A Microstrip Dielectric Phase Shifter Can Suppress High Frequency Radiation Loss
A radiation loss, microstrip line technology, used in antennas, waveguide devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of large loss, reduce energy transmission rate, large loss, etc., achieve simple production, suppress high-frequency radiation loss, reduce Effects of Radiation Loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
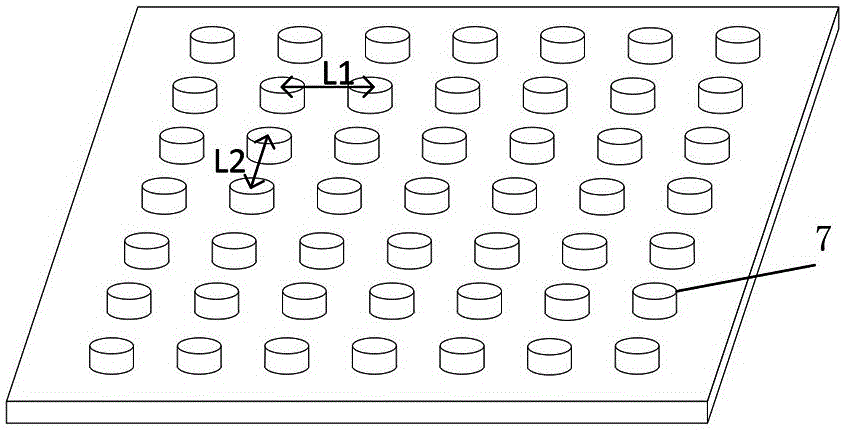
[0029] Embodiment 1: as Figure 4 As shown, holes 5 are drilled on the reference ground electrode layer 2 , and the distance between adjacent holes 5 is less than or equal to λ / 2; the height of the photonic crystal structure 7 is the thickness of the reference ground electrode layer 2 . The hole 5 is cylindrical, and there is no filler in the hole 5 . In other examples, some materials other than metal electrodes can also be filled in the cylindrical hole 5 .
[0030] When making, use the order from bottom to top to make. First, a layer of metal is made on the substrate 1 as the reference ground electrode layer 2; then, through a series of semiconductor processes such as glue coating, photolithography, and corrosion, periodic holes 5 are etched on the reference ground electrode layer 2; then , make a dielectric thin film layer 3 on the reference ground electrode layer 2; finally make a layer of metal on the dielectric thin film layer 3, and etch out the shape of the required t...
Embodiment 2
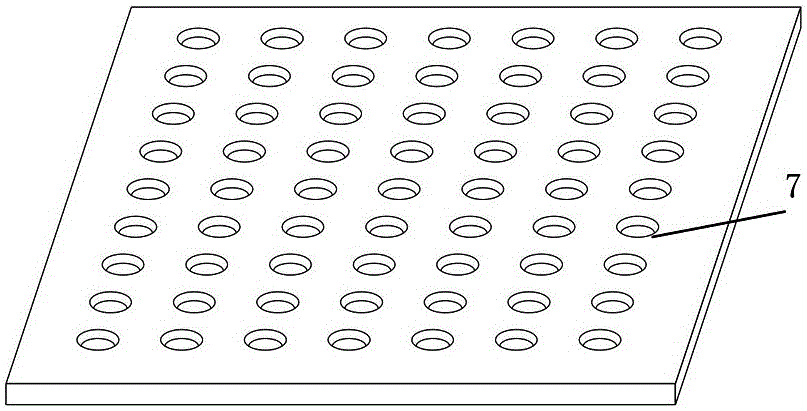
[0031] Embodiment 2: as Figure 5 As shown, cylindrical holes 5 are drilled on the dielectric film layer 3 , the spacing between adjacent holes 5 is less than or equal to λ / 2, and the height of the photonic crystal structure 7 is the thickness of the dielectric film layer 3 . The cylindrical hole 5 may have no filler, and there is no filler in the hole 5 . In other examples, it is also possible to choose to fill the cylindrical hole 5 with some material different from the metal electrode.
[0032] When making, use the order from bottom to top to make. First, make a layer of metal on the substrate 1 as the reference ground electrode layer 2; then make a dielectric thin film layer 3 on the reference ground electrode layer 2; Periodic holes 5 are etched on the thin film layer 3; finally, a layer of metal is formed on the dielectric thin film layer 3, and the shape of the required transmission line layer 4 is etched through a series of semiconductor processes such as glue coating...
Embodiment 3
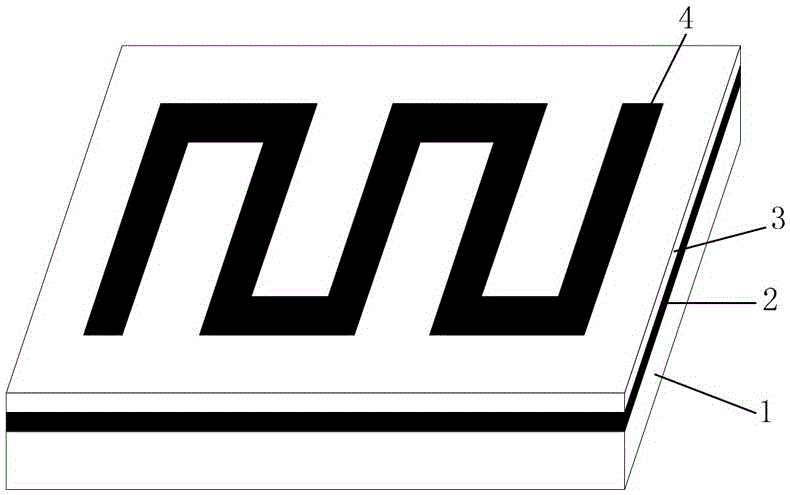
[0033] Embodiment 3: as Figure 6 As shown, cylindrical metal pillars 6 are made in the blank space around the transmission line layer 4 , the distance between adjacent pillars 6 is less than or equal to λ / 2, and the height of the pillars 6 is the same as the thickness of the transmission line layer 4 .
[0034] When making, use the order from bottom to top to make. First, make a layer of metal on the substrate 1 as the reference ground electrode layer 2; then make a dielectric film layer 3 on the reference ground electrode layer 2; then make a layer of metal on the dielectric film layer 3; finally, in the transmission line layer On the metal layer 4, through a series of semiconductor processes such as gluing, photolithography, and corrosion, the shape of the transmission line layer 4 required and the pillars 6 forming the photonic crystal structure 7 are etched out.
[0035] It can be understood that, in addition to the single-layer photonic crystal structure 7 in the above ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com