Method for separating circulating tumor cells from blood
A tumor cell and blood technology, applied in the field of biological and medical detection, can solve the problems of low cell purity, cumbersome operation, and difficult long-term storage of chips, and achieve the effect of improving purity, easy operation, and reducing non-specific adsorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
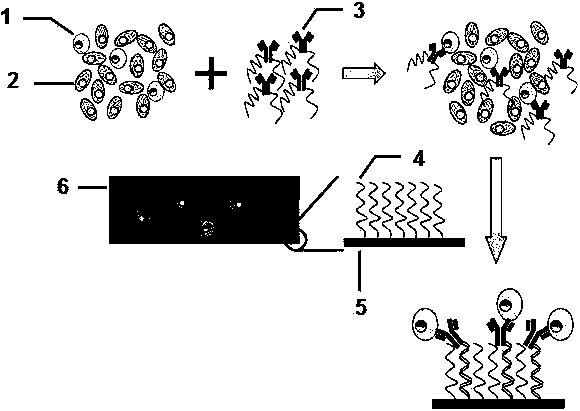
[0029] Example 1 Microfluidic chip substrate loaded with polynucleotide
[0030] The polynucleotide with the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 was dissolved in pure water to prepare a solution with a concentration of 400 μM, and then diluted with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) at a volume ratio of 2:1 to a solution with a final concentration of 267 μM. At the same time, the polydimethylsiloxane PDMS (RTV615, purchased from General Electric Company) microfluidic chip used to infuse polynucleotides was attached to polylysine glass (purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific Thermo Fisher Scientific company), placed in an oven at 80°C for 2 hours. After the treatment, a constant-flow pump was used to infuse the polynucleotide solution with a concentration of 267μM. After filling, it was placed in a drying oven to dry. After the liquid in the channel was completely dried, the microfluidic chip was removed and the glass was placed in an oven. Treat it at ℃ for 4 hours, then quickly wash out the...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2 Production of "fishbone type" CTC capture chip
[0032] A "fishbone type" PDMS chip with periodic surface unevenness structure (see Wang, ST; Liu, K.; Liu, JA et al, .Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.2011, 50, 3084-3088 for manufacturing method ) Paste on the poly-lysine glass loaded with polynucleotides to ensure that the microchannel of the "fishbone" chip overlaps with the base polynucleotide area, and place the chip in an oven at 80°C for 2 hours. After the treatment is complete After the chip returns to room temperature, fix it with a clamp. The "fishbone" chip has an entrance and an exit. The channel is a continuous S-shaped, with a width of 1mm and an overall length of 200mm. The cross-section of the chip has a periodic uneven structure and is made of two layers of SU8 photoresist. The thickness of the lower photoresist is 70μm, the thickness of the upper photoresist is 35μm, and the fishbone patterns on the upper layer are periodically arranged. The width of the "fishb...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Example 3 "Fishbone" chip captures rare tumor cells in blood
[0034] First, the "fishbone" chip is perfused with 3% bovine serum albumin (BSA) through a constant flow pump, and the chip is sealed by standing at room temperature for 1 hour. Suspend colon cancer tumor cells HCT116 in the cell culture medium, stain them red with the cell membrane red fluorescent probe DiI (purchased from Biyuntian), and then mix 1000 HCT116 cells with 1 ml of anticoagulated whole blood from healthy people At the same time, add 1 microliter of 1mg / ml epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM)-labeled single-stranded polynucleotide complex (sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2, wherein the 5 end of the sequence, that is, the left end is labeled with amino, will The single-stranded polynucleotide is labeled on the antibody using Solulink's Antibody-Oligonucleotide All-in-One Conjugation Kit), mixed thoroughly for half an hour and then passed through the "fishbone type" with a syringe and a constant ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com