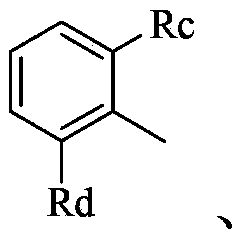
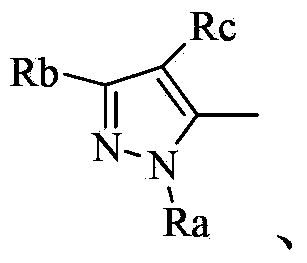
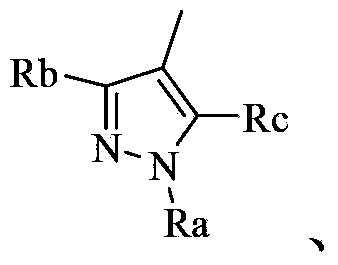
Novel quinazoline (sulfur) ketone compound and application
A ketone compound, quinazoline technology, applied in the chemical, application, organic chemistry and other directions for biological control, can solve problems such as applications that have not been reported in the literature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0252] Example 1: Preparation of compound 11
[0253]
[0254] Add 0.30g (0.001mol) of benzylamine (II-1) and 0.12g (0.0012mol) of triethylamine into 20mL of dichloromethane, and add 0.21g (0.0011mol) of 1,3-dimethyl- A solution of 4-chloro-5-pyrazolecarboxylic acid chloride in 10 mL of dichloromethane. After dripping, continue to stir the reaction at room temperature for 1 hour. TLC monitors the completion of the reaction. Pour the reaction mixture into 20 mL of water. Separate the organic layer. Wash with 10 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid, saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution, and saturated brine, dry with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and desolvate under reduced pressure. The residue is separated by column chromatography to obtain a pure product of 0.37 g, yield 82.0%, melting point 158-159°C .
Embodiment 2
[0255] Example 2: Preparation of compound 12
[0256] method 1:
[0257]
[0258] Add 0.30 g (0.001 mol) of benzylamine (II-1) and 0.12 g (0.0012 mol) of triethylamine to 20 mL of dichloromethane, and add 0.23 g (0.0011 mol) of 1-methyl-3-ethyl dropwise with stirring at room temperature A 10mL dichloromethane solution of 4-chloro-5-pyrazolecarboxylic acid chloride, and then continue to stir and react at room temperature for 1 hour,
[0259] After the reaction was monitored by TLC, the reaction mixture was poured into 20 mL of water, and the organic layer was separated. The organic layer was washed with 10 mL each of 5% diluted hydrochloric acid, saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution, and saturated brine, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and desolvated under reduced pressure. The residue was separated by column chromatography to obtain 0.40 g of pure product, the yield was 85.0%, and the melting point was 159-160°C.
[0260] Method 2:
[0261] 1) Preparation of intermedi...
Embodiment 3
[0267] Example 3: Preparation of compound 34
[0268]
[0269] Add 0.32g (0.001mol) of benzylamine (II-1) and 0.12g (0.0012mol) of triethylamine into 20ml of dichloromethane, and add dropwise 0.23g (0.0011mol) of 1-methyl-3- (Trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid chloride in 10ml of dichloromethane. After dripping, continue to stir the reaction at room temperature for 1 hour. TLC monitors the reaction to the end. Pour the reaction mixture into 30ml of water and shake to separate the organic The organic phase was washed successively with dilute hydrochloric acid, sodium bicarbonate aqueous solution and saturated brine, and then dried to obtain the product, which was washed with ethyl acetate to obtain a white solid. The pure product was obtained by column chromatography, 0.41g, and the yield was 86.0%. Melting point 179-180°C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com