Transistor with high electronic mobility
A high electron mobility, transistor technology, used in circuits, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of high activation energy, reduced device performance, low hole concentration, etc., to improve the breakdown voltage and improve the concentration effect. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
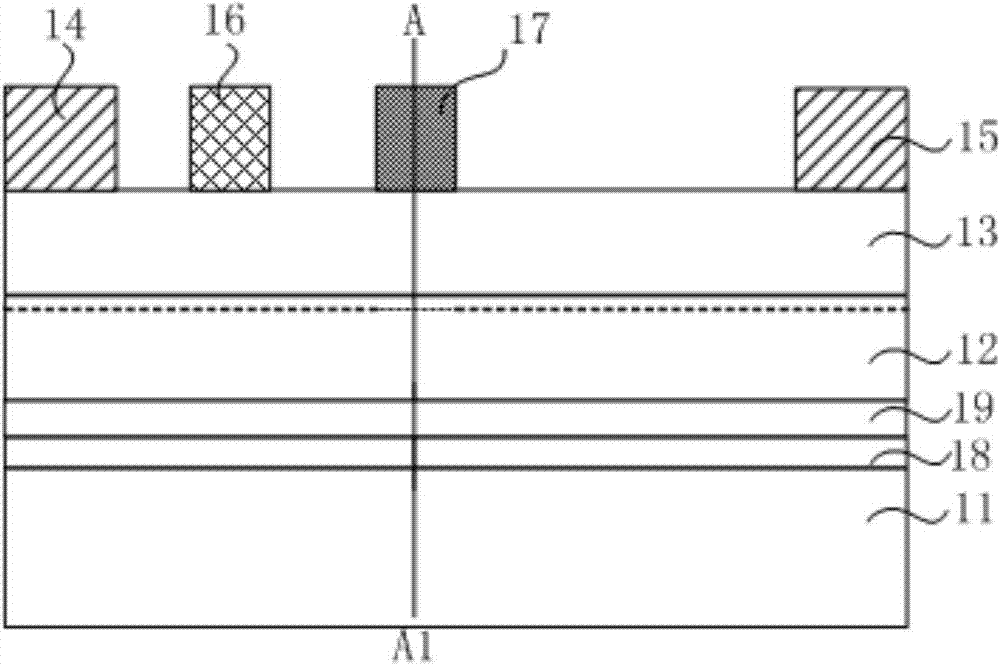
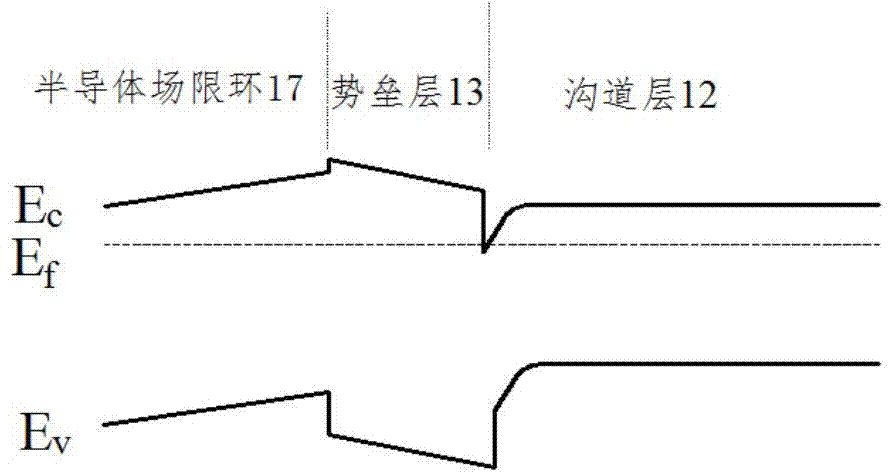
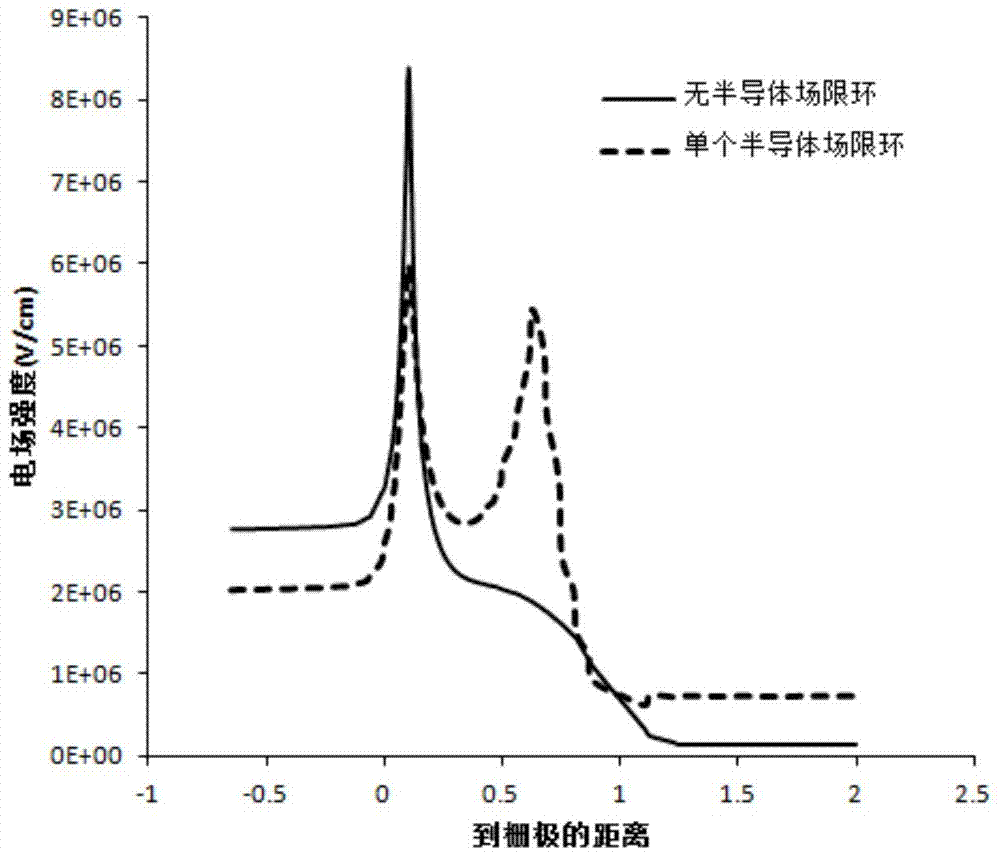
[0039] figure 1 is a structural diagram of a high electron mobility transistor provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, figure 2 It is a high electron mobility transistor provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention. figure 1 The energy band diagram in the direction of AA1, now combined with figure 1 and figure 2 Embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described.
[0040] See figure 1 , the high electron mobility transistor includes a substrate 11, a channel layer 12 on the substrate 11, a barrier layer 13 on the channel layer 12, a source 14 on the barrier layer 13, and a drain 15 And a Schottky gate 16 located between the source 14 and the drain 15 , and a semiconductor field confining ring 17 located between the Schottky gate 16 and the drain 15 on the barrier layer 13 .
[0041] In this embodiment, the material of the substrate 11 may be gallium nitride, silicon, sapphire, silicon carbide, aluminum nitride or other semiconductor materials.
[0...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Figure 4 It is a structural diagram of a high electron mobility transistor provided in Embodiment 2 of the present invention, please refer to Figure 4 , the high electron mobility transistor comprises a substrate 11, a nucleation layer 18 on the substrate 