Indole-3-acetic acid molecularly imprinted magnetic cellulose microsphere and preparation method and applications thereof
A technology of cellulose microspheres and molecular imprinting, which is applied in the direction of microsphere preparation, microcapsule preparations, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of complex steps, interference quantification, and high cost of IAA detection methods, and achieve long-term storage. Low preparation cost and good surface uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
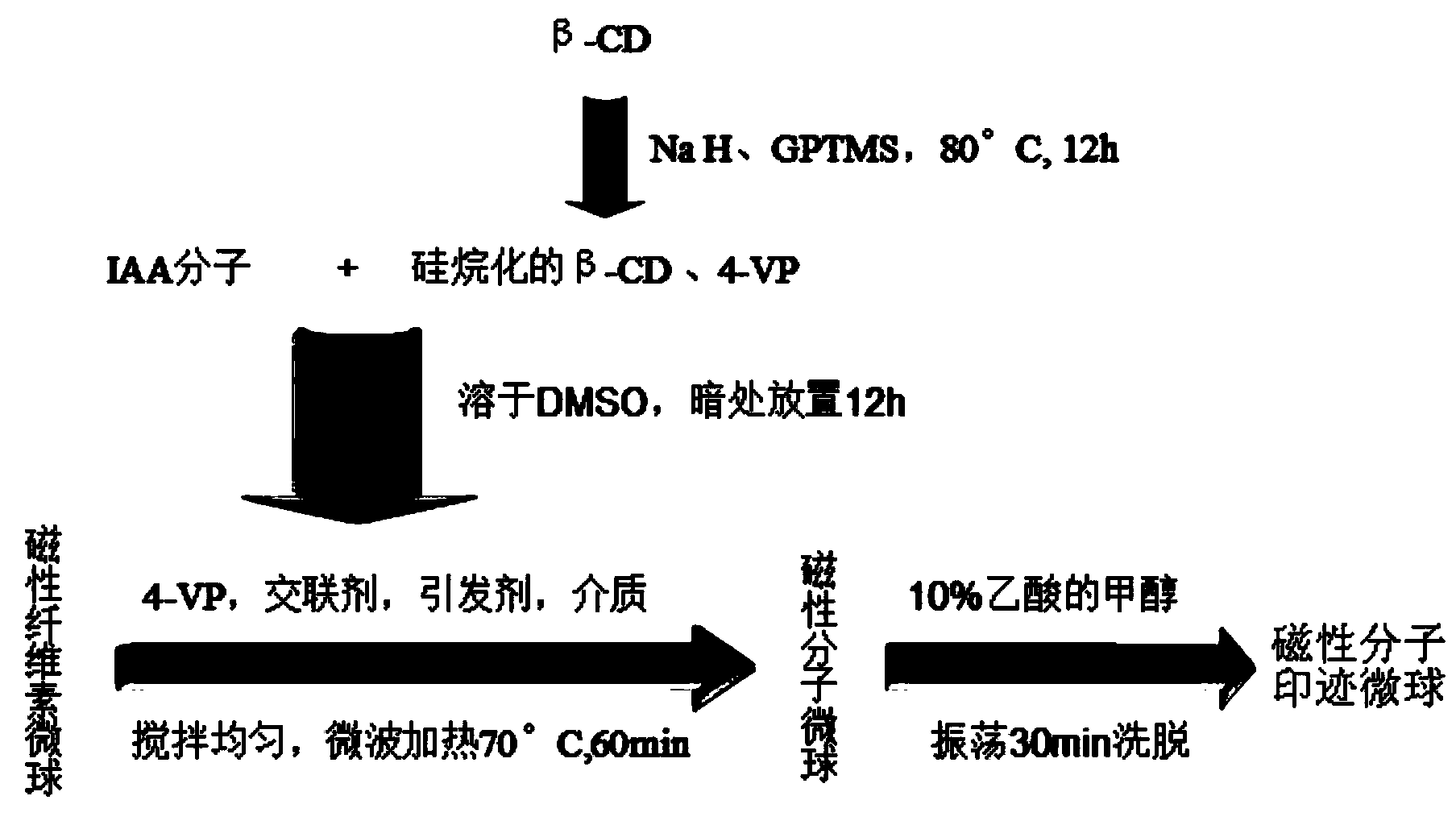
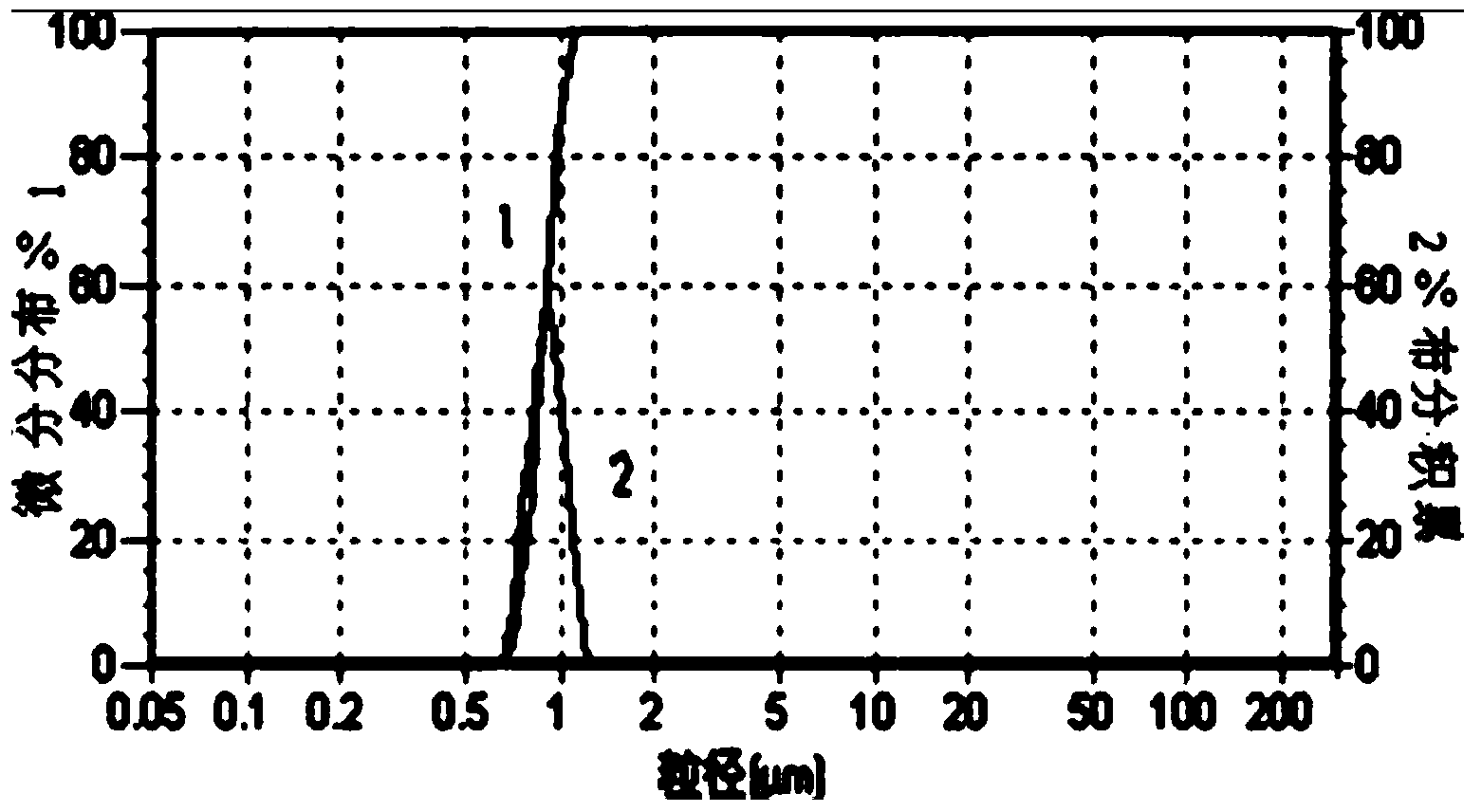
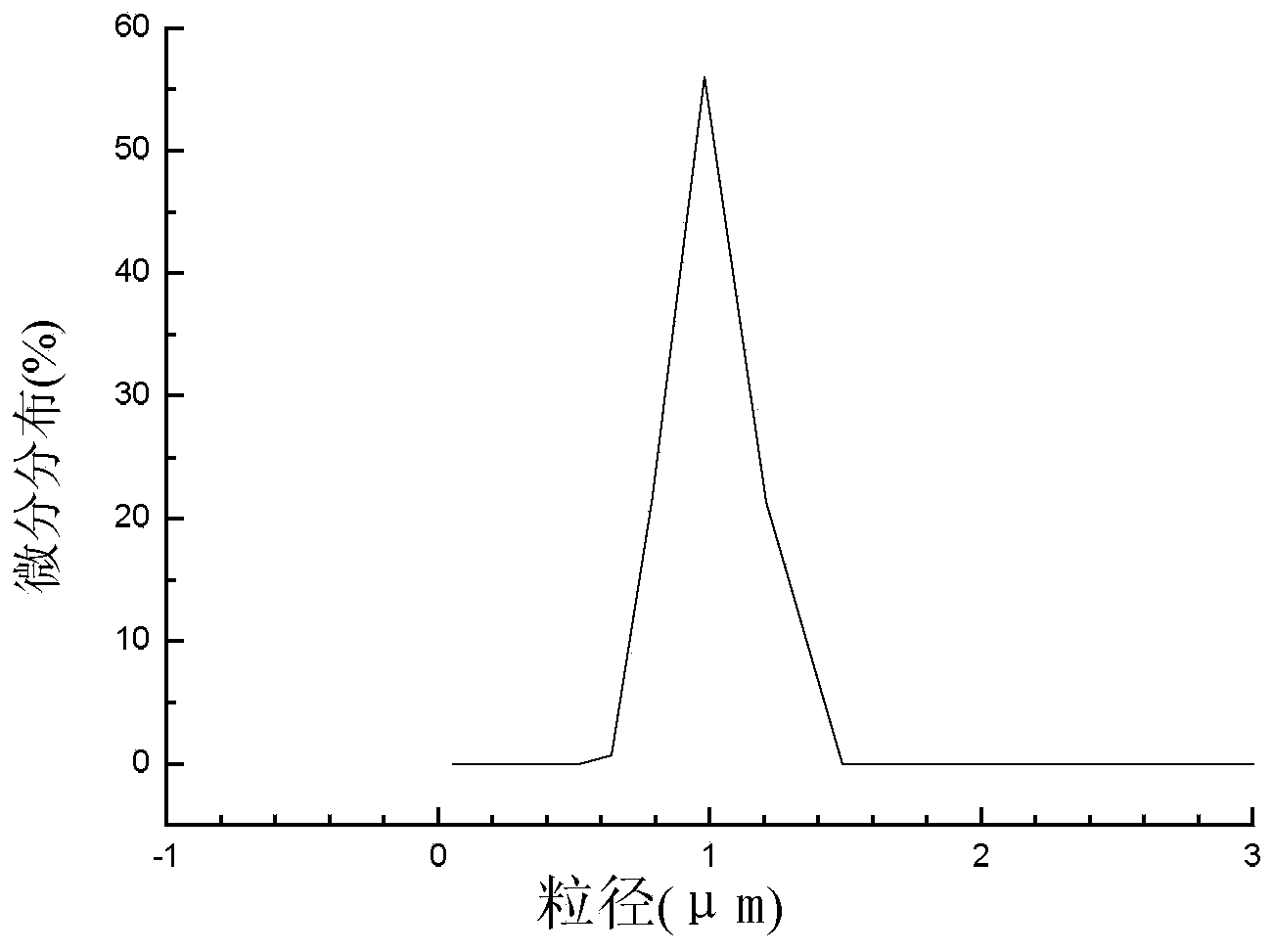
[0034] Specific embodiment 1: In this embodiment, an indole-3-acetic acid molecularly imprinted magnetic cellulose microsphere is composed of 1.0-1.2 mmol of IAA, 4.0-4.2 mmol of 4-VP (4-vinylpyridine), 2.0-2.1 g silanized β-CD (β-cyclodextrin), 10-12mL DMSO, 0.05g-0.10g nano-magnetic cellulose microspheres, 23-24mmol cross-linking agent, 79-80mmol styrene ( ST), 0.6-0.7 mmol of initiator and 80-85 mL of water.
[0035] The beneficial effect of this implementation mode:
