix or a square matrix, a pit is dug in the middle of a connecting line between every two adjacent trees in the transverse and the longitudinal directions; every two adjacent trees in the transverseand the longitudinal directions share one pit; and four pits are dug on the periphery of each masson pine; stress tolerance health protection mycorrhiza fungicide and organic fertilizer are mutually spaced and placed in the four pits on the periphery of each tree, and earthing is performed then. The stress tolerance health protection mycorrhiza fungicide is compounded and formulated by mycorrhizafungicide and naphthylacetic acid or indole-3-acetic acid, and the mycorrhiza fungicide is fermented by lactarius akahatsu and lactariushatsudake through solid fermentation stock culture; and biological organic fertilizer provides necessary nutrient for the growth of masson pines, and the stress tolerance health protection mycorrhiza fungicide facilitates the rootage and growth of the masson pines, so that the stress tolerance of the masson pines as well as the soil condition and micro ecology environment are improved, the survival rate and growth rate of the masson pines are enhanced, the rich water loss is reduced, and the competition for weeds below the masson pines and shrub for fertilizer is alleviated.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
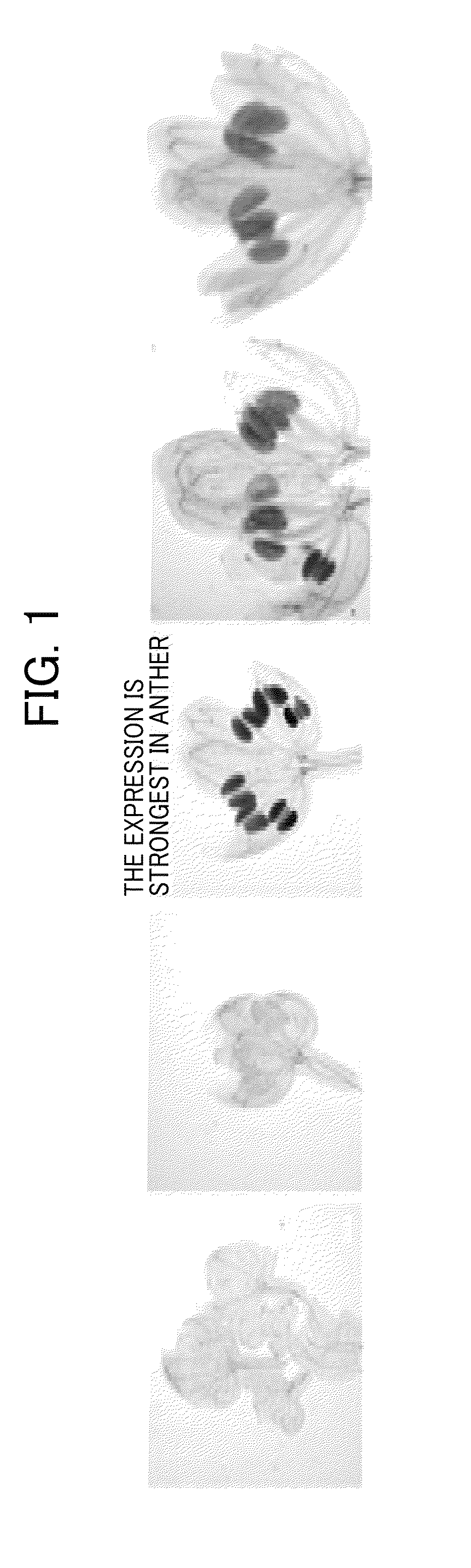
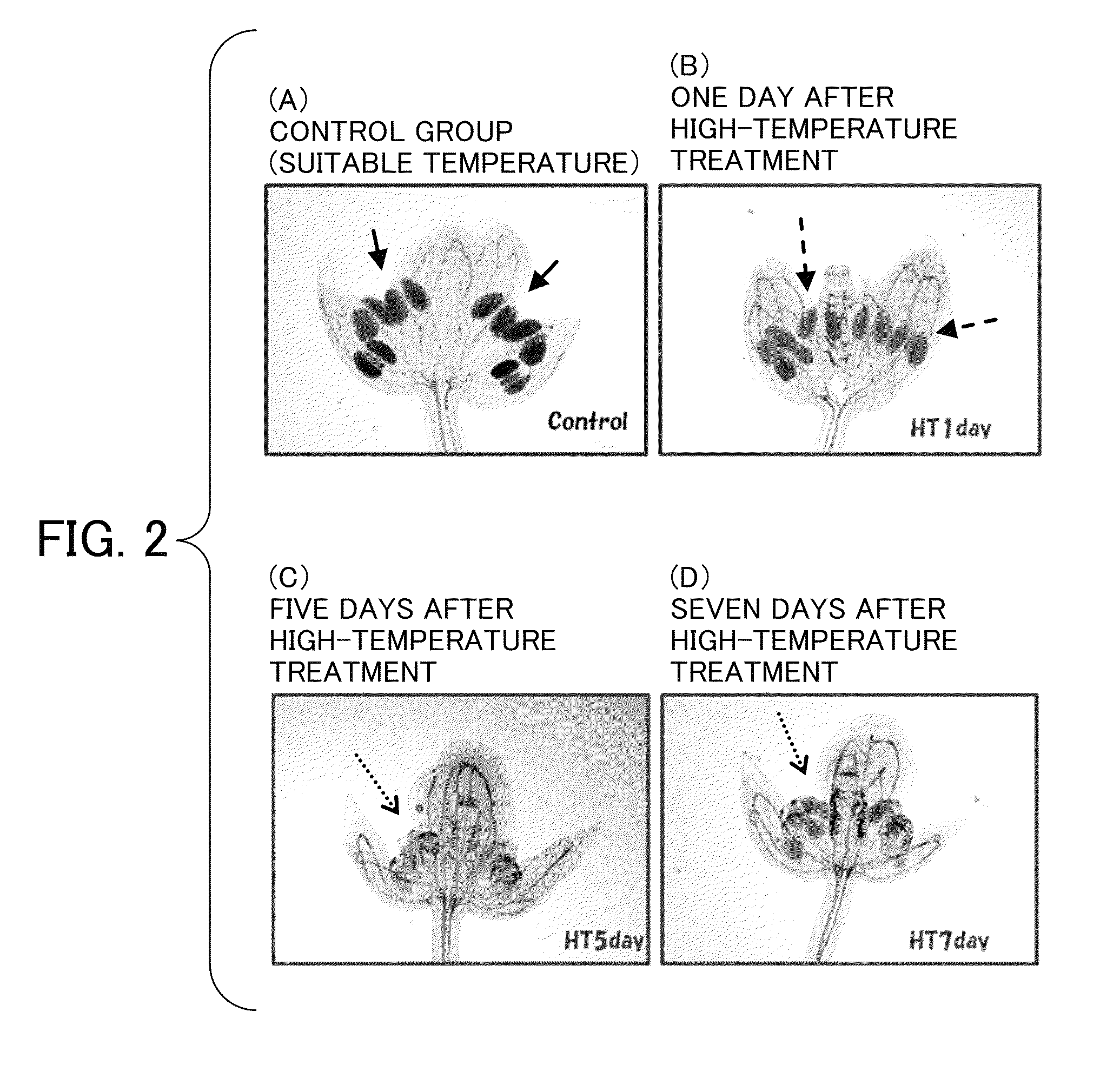
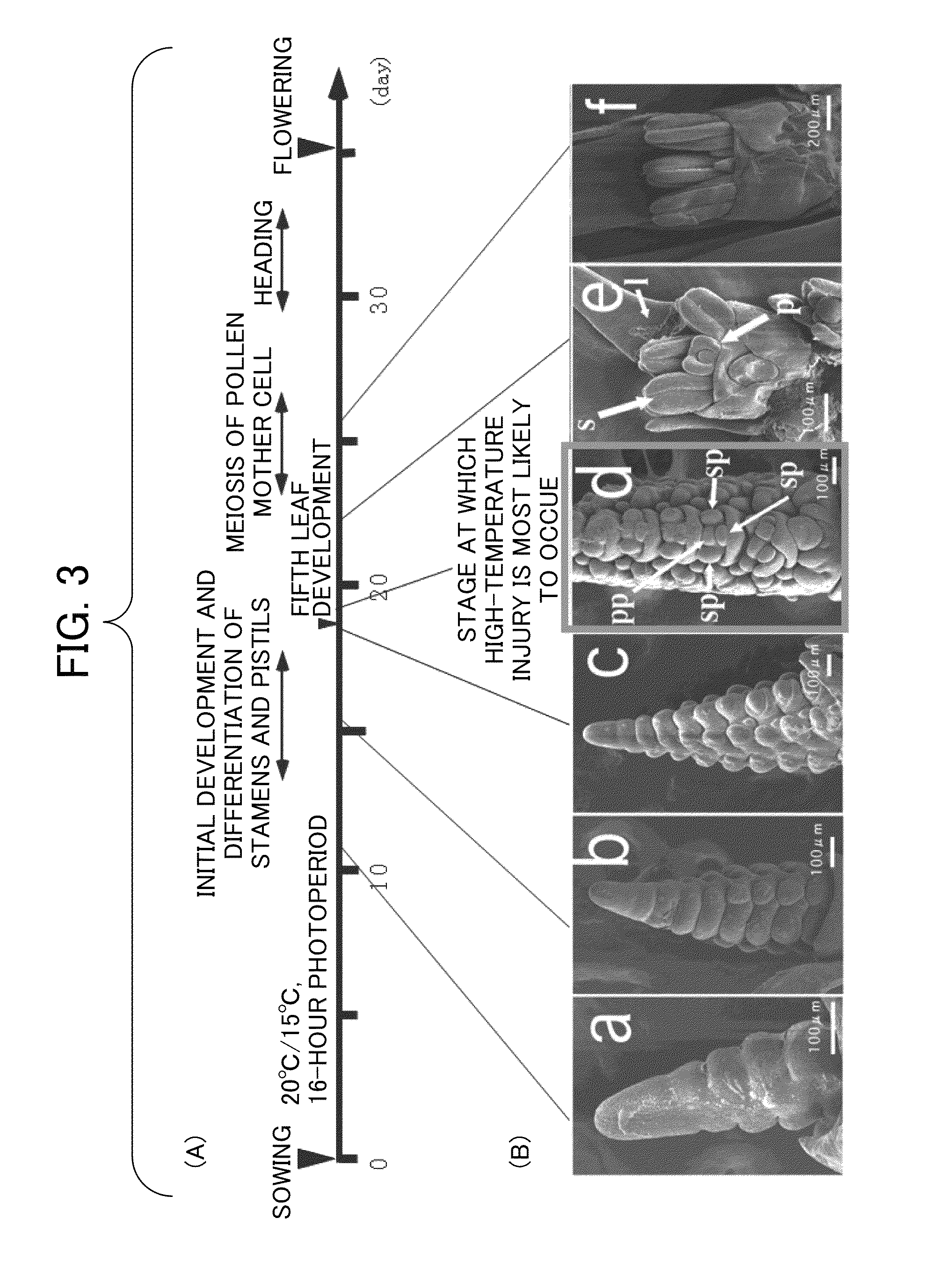
Method of restoring male sterility in gramineous plants and male sterility restorative agent
The present invention provides a method and a composition for restoring pollen fertility by suppressing formation insufficiency in a pollen formation process due to a high-temperature or low-temperature stress. The present invention provides a fertility restorative agent comprising an auxin as an active ingredient, and a method for restoring the fertility of a plants of the family Poaceae, comprising spreading an auxin. Moreover, the present invention provides a fertility restorative agent containing as an active ingredient a substance which inhibits auxin action, and a method for restoring the fertility of rice plant, including spreading a substance which inhibits auxin action. Preferably, the auxin is 10−4 M to 10−7 M of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), 4-chloroindoleacetic acid, phenylacetic acid, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), α-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA), 2,6-dichlorobenzoic acid, indolebutyric acid (IBA), 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid, ethyl 5-chloroindazoleacetate, naphthoxyacetic acid or 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Preparation method and application of indole acetic acid (IAA) molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP)
