Method for preconcentration and wall breaking and extraction of microorganism oil
A technology of microorganisms and microbial cells, which is applied to the dissolution of microorganisms, the preparation method of peptides, and the production of fats, etc. It can solve the problems of simultaneous concentration and wall breaking, high energy consumption, and large solvent consumption, etc. Effect of Wall Equipment Input and Operating Costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] Embodiment 1: the influence of different pH values on the viscosity of fermented liquid and concentration efficiency
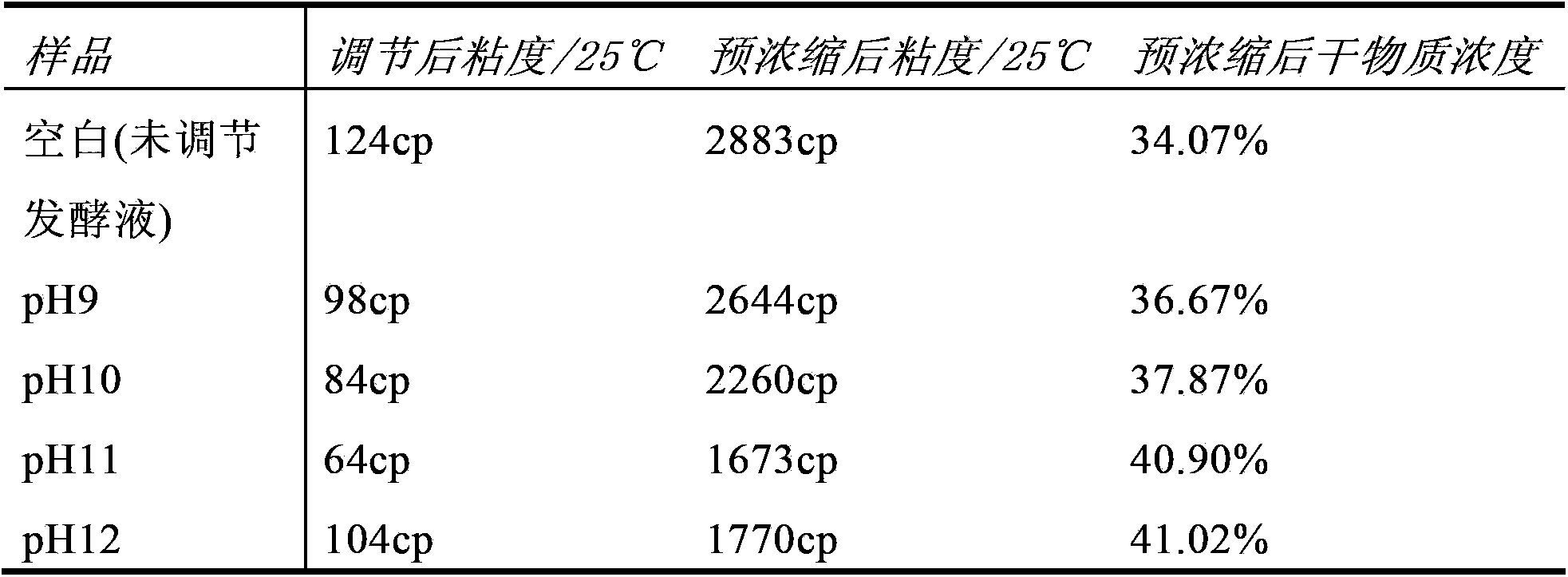
[0073] Weigh 500 g of fermentation broth (Schizochytyium sp. self-cultivation, biomass content 15.5% after sterilization, dry basis oil content 38.7%) 500g, respectively adjust the pH value of the fermentation broth to pH9, pH10, pH11, pH12, and use a rotary evaporator to evaporate and concentrate ( 9000Pa, 80°C, 30min), to investigate the viscosity change and concentration efficiency. Viscosity detection: according to the method in GB / T22427.7-2008 starch viscosity determination; dry matter concentration detection: according to GB / T20264-2006, two-time drying method for grain and oil moisture. The results are shown in Table 1 below.
