Method for adsorption and removal of pentavalent inorganic arsenic in water
An inorganic arsenic and water removal technology, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of activated carbon accumulation adsorption and adsorption capacity, limitation of treatment efficiency and practical promotion and application, and uneven distribution of metal oxide deposition, so as to improve arsenic removal efficiency, The effect of easy removal efficiency and convenient operation and maintenance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The technical solutions of the present invention include but are not limited to the specific examples listed below.
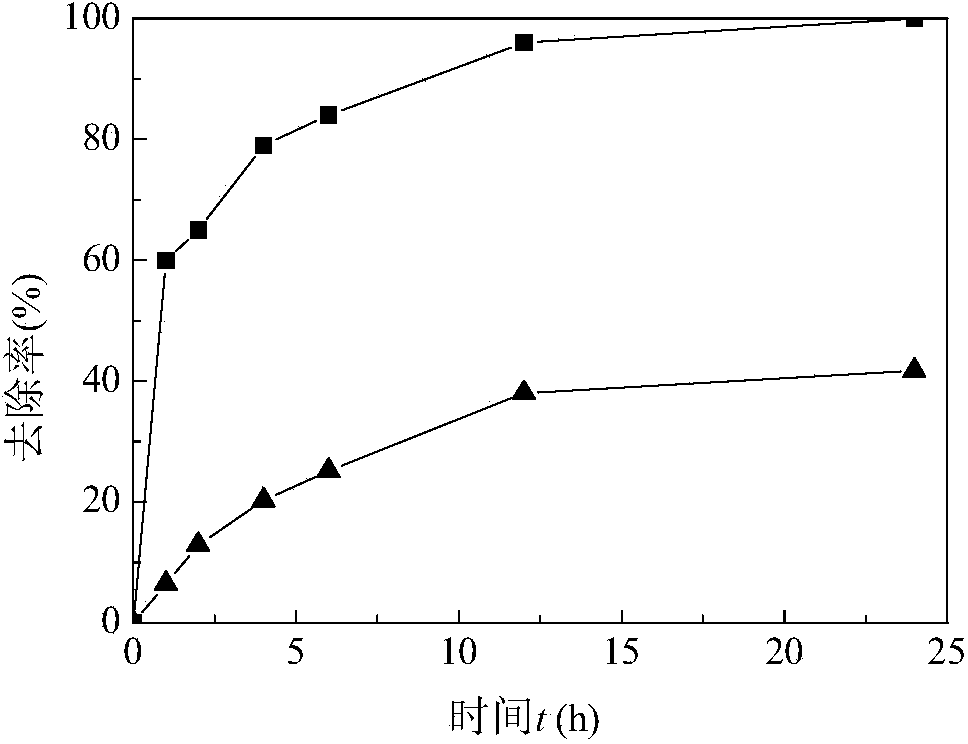
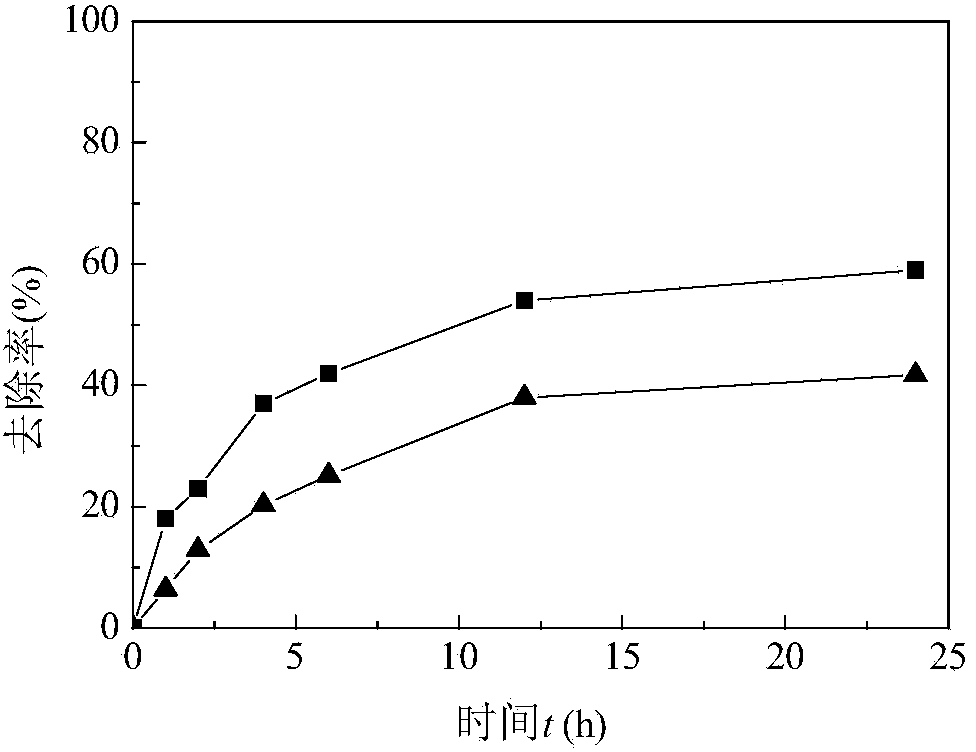
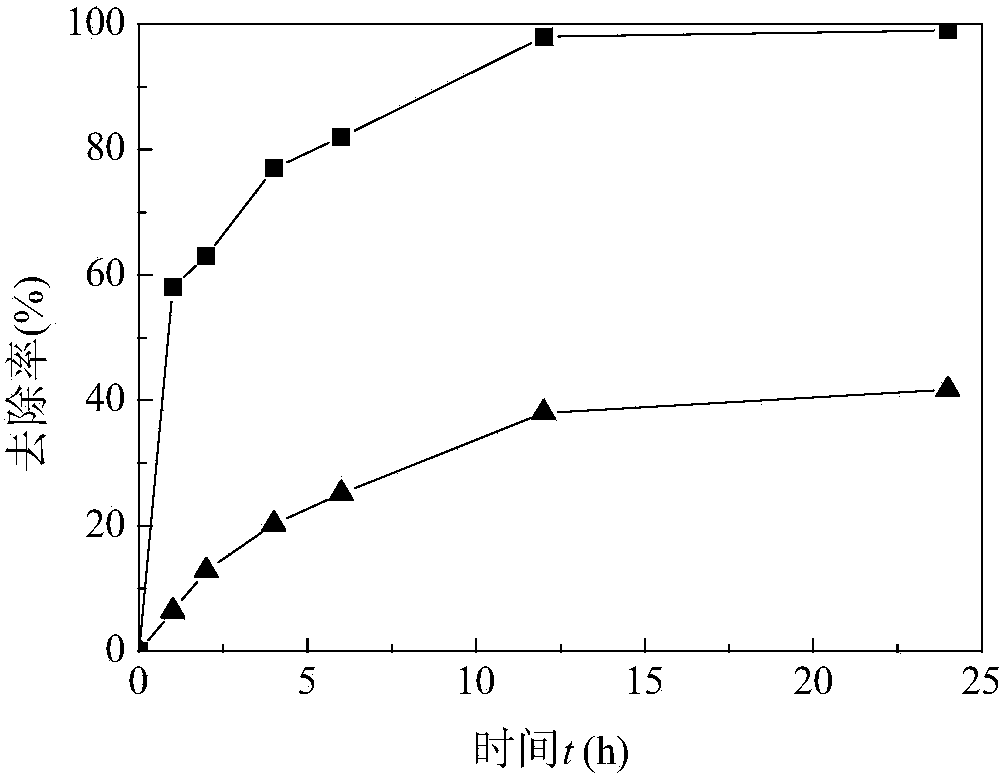
[0027] Method 1: Add ferrous chloride and activated carbon to the water containing As(V) to be treated (the content of As(V) is 5mg / L), and the dosage of ferrous chloride is based on Fe 2+ The molar ratio of As(V) and As(V) is 8:1; the dosage of activated carbon is based on the ratio of activated carbon to Fe 2+ The mass ratio is calculated at 20:1; after mixing, the pH of the solution is controlled around 7.0, the temperature is controlled around 25°C, and the mixture is shaken and mixed at 150r / min to make the adsorbent fully play its role in the solution. After stabilization, wait for The removal rate of As(V) in the treated water is close to 100%. figure 1 Shown is the process of removing As(V) in water by method 1 adsorption, and the comparison with the adsorption of pure activated carbon. It can be seen that method 1 removes As(V) in water signifi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com