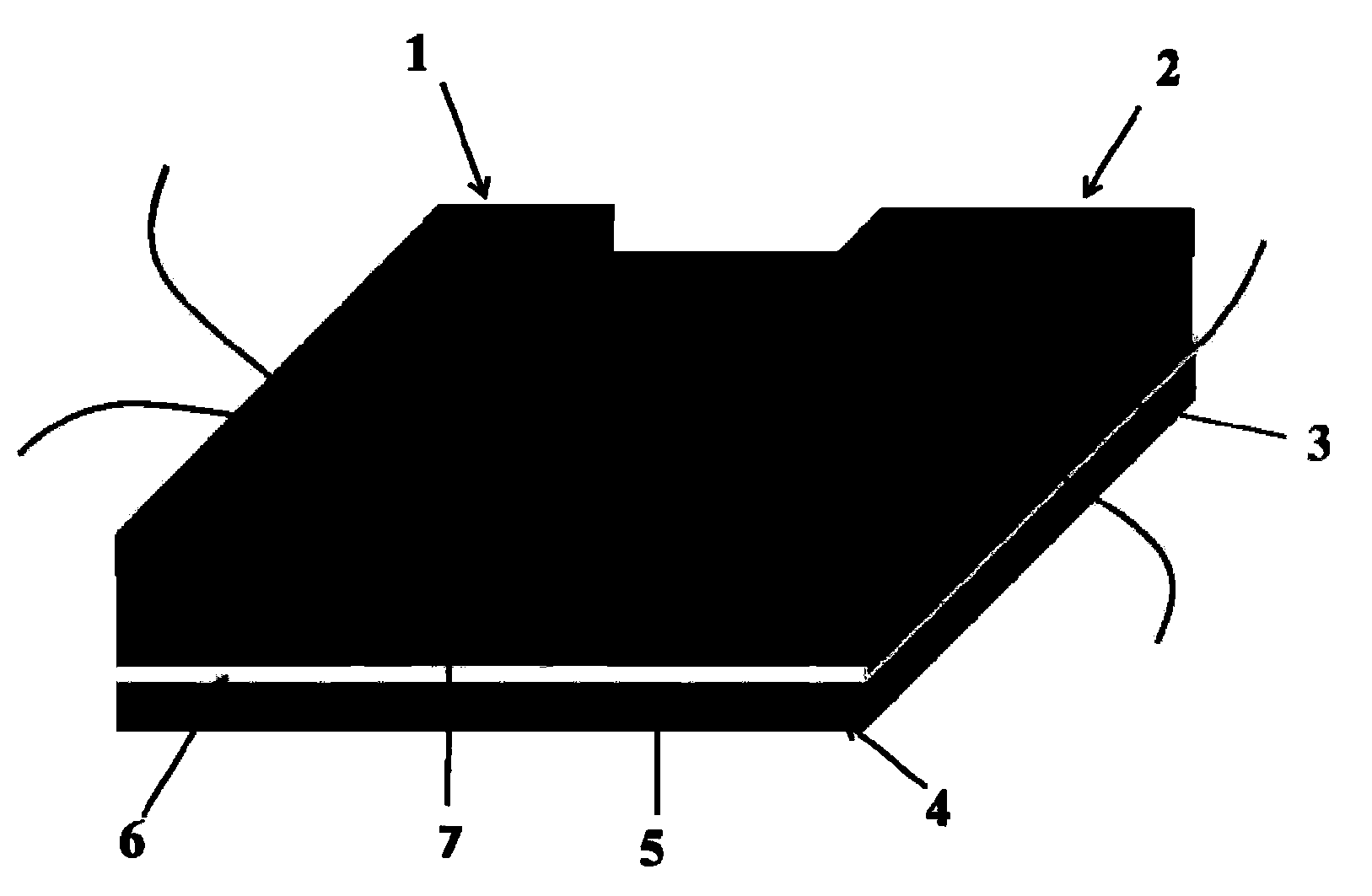
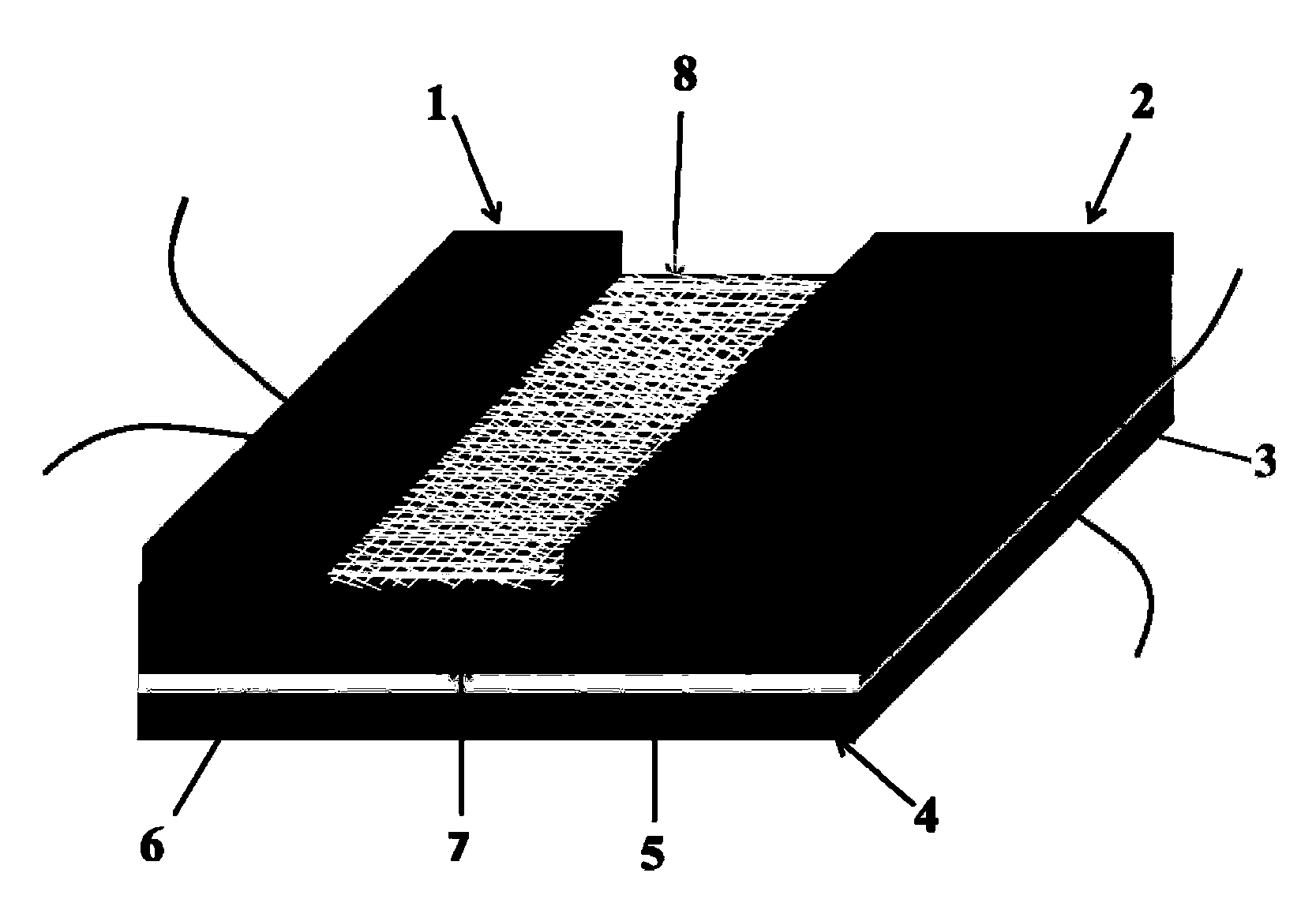
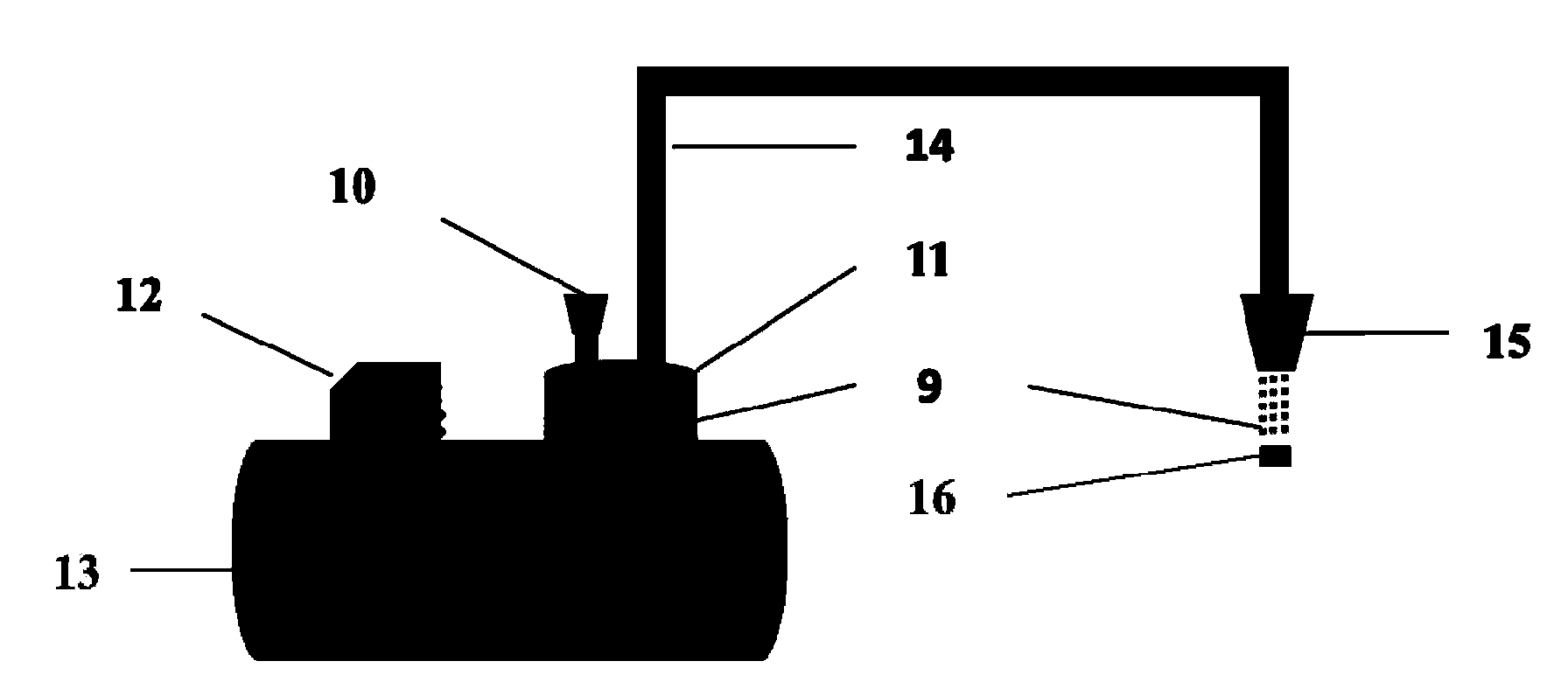
Mixing potential NO2 sensor based on sand-blast machining porous YSZ (Yttria Stabilized Zirconia) base plate and preparation method of sensor
A hybrid potential type, sandblasting technology, applied in the direction of material electrochemical variables, can solve the problems of limited performance improvement, small modification area, etc., to achieve multiple active sites, controllable roughness and surface area, good thermal stability and chemical stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Example 1: The YSZ substrate used in the sandblasting experiment, the sand particle size used is 40 μm, and the roughness is 364 nm.
[0055] The manufacturing process is to use the YSZ substrate with the roughness of 364nm processed by sandblasting to make the sensor device. Other manufacturing processes are the same as the comparative example.
