Plant growing medium produced by using reverse flotation phosphate tailing and preparation method thereof
A technology of planting base material and phosphorus tailings, applied in the direction of phosphate fertilizer, application, fertilizer mixture, etc., can solve the problems of easy loss, preparation of planting base material without phosphorus tailings, etc., and achieve cost saving, low cost and simple construction procedures Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~5
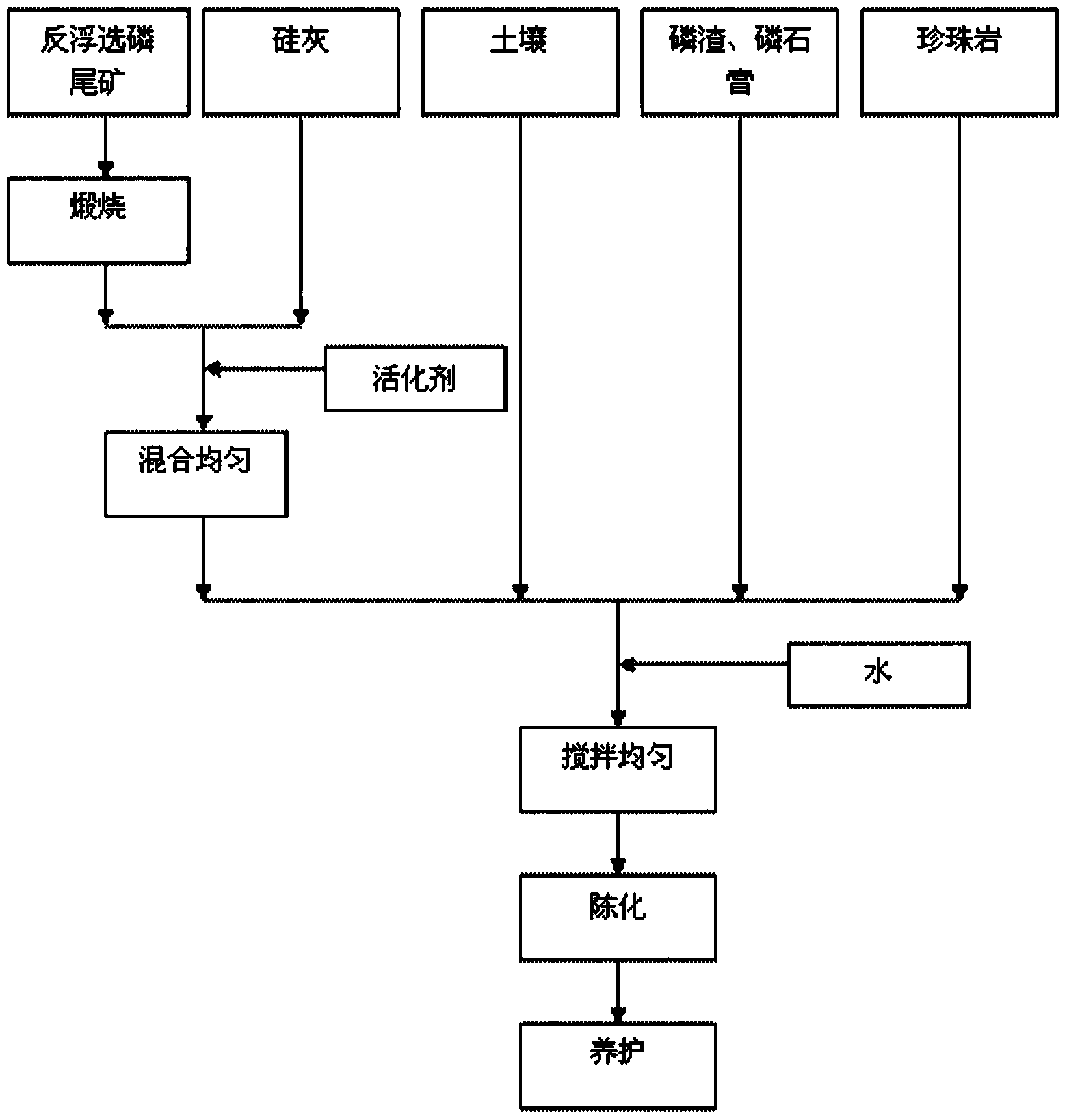
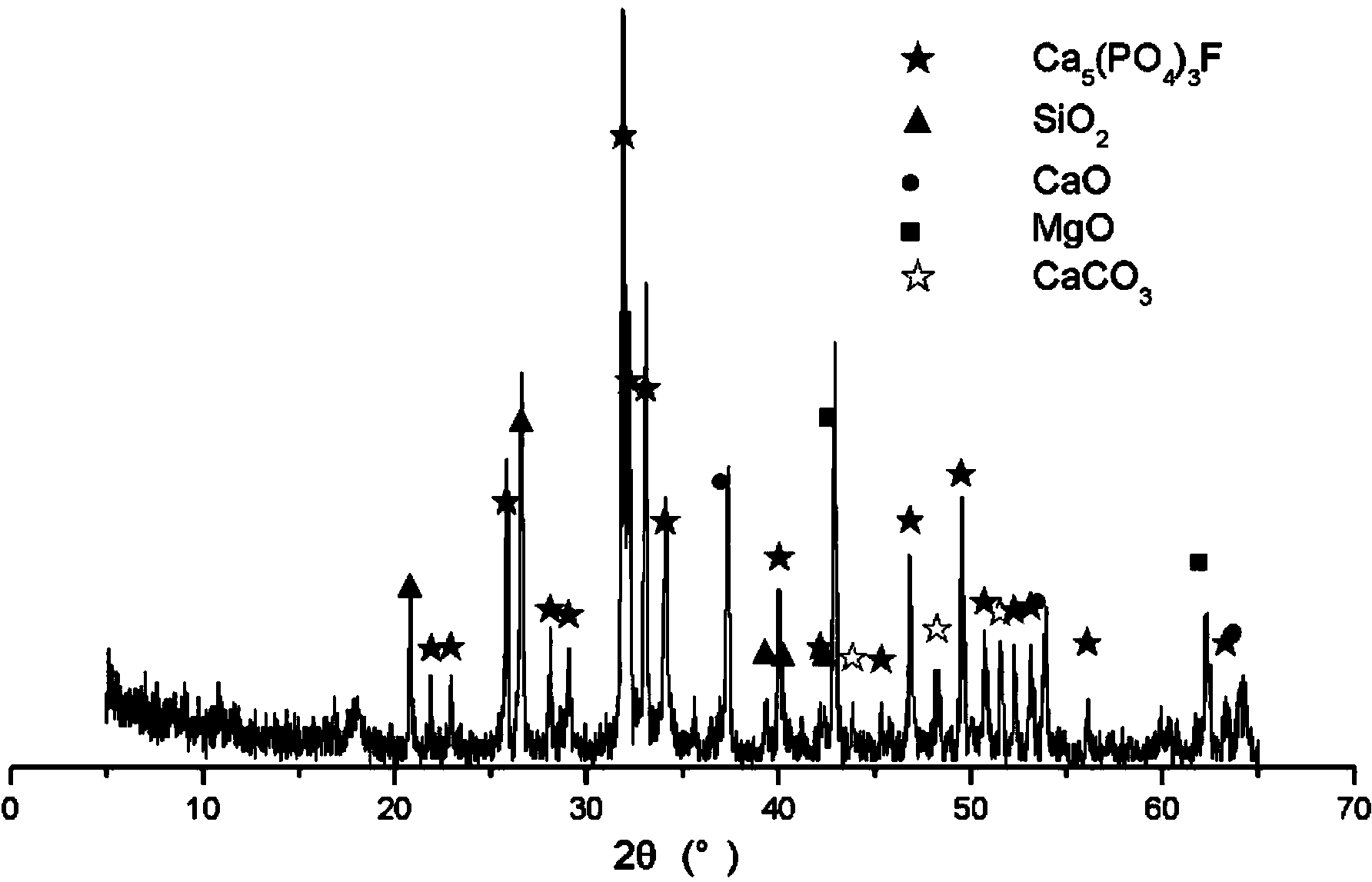
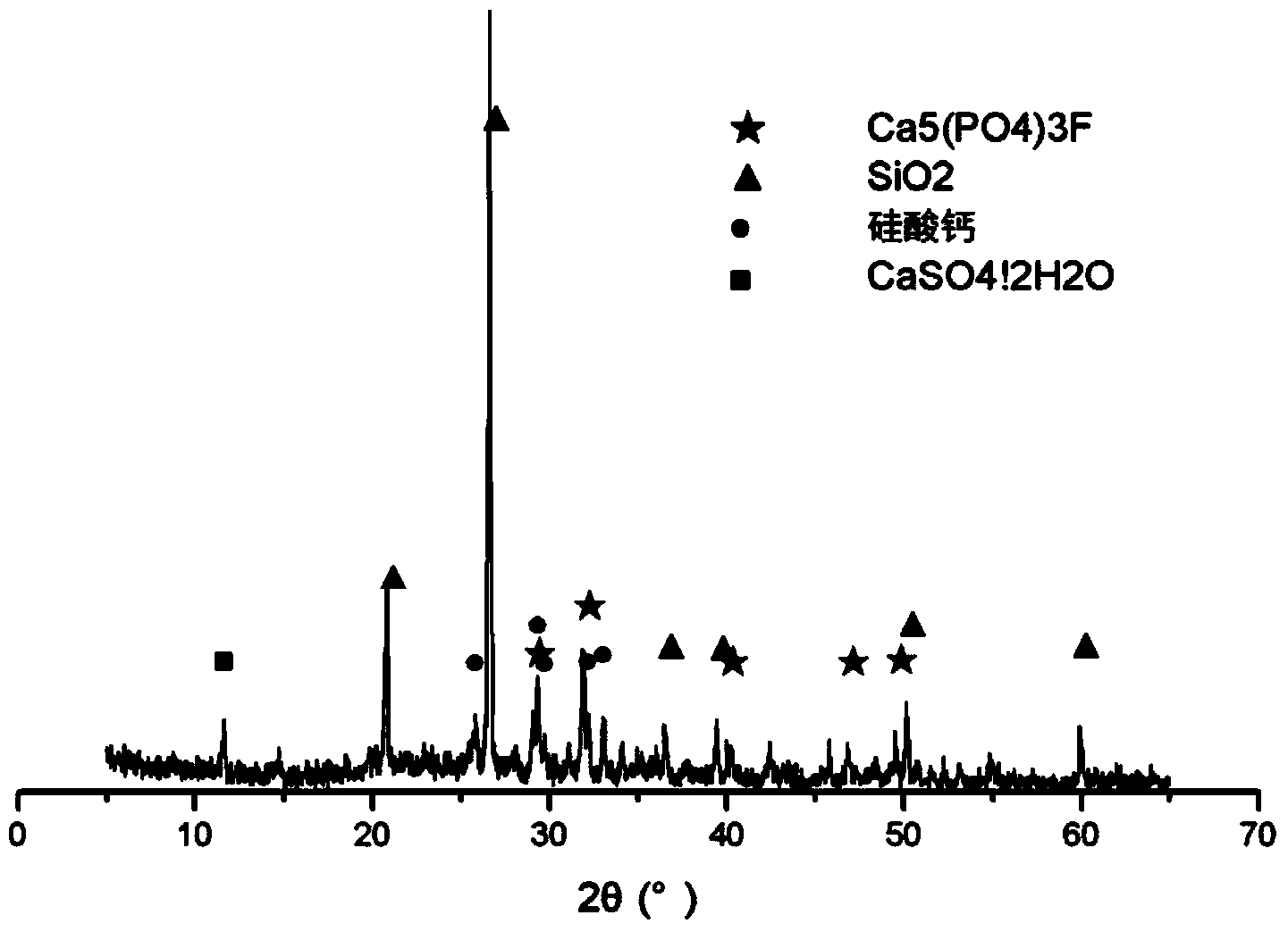
[0044] The reverse flotation phosphorus tailings were calcined at 900°C, the XRD diffraction pattern of the calcined product is shown in figure 2 , the main components of reverse flotation phosphorus tailings are dolomite, apatite and quartz minerals in the form of collophanite. After high-temperature calcination, dolomite is decomposed into calcium oxide and magnesium oxide, and the quality of