InactiveCN102702565AEffective combinationEasy to handleComponent separationFibre treatmentFunctional monomerMolecularly imprinted polymer
The invention belongs to the field of analytical chemistry and particularly relates to a preparation method and application of indole acetic acid (IAA) molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP). The preparation method and the application are suitable for enriching and analyzing growth hormone plant samples. According to the method, IAA is used as template molecules, a functional monomer, a crosslinking agent and initiator are added so as to obtain a prepolymerization solution; and reaction is performed at the temperature of 60 DEG C for more than 8 hours, and the template modules are removed so as to obtain the IAAMIP. The IAAMIP can be used for a solid-phase micro-extraction (SPME) coating. The treated quartz fiber is inserted in the prepolymerization solution and is subjected to thermal-initiation polymerization; after reaction, the quartz fiber is taken out, aged and coated repeatedly; the template modules are cleaned completely; and finally the fiber is inserted into a micro-extraction device for subsequent extraction. The IAA-MIP and SPME (MISPME) coating is easy to prepare, controllable in thickness, high in selectivity and good in enrichment effect, and can be used repeatedly. An extraction head is combined with liquid chromatogram, so that two kinds of growth hormone in the plant samples can be efficiently extracted and separated.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Biological fertilizer, method for obtaining same and use thereof as a plant growth stimulator
ActiveUS20110045976A1Reduce the temperatureIncrease contact areaBiocideBacteriaFluidized bed dryingGrowth stimulant
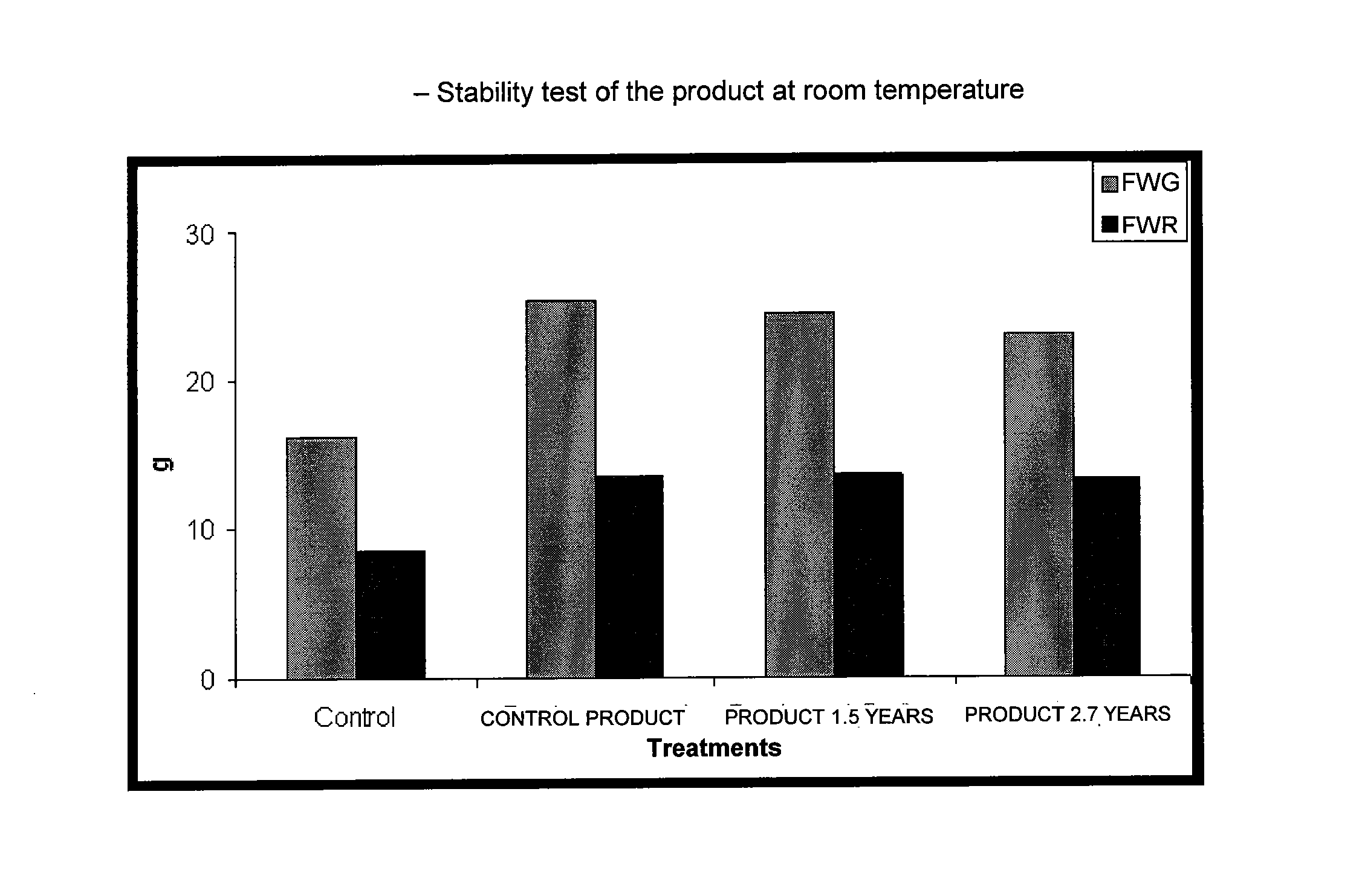
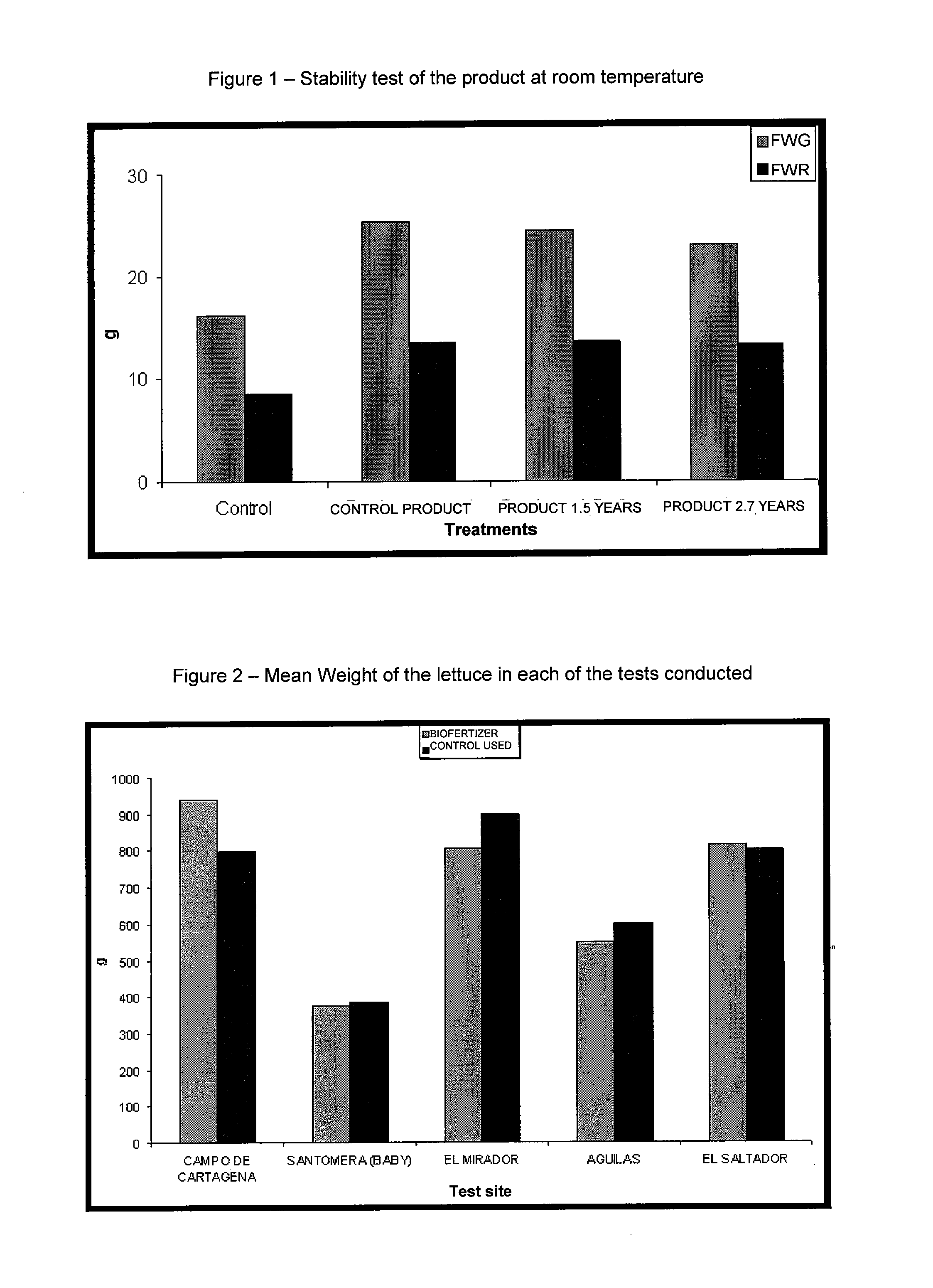
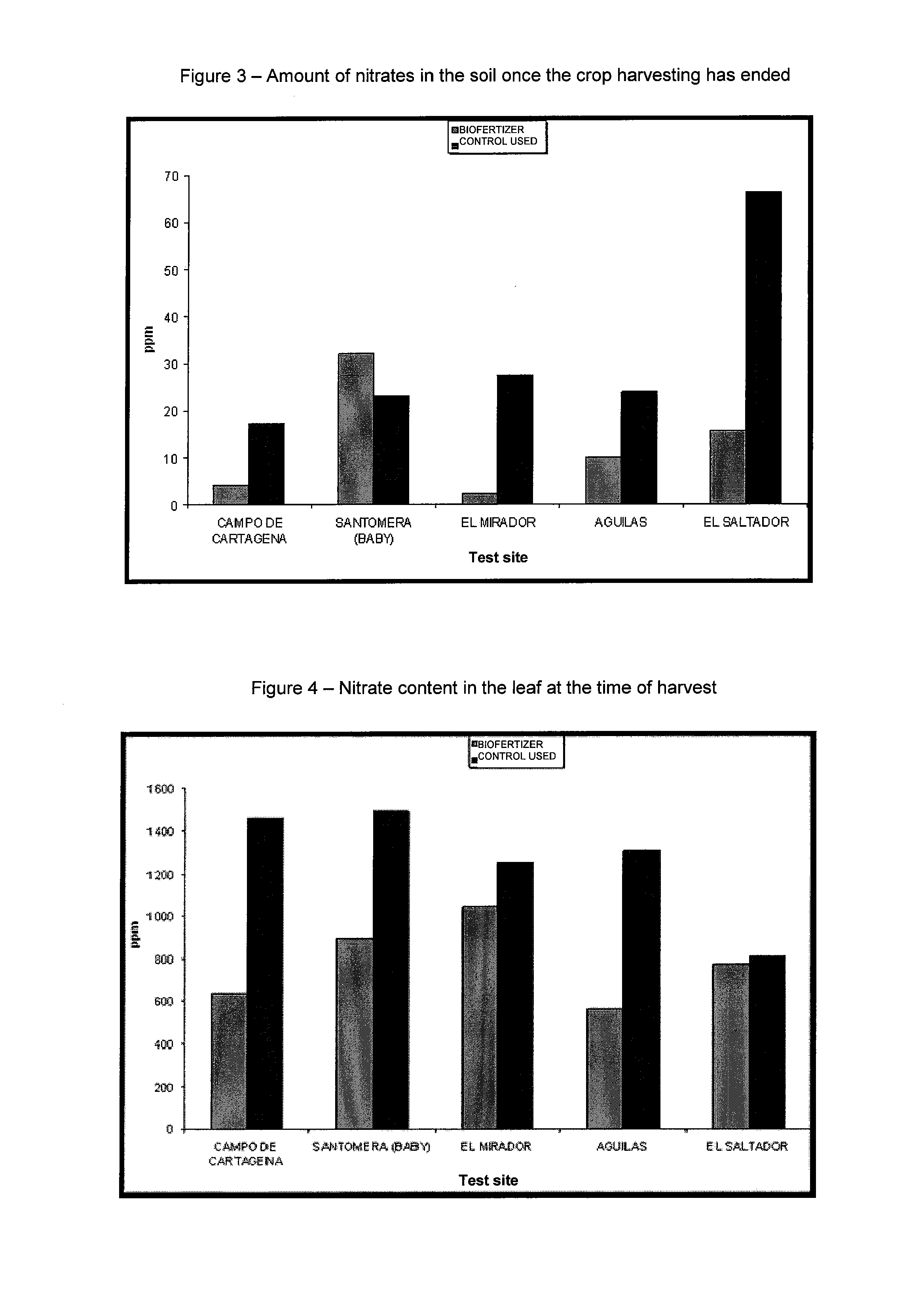
The invention relates to a novel biological fertiliser, a method for obtaining same and the use thereof as a plant growth stimulator, said fertiliser comprising a pure culture of strain C3 of Pantie dispersal, a pure culture of strain M3 of Azospirillum brasilense and indole-3 acetic acid, all of which are immobilised in a single solid medium acting as a slow release system. The method includes the following main steps: culture of the microorganisms; immobilisation of the cells, nutrients and other substances in the medium; and a single fluid bed drying step which enables lower temperatures to be used and lower moisture contents to be obtained, thereby providing the fertiliser with greater stability. The action of the fertiliser commences upon contact with the plant.
