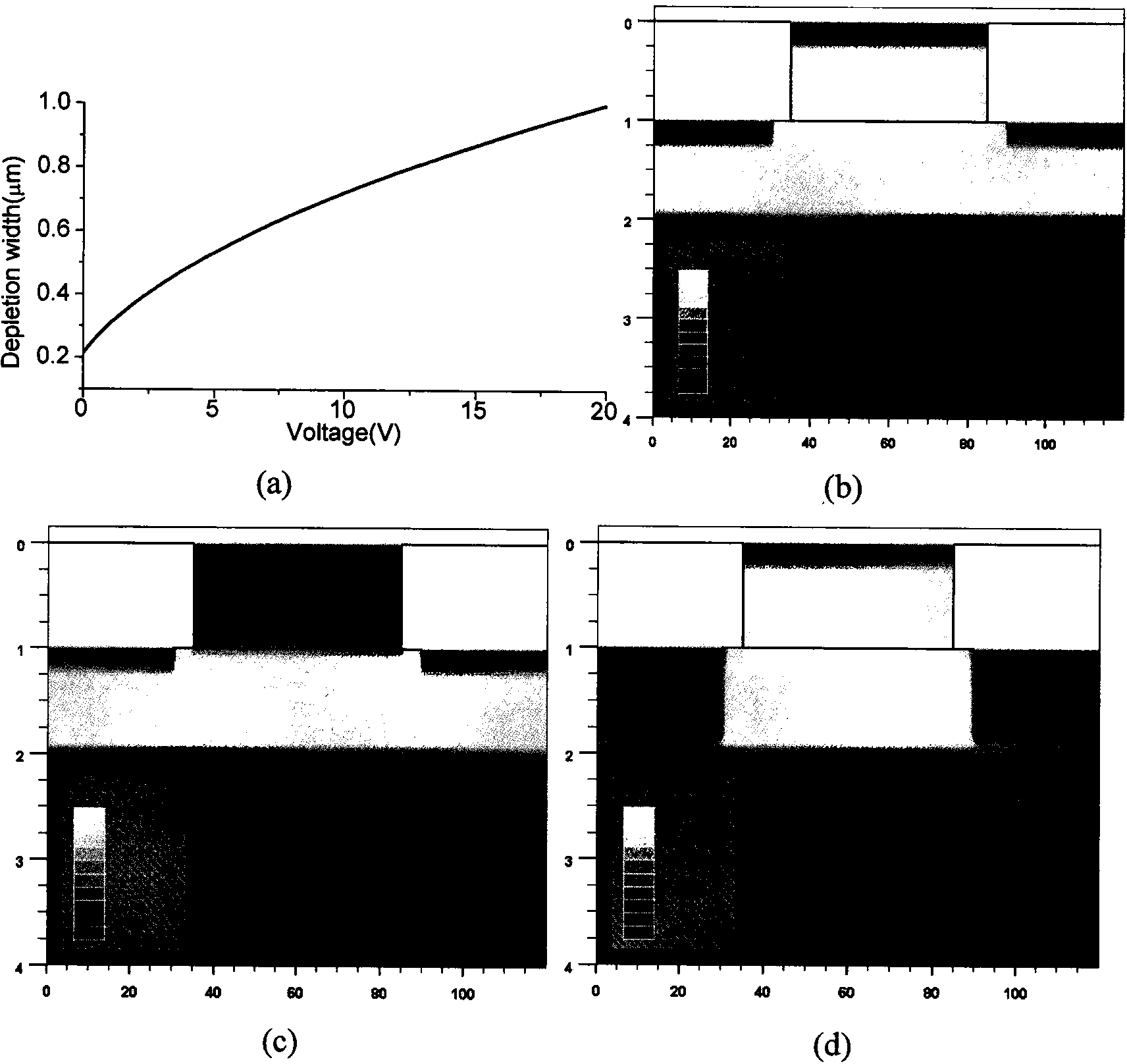
Patents
Literature
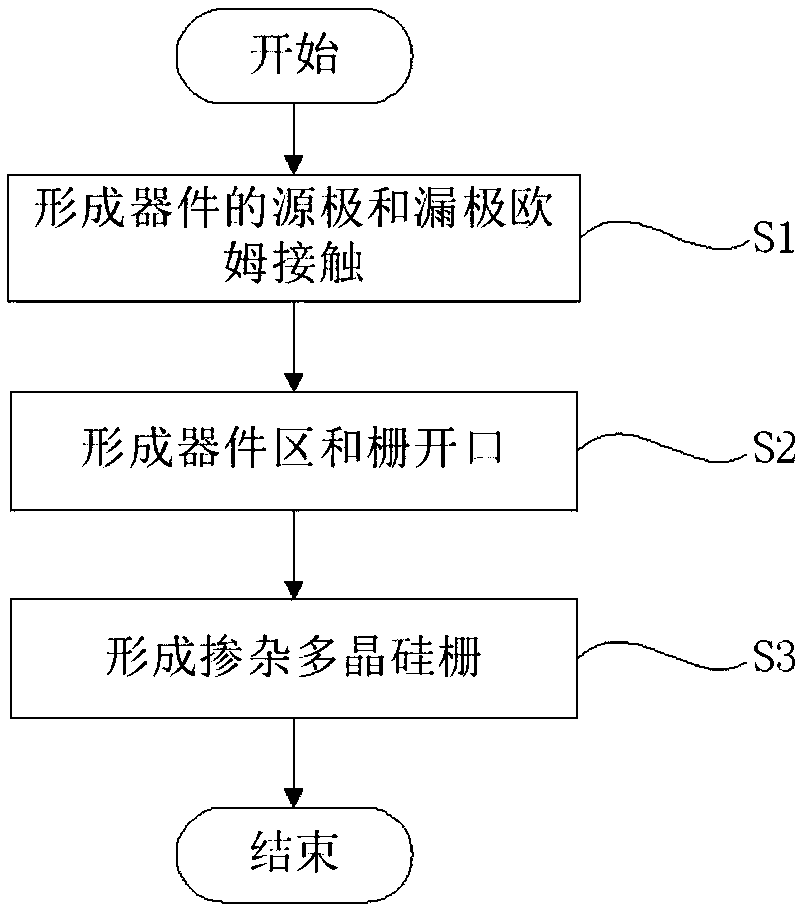
50 results about "Schottky gate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
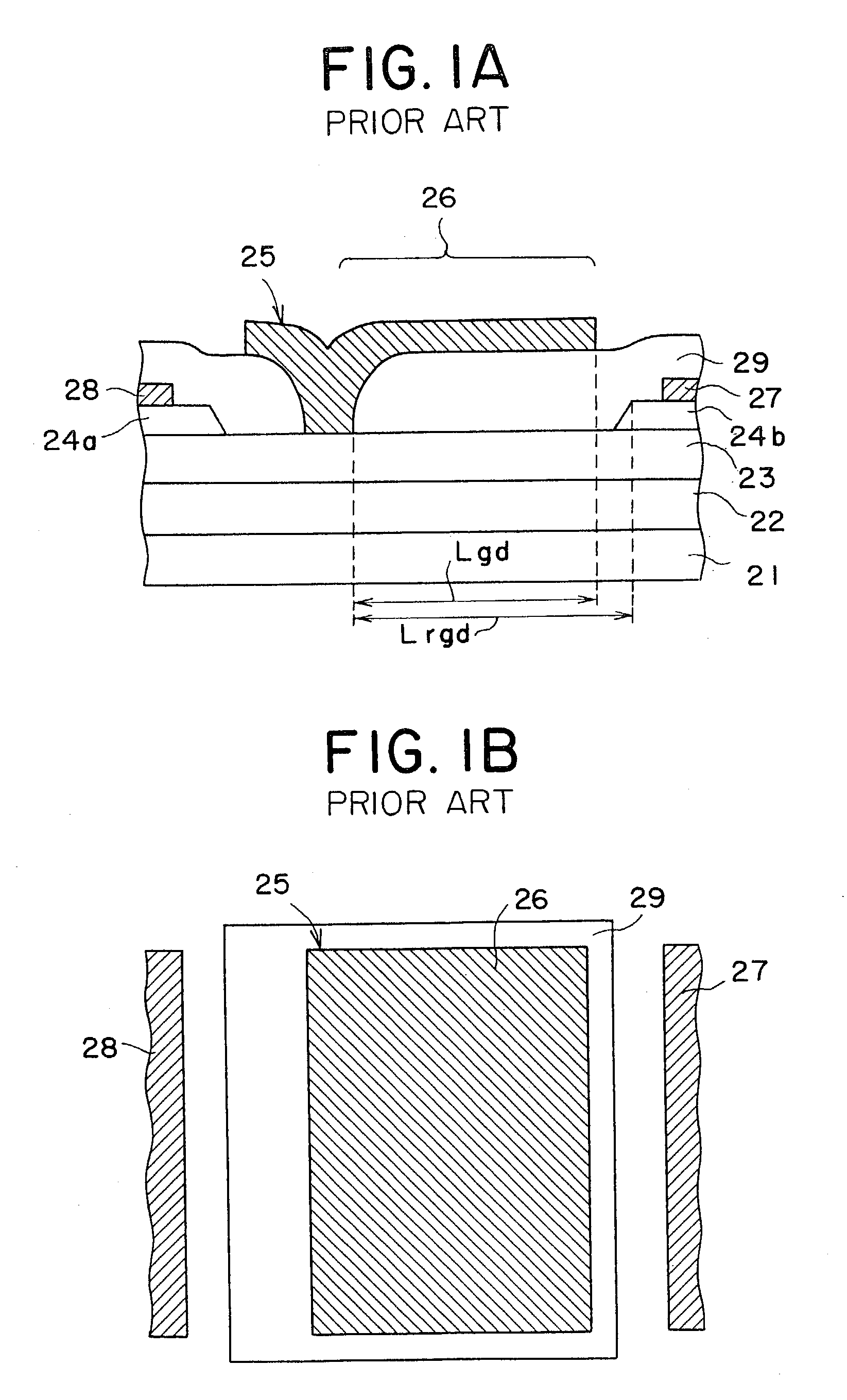
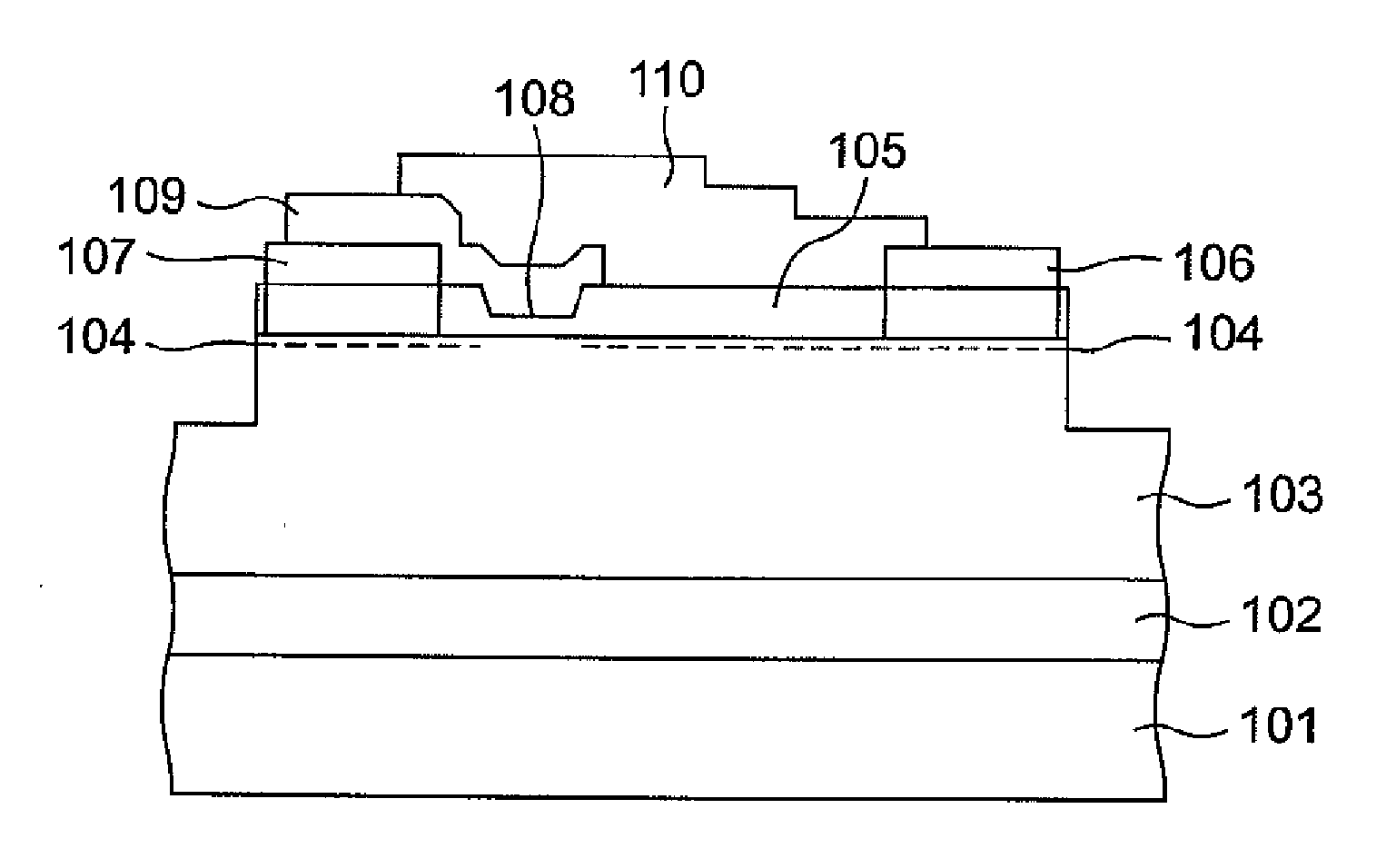
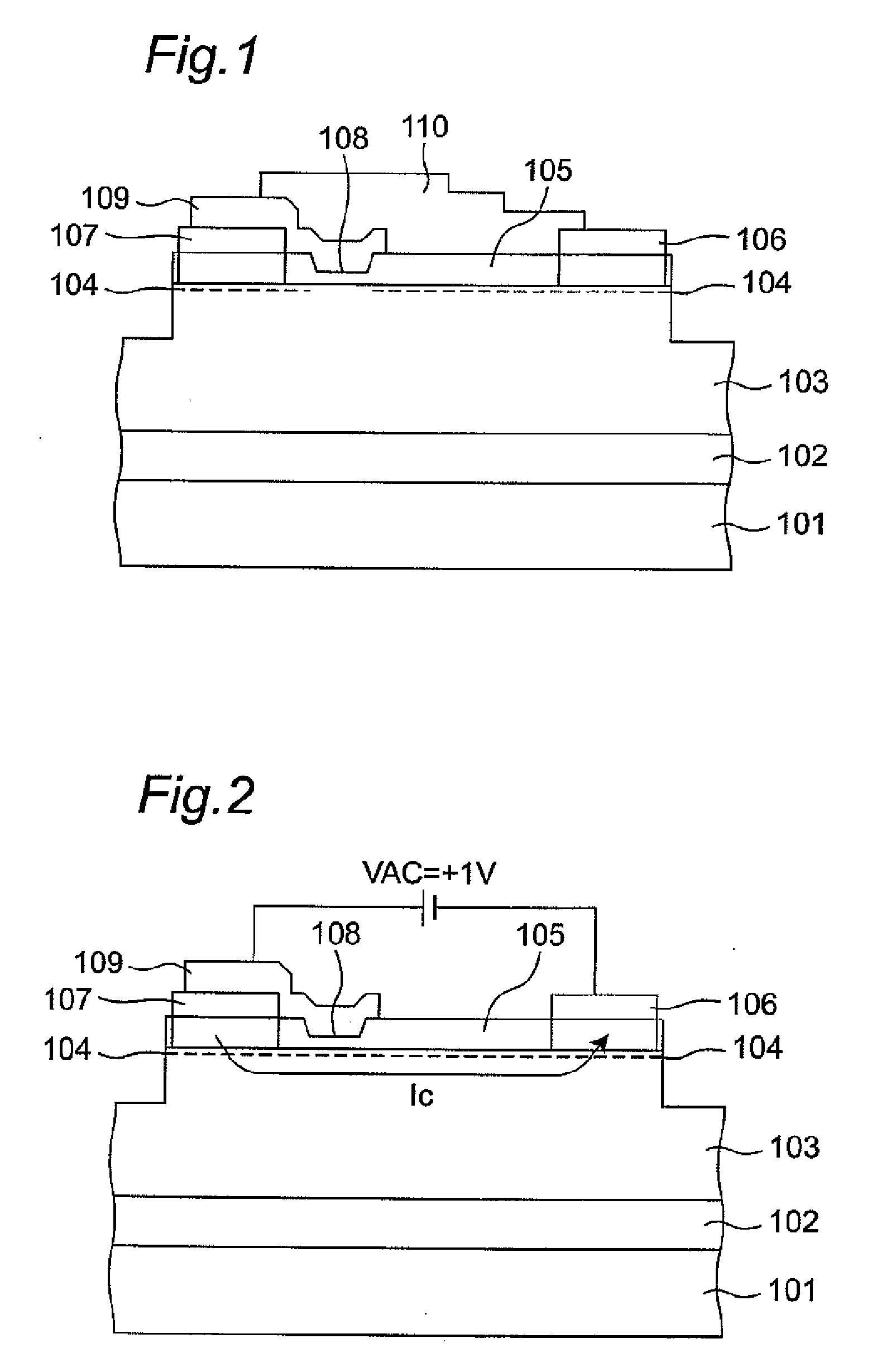
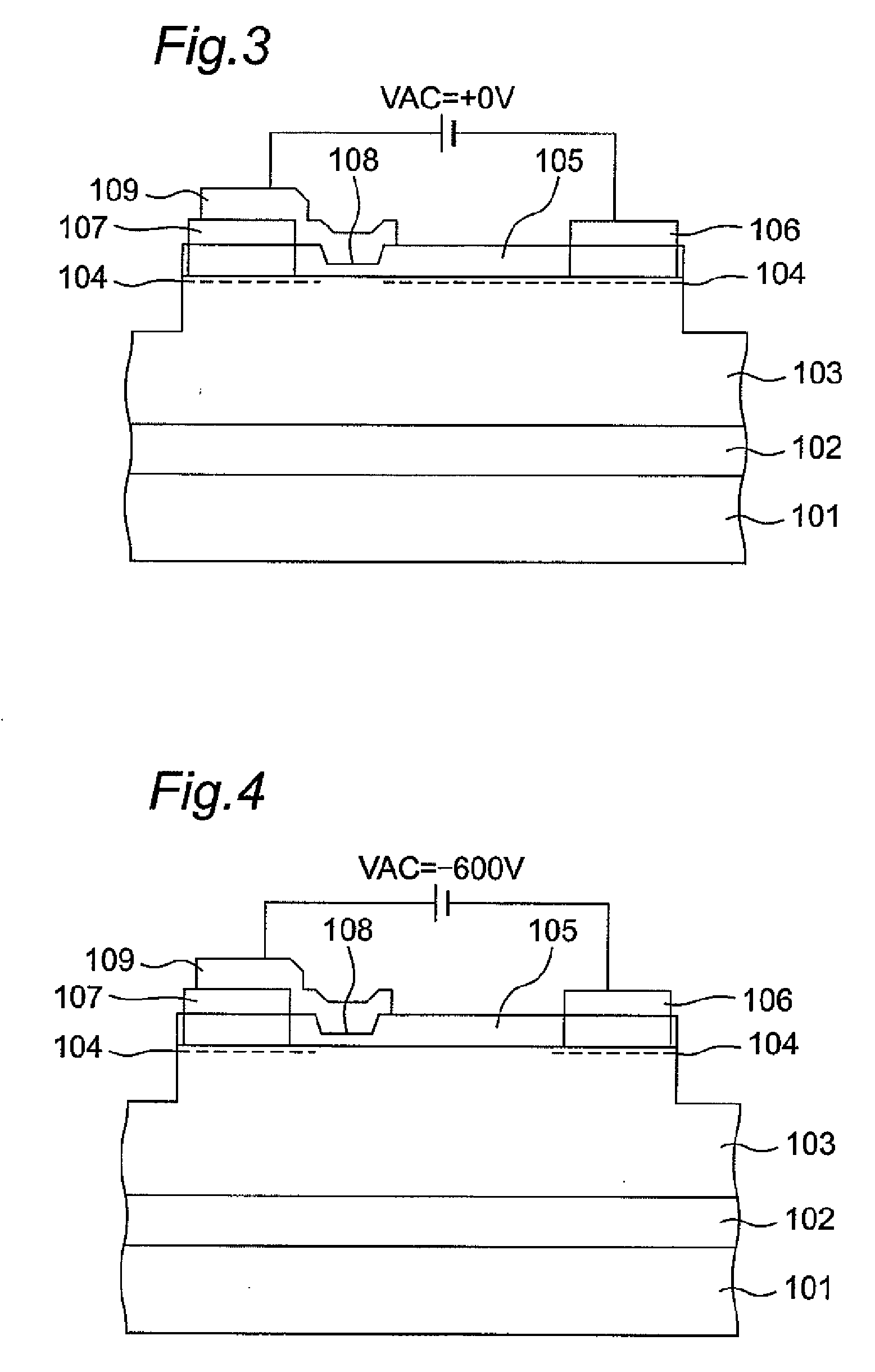
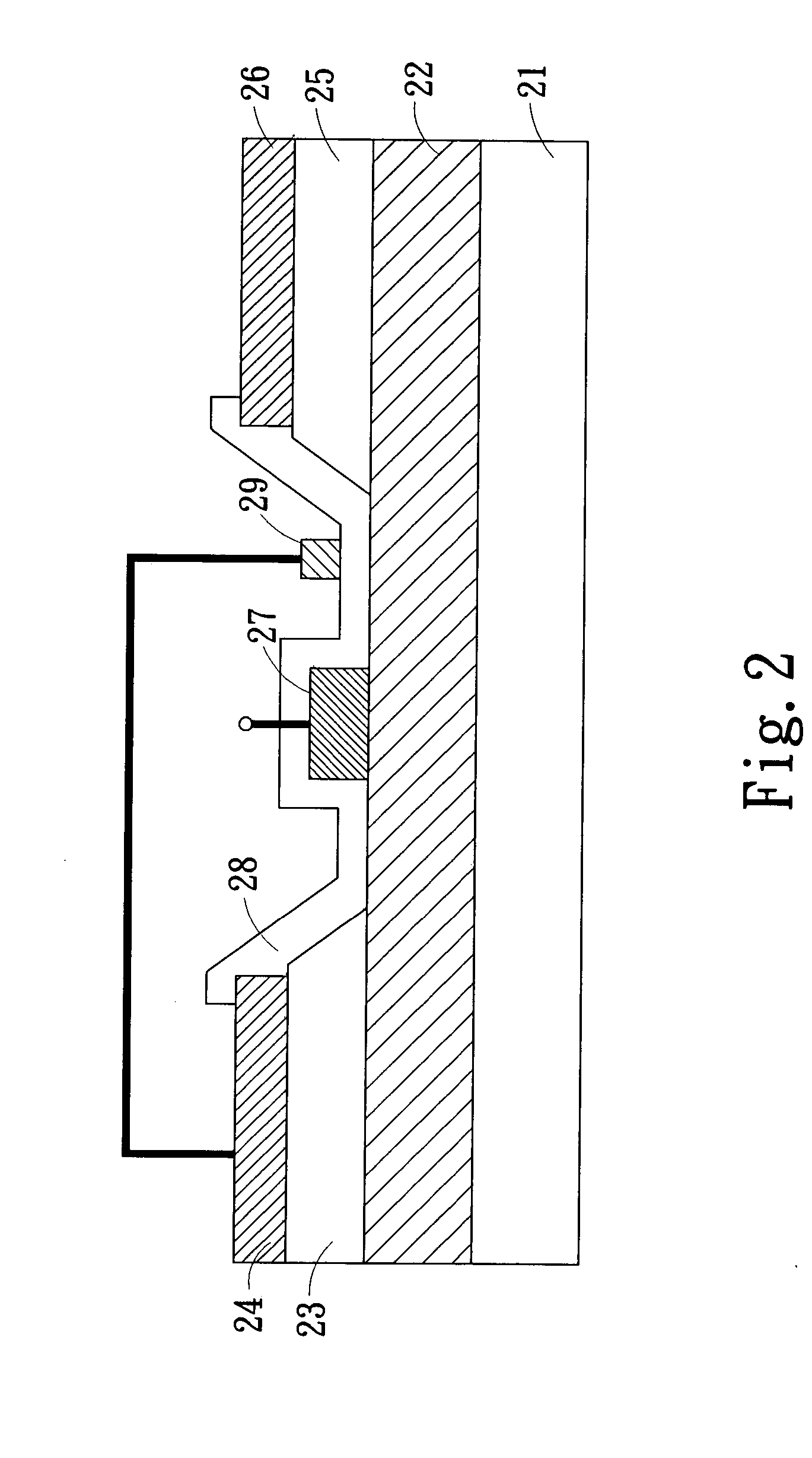
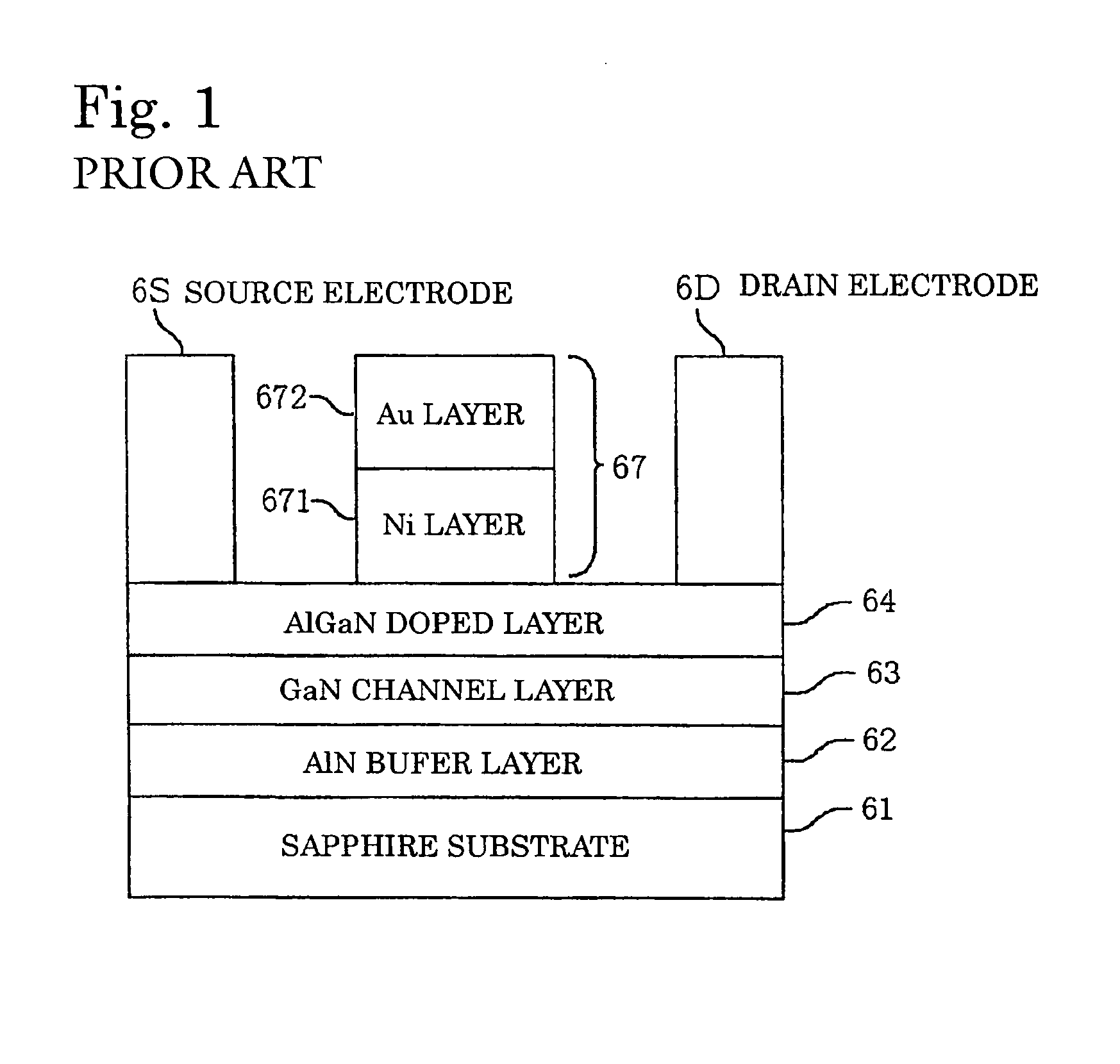
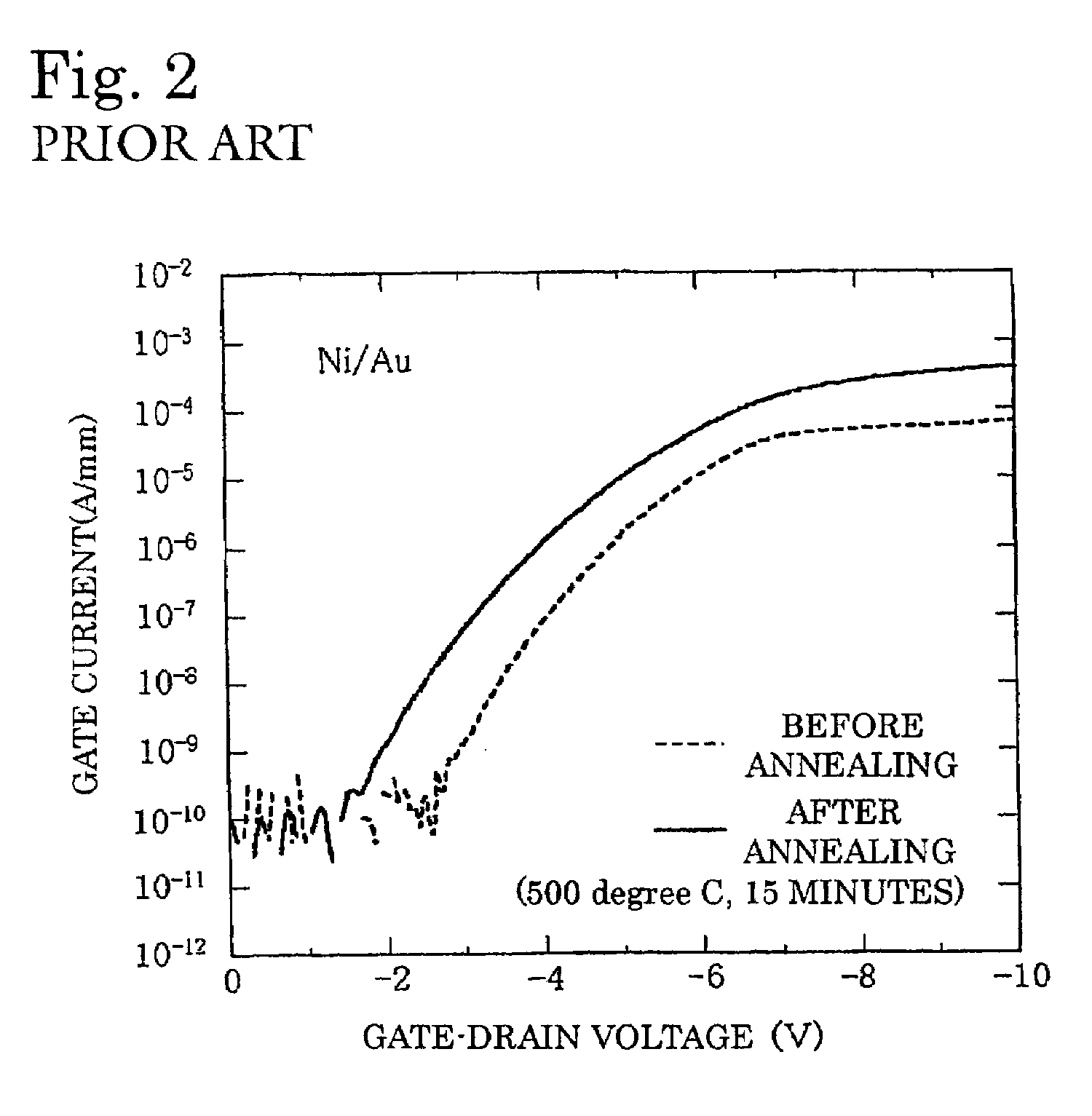
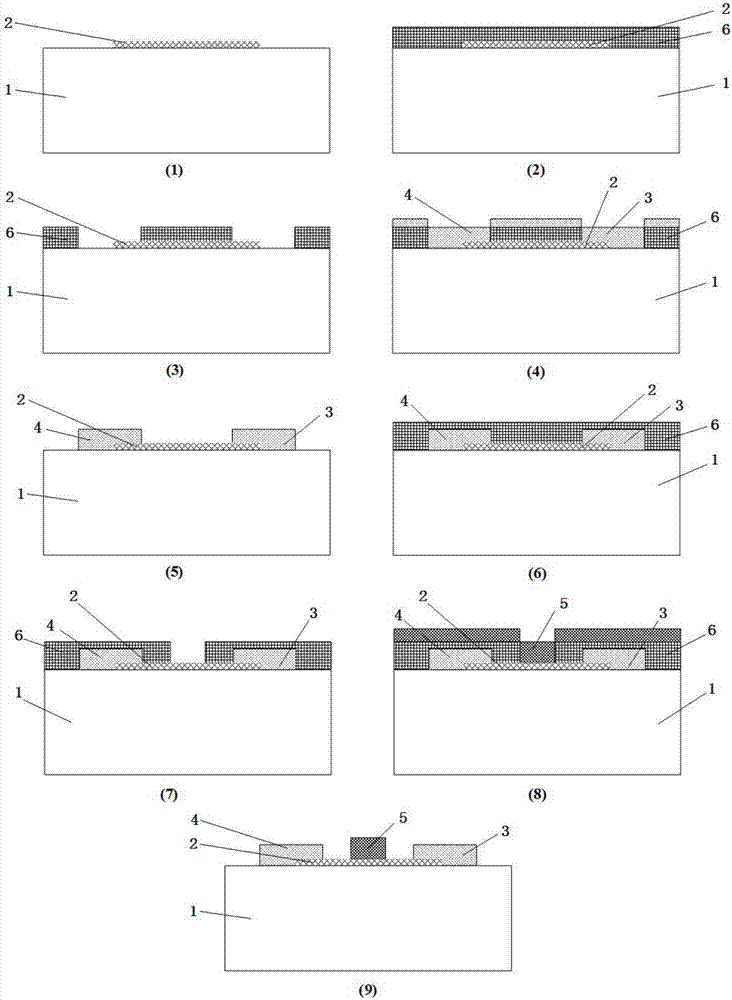
