Graphitization furnace surplus energy utilization method based on forced cooling
A graphitization furnace and forced cooling technology, applied in furnace cooling devices, chemical instruments and methods, furnaces, etc., can solve the problems of poor quality and variety of processed products, reduce heat loss, slow cooling speed, etc., and achieve important energy saving and emission reduction Benefits and economic and social benefits, reduce overall energy consumption, and speed up the production cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0014] The forced cooling-based graphitization furnace residual energy utilization method proposed by the present invention will be described in detail in combination with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
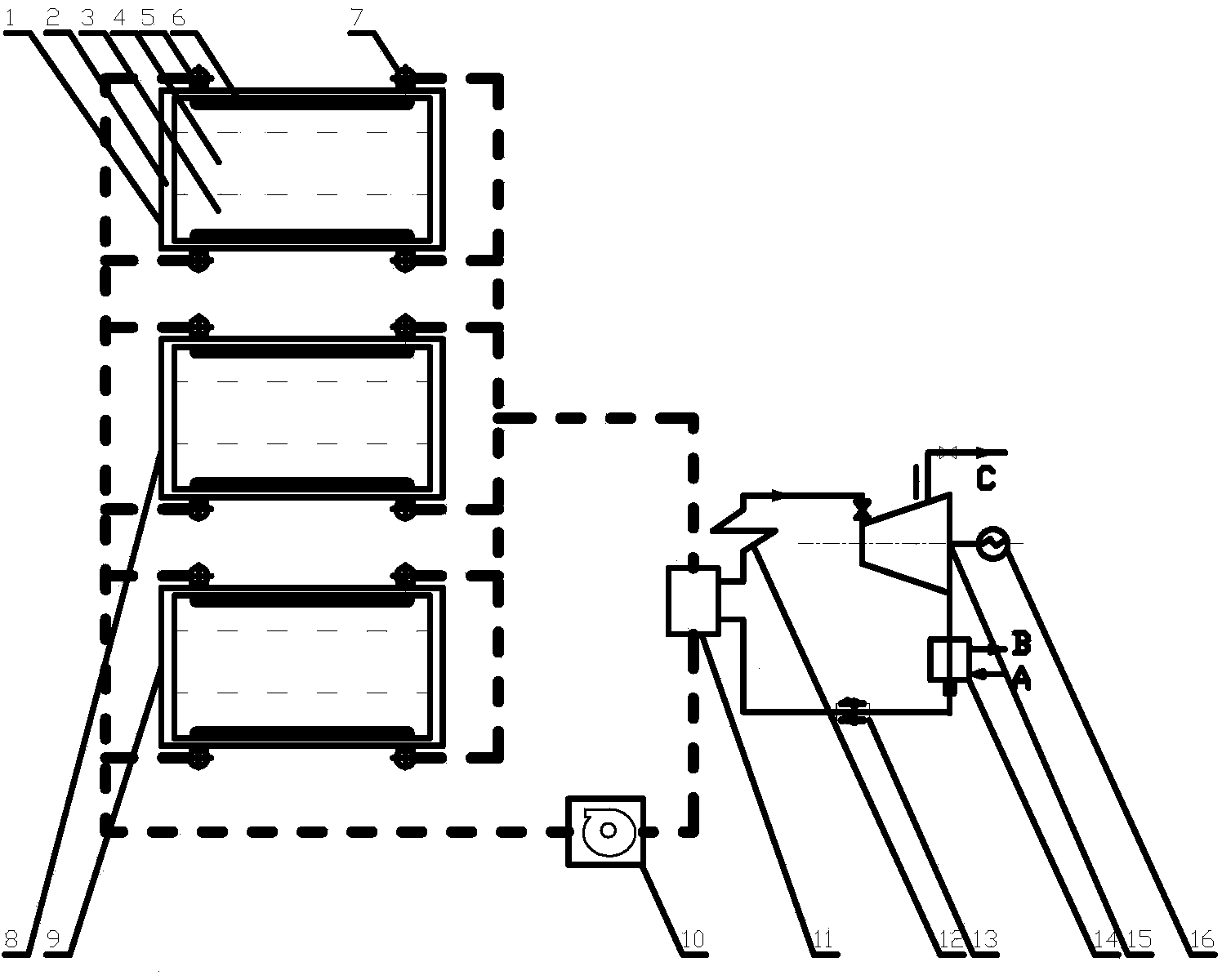
[0015] Specific embodiments of the present invention are as follows: a graphitization furnace residual energy utilization method based on forced cooling, wherein the graphitization furnace 1 is a cuboid furnace structure, and is respectively an outer wall 2, an insulation layer 3 and a furnace core 4 from outside to inside, A graphitization furnace production line includes multiple independent graphitization furnaces 1, No. 2 graphitization furnace 8, and N. The forced cooling device of the furnace, the waste heat boiler and the steam turbine generator set, the fan and the connecting pipeline are composed, and the forced cooling device is a group of cooling coils 6, which are embedded in the insulation layer 3 in the graphitization furnace, close to the outer wall ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com