Owner:PROBELTE SA
Treatment method for goat milk whey protein for studying proteomics
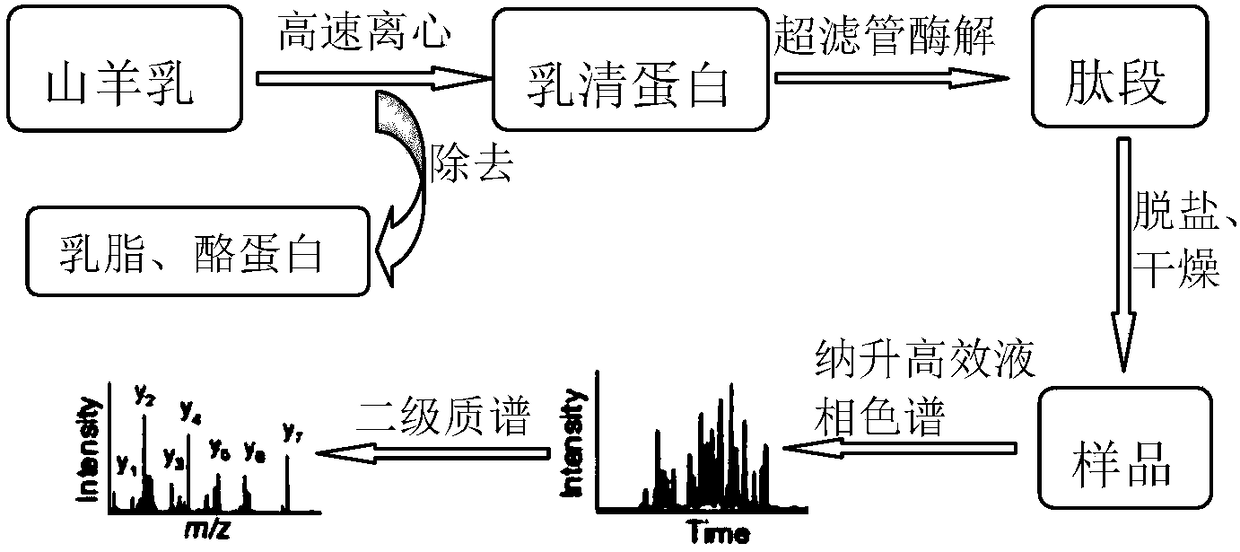
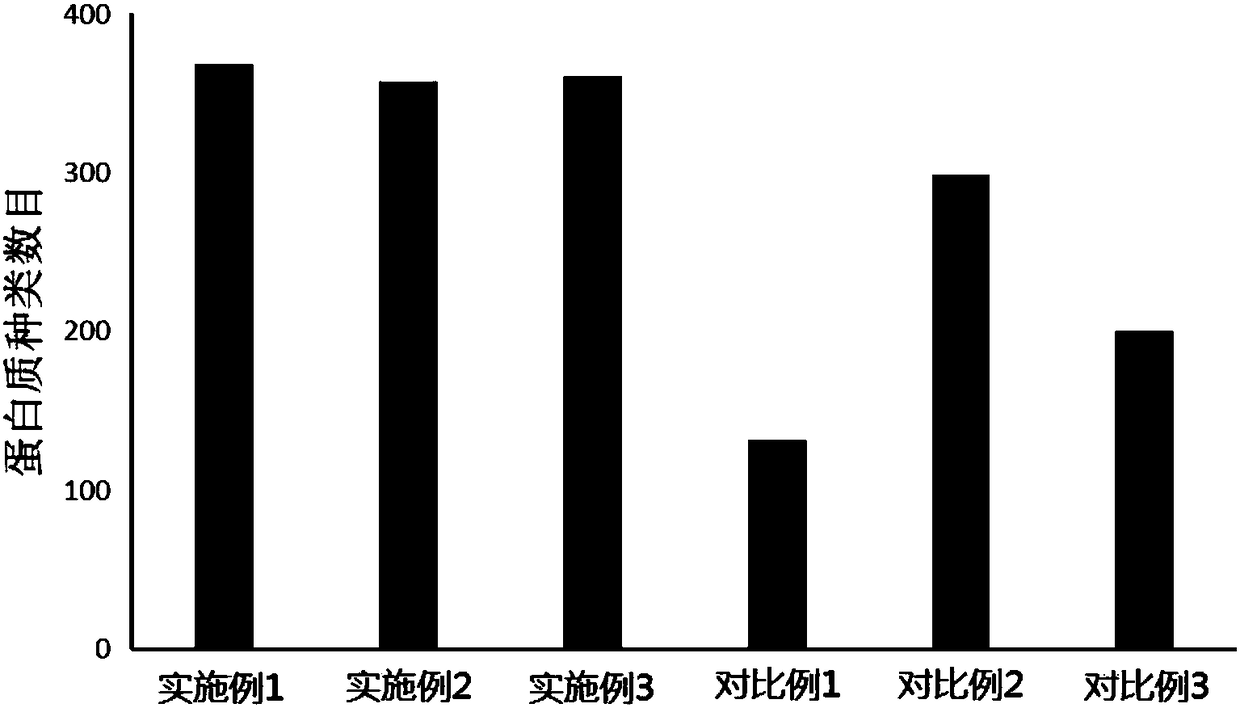
InactiveCN108359704AImprove extraction efficiencyImprove stabilityPeptide preparation methodsFermentationHydrolysateUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a treatment method for goat milk whey protein for studying proteomics and belongs to the technical field of whey protein extraction and treatment methods. The treatment methodcomprises the following steps of taking a goat milk sample, performing high-speed centrifugation to acquire coarsely separated whey, then performing ultrahigh-speed centrifugation to remove casein, and performing precipitation and purification with precooled acetone to obtain a whey protein sample; adding dithiothreitol and indole-3-acetic acid for reductive alkylation, and adding a trypsin solution for ultrafiltration tube inside enzymolysis incubation to obtain polypeptide enzymatic hydrolysate; and performing desalting treatment on the polypeptide solution, performing centrifugal concentration and drying to dissolve a peptide fragment sample again, and performing direct computer analysis. The treatment method provided by the invention is simple and convenient to operate, high in extraction rate, strong in stability and high in flux, more easily realize high-flux detection of proteomics, particularly to low abundance proteins, and has a better popularization and application prospecton the aspect of goat milk whey protein proteomics study.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Bacillus megatherium T482, microbial agent and preparation method of microbial agent
ActiveCN106011003ASimple processScalable productionPlant growth regulatorsBacteriaAcetic acidMicroorganism
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial agents, in particular to bacillus megatherium T482, a microbial agent and a preparation method of the microbial agent. The bacillus megatherium T482 is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the collection number is CCTCCM 2015754. The preparation method of the microbial agent comprises the following steps of (1) separating and sieving; (2) purifying and storing; (3) solid fermenting and culturing; (4) preparation of microbial agent, so as to obtain the bacillus megatherium T482. The microbial agent has the advantages that the bacillus megatherium T482 has higher nitrogenase activity and IAA (indole acetic acid) secreting capability, the nitrogenase activity is 1000-1200nmol / (mL h), and the IAA secreting amount is 200-300mg / L in the growth and metabolism process; the microbial agent is a new microbial agent, and the application prospect in agricultural production is good.