[0074] The influence of table 1 different pH on the viscosity of fermented liquid and concentration efficiency
[0075]
[0076] It can be seen from Table 1 that the addition of alkali to adjust the pH can reduce t...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Embodiment 2: the impact of different alkalis on the foaming phenomenon in the pre-concentration process
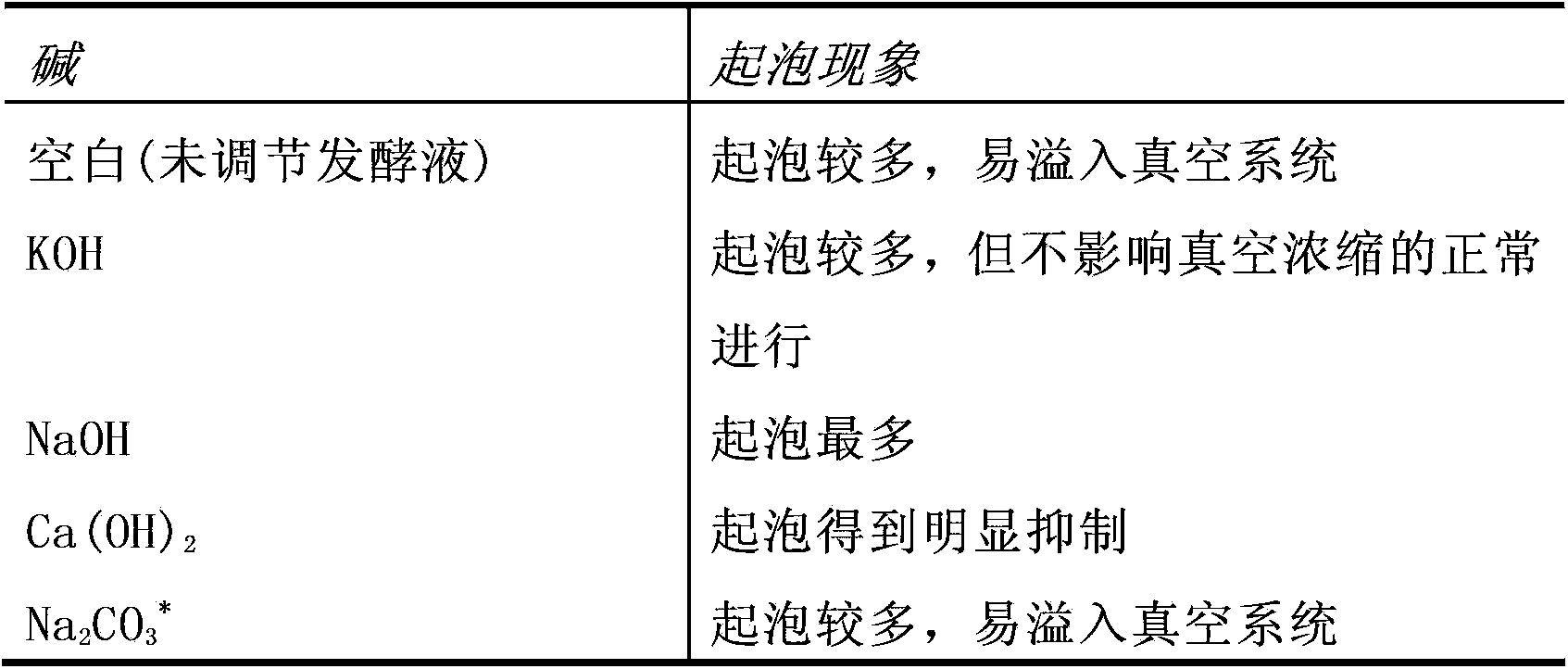
[0078] Weigh 500 g of the fermentation broth (obtained by Schizochytrium sp. self-cultivation, after sterilization, the biomass content is 15.5%, and the dry basis oil content is 38.7%), and different lyes are used to adjust the fermentation broth to pH 12, and vacuum pre-concentration (9000Pa, 80°C, 30min), foaming.
[0079] The results are shown in Table 2.