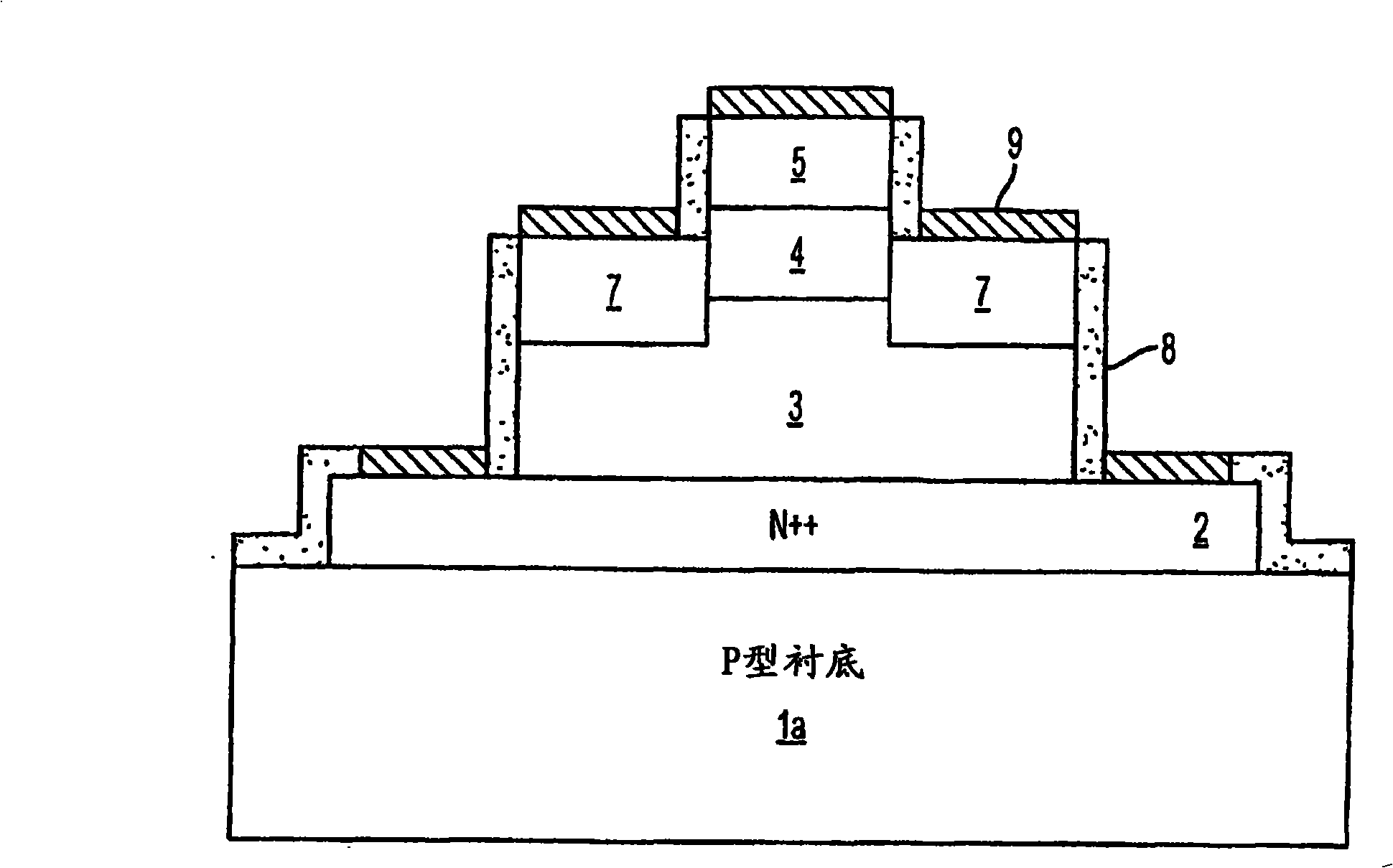
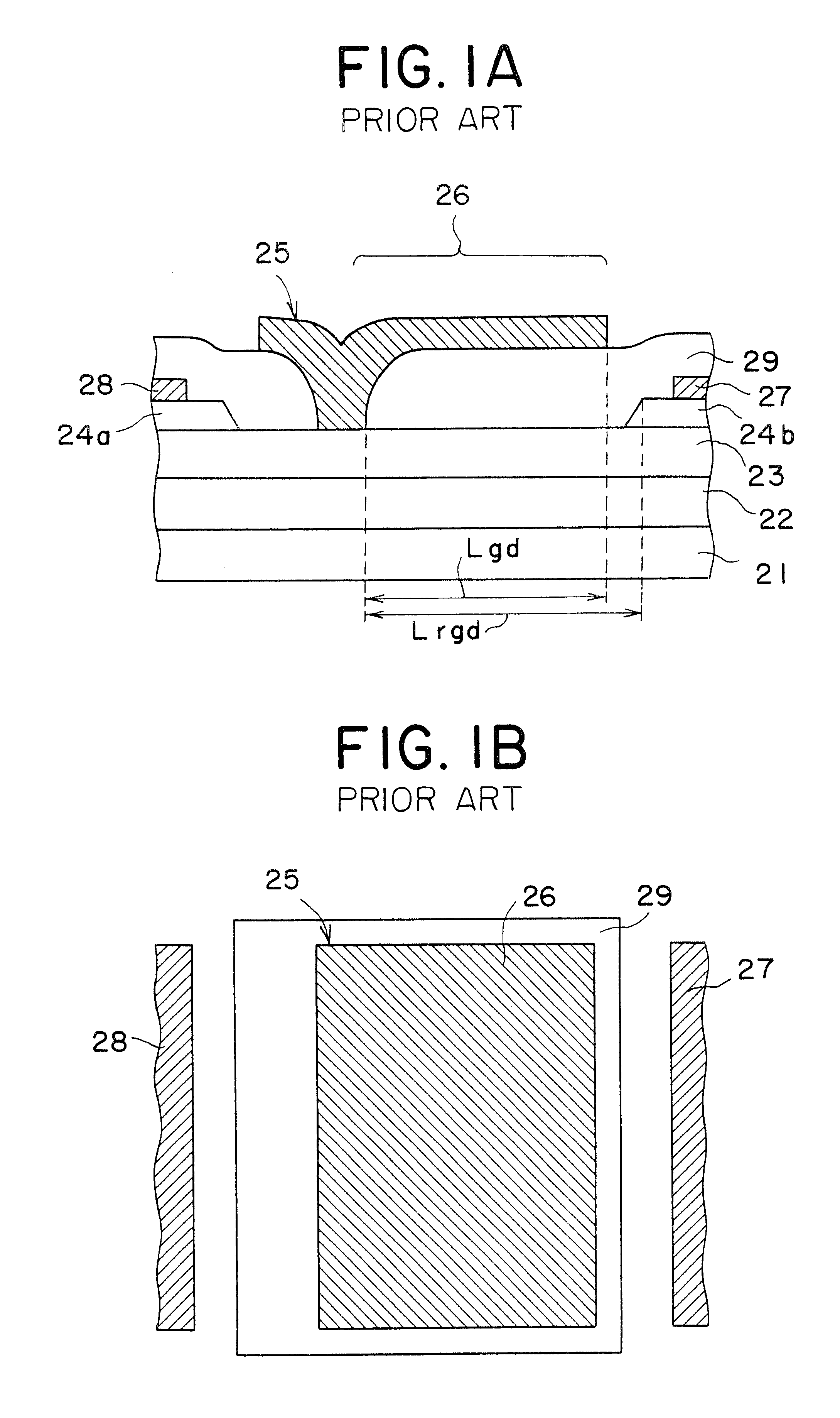
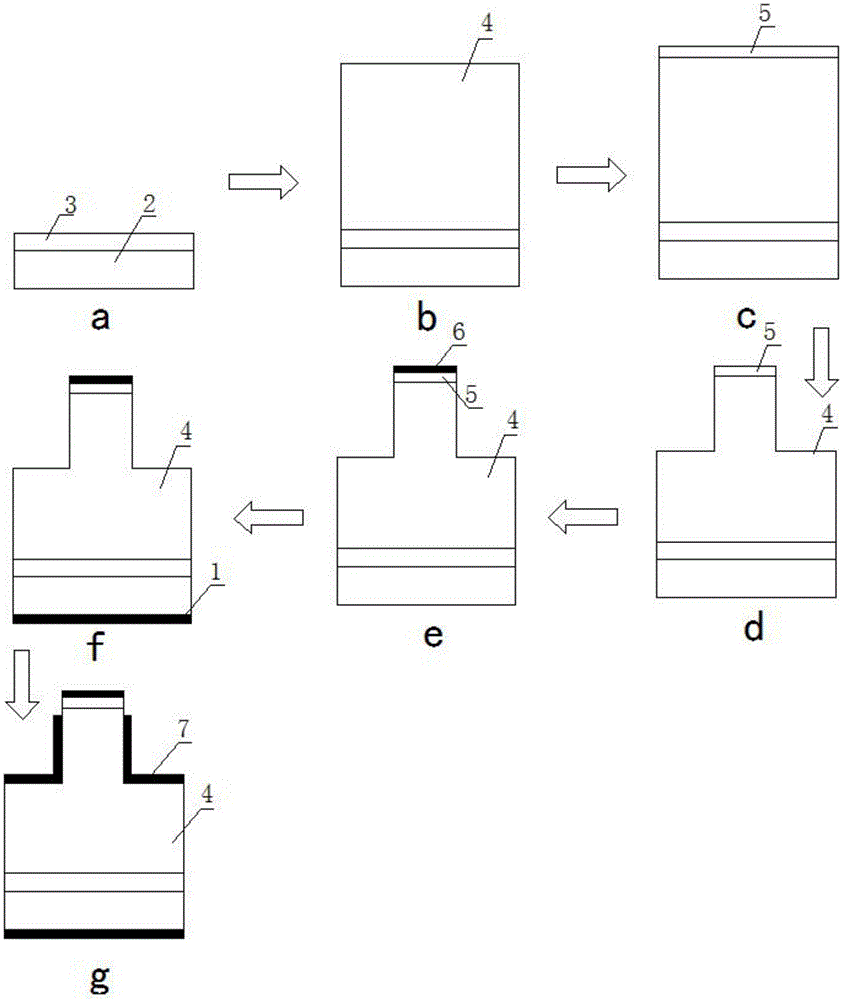
Semiconductor device having schottky junction electrode
InactiveUS20050151255A1Improve heat resistanceImprove power performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSchottky barrierDevice material
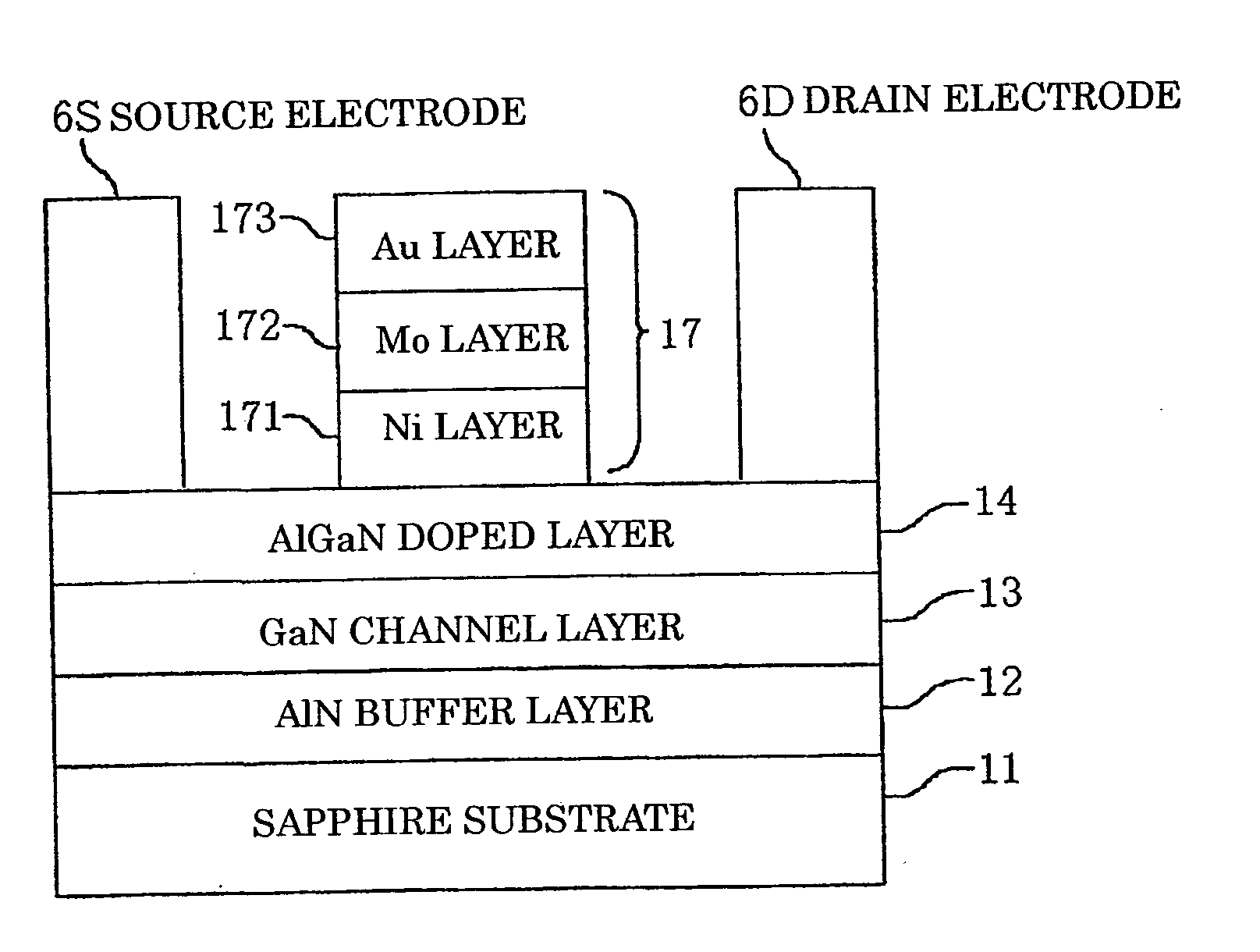
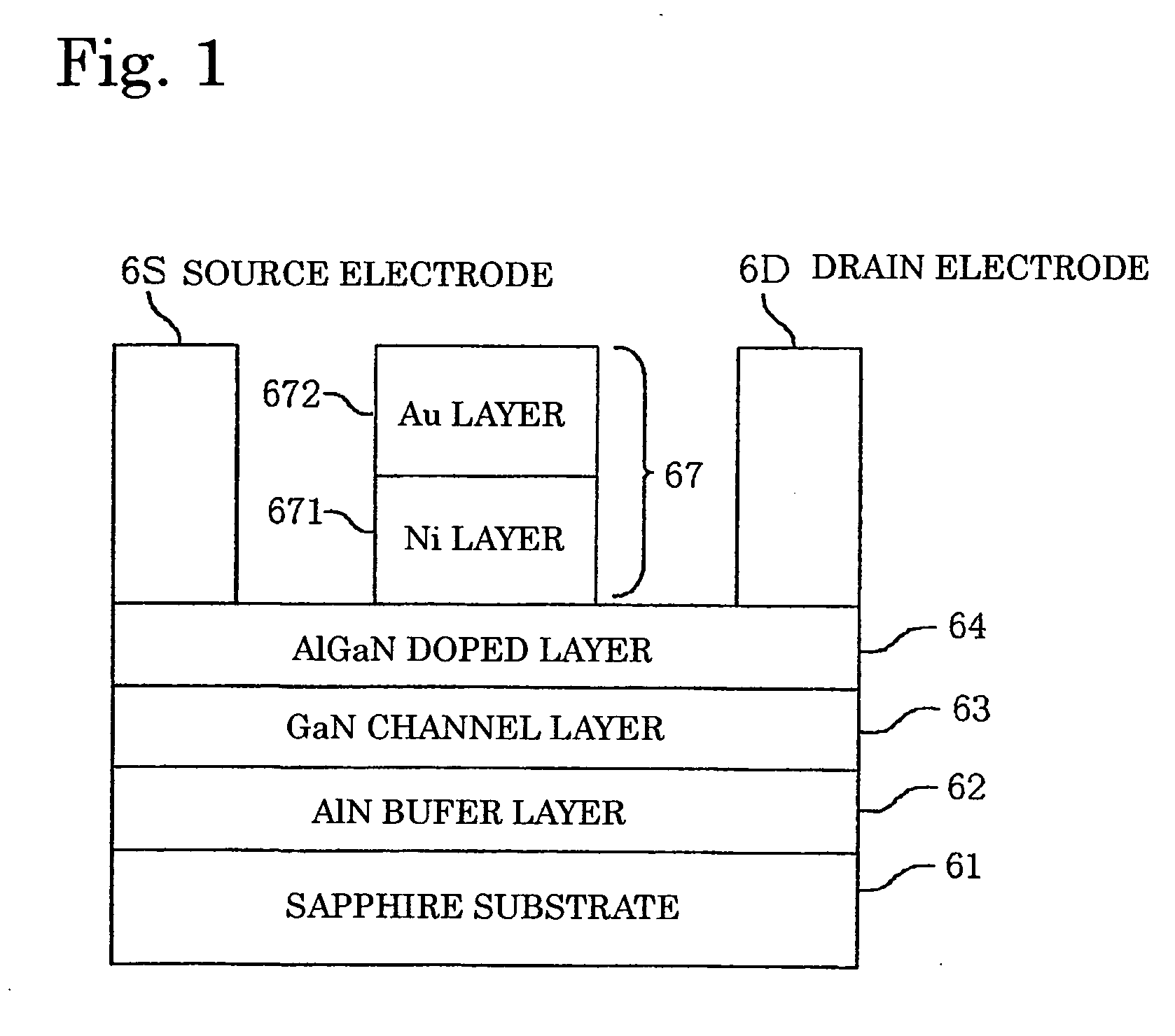
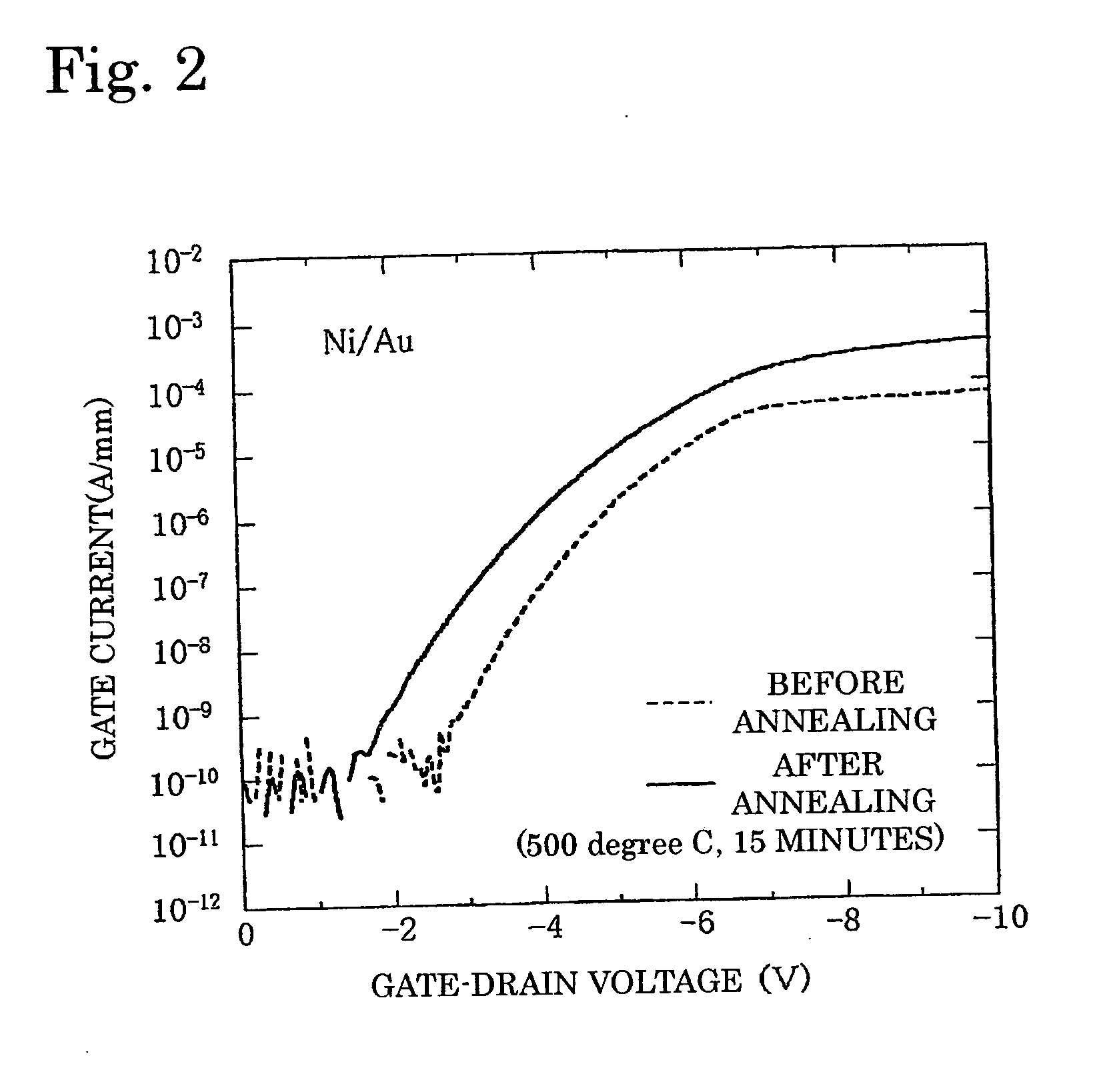
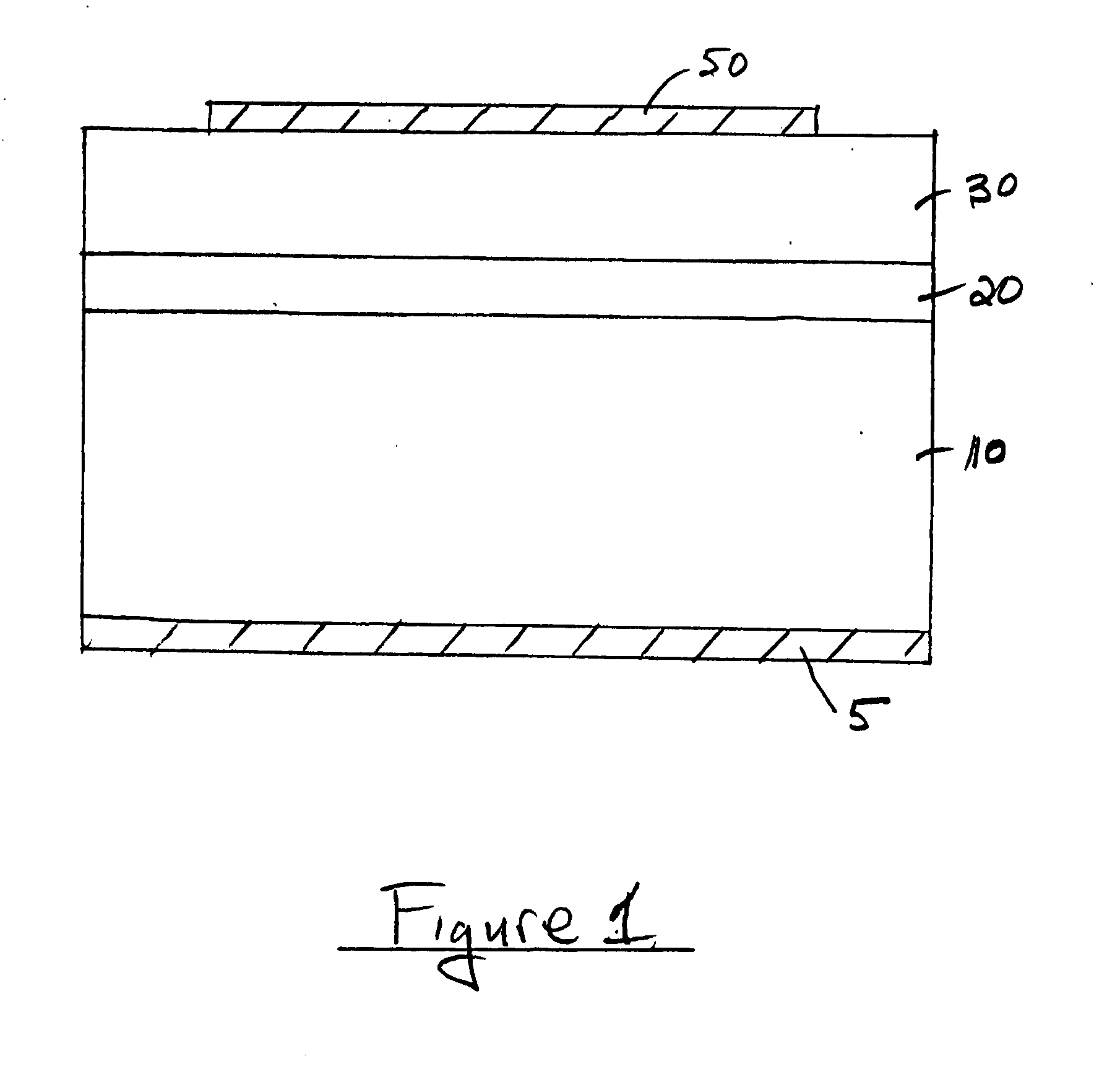