Owner:DONGGUAN BAODE BIOLOGICAL ENG
Scindapsus aureus rooting medium and scindapsus aureus rooting culture method
InactiveCN106613974APromote rootingHigh transplant survival ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsShootPlant growth
The invention discloses a scindapsus aureus rooting medium which is prepared from MS minimal medium, naphthylacetic acid, indole-3-acetic acid, mashed potato, saccharose and agar powder. According to the scindapsus aureus rooting medium and the scindapsus aureus rooting culture method, the MS culture medium is used as the minimal medium and is combined with the specific concentration of naphthylacetic acid, an indole-3-acetic acid plant growth regulator, the mashed potato, the saccharose and the agar powder; thus, the rooting medium can effectively promote the scindapsus aureus crowd shoots to root. When the rooting medium is used for performing rooting culture of the scindapsus aureus crow shoots, the rooting rate can reach 96% or more, the root systems grow well, and the transplanting survival rate is high; thus, the method provides technical support for industrialization, popularization and application of scindapsus aureus tissue culture.
Owner:东方上彩现代农业有限公司
Screening method and application of Raoultella planticola strain SRPG-4 producing ACC (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid) deaminase activity
InactiveCN104450550AImprove germination rateReduce dosagePlant growth regulatorsBacteria1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acidScreening method
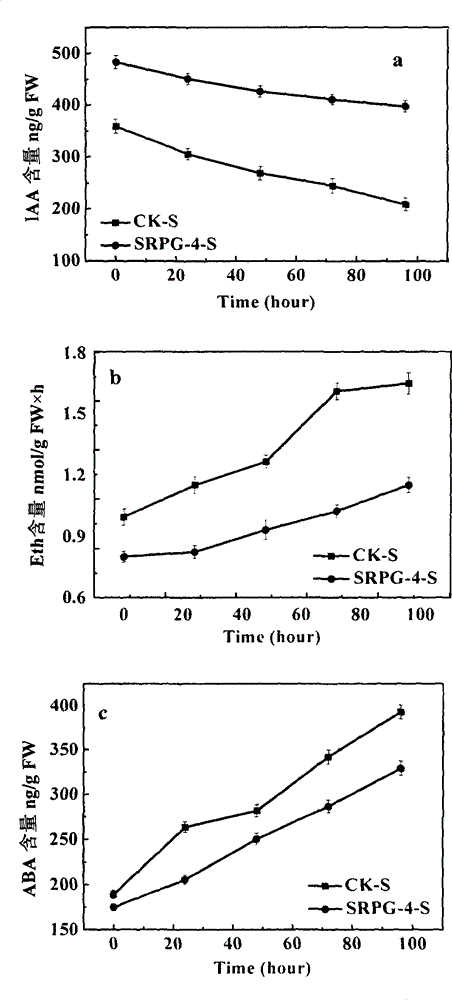
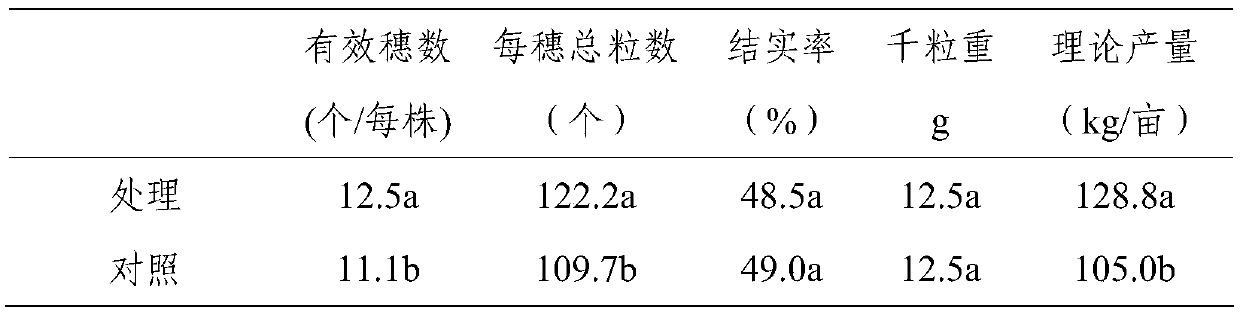
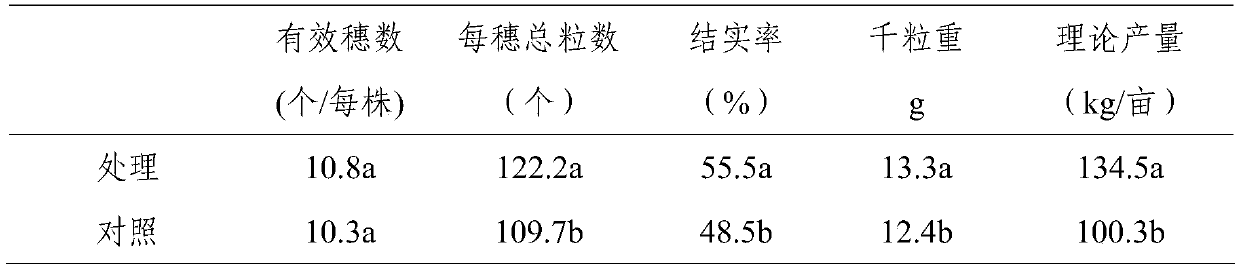
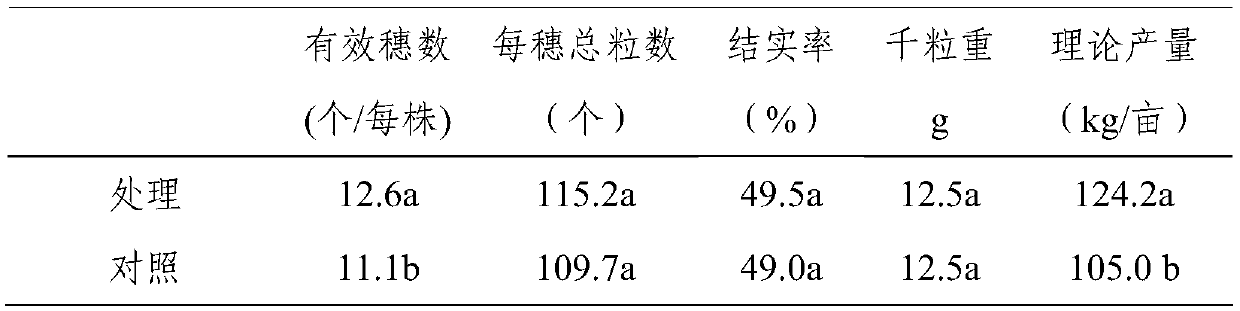
The invention provides a screening method (comprising four steps of gathering, preliminary screening, secondary screening and identifying) and an application of a Raoultella planticola strain SRPG-4 producing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) deaminase activity, wherein the strain is identified as Raoultella planticola SRPG-4 with a preservation number of CGMCC No.9392. The strain SRPG-4 obtained by the method provided by the invention can grow well in an ADF (Augmented Dickey-Fuller) culture medium, and the ACC specific enzymatic activity of the strain reaches 0.832+ / -0.032U / mg. Under a salinization condition, the application of an SRPG-4 bacterium solution has an obvious effect of improving the germination rate, the planting percent and the biomass accumulation of cotton, and can adjust the output of an auxin (IAA namely indole-3-acetic acid) and relieving the generation of ethylene (Eth) and a cytokinin (ABA), thereby relieving salt stress. The strain screened by the method provided by the invention is derived from northwest arid areas, has strong adaptive capacity to environment and has advantages of stable application effect and the like, so that the strain used for developing a microorganism bacterium agent has a wide application prospect to solve the problem of soil salinization.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY +1
Growth regulating agent capable of improving hybrid rice seed production and sterile line seed reproduction yield and application
InactiveCN105494372AHigh spike rateReduce degradationPlant growth regulatorsBiocideAcetic acidSide effect
