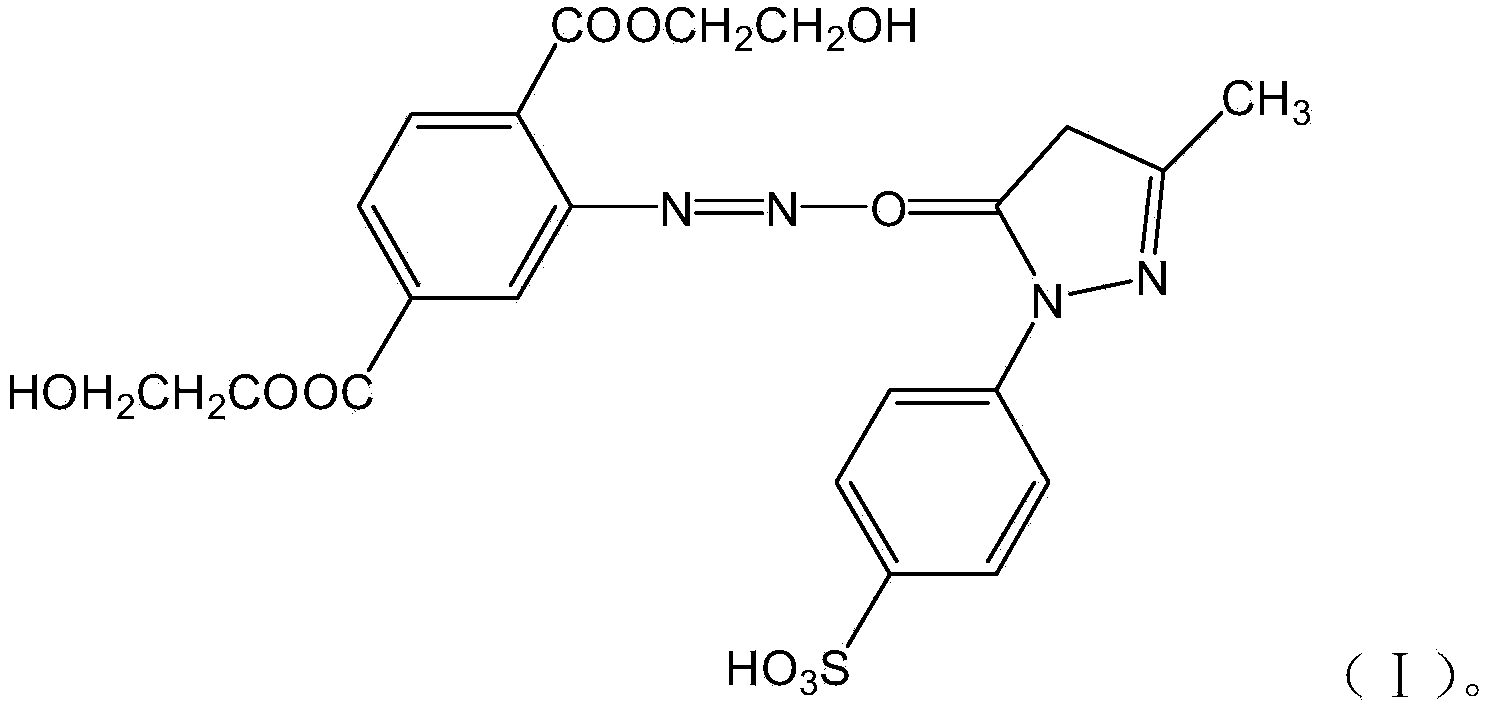
Method for preparing yellow azo dyes by degrading waste polyester fibers
A technology of yellow azo and waste polyester, applied in the direction of azo dyes, monoazo dyes, organic dyes, etc., can solve the problems of soil ecological balance destruction, air and water pollution, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] (1) Ethylene glycol degradation of waste polyester: heat and dissolve 2 parts by weight of zinc acetate in 400 parts by weight of ethylene glycol, add 100 parts by weight of waste polyester after cleaning, drying and crushing, and heat to 198 ° C for 3 hours , continuous stirring and nitrogen protection are required during the reaction. After the reaction, under the environment of nitrogen protection and condensed water circulation, the mixed solution was cooled to below 140°C, and then removed for later use. Dilute the cooled mixed solution into deionized water at 90°C, vacuum filter, cool and crystallize the filtrate, repeat the above operation 3 times, and dry in vacuum at 55°C for 24 hours to obtain the degradation product BHET monomer with a purity of 97%. The rate is 91.0%.
[0022] (2) Nitrification reaction of BHET:
[0023] Mix 1 part by weight of the BHET monomer obtained in step (1) with 0.4 parts by weight of concentrated sulfuric acid at 6°C and stir even...
Embodiment 2
[0035] (1) Ethylene glycol degradation of waste polyester: heat and dissolve 1.5 parts by weight of zinc acetate in 300 parts by weight of ethylene glycol, add 100 parts by weight of waste polyester after cleaning, drying and crushing, and heat to 196 ° C for 4.5 hours , continuous stirring and nitrogen protection are required during the reaction. After the reaction, under the environment of nitrogen protection and condensed water circulation, the mixed solution was cooled to below 140°C, and then removed for later use. Dilute the cooled mixed solution into deionized water at 90°C, vacuum filter, cool and crystallize the filtrate, repeat the above operation 3 times, and dry in vacuum at 55°C for 24 hours to obtain the degradation product BHET monomer with a purity of 96%. The rate is 89.8%.
[0036] (2) Nitrification reaction of BHET:
[0037]Mix 1 part by weight of the BHET monomer obtained in step (1) with 0.5 parts by weight of concentrated sulfuric acid at 5°C and stir e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com