Process for preparing light magnesium carbonate from boron mud
A light magnesium carbonate and process technology, applied in the direction of magnesium carbonate, can solve the problems that are not conducive to industrial production, high energy consumption in the pyrolysis stage, and inability to overcome limitations, so as to achieve maximum use value and promotion value, and low equipment requirements , low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
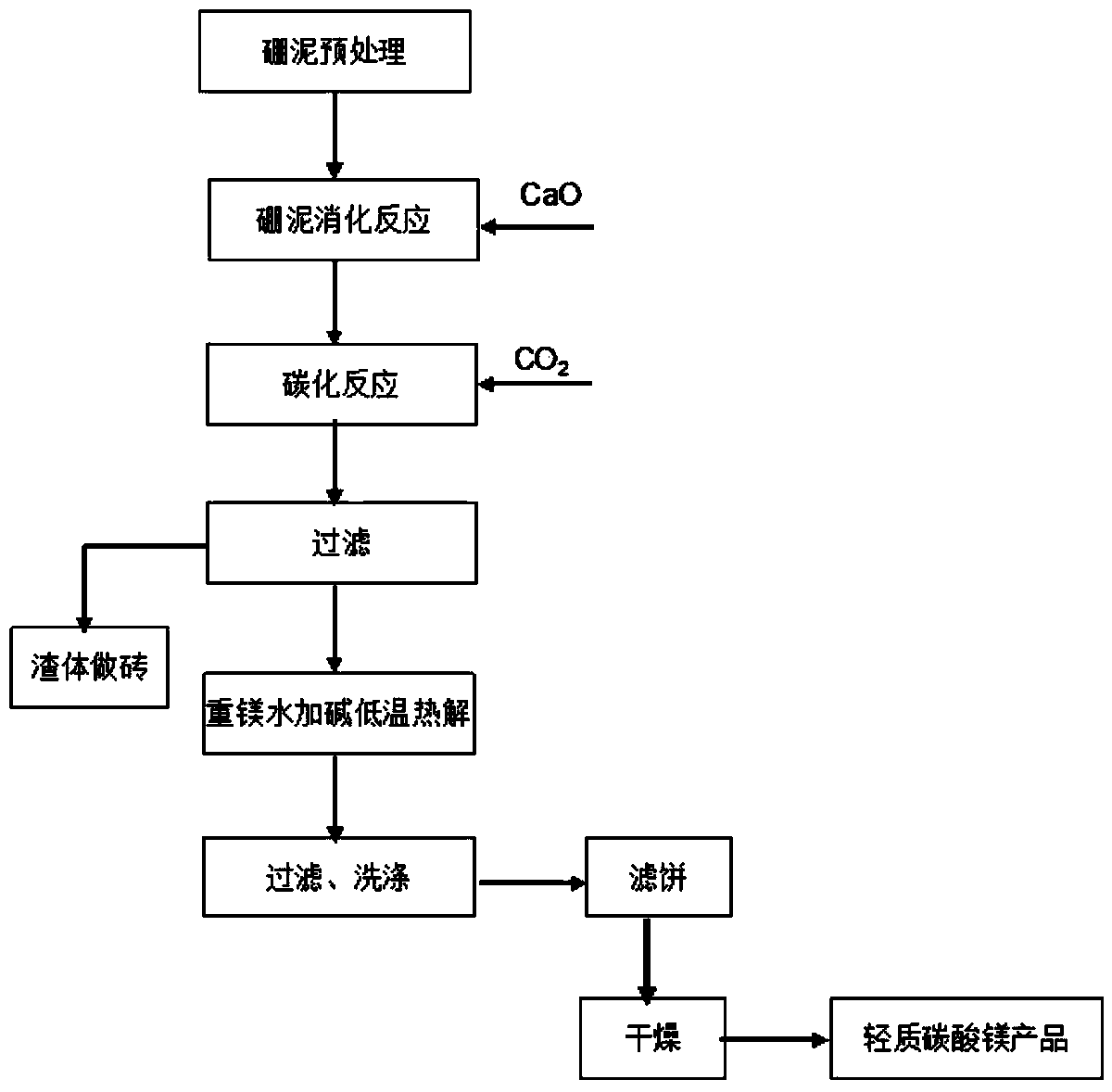
[0042] Digestion: Weigh 1kg of boron mud, 400g of calcium oxide and 3kg of water and stir evenly, the reaction temperature is 85°C, and the reaction time is 3.5 hours to obtain a digestion mixture;
[0043] Carbonization: Pour the above-mentioned digestion mixture into the carbonization tank, add 6kg of water at 10°C to the carbonization tank, and open the circulating water for external cooling to keep the carbonization temperature between 20-30°C. Carbon dioxide gas of about 0.4MPa, carbonized for 1 hour;
[0044] Purification: filter the carbonized mixture, add any alkali or any combination of alkalis mentioned above to the filtrate, the amount of alkali added is 0.015% of the weight of the boron mud, pyrolyze at 45°C for 2 hours, and then suction filter , wash and dry. Calculate the pyrolysis rate (96%) according to the magnesium bicarbonate content in the solution before and after the reaction. As determined by complexometric titration, the quality of the product conform...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Digestion: Weigh 1 kg of boron mud (magnesia content is 40%), 600 g of calcium oxide and 6 kg of water are stirred evenly, the reaction temperature is 100 ° C, and the reaction time is 2 hours to obtain a digestion mixture;
[0047] Carbonization: Pour the above-mentioned digestion mixture into the carbonization tank, add 12kg of water at 20°C to the carbonization tank, and open the circulating water for external cooling to keep the carbonization temperature between 20-30°C. Carbon dioxide gas of about 0.4MPa, carbonized for 1 hour;
[0048] Purification: filter the carbonized mixture, add any alkali or any combination of alkalis mentioned above to the filtrate, the amount of alkali added is 0.02% of the weight of the boron mud, pyrolyze at 50°C for 1 hour, and pump Filter, wash and dry. Calculate the pyrolysis rate (97%) according to the magnesium bicarbonate content in the solution before and after the reaction. As determined by complexometric titration, the quality...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Digestion: weigh 1 kg of boron mud (magnesia content is 40%), 500 g of calcium oxide and 4 kg of water and stir evenly, the reaction temperature is 95 ° C, and the reaction time is 2.5 hours to obtain a digestion mixture;
[0051] Carbonization: Pour the above-mentioned digestion mixture into the carbonization tank, add 15kg of water at 20°C to the carbonization tank, and open the circulating water for external cooling to keep the carbonization temperature between 20-30°C. Carbon dioxide gas of about 0.4MPa, carbonized for 1 hour;
[0052] Purification: filter the carbonized mixture, add any alkali or any combination of alkalis mentioned above to the filtrate, the amount of alkali added is 0.01% of the weight of the boron mud, pyrolyze at 55°C for 1 hour and then suction filter , wash and dry. Calculate the pyrolysis rate (97.5%) according to the magnesium bicarbonate content in the solution before and after the reaction. As determined by complexometric titration, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com