A process method and device for delayed coking
A technology of delayed coking and process method, applied in cracking, petroleum industry, non-catalytic thermal cracking and other directions, can solve the problems of liquid fraction easily containing coke powder, affecting the separation effect of vacuum fractionation tower, etc. the effect of
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
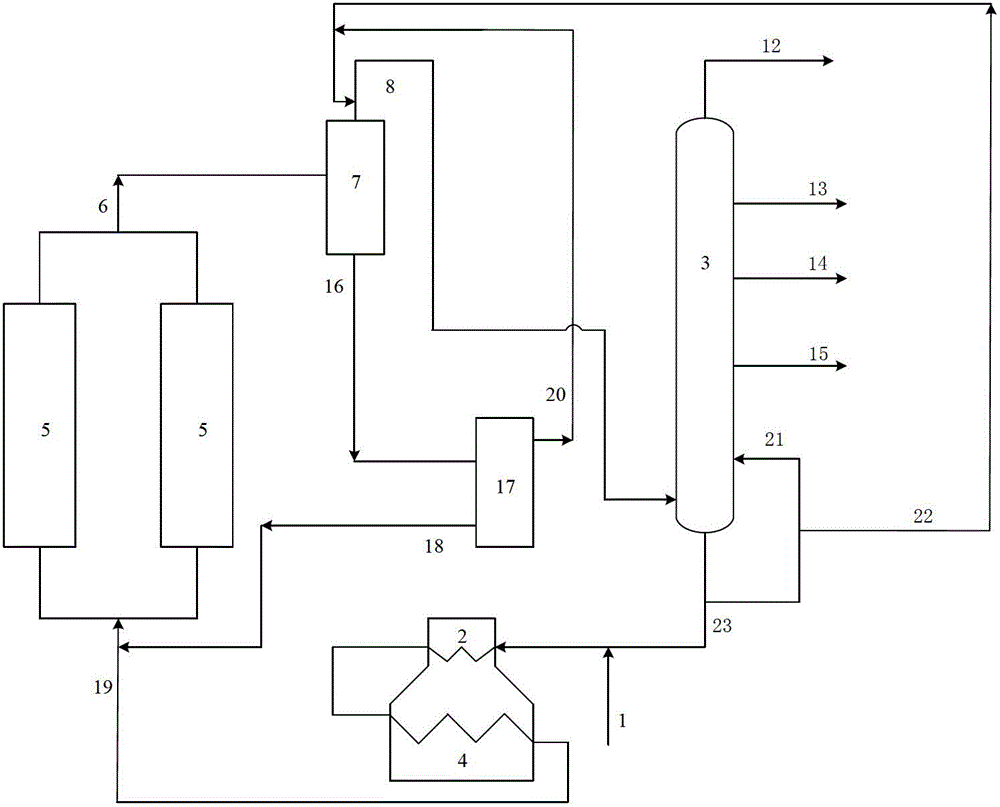
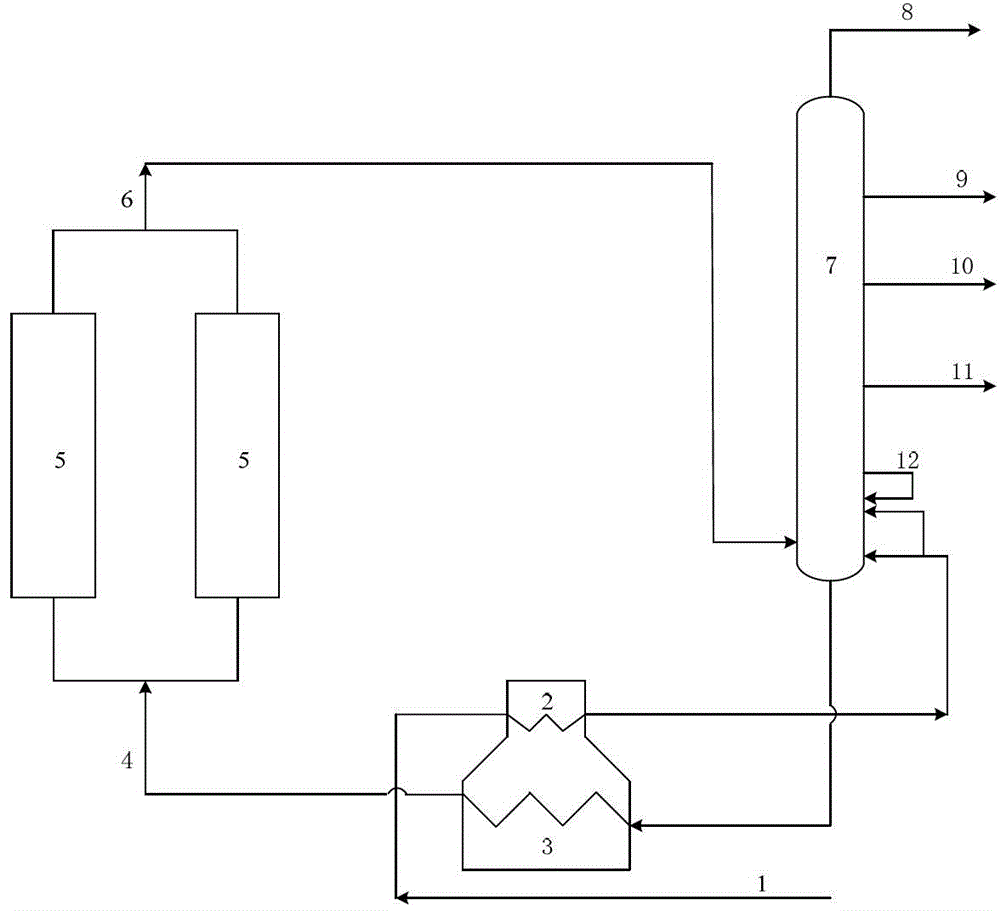
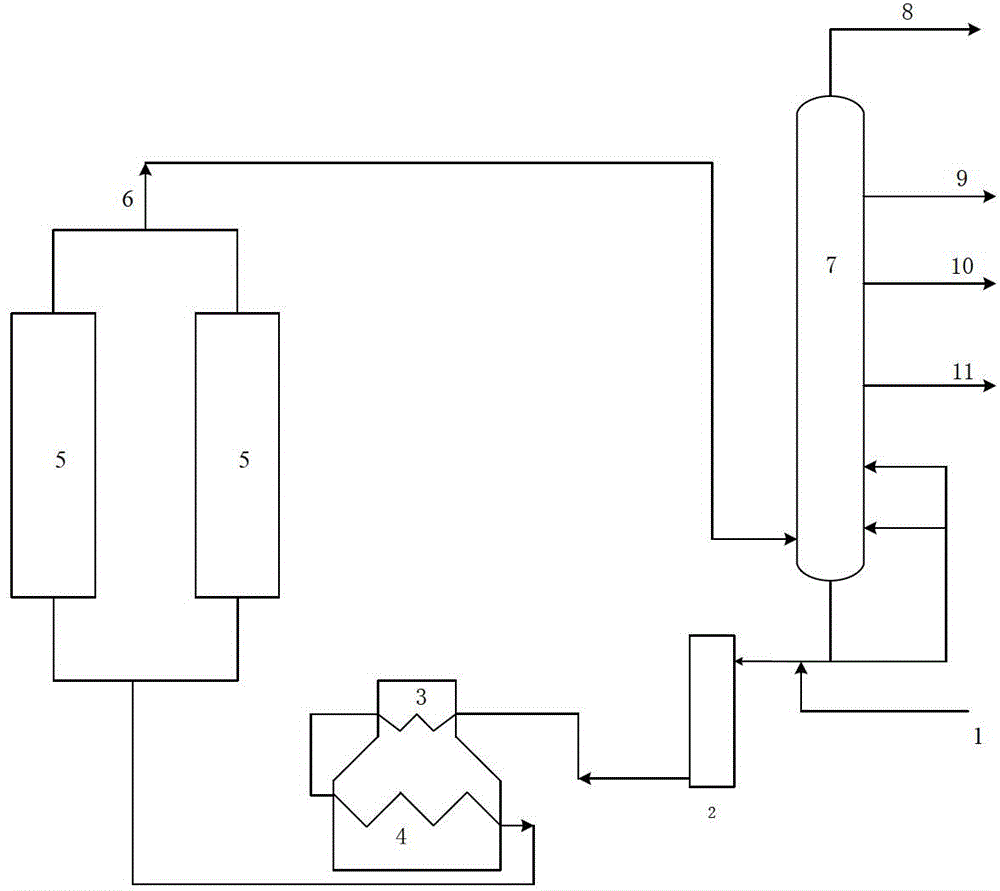
[0028] In this embodiment, the attached figure 1 The process flow, this embodiment illustrates the situation of using a higher circulation ratio of 0.4 and a higher furnace outlet temperature of 503°C. In actual working conditions, when the circulation ratio is 0.4, the outlet temperature of the heating furnace of the coking unit generally does not exceed 500°C.
[0029] After the raw material oil from pipeline 1 is mixed with part of the bottom oil from the fractionation tower from pipeline 23, it passes through the convection section 2 and the radiation section 4 of the heating furnace in sequence, and enters the coke tower 5 after heating up to 503°C for reaction. The circulation ratio is 0.4:1 ( In the feed to the coke tower, the mass ratio of the non-fresh raw material oil part to the fresh raw material oil part); the generated coke stays in the coke tower, and the coked oil gas generated enters the flash tower, and the top oil of the settling tank and the extracted part ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] In this embodiment, the attached figure 1 The process flow, this embodiment illustrates the process when the low circulation ratio and low heating furnace outlet temperature often adopted in current actual production are adopted.
