Method for leaching and loading drug solution by using nanometer porous polylactic acid material
A polylactic acid material and nanoporous technology, which is applied in the fields of materials and chemicals, can solve the problems of low drug loading and limited drug loading efficiency of polylactic acid, and achieve the effects of large drug loading, high drug loading stability and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] A method for drug loading using a drug solution of nanoporous polylactic acid material, comprising the following steps:
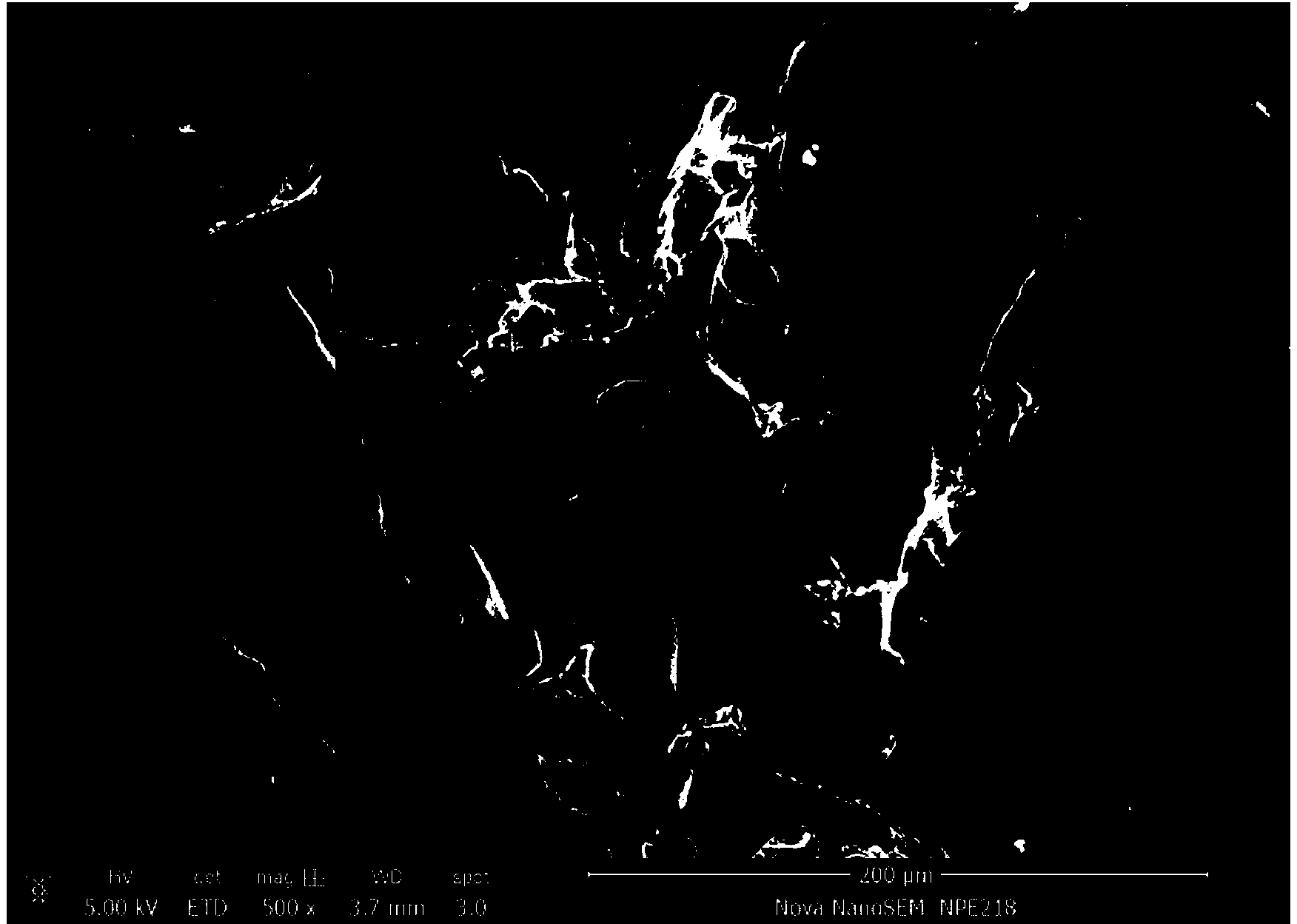
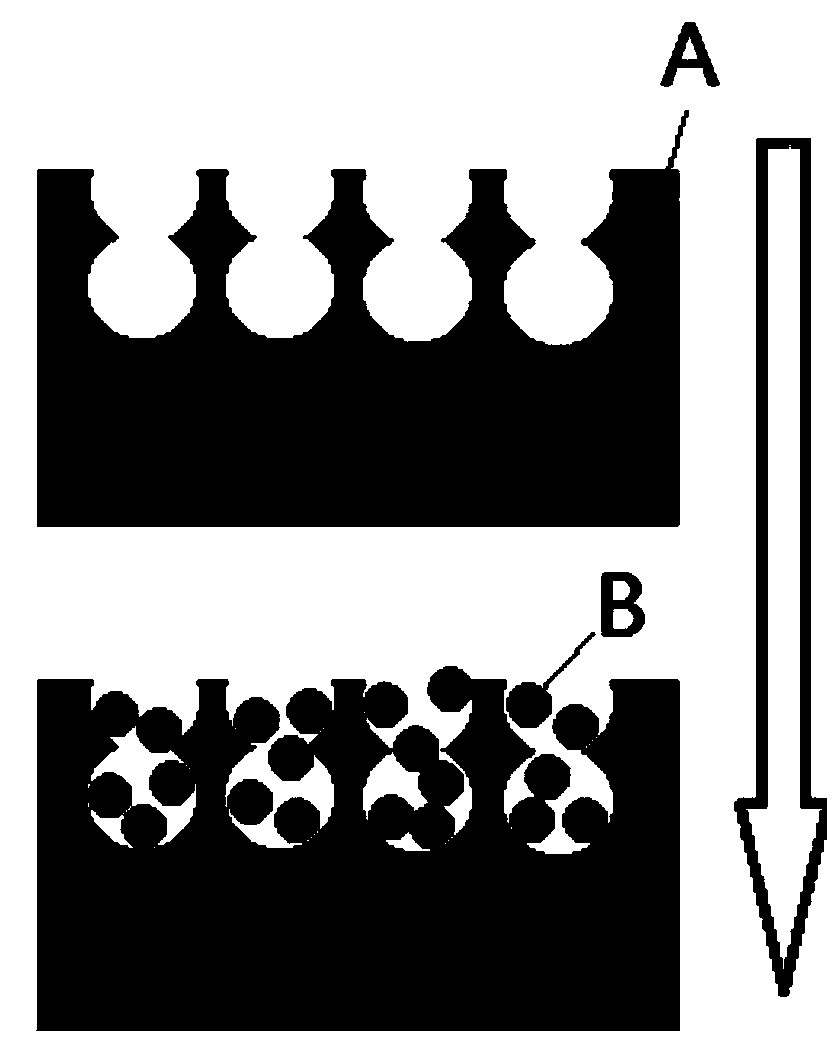
[0016] 1) The medical-grade polylactic acid with a molecular weight of 200,000 was made into a porous material by leaching NaCl salt particles. The scanning electron microscope picture is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the pore diameter is about 100 microns, and there are micropores and cracks of about 50-500 nanometers on the pore wall. Such as figure 2 shown.
[0017] 2) Immerse the microporous polylactic acid A obtained in step (1) in an aspirin solution with a concentration of 5 mol / L, rinse and soak for 3 hours, and the aspirin molecule B will attach to the surface micropores of the microporous polylactic acid A, as image 3 shown.
[0018] 3) The microporous polylactic acid is taken out from the drug solution, and vacuum-dried at room temperature for 30 minutes to obtain the microporous polylactic acid material loaded with aspirin.
Embodiment 2
[0020] 1) The medical-grade polylactic acid with a molecular weight of 500,000 is made into a porous material by leaching NaCl salt particles. The pore diameter is about 200 microns, and there are micropores and cracks about 200 nanometers on the pore wall.