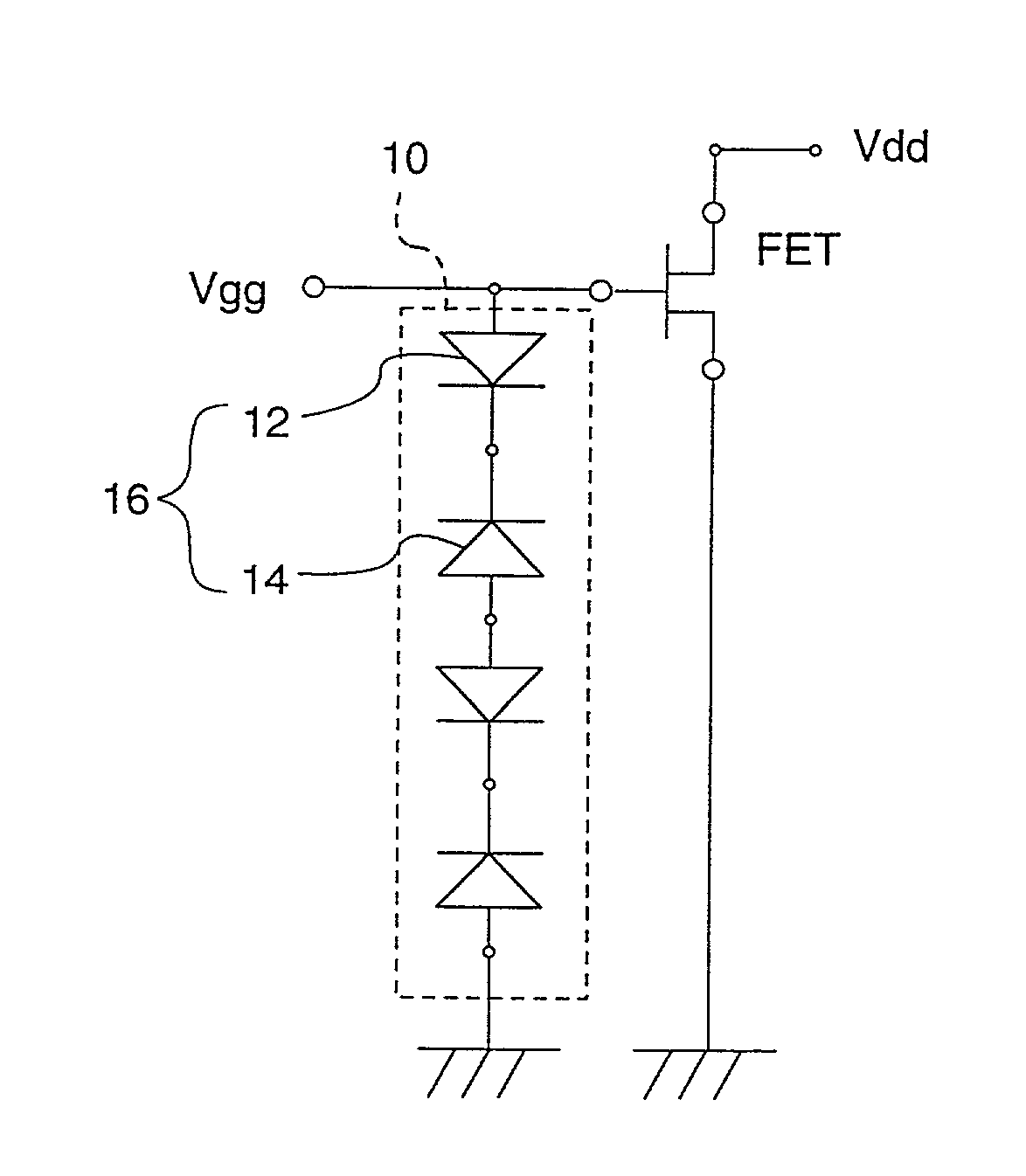
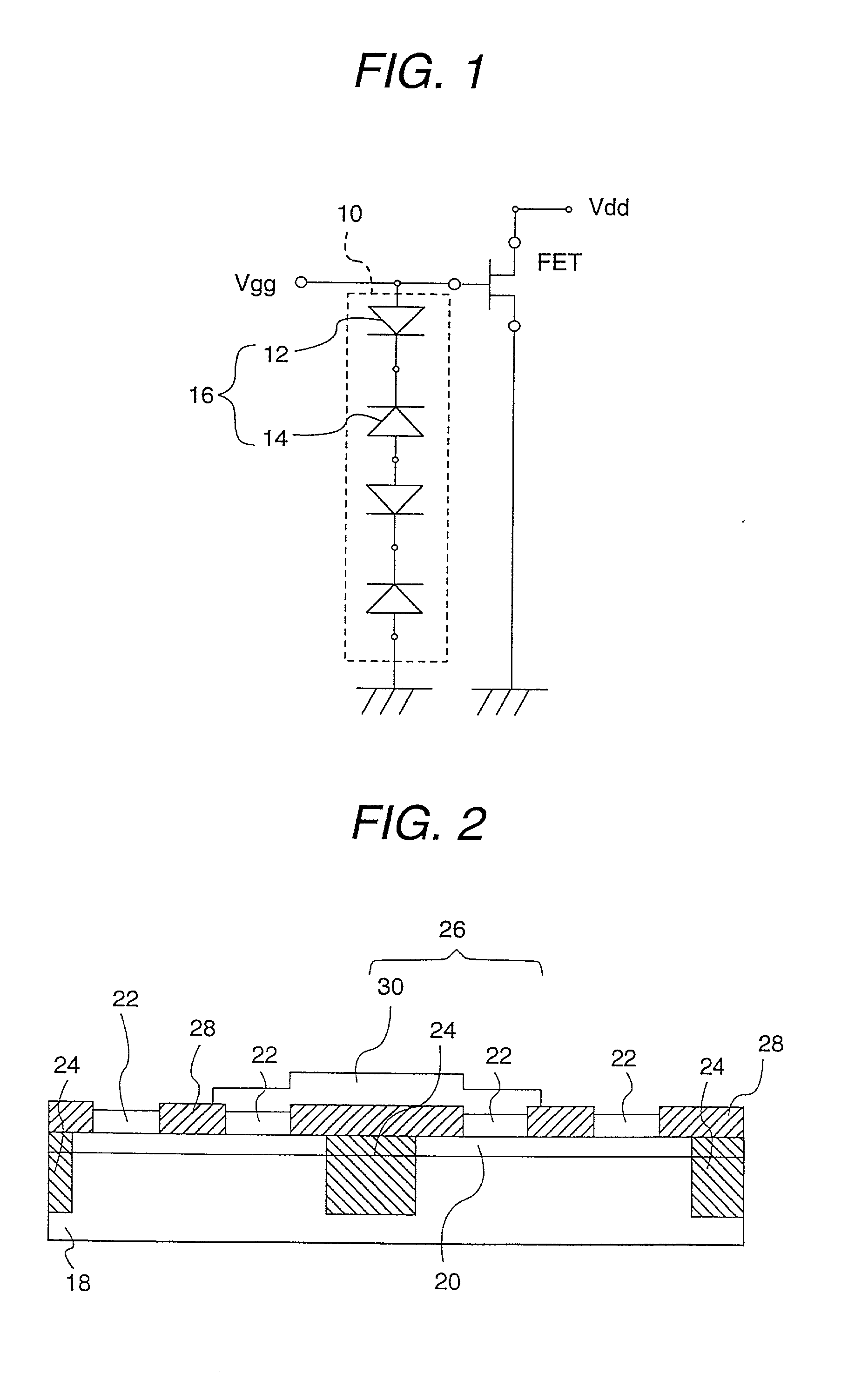
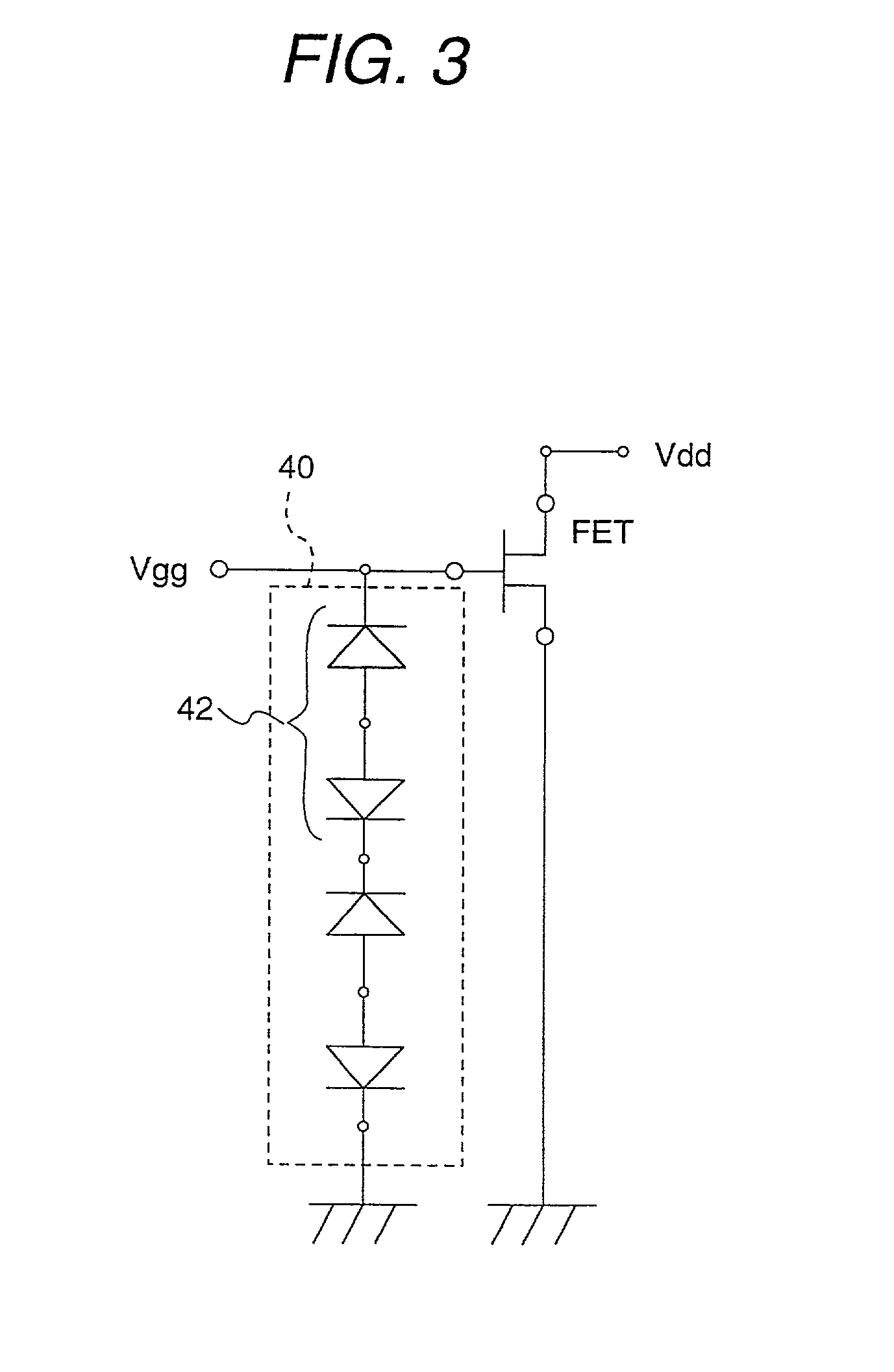
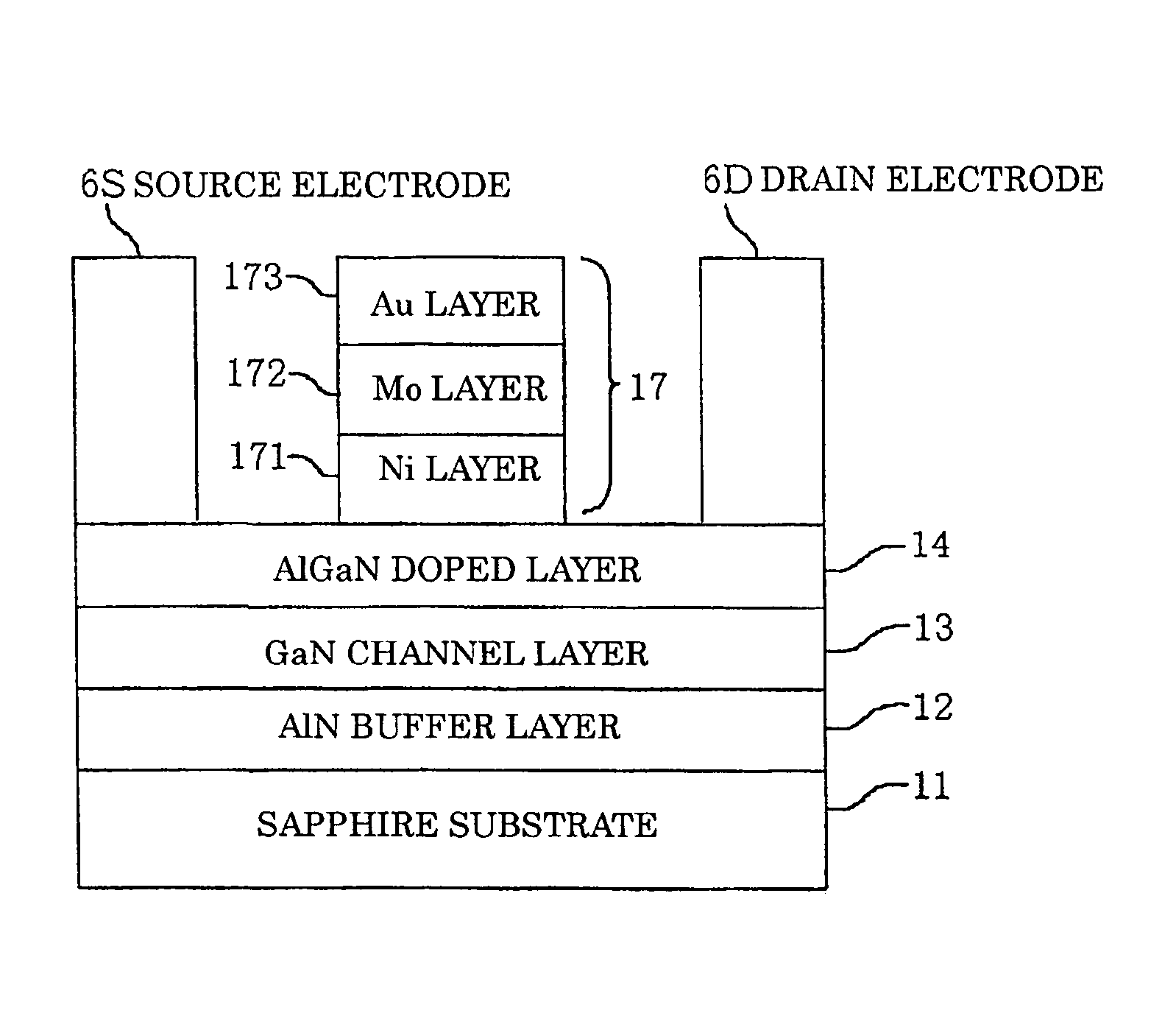
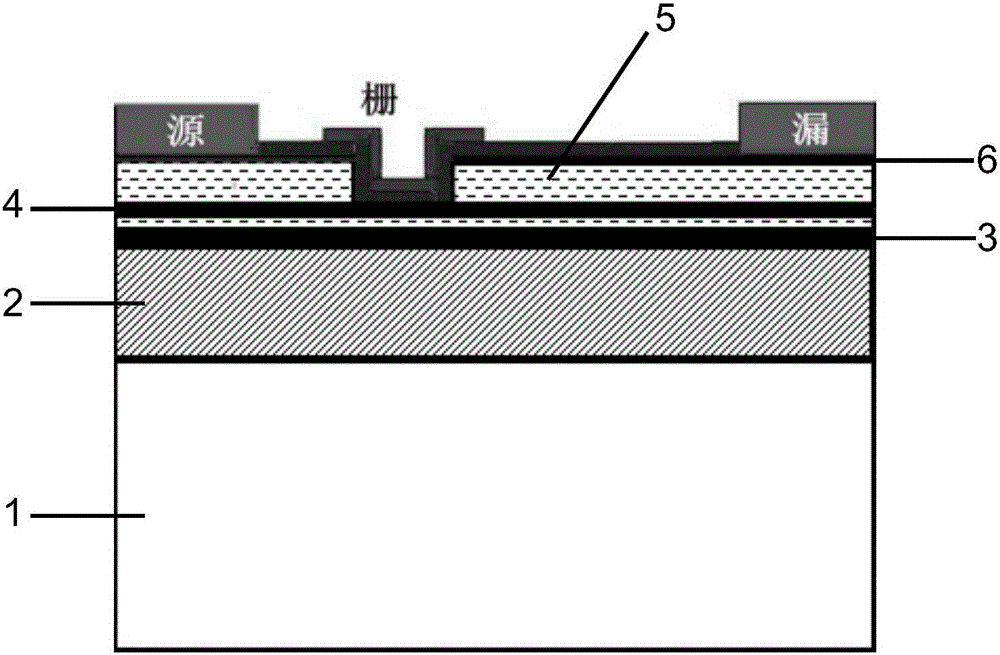
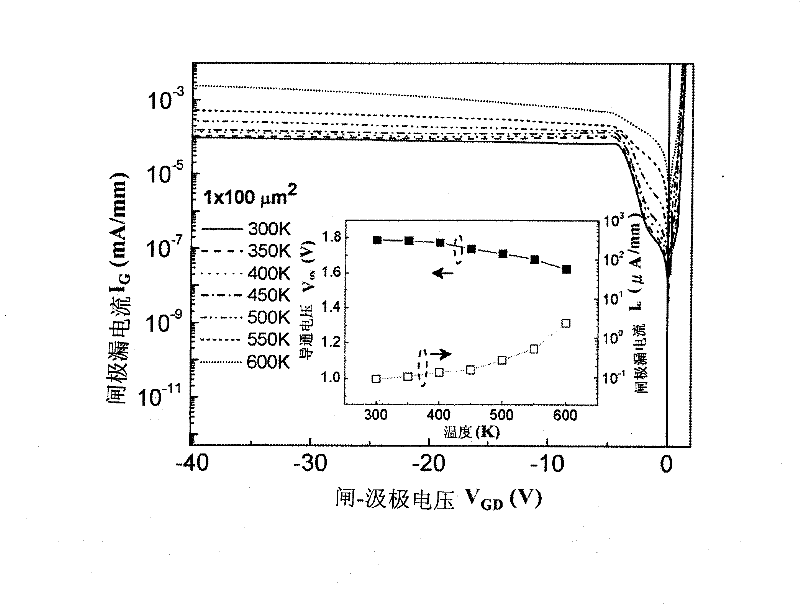
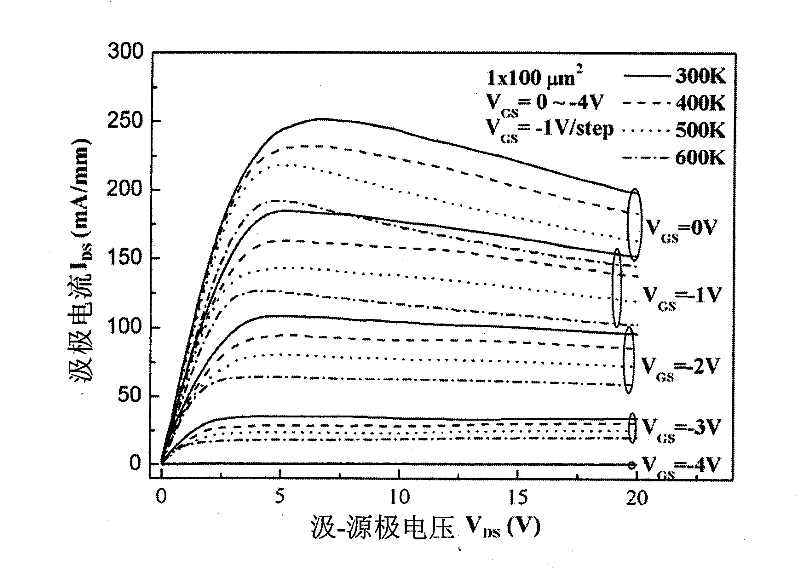
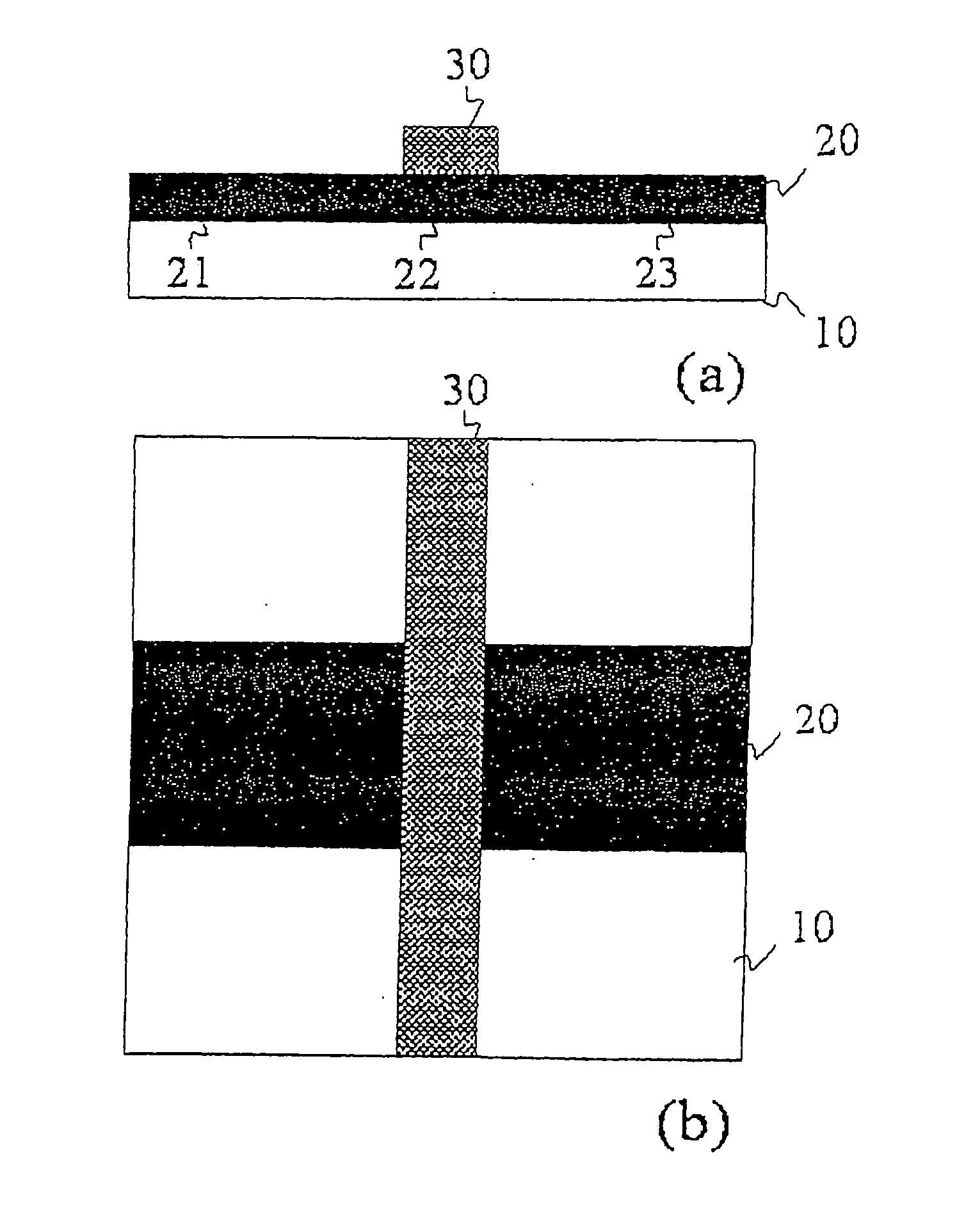
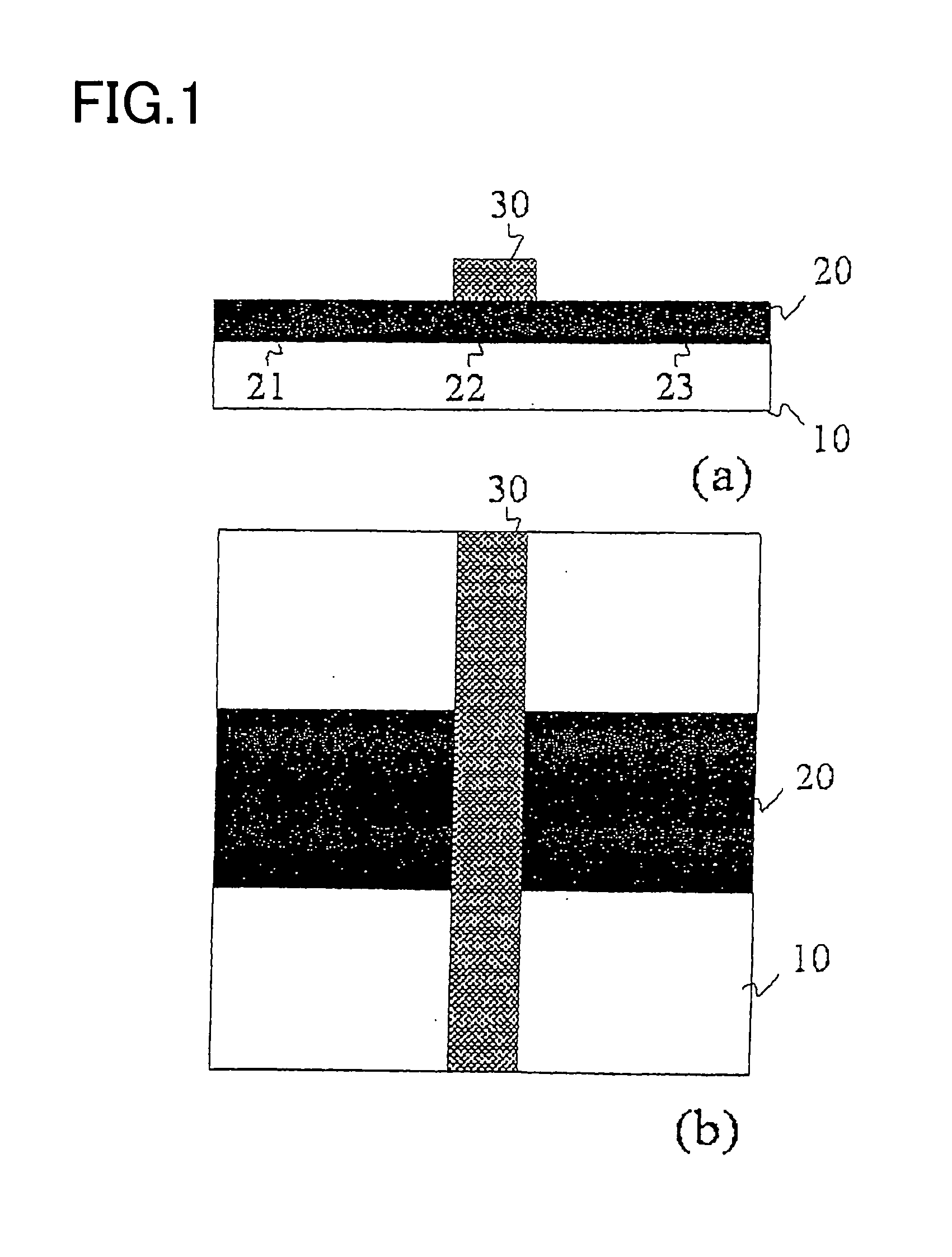
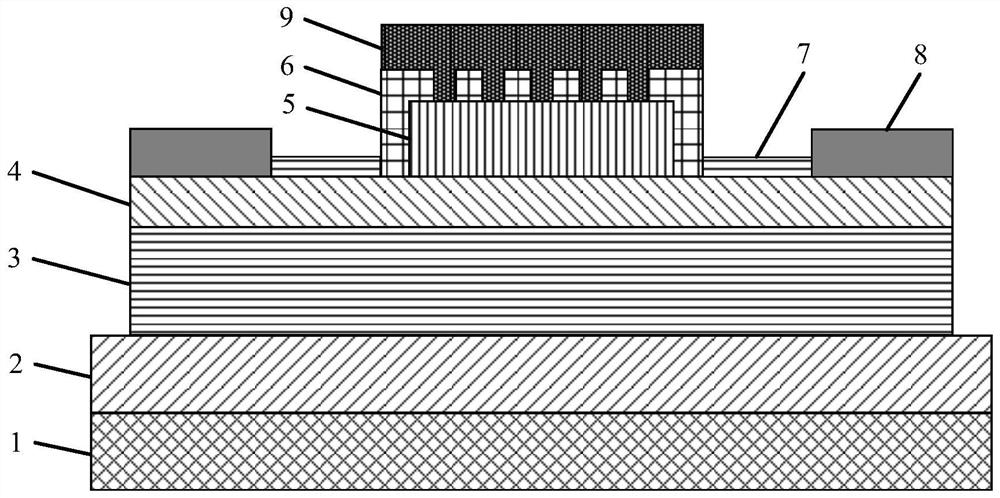
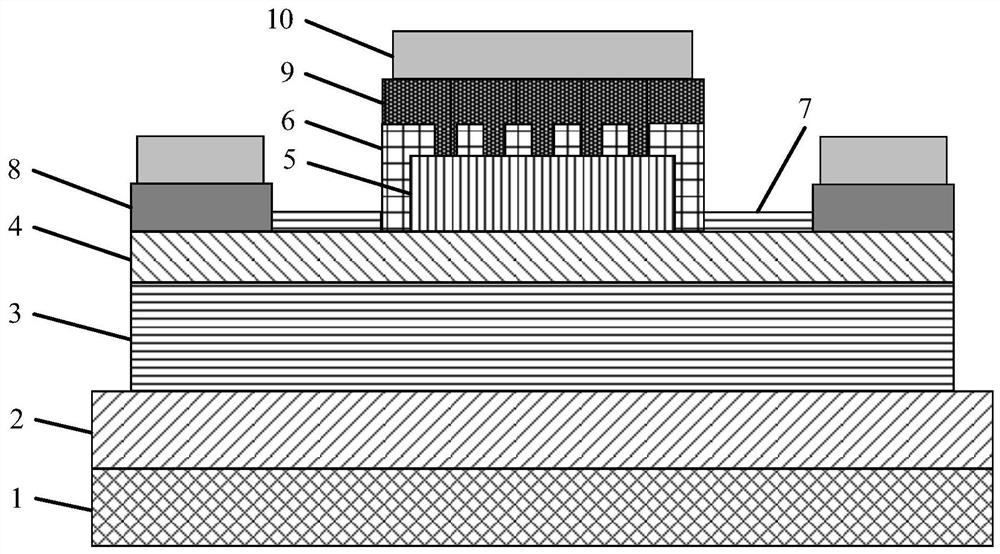
A GaN semiconductor device with improved heat resistance of the Schottky junction electrode and excellent power performance and reliability is provided. In this semiconductor device having a Schottky gate electrode 17 which is in contact with an AlGaN electron supplying layer 14, a gate electrode 17 comprises a laminated structure wherein a first metal layer 171 formed of any of Ni, Pt and Pd, a second metal layer 172 formed of any of Mo, Pt, W, Ti, Ta, MoSi, PtSi, WSi, TiSi, TaSi, MoN, WN, TiN and TaN, and a third metal layer formed of any of Au, Cu, Al and Pt. Since the second metal layer comprises a metal material having a high melting point, it works as a barrier to the interdiffusion between the first metal layer and the third metal layer, and the deterioration of the gate characteristics caused by high temperature operation is suppressed. Since the first metal layer contacting the AlGaN electron supplying layer 14 has a high work function, the Schottky barrier is high, and superior Schottky contact is obtained.
