Ultrahigh-sensitivity probe for disease marker or pathogen detection, as well as preparation method and application of ultrahigh-sensitivity probe
A pathogen detection and marker technology, applied in the fields of biomedical engineering and nanomedicine, can solve the problems of expensive reagents and skilled workers, limit the application of early detection of diseases, and limit the wide application, and achieve low cost of reagent consumables, simple detection methods, The effect of high-throughput detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example
[0040] 1. Preparation example (1): The chemical substances used in the following steps are commercially available.
[0041] A preparation of an ultra-high sensitivity probe for disease marker or pathogen detection and a detection method for disease pathogen (taking EV71 as an example), comprising the following steps:
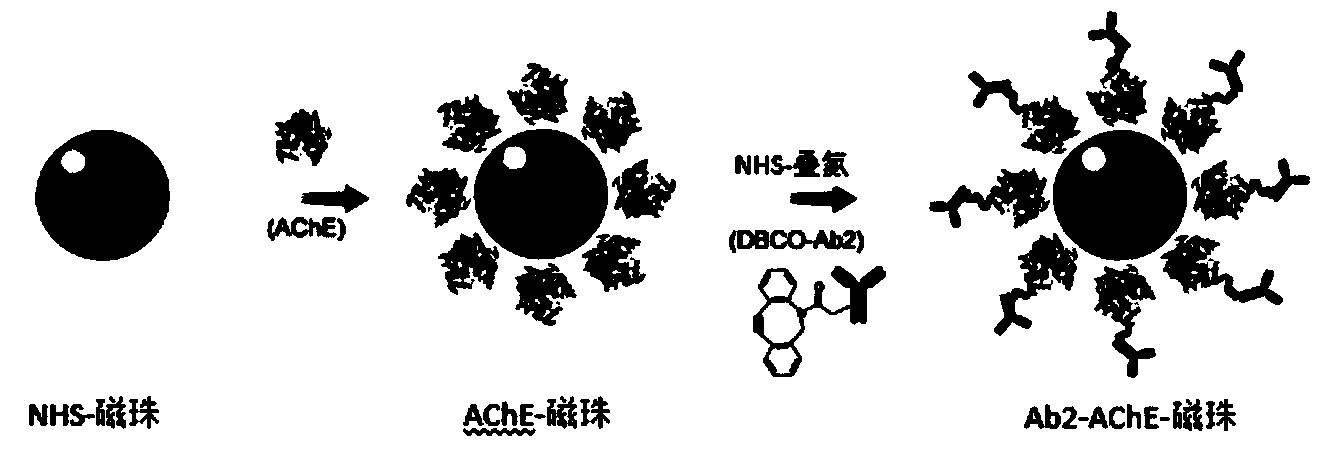
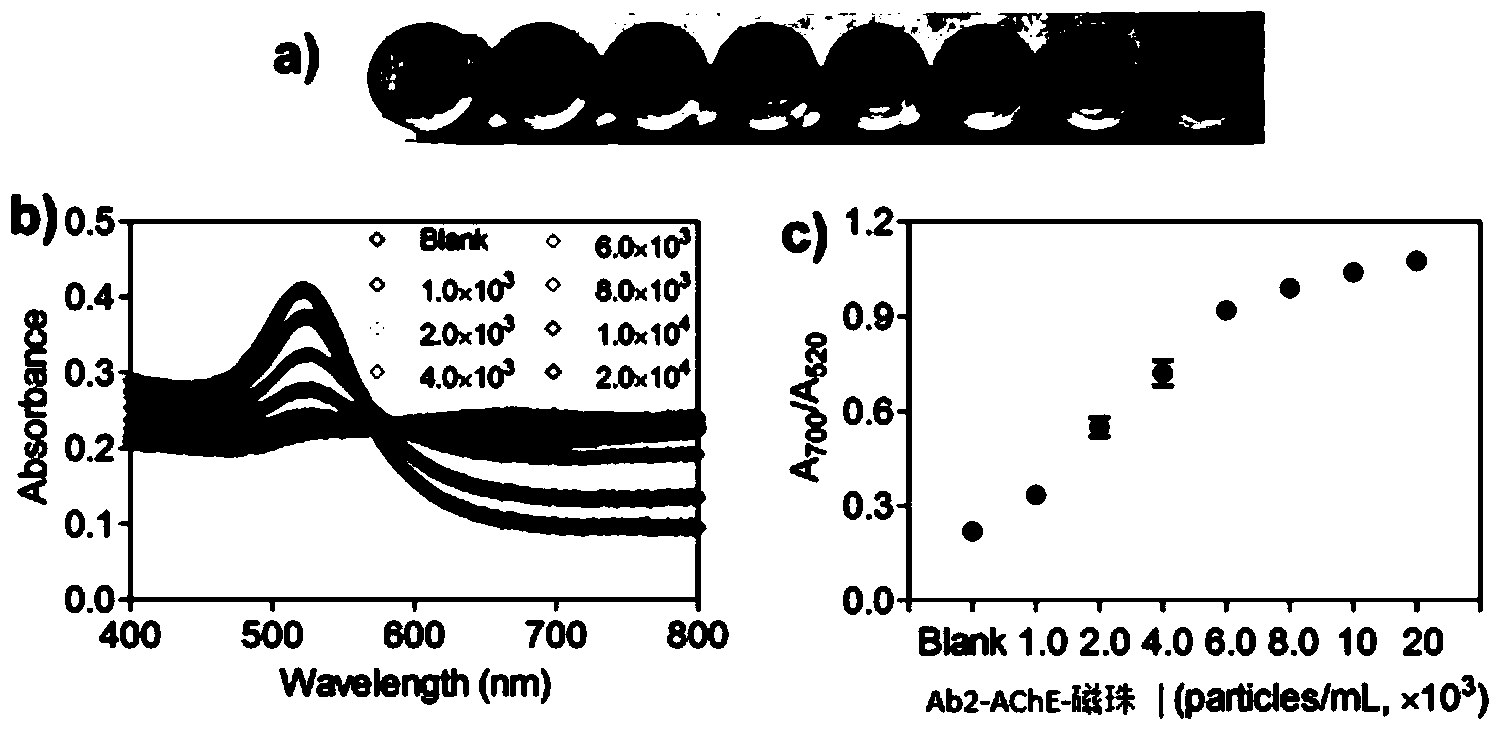
[0042] 1) Take 100 μL of NHS-activated magnetic bead nanoparticles (10 mg / mL) in a small centrifuge tube, and wash it once with hydrochloric acid (1 mM, 4° C.) with the help of a magnetic stand. Afterwards, 100 μL of acetylcholinesterase (1 mg / mL) dissolved in PBS was added, and vortexed for 30 seconds. Afterwards, the mixture was placed in a shaker to react for 2 hours, and the reaction condition was room temperature. For the first 30 minutes, vortex the centrifuge tubes for 15 seconds every 5 minutes. For the remaining 90 minutes, the small centrifuge tube was vortexed for 15 seconds every 15 minutes to obtain magnetic bead nanoparticles bound to acetylcholi...