[0056] Table 1 lists the devices made of unprocessed YSZ and sandblasted YSZ substrates with a roughness of 364nm at different concentrations of NO 2 The difference between the electromotive force in the atmosphere and the electromotive force in the air (ΔV) varies with NO 2 As can be seen from the table, the sensitivity of the device made of the YSZ substrate with a roughness of 364nm after sand blasting has some improvement, but the change is not much.
[0057] Table 1. ΔV vs. NO 2 change in concentration
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2: The YSZ substrate used in the sandblasting experiment has a sandblasting particle size of 60 μm and a roughness of 649 nm.
[0059] The manufacturing process is to use YSZ with a roughness of 649 nm as a substrate to manufacture a sensing device by sandblasting. Other manufacturing processes are the same as the comparative example.
[0060] Table 2 lists the devices made of unprocessed YSZ and sandblasted YSZ substrates with a roughness of 649nm at different concentrations of NO 2 The difference between the electromotive force in the atmosphere and the electromotive force in the air (ΔV) varies with NO 2 It can be seen from the table that the sensitivity of the device made of the YSZ substrate with a roughness of 649nm after sandblasting has been greatly improved.
[0061] Table 2. ΔV vs. NO 2 change in concentration
[0062]
[0063]
Embodiment 3
[0064] Example 3: The YSZ substrate used in the sandblasting experiment has a sandblasting particle size of 80 μm and a roughness of 775 nm.
[0065] The manufacturing process is to use YSZ with a roughness of 775nm sandblasting as a substrate to make a sensing device. Other manufacturing processes are the same as the comparative example.
[0066] Table 3 lists the devices made of unprocessed YSZ and sandblasted YSZ substrates with a roughness of 775nm at different concentrations of NO 2 The difference between the electromotive force in the atmosphere and the electromotive force in the air (ΔV) varies with NO 2 As can be seen from the table, the sensitivity of the device made of the sandblasted YSZ substrate with a roughness of 775nm is optimally improved.
[0067] Table 3. ΔV vs. NO 2 change in concentration
[0068]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com