The invention provides a growth regulating agent capable of improving hybrid rice seed production and sterile line seed reproduction yield. The growth regulating agent is prepared from the following components: 2,4-epibrassinolide, indole-3-acetic acid, zeatin and water, and the pH value is 5.8 to 6.5. By using the growth regulating agent provided by the invention, in hybrid rice seed production and sterile line seed reproduction, the productive tiller percentage of a sterile line can be improved, so as to increase the number of productive ear, floret degeneration can be reduced, so as to increase kernels per spike, grouting is promoted, so as to improve ripening rate and / or increase thousand seed weight, and finally the hybrid rice seed production yield and the sterile line seed reproduction yield are improved. The growth regulating agent is simple and easy in preparation method, is good in product stability, strong in efficiency, safe and reliable, free of side effect and is suitable for popularization and application in hybrid rice seed production.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Rooting nutrient solution
The invention relates to a rooting nutrient solution, which contains indole-3-acetic acid sodium salt, NAA, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, copper sulphate, magnesium sulfate, sodium chloride, ammonium molybdate, potassium iodide and distilled water. When used, 4-8 drops of the product are added into 200 mL of water. The invention has the advantages of convenient usage, small amount and fast effectiveness.
Owner:TIANJIN BEIFANG LANDSCAPE ECOLOGY INST OF SCI & TECH
High yield corn seed treatment method
InactiveCN104855001AImprove stress resistanceGrowth inhibitionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsSeed treatmentNaphthalene
A high yield corn seed treatment method includes seed treatment, field planting, field management and water and fertilizer management, an excellent hybrid corn variety corn seed, which is close planting resistant, dwarf, lodging resistant, compact in plant type, mature in living stalk, suitable in mature period, free of balding fruit cluster, and resistant to diseases and insects, is selected, and is treated by corn special organic seed clothing, and the organic seed clothing treatment includes the following components: actinomycin, bacillus subtilis, azospirillum, fulvic acid, spicy powder, indole acetic acid, trace elements, alpha-sodium naphthalene acetate growth regulator, EDTA-2 Na chelating agent, humic acid and peat.
Owner:张萍
Sandy plant tissue culture medium, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108419678AEasy to trainPromote rapid reproductionHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSucroseNutrient solution
The invention discloses a sandy plant tissue culture medium, a preparation method thereof and an application thereof. The sandy plant tissue culture medium consists of river sand, nutrient solution, plant growth regulator, ascorbic acid, polyvinylpyrrolidone and fungicide, wherein with 1 liter as the standard, the nutrient solution accounts for 100-200 milliliters per liter, the various plant growth regulator such as 6-BA (6-Benzylaminopurine), NAA (1-naphthlcetic acid), IBA (indole-3-butytric acid) and IAA (indole-3-acetic acid) each account for 0.01-10.0 milliliters, the ascorbic acid accounts for 0.1-5.0 grams per liter, the polyvinylpyrrolidone accounts for 1-5 grams per liter, the fungicide accounts for 3-15 grams per liter, and the river sand accounts for the remaining volume, and the nutrient solution includes MS nutrient solution, sucrose, Zt, 6-BA and NAA. The preparation method of the sandy plant tissue culture medium includes various steps such as pretreatment, culture medium preparation, and post-formulation treatment. The sandy plant tissue culture medium can be widely applied to the tissue culture of of lianas, herbaceous plants and woody plants. The sandy plant tissue culture medium, the preparation method thereof and the application thereof have the advantages that with fine clean river sand as solid medium instead of agar, the cost of the culture medium is reduced; the river sand can be recycled for multiple times; accurately adjusting the pH of the nutrient solution, plant growth hormone and plant organic nutrient solution in plant tissue culture medium isunnecessary.
Owner:CHUXIONG NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com