Method for preparing j-acid and method for comprehensive treatment and resource utilization of j-acid wastewater
A comprehensive treatment and resource utilization technology, applied in the field of comprehensive treatment and resource utilization of J-acid wastewater, to achieve the effects of reduced treatment costs, no solvent entrainment, and reduced wastewater treatment costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
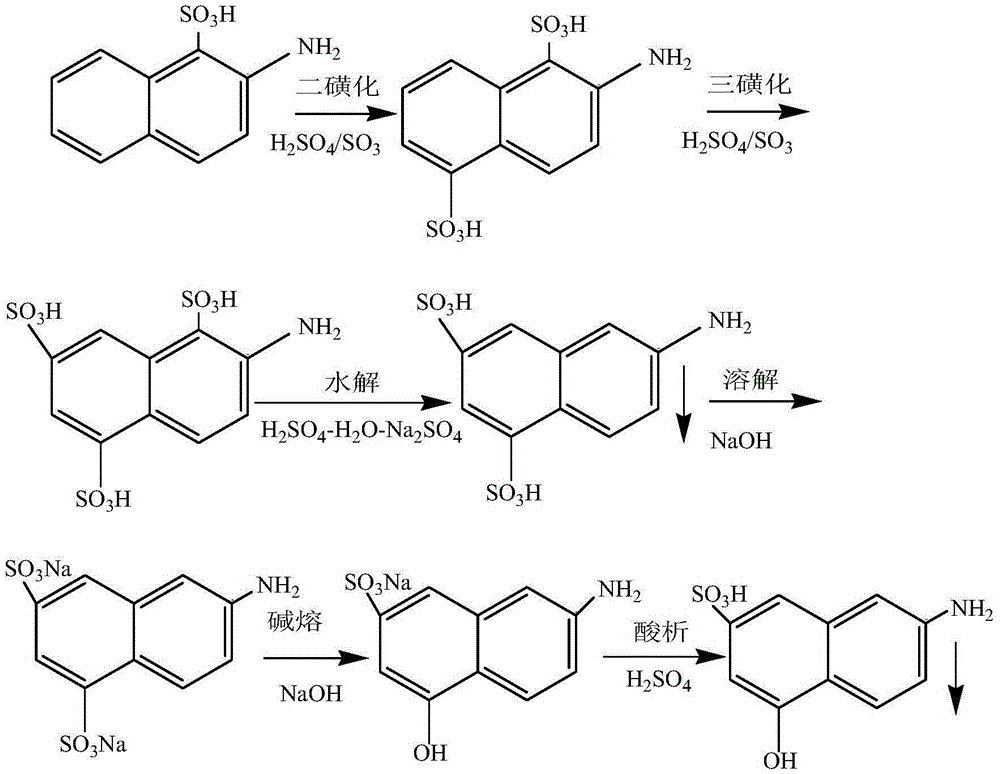
[0041] This example provides a kind of production method of J acid, comprises the steps:
[0042] (1) Ammonification: Ammonia solution is prepared, ammonium bisulfite solution is added to the preparation kettle, and then an appropriate amount of ammonia gas is introduced to make ammonia solution. Add the ammoniated solution and sodium 2-hydroxynaphthalenesulfonate into the ammoniated kettle, open the jacket of the reactor and let in steam for heating, control the temperature in the kettle to be around 150°C, and carry out the ammoniation at 0.95MPa at a temperature of 150-155°C. The reaction was carried out and kept for 7 hours to generate 2-naphthylamine-1-sodium sulfonate. After the heat preservation is completed, the steam valve is closed, and the ammoniated solution is transferred to the acidification kettle.
