Method for removing trace thallium contained in water
A micro-dosage technology, applied in the field of removal of micro-thallium in water, can solve the problems of complex processing technology, difficult recovery of heavy metals, high operating cost, etc., and achieve the effect of simple technical process, low operating cost, and easy precipitation and separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0015] Specific implementation mode 1: The method for removing trace amounts of thallium in water described in this implementation mode is specifically carried out according to the following steps:
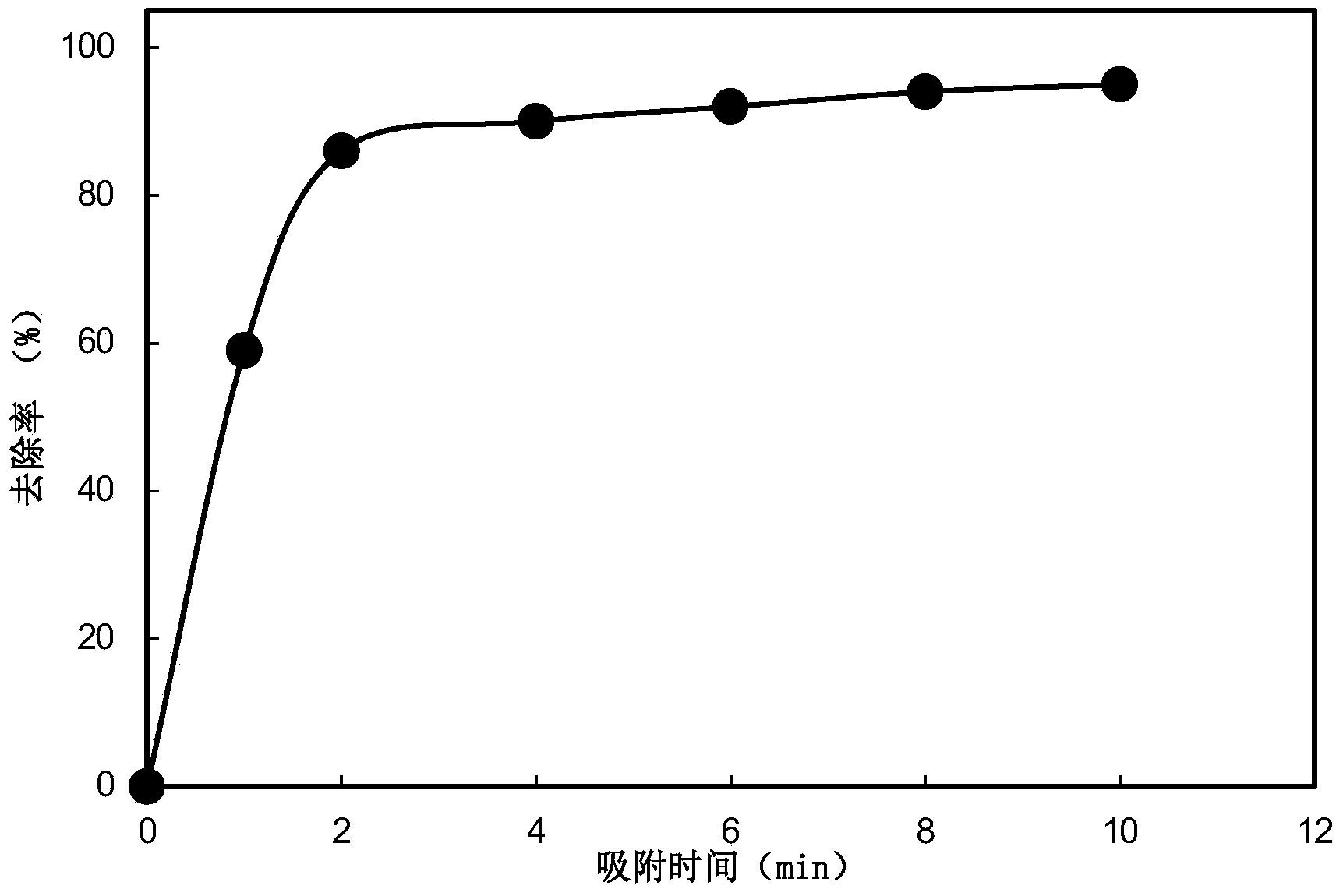
[0016] 1. Add ferrate to the water containing a small amount of thallium, and then react at a speed of 260r / min to 350r / min for 1min to 5min to obtain a mixed solution; the dosage of ferrate is 1mg / L ~25mg / L;
[0017] 2. At a rotating speed of 150r / min to 250r / min, the mixed solution obtained in step 1 was continuously stirred and adsorbed for 5min to 10min to obtain the mixed solution after adsorption;
[0018] 3. Add a coagulant to the mixed solution after adsorption, and then go through coagulation, precipitation and filtration in order to remove trace thallium in the water; the dosage of the coagulant is 1mg / L~45mg / L .
[0019] The ferrate added in step 1 of this embodiment is potassium ferrate or sodium ferrate. In this embodiment, in the selection of ferrate, it is based ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0024] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that: the dosage of ferrate described in Step 1 is 1 mg / L-20 mg / L. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0025] Embodiment 3: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 in that: the dosage of ferrate described in step 1 is 15 mg / L. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com