[0032] Using the same vacuum residue raw material as in Example 1. After the raw material oil from pipeline 1 is mixed with part of the bottom oil from the fractionation tower from pipeline 23, it passes through the convection section 2 and the radiation section 4 of the heating furnace in turn, and enters the coke tower 5 after the temperature rises to 496°C for reaction. The circulation ratio is 0.1:1 ( In the feed to the coke tower, the mass ratio of the non-fresh raw material oil part to the fresh raw material oil part); the generated coke stays in the coke tower, and the coked oil gas generated enters the flash tower, and the top oil of the settling tank and the extracted part of the fractionation tower The bottom oil is mixed as reflux...
Embodiment 3
[0034] In this embodiment, the attached figure 1 The flow process of this embodiment illustrates the technological situation when the process method adopts a low circulation ratio and a higher heating furnace outlet temperature.
[0035] Using the same vacuum residue raw material as in Example 1. After the raw material oil from pipeline 1 is mixed with part of the bottom oil from the fractionation tower from pipeline 23, it passes through the convection section 2 and the radiation section 4 of the heating furnace in sequence, and enters the coke tower 5 for reaction after heating up to 503°C. The circulation ratio is 0.1:1 ( In the feed to the coke tower, the mass ratio of the non-fresh raw material oil part to the fresh raw material oil part); the generated coke stays in the coke tower, and the coked oil gas generated enters the flash tower, and the top oil of the settling tank and the extracted part of the fractionation tower The bottom oil is mixed as reflux oil and inject...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com