[0080] The impact of table 2 different alkalis on the foaming phenomenon in the preconcentration process
[0081]
[0082] *: Na 2 CO 3 Adjust the sample pH to 10.42
Embodiment 3
[0083] Embodiment 3: the oil extraction rate after different alkali preconcentration
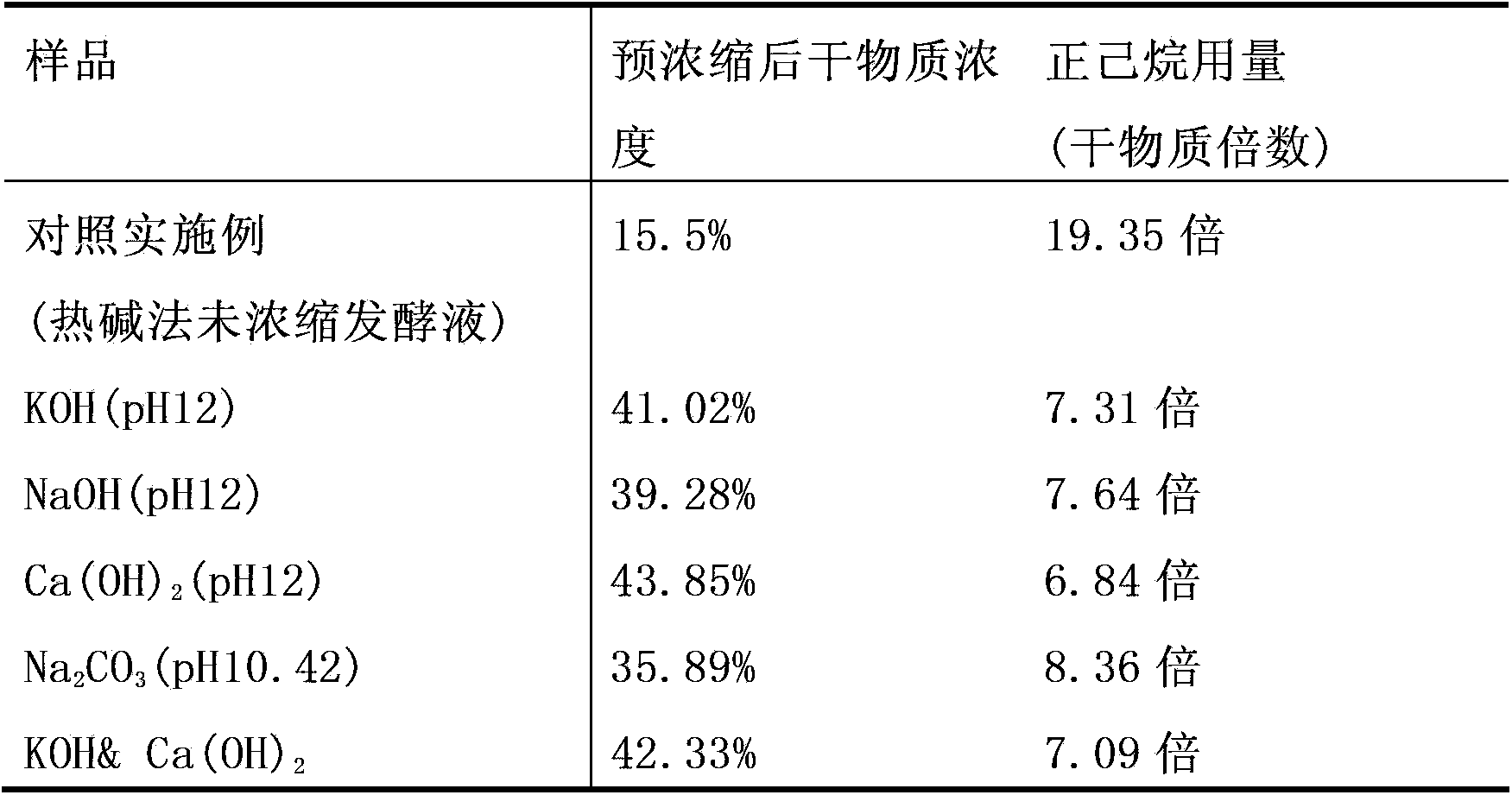
[0084] Weigh 1000g of fermentation broth (obtained by Schizochytrium sp. self-cultivation, after sterilization, biomass content 15.5%, dry basis oil content 38.7%), adjust the pH of the fermentation broth with different lye, and then concentrate at 80°C and 44000Pa for 30min to investigate oil recovery rate difference. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0085] Table 3 Oil extraction rate after different alkali preconcentration
[0086] alkali
Blank (concentrated sample without alkali)
0
KOH (pH11)
62.65%
KOH(pH11.5)
76.07%
KOH(pH12)
80.47%
KOH(pH12.5)
79.31%
[0087] KOH(pH13)
58.60% (produce more saponins)
NaOH (pH12)
87.19%
Ca(OH) 2 (pH12)
49.91%
Na 2 CO 3 (pH10.42)
37.84%
KOH&Ca(OH) 2 *
70.39%
[0088] *First adjust the pH...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com