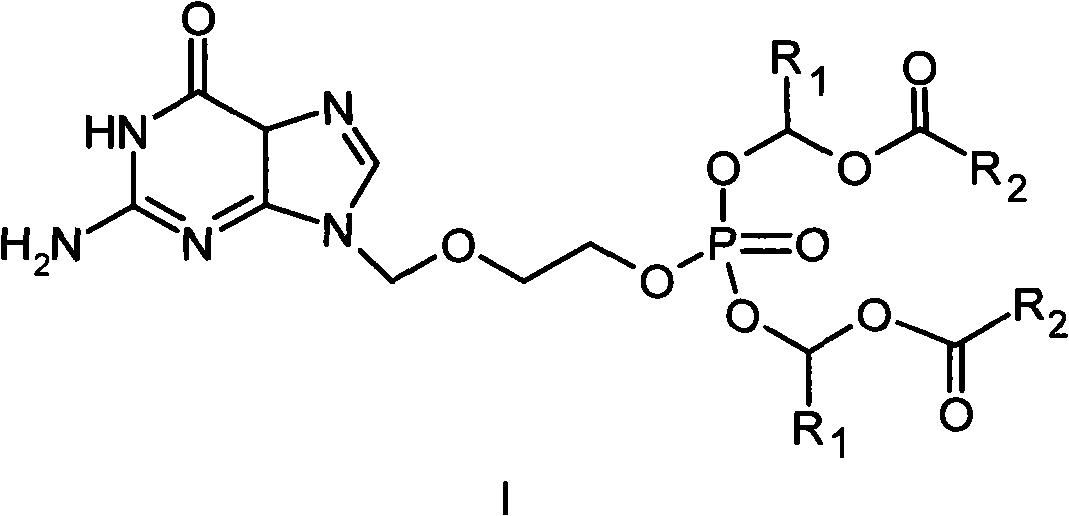
Phosphate derivative of acyclovir and medical application thereof
A derivative, nucleoside phosphate technology, applied in the field of phosphate derivatives of acyclovir, can solve the problems of carcinogenicity, easy to produce drug resistance, easy to rebound, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
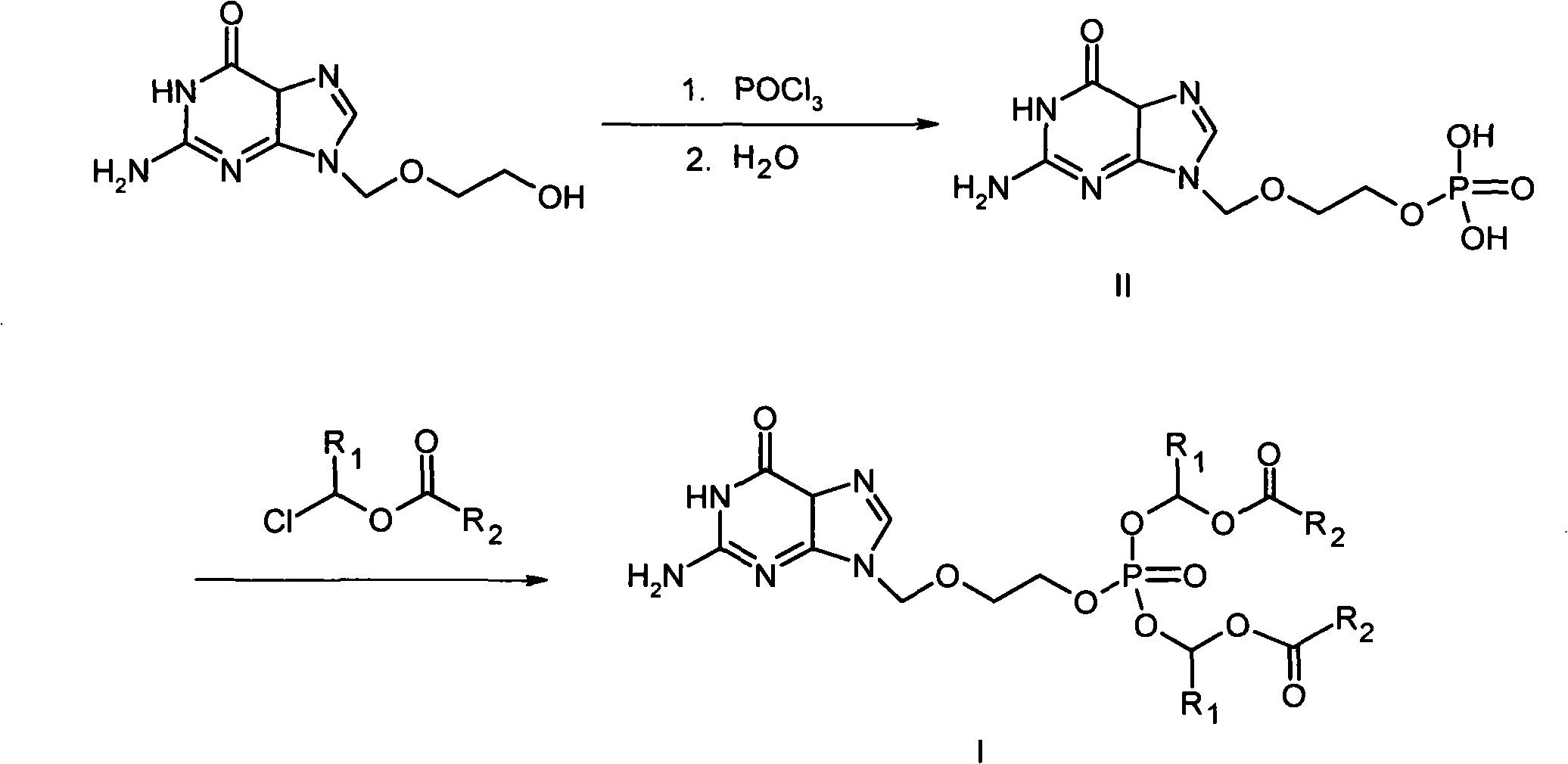
[0021] The preparation of embodiment 1 acyclovir phosphate (II)
[0022] In a sealed reactor, add 227 g (1.0 mol) anhydrous acyclovir (water content less than 0.1%), 5000 ml triethyl phosphite, pass nitrogen, and stir and cool the reaction mixture to -15°C to -20°C °C. Under nitrogen, 137 g (1.2 mol) phosphorus oxychloride was mixed with 400 ml of anhydrous dichloromethane, the mixture was cooled to -15°C to -0°C, pumped into the reactor, flow rate 50 ml / min, cooled to maintain the temperature of the reaction mixture from -15°C to -20°C. Continue stirring until the unreacted acyclovir is below 3%.