preparation example (2
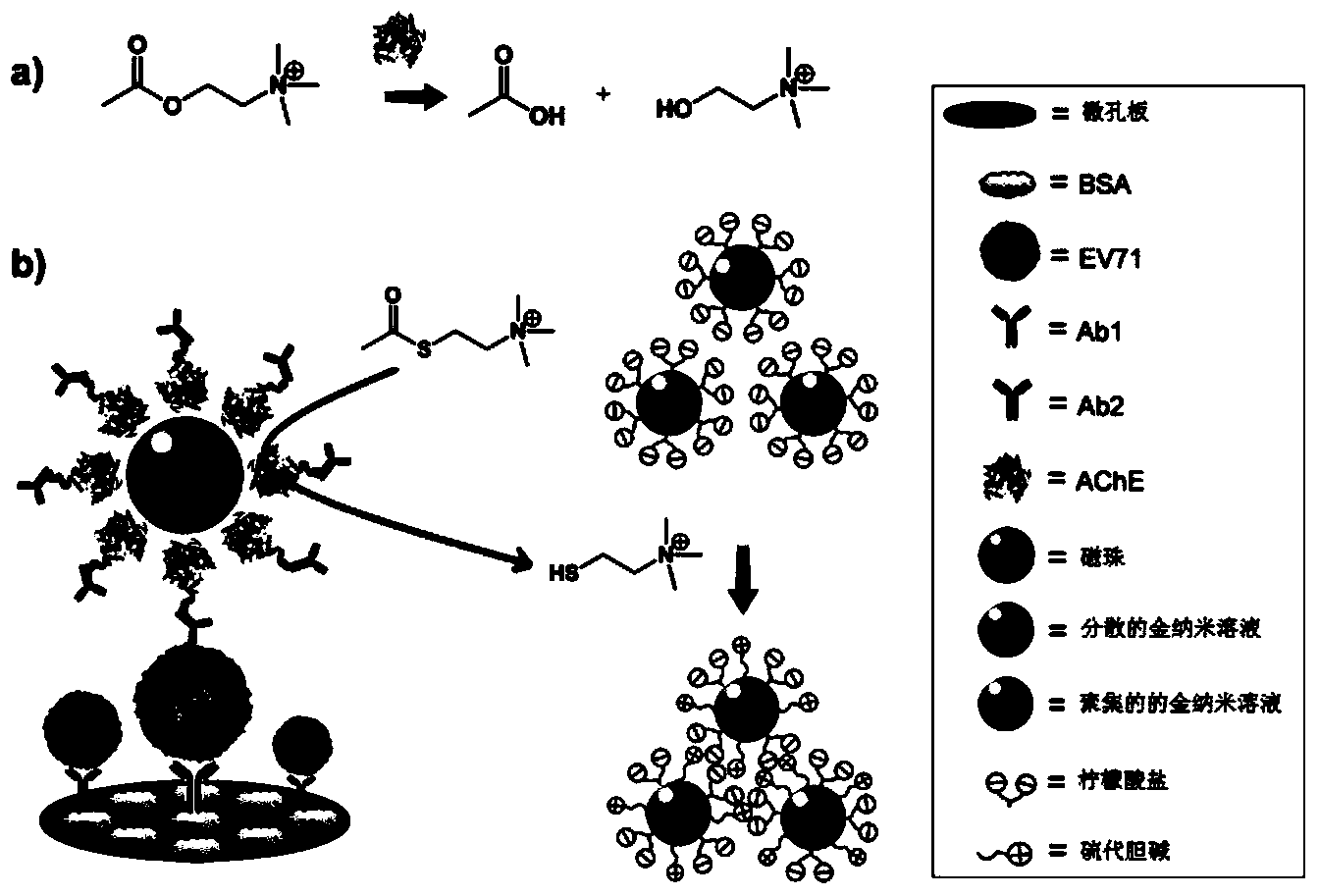
[0051] The preparation of the nanoparticle microsphere probe that does not contain magnetic beads and the detection method used for disease pathogens (taking EV71 as an example) include the following steps:
[0052] 1) Take 100 μL of acetylcholinesterase (1 mg / mL) dissolved in PBS, add 5 μL of NHS-activated azide group (1 mM), and react at room temperature for 30 minutes.
[0053] 2) Take 1 mL of anti-EV71 detection antibody (1 mg / mL), the antibody buffer environment is PBS (pH=7.4), take 33 μL of NHS-activated DBCO (10 mM) and add it to the antibody, and the molar ratio of DBCO to antibody is 50:1. After reacting at room temperature for 30 minutes, 1M Tris-HCl (pH=8.0) was added to terminate the reaction.
[0054] 3) The final concentration of Tris is 50 mM, and the termination reaction lasts for 5 minutes. That is, the antibody solution coupled with DBCO is obtained. Take 10 μL of the antibody solution coupled with DBCO (1 mg / mL) and add it to 1 mL of magnetic bead nanopart...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com