11, a buffer layer 19 on the nucleation layer 18, a channel layer 12 on the buffer layer 19, a channel layer on the The barrier layer 13 on the barrier layer 12, the source 14 on the barrier layer 13, the drain 15 and the Schottky gate 16 between the source 14 and the drain 15, the Schottky gate 16 on the barrier layer 13 At least two semiconductor field confining rings between the base gate 16 and the drain 15 .
[0060] The second embodiment is based on the first embodiment above, and the difference from the first embodiment is that the high electron mobility transistor provided by the second embodiment includes a Schottky gate 16 and a drain 15 on the barrier layer 13 There are at least two semiconductor field con...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Figure 5 It is a structural diagram of a high electron mobility transistor provided in Embodiment 3 of the present invention, please refer to Figure 5 , the high electron mobility transistor comprises a substrate 11, a nucleation layer 18 on the substrate 11, a buffer layer 19 on the nucleation layer 18, a channel layer 12 on the buffer layer 19, a channel layer on the The barrier layer 13 on the barrier layer 12, the source 14 on the barrier layer 13, the drain 15 and the Schottky gate 16 between the source 14 and the drain 15, the Schottky gate 16 on the barrier layer 13 At least two semiconductor field confinement rings between the base gate 16 and the drain 15, the composition of the at least two semiconductor field confinement rings is uniform, and the thickness of the at least two semiconductor field confinement rings is close to the Schottky gate The electrode 16 gradually decreases towards the drain electrode 15.
[0068] In this embodiment, the present inve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com