Owner:NEC CORP
Schottky gate field effect transistor
InactiveUS20030132463A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringContact layer
A Schottky gate FET including a gate electrode having a gate extension, a drain electrode and a drain contact layer overlying a semi-insulating substrate, wherein the gate extension overlies at least part of the drain electrode and the drain contact layer. The vertical overlapping between the gate extension and the drain contact region prevents the current reduction to make the circuit module mounting the Schottky gate FET non-usable.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
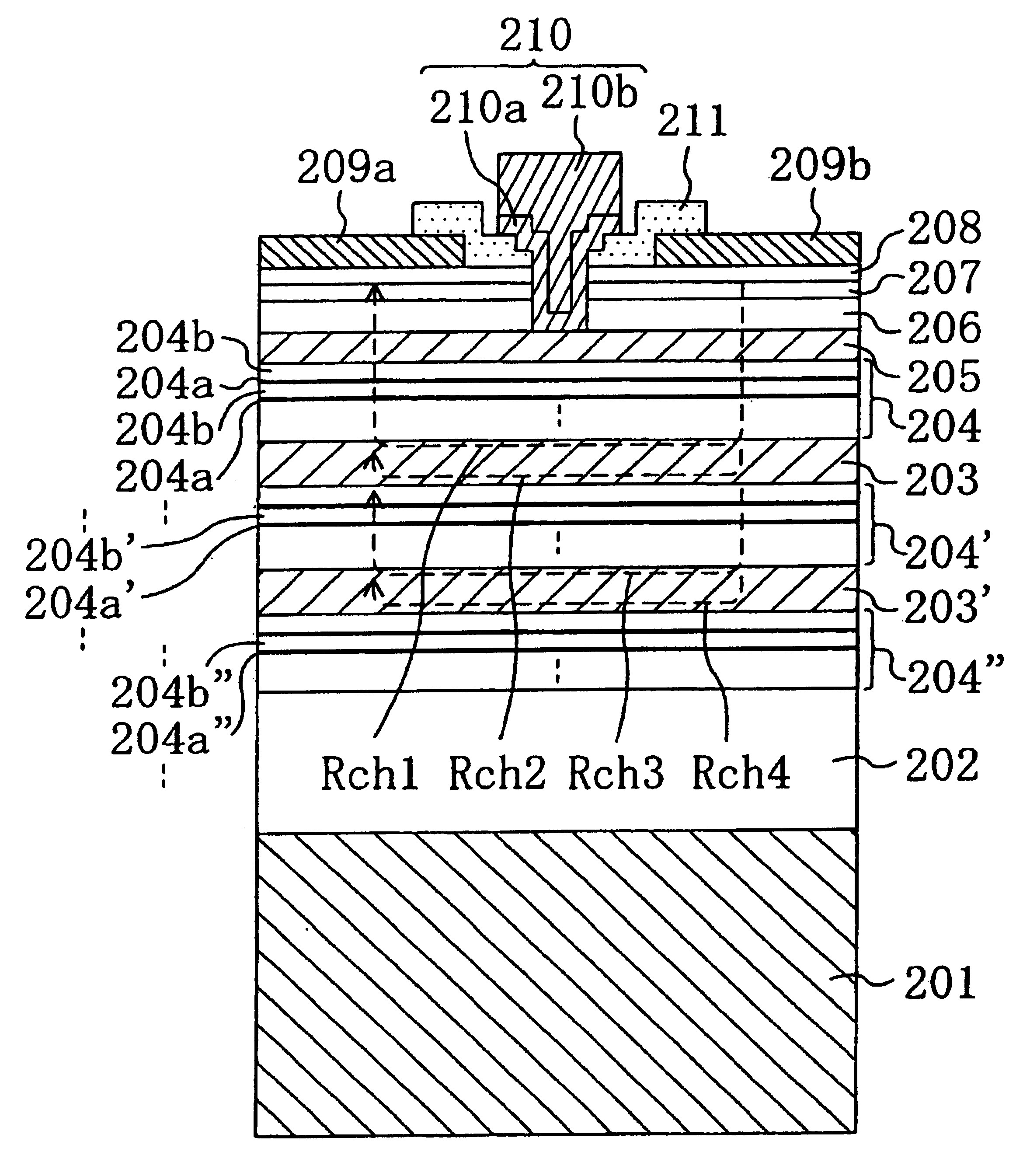
Semiconductor device having a high breakdown voltage for use in communication systems
InactiveUS6903383B2Improve breakdown voltageLower resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCommunications systemCharge carrier
A HEMT has an InAlAs layer (202), an InGaAs layer (203), a multiple δ-doped InAlAs layer (204) composed of n-type doped layers (204a) and undoped layers (204b) which are alternately stacked, an InP layer (205), a Schottky gate electrode (210), a source electrode (209a), and a drain electrode (209b) on an InP substrate (201). When a current flows in a region (channel region) of the InGaAs layer (203) adjacent the interface between the InGaAs layer (203) and the multiple δ-doped InAlAs layer (204), a breakdown voltage in the OFF state can be increased, while resistance to the movement of carriers passing through the multiple δ-doped InAlAs layer (204) as a carrier supplying layer is reduced.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Methods of fabricating silicon carbide metal-semiconductor field effect transistors
InactiveUS7067361B2Improve performanceReduce the impactSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate effectDeep level
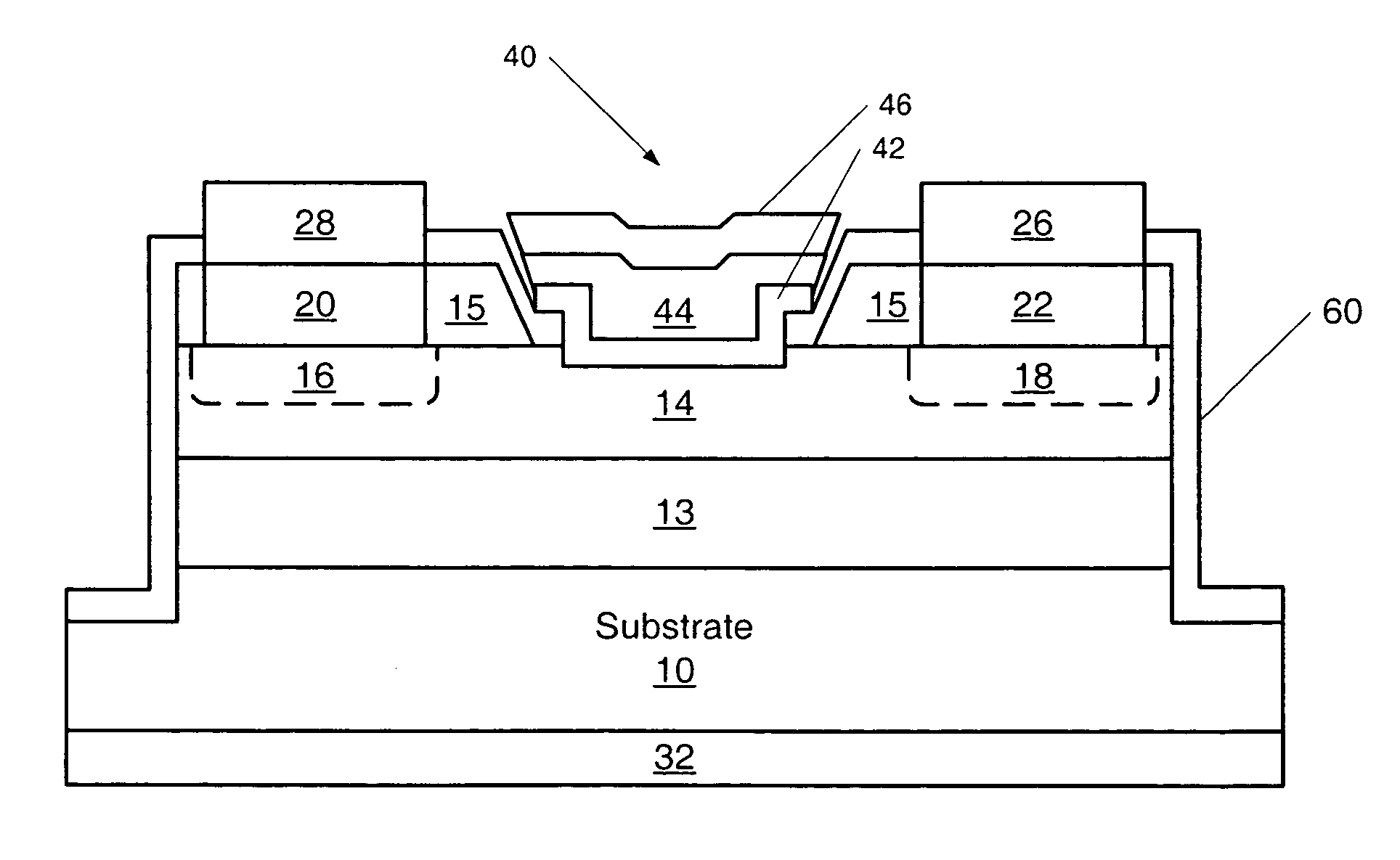
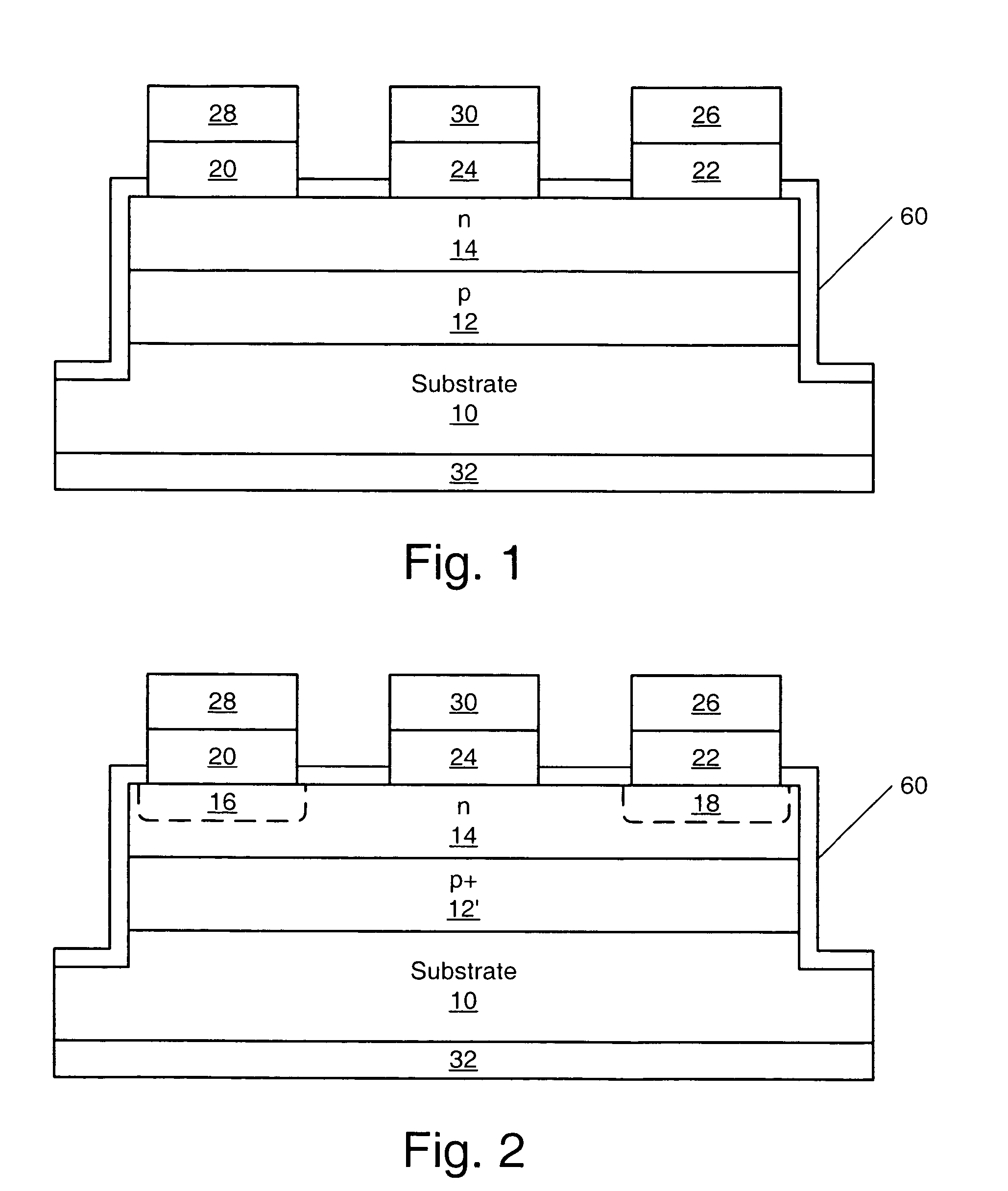
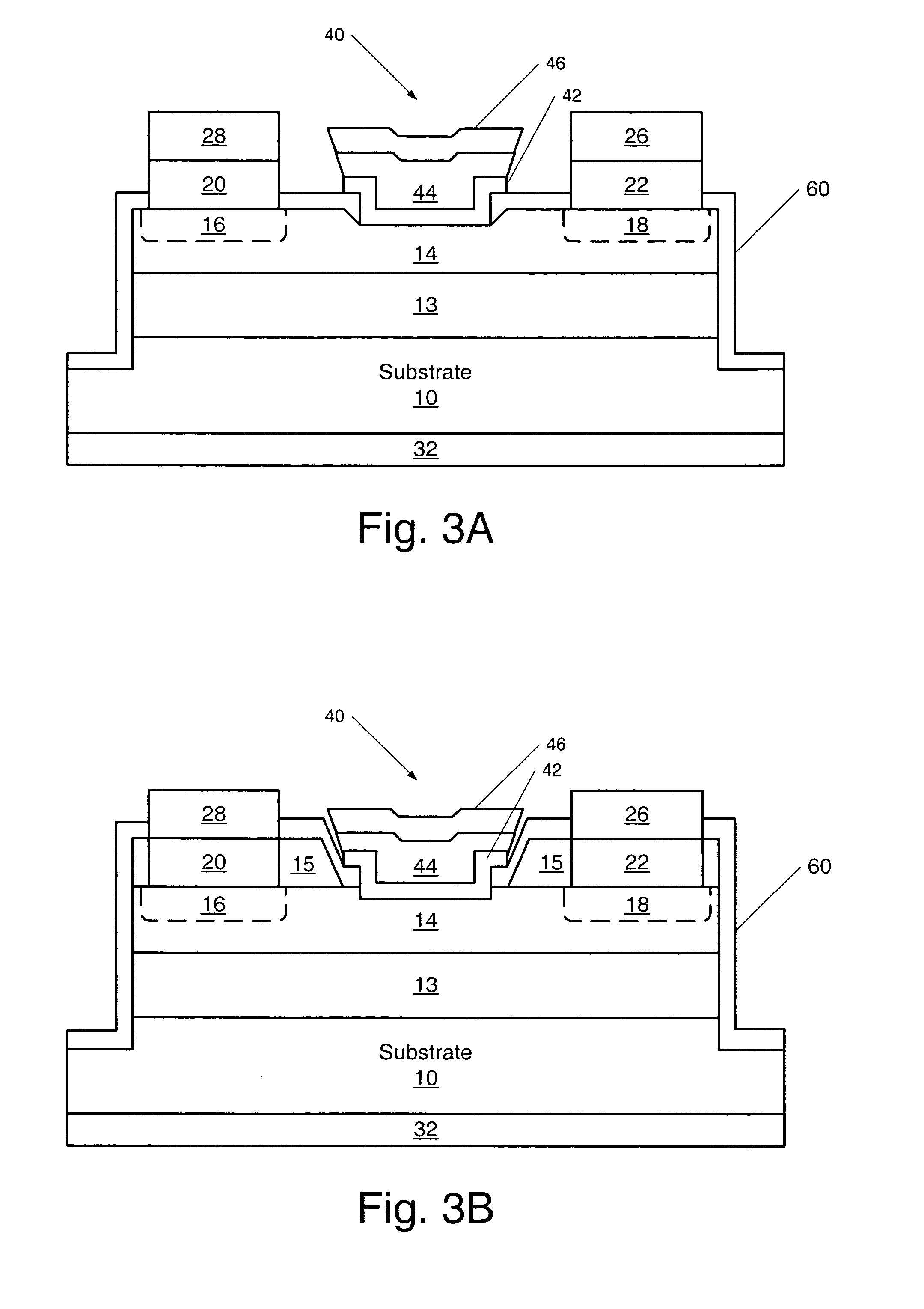
SiC MESFETs are disclosed which utilize a semi-insulating SiC substrate which substantially free of deep-level dopants. Utilization of the semi-insulating substrate may reduce back-gating effects in the MESFETs. Also provided are SiC MESFETs with a two recess gate structure. MESFETS with a selectively doped p-type buffer layer are also provided. Utilization of such a buffer layer may reduce output conductance by a factor of 3 and produce a 3 db increase in power gain over SiC MESFETs with conventional p-type buffer layers. A ground contact may also be provided to the p-type buffer layer and the p-type buffer layer may be made of two p-type layers with the layer formed on the substrate having a higher dopant concentration. SiC MESFETs according to embodiments of the present invention may also utilize chromium as a Schottky gate material. Furthermore, an oxide-nitride-oxide (ONO) passivation layer may be utilized to reduce surface effects in SiC MESFETs. Also, source and drain ohmic contacts may be formed directly on the n-type channel layer, thus, the n+ regions need not be fabricated and the steps associated with such fabrication may be eliminated from the fabrication process. Methods of fabricating such SiC MESFETs and gate structures for SiC FETs as well as passivation layers are also disclosed.
Owner:CREE INC
Rectifier
InactiveUS20080105902A1Rise voltage can be loweredLower threshold voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionSchottky gate
In the rectifier, a barrier layer and a channel layer constitute a heterojunction portion, and a two-dimensional electron gas channel is generated in the vicinity of a boundary between the channel layer and the barrier layer. A Schottky gate electrode is connected to an anode ohmic electrode and extends from above the anode ohmic electrode over to the barrier layer and a recess formed in the barrier layer is covered with the Schottky gate electrode. The two-dimensional electron gas channel located just below the recess is depleted by the influence of the Schottky gate electrode in a state in which there is no application voltage. By virtue of the formation of the recess in the barrier layer, the threshold voltage at which electrons are generated in the two-dimensional electron gas channel located just below the gate electrode is lowered, and the rise voltage can be made lower than that of the conventional Schottky diode.
Owner:SHARP KK
Schottky gate metallization for semiconductor devices
InactiveUS20080023726A1Inhibited DiffusionTransistorSolid-state devicesContact formationSemiconductor materials
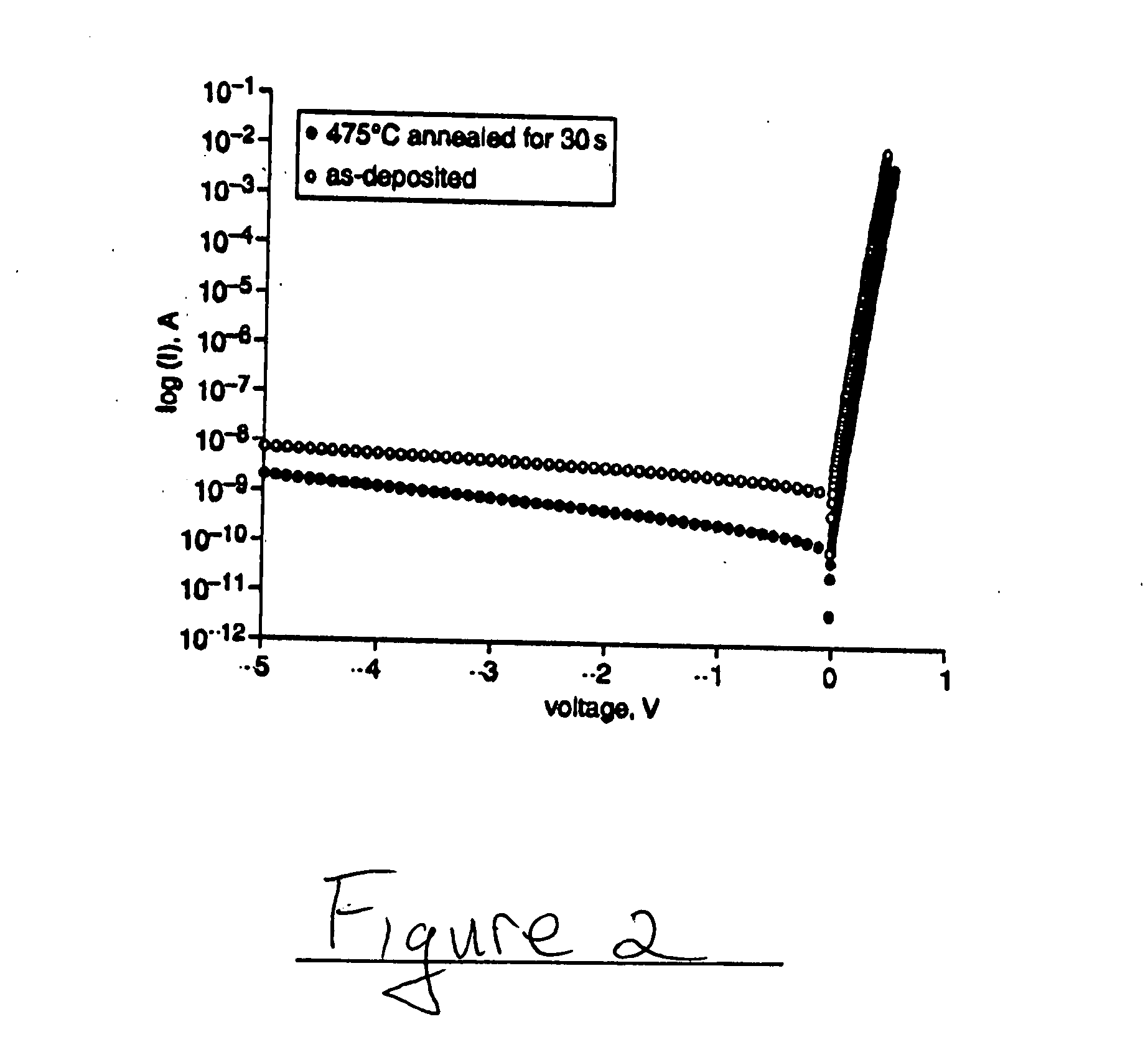
A method of forming a Schottky barrier contact to a semiconductor material, includes the following steps: depositing an iridium contact on a surface of the semiconductor material; and annealing the iridium contact to form a Schottky barrier contact to the semiconductor material. For an example of an iridium Schottky contact on an InAlAs semiconductor material, the annealing temperature is preferably in the range about 350° C. to 500° C.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Semiconductor devices integrating high-voltage and low-voltage field effect transistors on the same wafer
InactiveUS20060202299A1Improve reliabilityImprove trustTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing technologyLow voltage
A field effect transistor (FET) with novel field-plate structure relates to a Schottky gate FET structure with field plate thereon for high voltage operations. The structure and fabrication processes thereof not only provide a reliable way to produce high-voltage FETs, but also allow the integration of conventional low-voltage FETs on the same wafer.
Owner:WIN SEMICON
Field effect transistor with novel field-plate structure
A field effect transistor (FET) with novel field-plate structure relates to a Schottky gate FET structure with field plate thereon for increasing the operation voltage. The structure can eliminate surface damages of unpassivated region and degradation of the interface property of gate contacts during plasma etching of dielectric film for gate recesses, and can be reliably used in wireless and satellite communications.
Owner:WIN SEMICON
Protection circuit of field effect transistor and semiconductor device
There is provided a protection circuit of a field effect transistor having a structure which can be fabricated without restricting a pattern layout and without increasing a process step. A protection circuit of a field effect transistor is a protection circuit of a Schottky gate HFET, and is a circuit in which a forward direction diode and a reverse direction diode are cascade-connected to form a diode unit and two such diode units are connected in series, and a gate line connected to a gate electrode of the HFET is grounded through the protection circuit. The diodes are diodes formed integrally with the Schottky gate HFET which is protected against surge breakdown, and are constituted as Schottky barrier diodes made of an n+-GaAs cap layer formed on a GaAs substrate and Schottky electrodes formed on the n+-GaAs cap layer.