[0021] 2) Immerse the microporous polylactic acid in a paclitaxel solution with a concentration of 1 mol / L, rinse and soak for 2 hours.
[0022] 3) The microporous polylactic acid is taken out from the drug solution, and vacuum-dried at room temperature for 30 minutes to obtain the paclitaxel-loaded microporous polylactic acid material.
[0023] 4) The foamy microporous polylactic acid is cold-pressed and granulated to make microspheres with a diameter of about 1 mm. The obtained microspheres are the sustained-release drug-loading materials of paclitaxel, which can be further used for medical purposes.
Embodiment 3
[0025] 1) The medical-grade polylactic acid with a molecular weight of 1 million is made into a porous material by leaching NaCl salt particles. The pore size is 10 microns, and there are micropores and cracks of 10 nanometers on the pore wall.
[0026] 2) Immerse the microporous polylactic acid in a paclitaxel solution with a concentration of 1 mol / L, rinse and soak for 2 hours.
[0027] 3) The microporous polylactic acid is taken out from the drug solution, and vacuum-dried at room temperature for 30 minutes to obtain the paclitaxel-loaded microporous polylactic acid material.
[0028] 4) The foamy microporous polylactic acid is cold-pressed and granulated to make microspheres with a diameter of about 1 mm. The obtained microspheres are the sustained-release drug-loading materials of paclitaxel, which can be further used for medical purposes.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com