quartz is also improved. mineral activity. The activated phosphorus tailings obtained after calcination are evenly dry-mixed with soil, then wet-mixed with water (see Table 1 for the ratio), aged, and finally sprayed onto rocky slopes to make vegetation substrates.
[0045] For simplicity of description, in the following descriptions, phosphorous tailings refer to reverse flotation phosphorous tailings unless otherwise specified, and active phosphorous tailings refer to calcined reverse flotation phosphorous tailings, and the percentages in the following descriptions are all mass perce...
Embodiment 6~10
[0053] In Examples 6-10, there is a method for preparing vegetation substrates by using reverse flotation phosphate rock tailings, and the distribution ratio of each component is shown in Table 2.
[0054] Table 2
[0055]
[0056] The dry materials described in Table 2 are soil, activated phosphorus tailings, phosphogypsum, phosphorus slag, perlite, fertilizer, silica fume and activator.
[0057] In Examples 6-10, the steps for preparing the planting substrate are as follows:
[0058] (1) Take active phosphorus tailings (calcined at 900°C), soil, silica fume, phosphogypsum, activator, perlite, phosphorus slag, fertilizer and water according to the proportioning of each component in Table 1;
[0059] (2) Dry mix and stir the active phosphorus tailings, silica fume and activator weighed in step (1) evenly (stir for 3 to 5 minutes), then add soil, phosphogypsum, phosphorus slag, perlite and fertilizer and dry mix and stir Evenly (stir for 3-5min), finally add weighed water,...
Embodiment 11~15
[0063] In Examples 11-15, there is a method for preparing vegetation substrates by using a large amount of flotation phosphate rock tailings, and the distribution ratio of each component is shown in Table 3 below.
[0064] table 3
[0065]
[0066] In Examples 11-15, the steps of preparing the above-mentioned planting substrates are the same as those in Examples 6-10.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com