Owner:SONY CORP
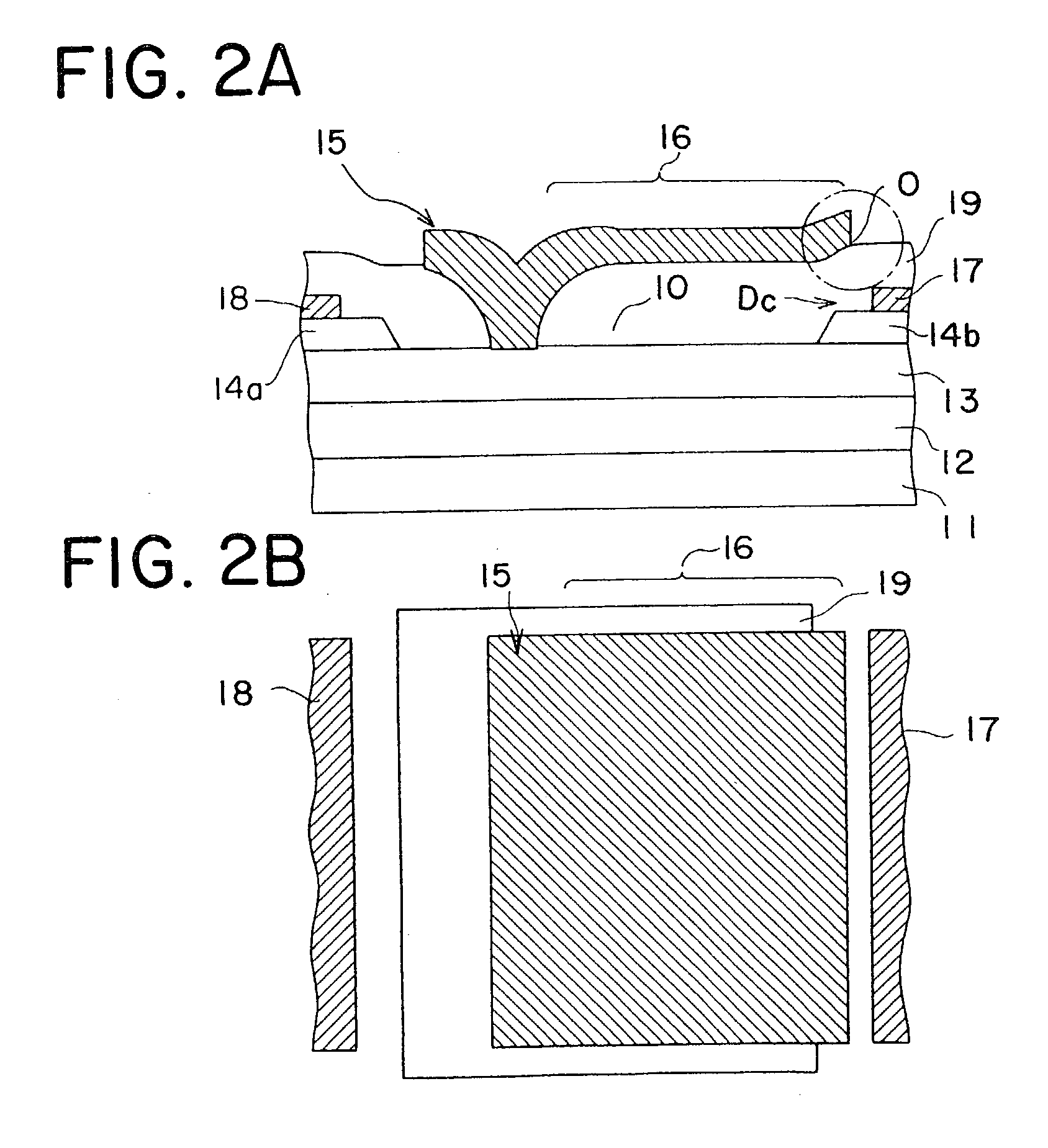
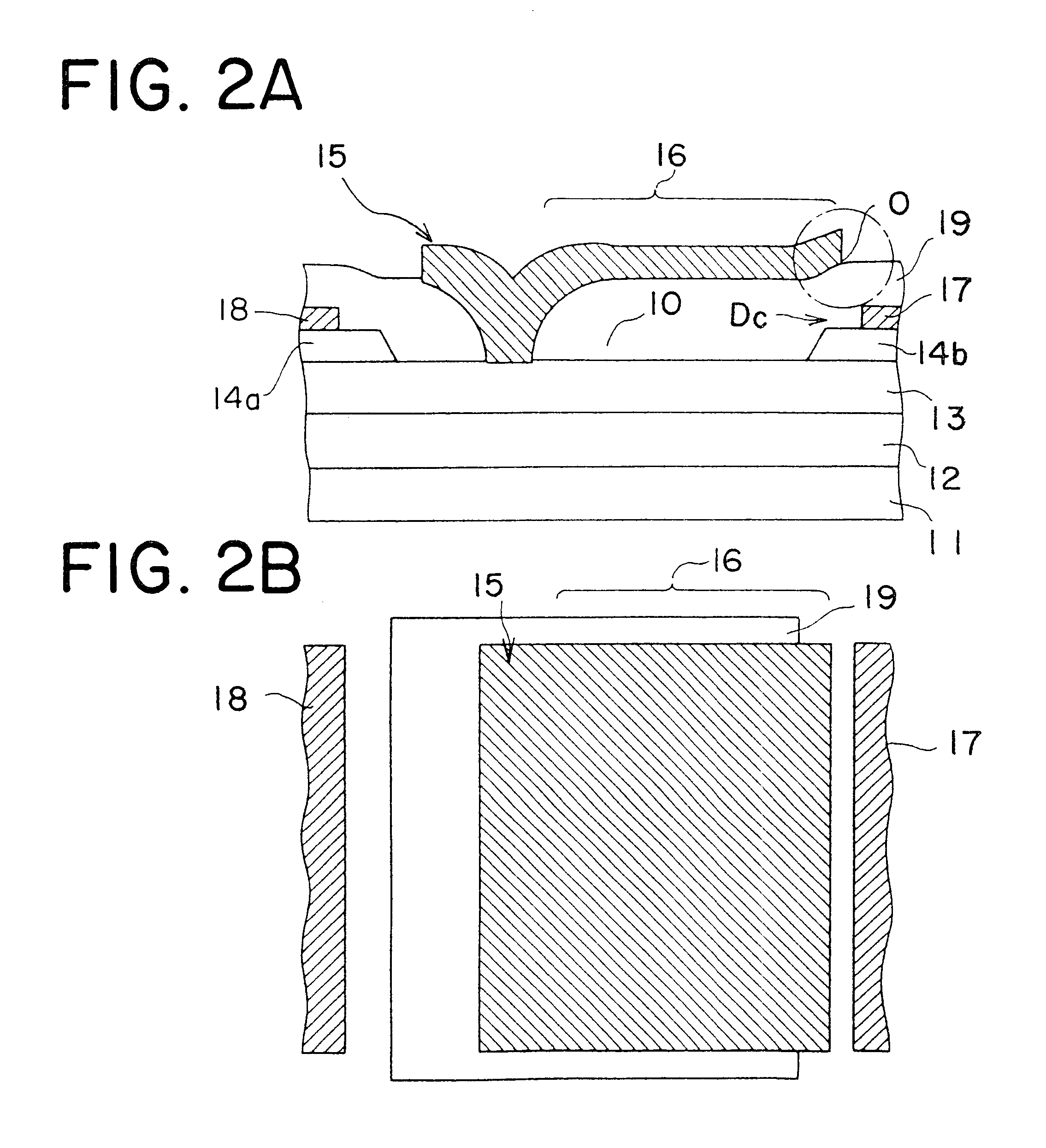
Semiconductor device having Schottky junction electrode
InactiveUS7071526B2Improve heat resistanceImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSchottky barrierDevice material
A GaN semiconductor device with improved heat resistance of the Schottky junction electrode and excellent power performance and reliability is provided. In this semiconductor device having a Schottky gate electrode 17 which is in contact with an AlGaN electron supplying layer 14, a gate electrode 17 comprises a laminated structure wherein a first metal layer 171 formed of any of Ni, Pt and Pd, a second metal layer 172 formed of any of Mo, Pt, W, Ti, Ta, MoSi, PtSi, WSi, TiSi, TaSi, MoN, WN, TiN and TaN, and a third metal layer formed of any of Au, Cu, Al and Pt. Since the second metal layer comprises a metal material having a high melting point, it works as a barrier to the interdiffusion between the first metal layer and the third metal layer, and the deterioration of the gate characteristics caused by high temperature operation is suppressed. Since the first metal layer contacting the AlGaN electron supplying layer 14 has a high work function, the Schottky barrier is high, and superior Schottky contact is obtained.
Owner:NEC CORP
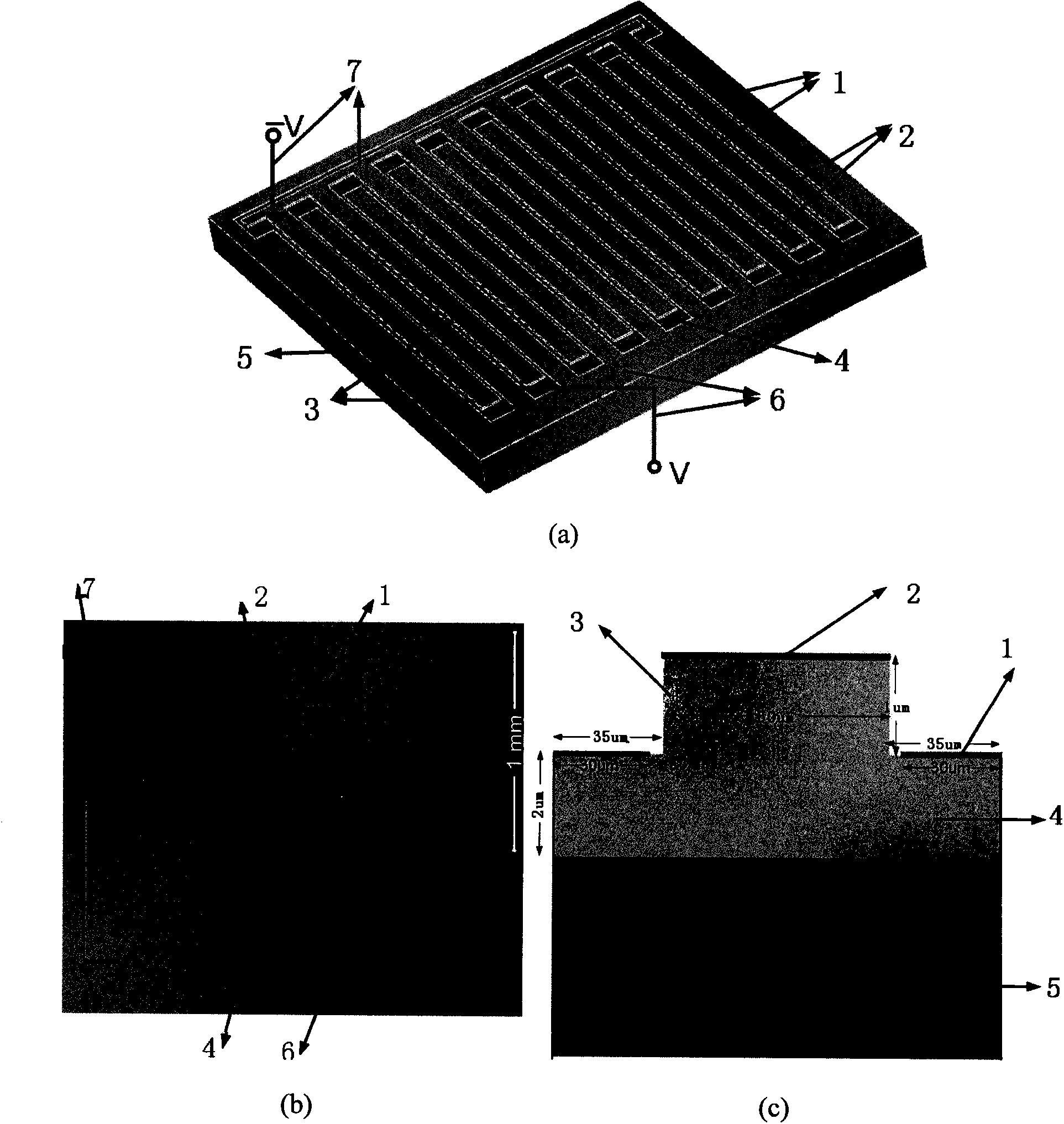
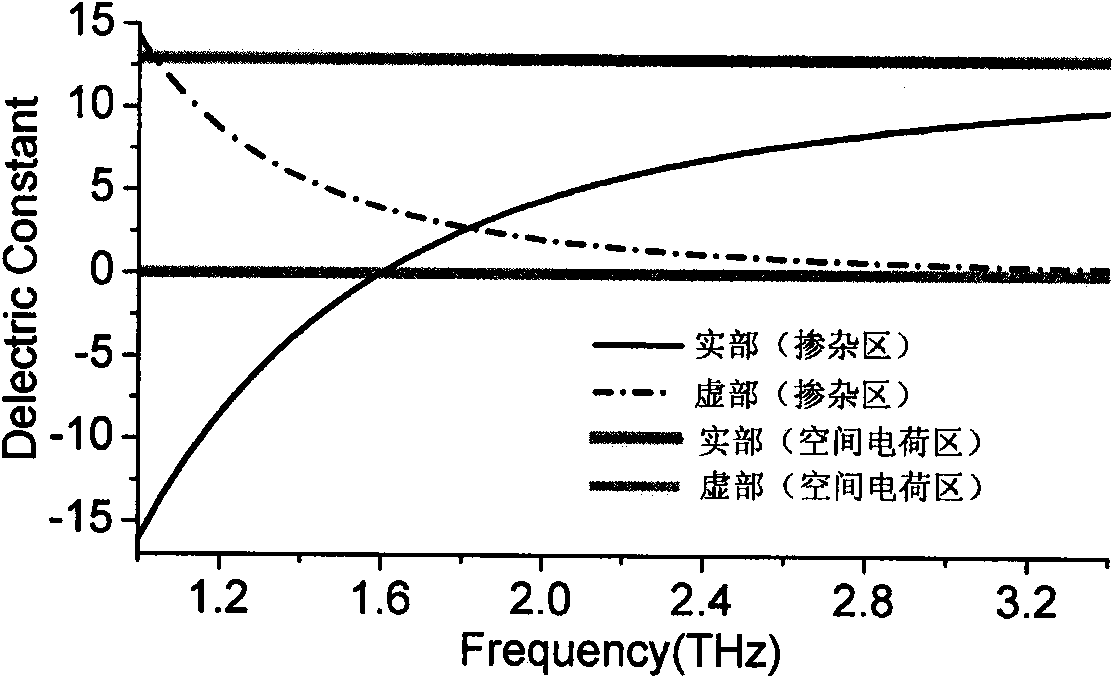
Schottky gate array type terahertz modulator
InactiveCN103457669ARealize the modulation functionRich scope of workElectromagnetic transmittersNon-linear opticsModulation functionElectron
The invention discloses a Schottky gate array type terahertz modulator and a regulation and control method thereof. A periodic gate type metal-semiconductor surface plasmon waveguide structure is adopted, the characteristics of Schottky contact formed by a metal-semiconductor interface and superposition of the Schottky contact and terahertz surface plasmon polariton position are utilized, a positive electrode and a negative electrode are led in and voltage is exerted, so that the terahertz modulation function of the Schottky gate array type terahertz modulator is achieved. The Schottky gate array type terahertz modulator combines a waveguide optical microstructure with a semiconductor electron device together, so that the Schottky gate array type terahertz modulator is well integrated with other electronic components and systems, and the optical functions of terahertz wave transmission and resonance oscillation are achieved. The Schottky gate array type terahertz modulator works from 2.2THz to 3.2THz, the working frequency can be tuned along with the working voltage, the maximum modulation depth is 16dB, and the highest modulation rate is 22MHz. The Schottky gate array type terahertz modulator is an on-chip electronically-controlled high-speed terahertz modulator which is in a small type and can be integrated, and the application requirements for terahertz broadband wireless communications are met.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
An enhanced high electron mobility transistor HEMT and a preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108987474AReduce depletionDecrease in depletionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricPower flow
A enhance HEMT and a preparation method thereof, the enhanced HEMT includes a GaN epitaxial wafer, source and drain electrodes located at both ends of the GaN epitaxial wafer and a gate electrode located between the source and drain electrodes, the gate electrode comprises a plurality of concave gate grooves, wherein a gate metal layer is directly deposited on the surface of the concave gate groove to form a Schottky gate electrode, or a gate dielectric layer and a gate metal layer are sequentially deposited to form a MIS gate electrode, and the bottom of the concave gate groove is located ina barrier layer of a GaN epitaxial wafer, the total length of the concave gate groove is equal to a preset gate length, and sufficient gate control capability is ensured; The depth of each concave gate groove decreases sequentially in the direction away from the source electrode, so that the electron depletion degree in the channel decreases sequentially, and sufficient electrons are ensured in the channel, so that the characteristics of large current can be maintained on the basis of realizing the enhanced type, the on resistance of the channel is reduced, and the power consumption of the device is reduced.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Schottky gate field effect transistor and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107146815ASimple preparation processImplement the arraySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesApplication areasPhotoresist
The invention discloses a preparation method of a schottky gate field effect transistor. According to the preparation method, a two-dimensional material is prepared on a substrate firstly, then the substrate and the two-dimensional material are coated with photoresist in a spin coating manner, and photoetching exposure and developing are performed to expose source and drain electrode windows; metal is coated, and the photoresist is washed off, and next, annealing in gas atmosphere is performed to form a source electrode and a drain electrode; next, the whole piece of a sample is coated with photoresist in a spin coating manner, and photoetching exposure and developing are performed to expose a gate electrode window; and next, metal is coated, and the photoresist is washed off to form the schottky gate field effect transistor. The schottky gate field effect transistor has the advantages of small dimensions, high switch ratio, high mobility, capability of well eliminating a short-channel effect and the like, so that the application field of a two-dimensional material device can be expanded.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Lateral trench field-effect transistors in wide bandgap semiconductor materials, methods of making
A junction field effect transistor is described. The transistor is made from a wide bandgap semiconductor material. The device comprise source, channel, drift and drain semiconductor layers, as well as p-type implanted or Schottky gate regions. The source, channel, drift and drain layers can be epitaxially grown. The ohmic contacts to the source, gate, and drain regions can be formed on the same side of the wafer. The devices can have different threshold voltages depending on the vertical channel width and can be implemented for both depletion and enhanced modes of operation for the same channel doping. The devices can be used for digital, analog, and monolithic microwave integrated circuits. Methods for making the transistors and integrated circuits comprising the devices are also described.