[0036] 1. The main raw material used in this embodiment is degradable and non-polluting cellulose material. Nanomagnetic cellulose microspheres have superparamagnetism, and can be positioned and separated in the presence of an external magnetic field;
[0037] This embodiment chooses Fe 3 o 4 Nano-magnetic particles are used as the magnetic inner core, and cellulose solution is used as the outer shell, which not only has the advantages of safety, non-toxicity and biodegradability, but also the microspheres...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the nano-magnetic cellulose microspheres are prepared according to the following steps:
[0041] 1. Prepare 0.5mol / L FeSO with distilled water heated to boiling for 3-5 minutes and then cooled to room temperature 4 solution and 1.0mol / L FeCl 3 solution, 0.5mol / L FeSO 4 solution and 1.0mol / L FeCl 3 The solution is mixed at a molar ratio of 1:1.5~2, stirred under nitrogen until homogenized to obtain a mixed solution, and then NH with a mass percentage of 25%~28% is added 3 ·H 2 O solution, adjust the pH value of the mixed solution to 11~13, stir at 800~1000rpm under nitrogen for 1.5~2h to obtain the product, put the product in a microwave heater, and heat it at 80°C~90°C under nitrogen Heating under low temperature for 1-1.5h, collecting the precipitate with a magnet, and then alternately washing with 8%-10% acetic acid and distilled water for 3-4 times to obtain Fe 3 o 4 particle;
[004...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0044] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that it is characterized in that the silanized β-CD is prepared according to the following steps: take β-CD and add it to anhydrous DMF to prepare Make a DMF solution of β-CD with a mass percentage of 20% to 22%, then add NaH to 30 to 35 mL of the above solution until NaH is saturated, and then perform magnetic stirring at 800 to 1000 rpm for 1 to 1.5 hours. During the stirring process Add 2~3mL of GPTMS to the solution, then react at 75℃~80℃ for 10~12h, wash the obtained precipitate with DMF, methanol and acetone in sequence to obtain silanized β-CD, then silanized β-CD at 100℃~ Vacuum-dry at 110°C for 12-14 hours, then place in a desiccator, and obtain silanized β-CD after drying. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com