[0043] (2) Acidification: Add a certain amount of dilute sulfuric acid into the acidification kettle, then transfer the ammoniated material into the acidification ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] This example provides a method for the comprehensive treatment and resource utilization of the J-acid waste water that a kind of embodiment 1 produces, specifically as follows:
[0052] (1) Wastewater reuse: 4500 liters of waste water of 30% of the total amount of J acid hydrolyzed waste water is used in the acidification process in the production process of tunic acid;
[0053] (2) Primary extraction: 10,500 liters of wastewater containing 70% of the total amount of J acid hydrolyzed wastewater is fully mixed with the extractant at a ratio of 1:1 to oil and water at normal temperature and pressure. Grade extraction, the extractant is composed of trioctylamine 30wt%, sulfonated kerosene 60% and tributyl phosphate 10%;
[0054] (3) Secondary extraction and back extraction: the extracted water of the primary extraction is fully mixed with the extractant at a ratio of 1:1 to oil and water at normal temperature and pressure for secondary extraction, the extraction phase is ...
Embodiment 3
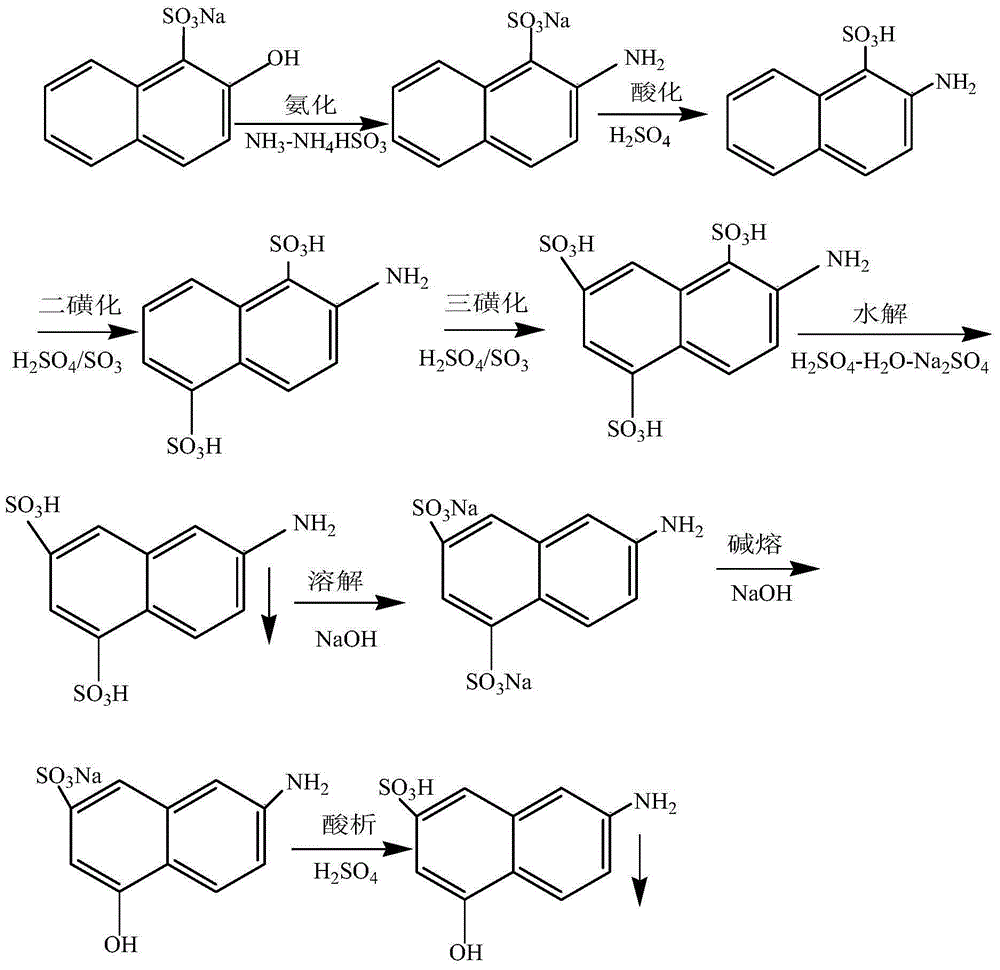
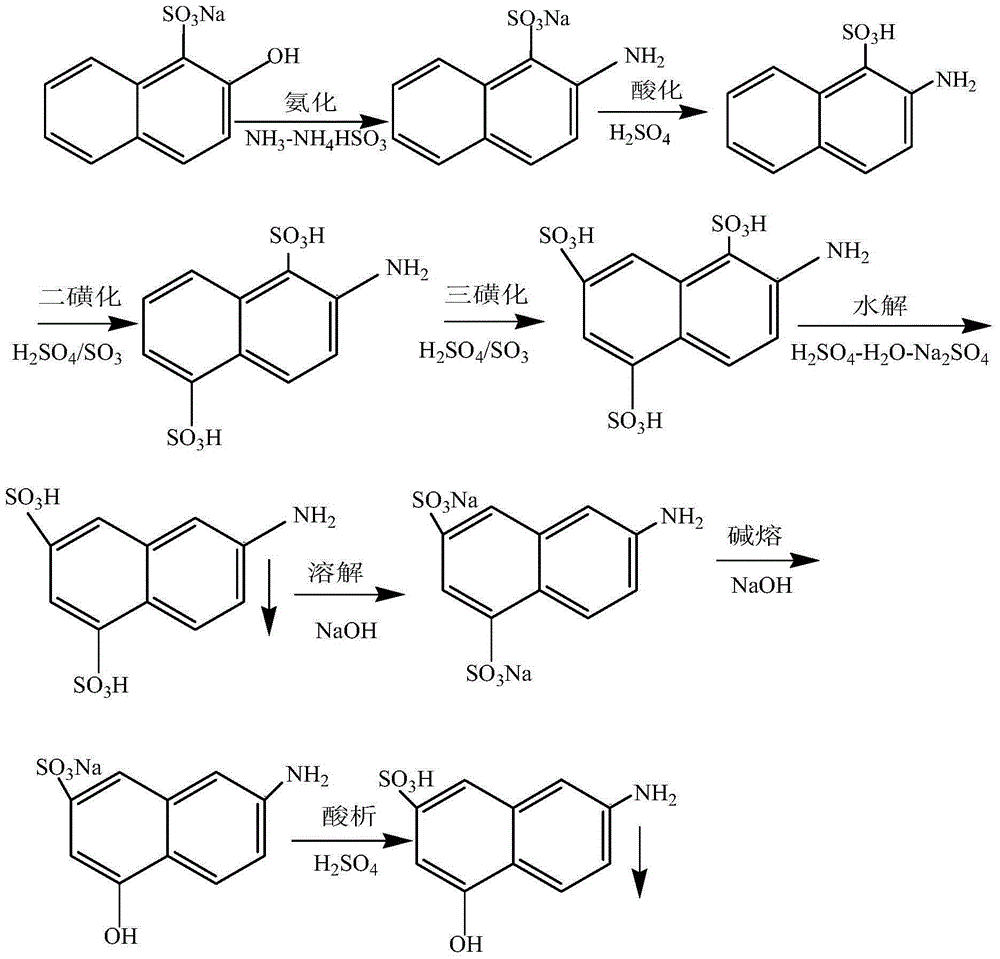
[0059] This example provides a kind of production method of J acid, and it is basically the same as embodiment 1. The difference is: the ammonification preparation solution used in the ammoniation in the production process of Tuburic acid is prepared with the liquid ammonia absorption wastewater reused in the previous batch reaction, and the acidified water in the production process of Tuburic acid is prepared with the hydrolyzed wastewater reused in the previous batch reaction. ; The part of the hydrolysis preparative liquid used in the J acid hydrolysis process is the filtrate obtained according to the step (5) of Example 2. Compared with Example 1, this method can reduce the water cost of J acid by about 30% and the cost of wastewater treatment by about 40%, and reduce environmental pollution.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com