[0023] The reaction mixture was poured into a mixture of 2000 ml of deionized water and 2000 grams of ice and cooled to maintain a temperature of 15°C. After the addition was complete, the mixture was warmed to 20°C to 25°C and stirred for 45-60 minutes. Add 5000 ml of dichloromethane, stir vigorously for 30 minutes, stand for 30 minutes, separate the layers, and discard the di...
Embodiment 2
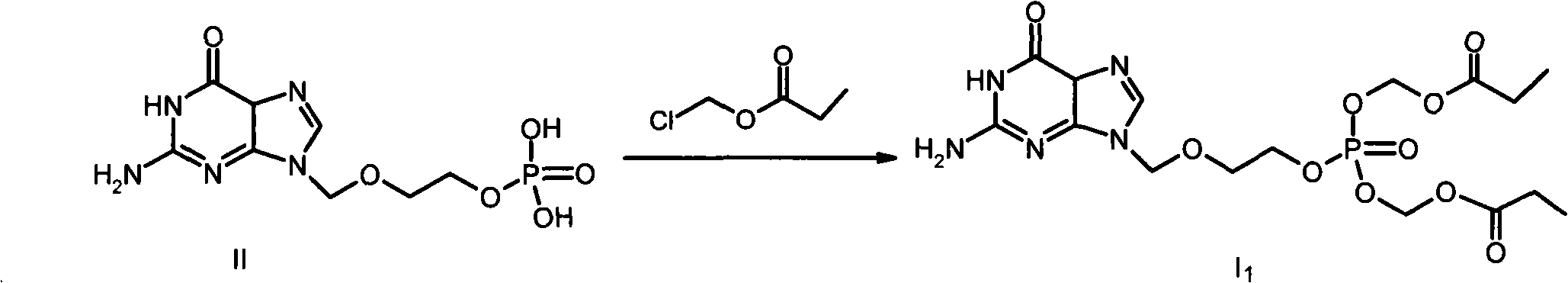
[0024] Example 2 2-[(guanin-9-yl)-methoxy]-ethyl-bis(propionyloxymethyl)-phosphate (I 1 ) preparation
[0025]
[0026] In 50mL of anhydrous DMF, add 3.1g (10mmoL) II and 2g (20mmoL) triethylamine, stir at room temperature for 10 minutes under nitrogen protection, add 4.6g (40mmoL) chloromethyl propionate, stir at room temperature under nitrogen protection React for 24 hours. Transfer to a separatory funnel, add 600 mL of water, extract with ethyl acetate (3×200 mL), combine the organic layers, and wash with saturated brine (3×200 mL). The oil layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, the desiccant was removed by filtration, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, the residue was separated by silica gel column chromatography, eluted with dichloromethane containing 5% methanol, the desired fractions were collected and evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure. get I 1 1.6g. 1 H-NMR (DMSO-d6, 400MHz) δ: 10.60 (s, 1H), 7.79 (s, 1H), 6.40 (bs, 2H), 5.6...
Embodiment 32-
[0027] Example 32-[(guanin-9-yl)-methoxy]-ethyl-bis(isobutyryloxymethyl)-phosphate (I 2 ) preparation
[0028]
[0029] With reference to the method of Example 2, chloromethyl isobutyrate is used instead of chloromethyl propionate to react with II, and the reaction product is separated by silica gel column chromatography to obtain I 2 , the yield is 27%. 1 H-NMR (DMSO-d6, 400MHz) δ: 10.65 (s, 1H), 7.81 (s, 1H), 6.5 (bs, 2H), 5.65-5.70 (m, 4H), 5.35 (s, 2H), 4.1 -4.0 (t, 2H), 3.7-3.6 (t, 2H), 2.53 (m, 2H), 1.13 (d, 12H).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com