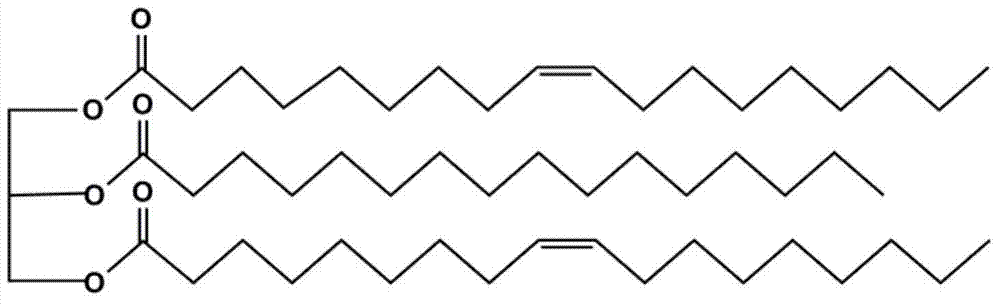
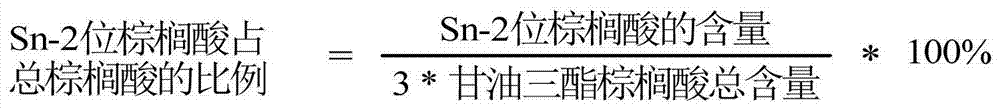Preparation method of synthetic human milk fat substitute (HMFS) of chrysalis oil source
A technology for breast milk fat and silkworm pupa oil, which is applied to milk substitutes, dairy products, applications and other directions, can solve problems such as the undeveloped utilization rate of silkworm pupa oil and the undeveloped market prospect, and achieve the effects of helping growth and development and reducing import pressure.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] This example illustrates the process of using lipase as a catalyst to catalyze the esterification reaction.
[0031] Refined silkworm chrysalis oil is obtained by physical pressing of silkworm chrysalis. Refined silkworm chrysalis oil was determined by gas chromatography, and it was found that silkworm chrysalis oil contained palmitic acid (C 16:0 ), palmitoleic acid (C 16:1 ), stearic acid (C 18:0 ), oleic acid (C 18:0 ), linoleic acid (C 18:2 ) and linolenic acid (C 18:3 ). After a large number of reaction experiments, it was found that the fatty acid content in each product reached the optimum when the reaction temperature was 65°C, the molar ratio was 1:5, the proportion of reaction enzyme was 5%, and the reaction time was 2 hours.
[0032] After mixing refined silkworm pupa oil (6.5g) and oleic acid (8.46g) in a molar ratio of 1:5, specific lipase Lipozyme RM IM5% (0.748g) was added, and the mixture was placed in a water-bath shaker at 65°C for 0.5h. After the...
Embodiment 2
[0036] This example illustrates the process of using lipase as a catalyst to catalyze the esterification reaction.
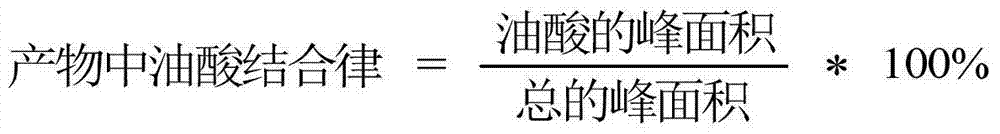
[0037] The refined silkworm chrysalis oil (6.5g) was mixed with oleic acid (2.82g) at a molar ratio of 1:1, then specific lipase Lipozyme RM IM3% (0.449g) was added, and the mixture was placed in a water-bath shaker at 65°C for 2 hours. After the reaction, 300 μL was taken out, 2 mL of n-hexane and 2 mL of 0.5 mol KOH-methanol solution were added to react in a water-bath shaker at 65 °C for 1 h, and then detected by gas chromatography, the oleic acid binding rate in silkworm chrysalis oil was measured to be 50.5%. The content of each fatty acid measured in the silkworm chrysalis oil in this example is shown in Table 2 below.
[0038] Table 2 The content of each fatty acid (FA) and the content of Sn-1, 2, and 3 fatty acids measured in silkworm chrysalis oil in Example 2
[0039]
Embodiment 3
[0041] This example illustrates the process of using lipase as a catalyst to catalyze the esterification reaction.
[0042] After mixing refined silkworm pupa oil (6.5g) and oleic acid (8.46g) in a molar ratio of 1:5, specific lipase Lipozyme RM IM5% (0.748g) was added, and placed in a 65°C water-bath shaker for 2h. After the reaction, 300 μL was taken out, and 2 mL of n-hexane and 2 mL of 0.5 mol KOH-methanol solution were added to react in a water-bath shaker at 65 °C for 1 h, and then detected by gas chromatography, the oleic acid binding rate in silkworm chrysalis oil was measured to be 54.4%. The content of each fatty acid measured in the silkworm chrysalis oil in this example is shown in Table 3 below.
[0043] Table 3 The content of each fatty acid (FA) and the content of Sn-1, 2, and 3 fatty acids measured in silkworm chrysalis oil in Example 3
[0044]
[0045] The data measured in this example is the data source of each fatty acid content of silkworm chrysalis oi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com