Cooling-control purification method of molten salt and impurity removal agent
An impurity removal and impurity technology, applied in the field of nitrate or nitrite purifier, can solve the problem of unused purification additives and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] This example demonstrates the method and steps for obtaining pure KCl by removing NaCl within one kilogram of KCl molten salt containing 5 weight percent (hereinafter referred to as wt%) NaCl.
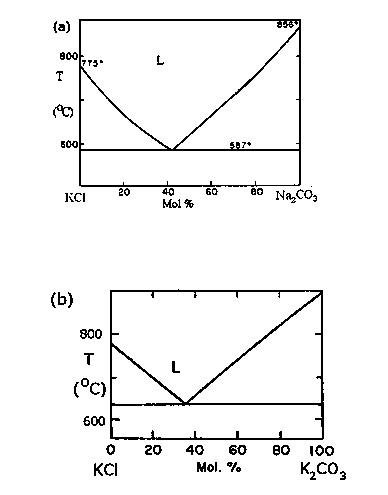
[0027] In this example, first heat one kilogram of this mixed salt to above 800°C to melt it completely, and then add ammonium bicarbonate in the salt bath, the amount of addition is equivalent to 200% of the NaCl molar amount (ie 0.855 mole), also That is 1.71 moles of ammonium bicarbonate (164.25 grams). In this way, sodium ions and carbonate will be combined to form sodium carbonate with a high melting point, its melting point is 865°C, and its eutectic temperature with KCl is 587°C. The generated sodium carbonate will be completely dissolved in the liquid KCl molten salt, such as Figure II shown. Transfer the molten salt to a constant temperature furnace at 590+2°C and cool it slowly, then pure KCl will gradually solidify, and after a period of time, most of the KCl has s...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Like the KCl molten salt containing 5 wt% sodium chloride in Example 1, 1.71 moles of ammonium sulfate or ammonium diphosphate was used as the impurity removal agent.
[0033] The results of this example show that after the addition of ammonium sulfate or ammonium diphosphate, the potassium chloride crystals are purified by controlling constant temperature cooling at 694°C and 738°C respectively. After one implementation, the purification effect was reduced to 1.12 and 1.25 mol% of NaCl respectively, which was equivalent to that of Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0035] For example, in the KCl molten salt containing 5 wt% sodium chloride in Example 1, the impurity removal agent uses 1.71 moles of ammonium hydroxide into KCl, and there is no purification effect after controlled cooling above the eutectic temperature. This is because the generated NaOH has a solid solubility of about 8 mol% in KCl. Therefore, sodium ions cannot be removed.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com