Owner:PI
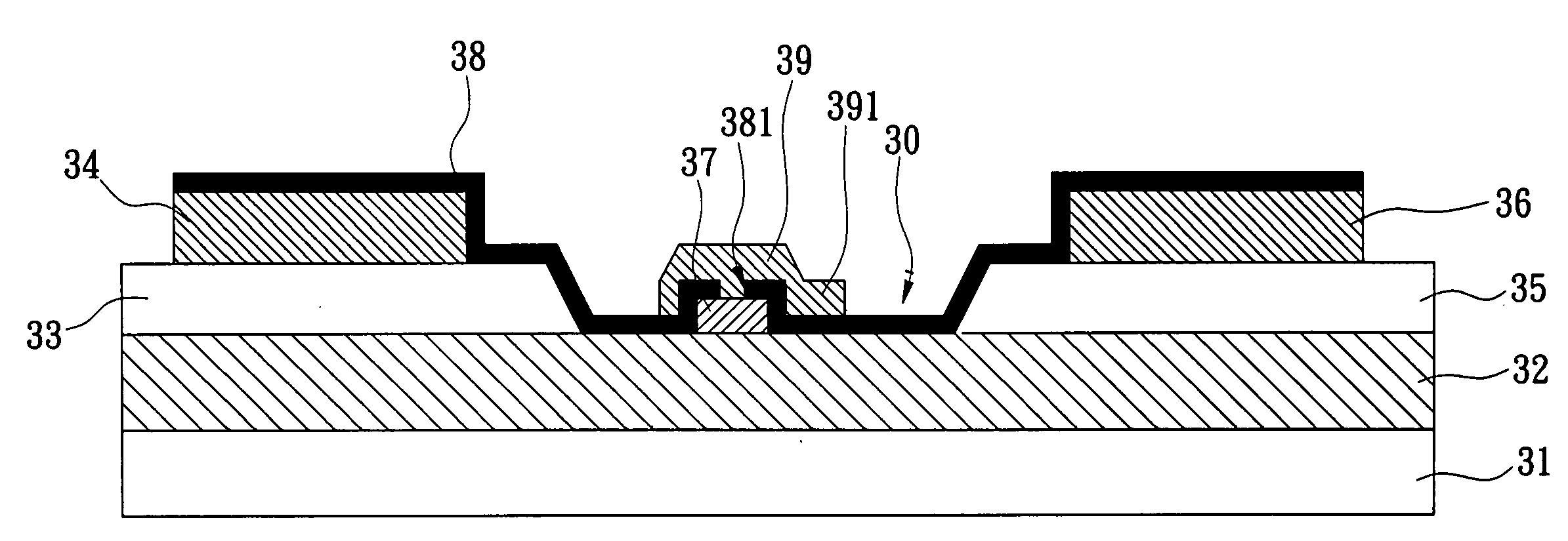
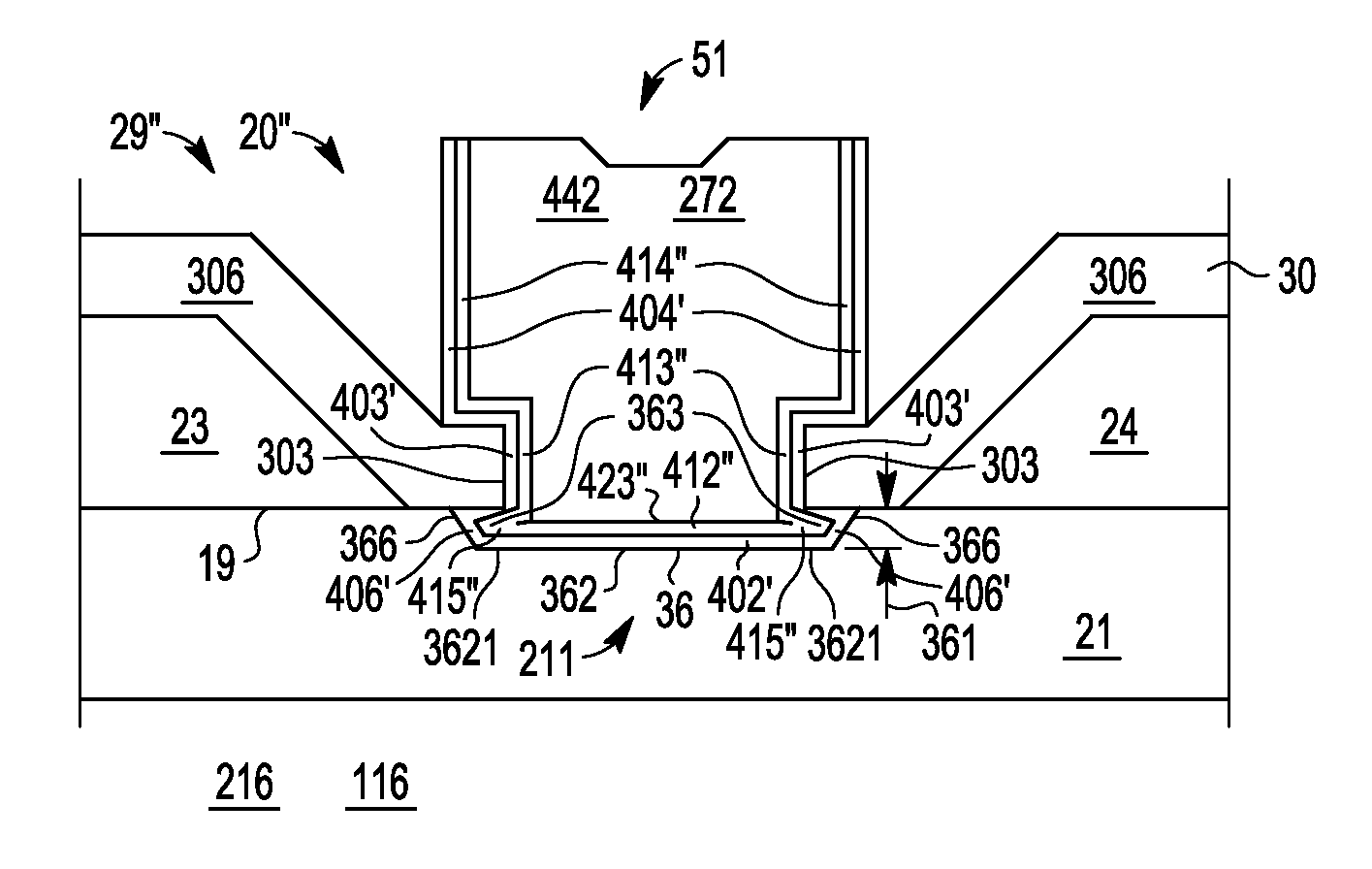
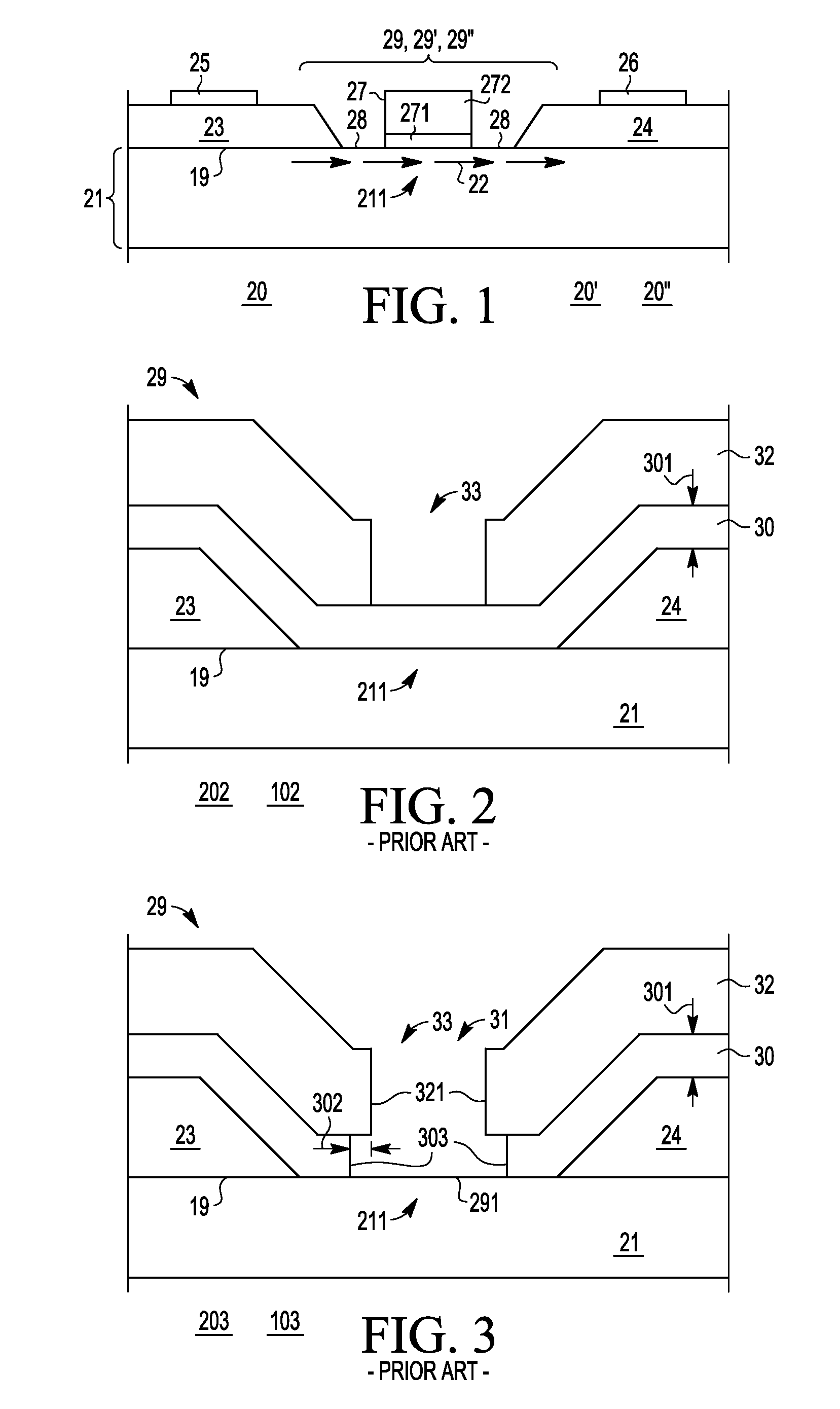
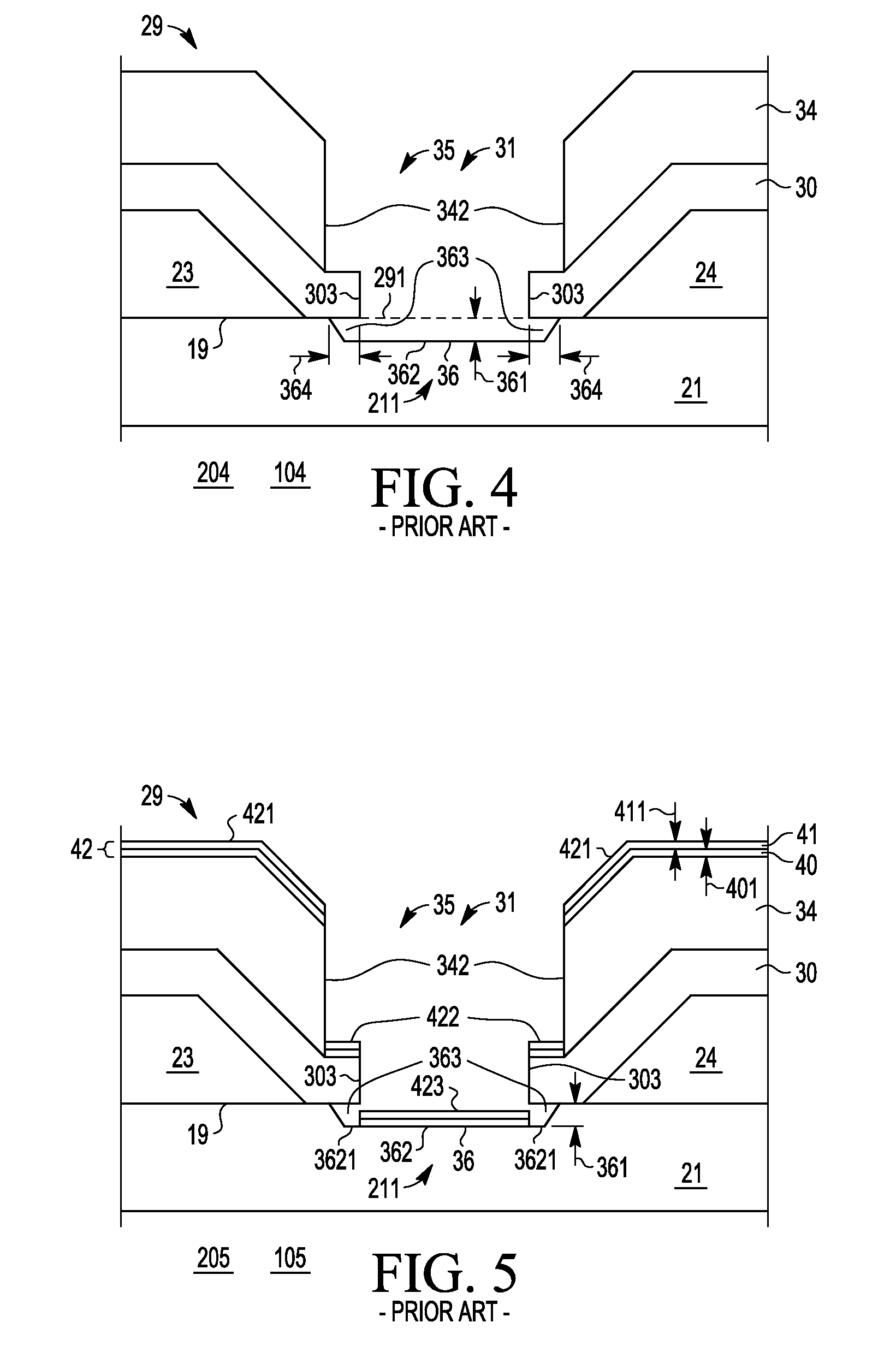
Field effect transistor gate process and structure
InactiveUS20100244178A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSchottky gate
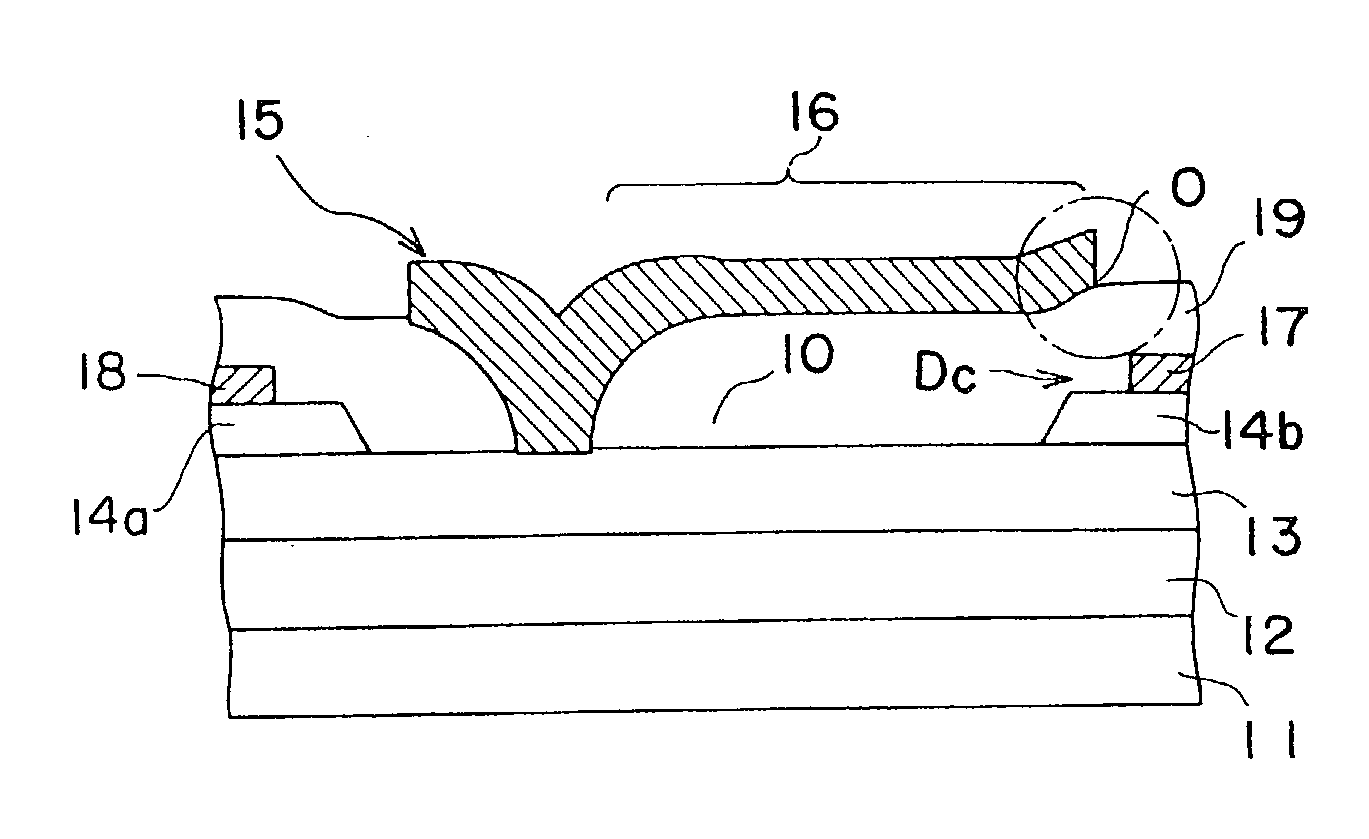
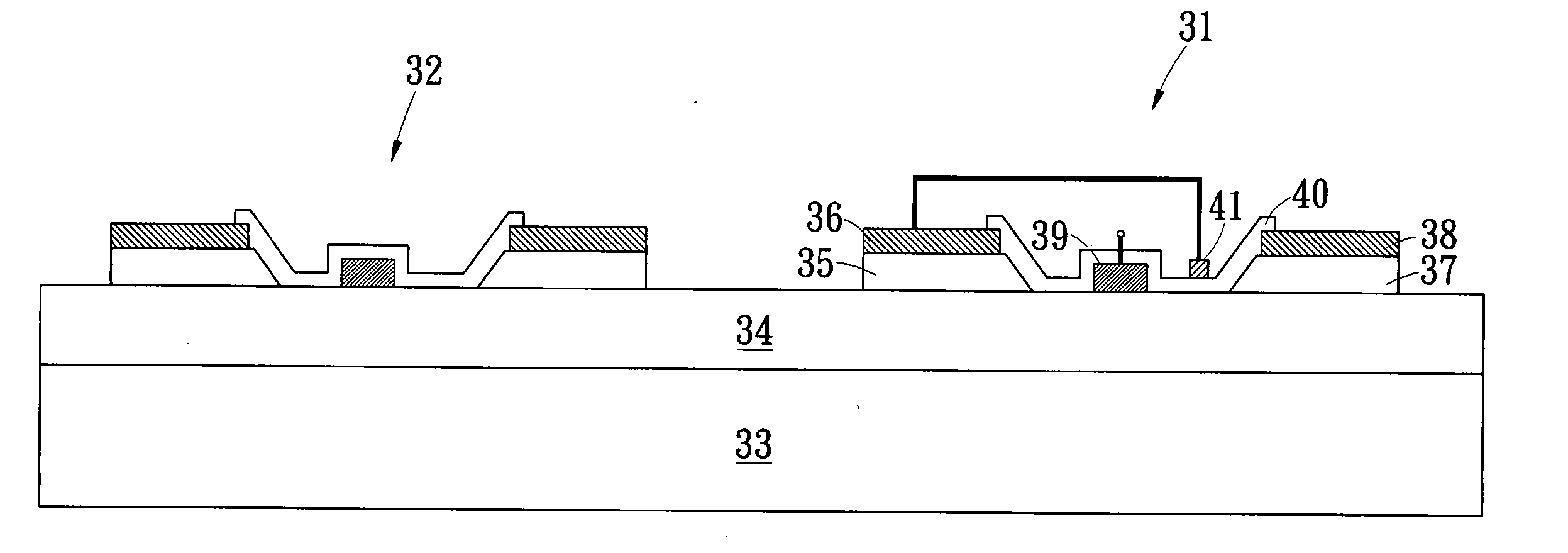
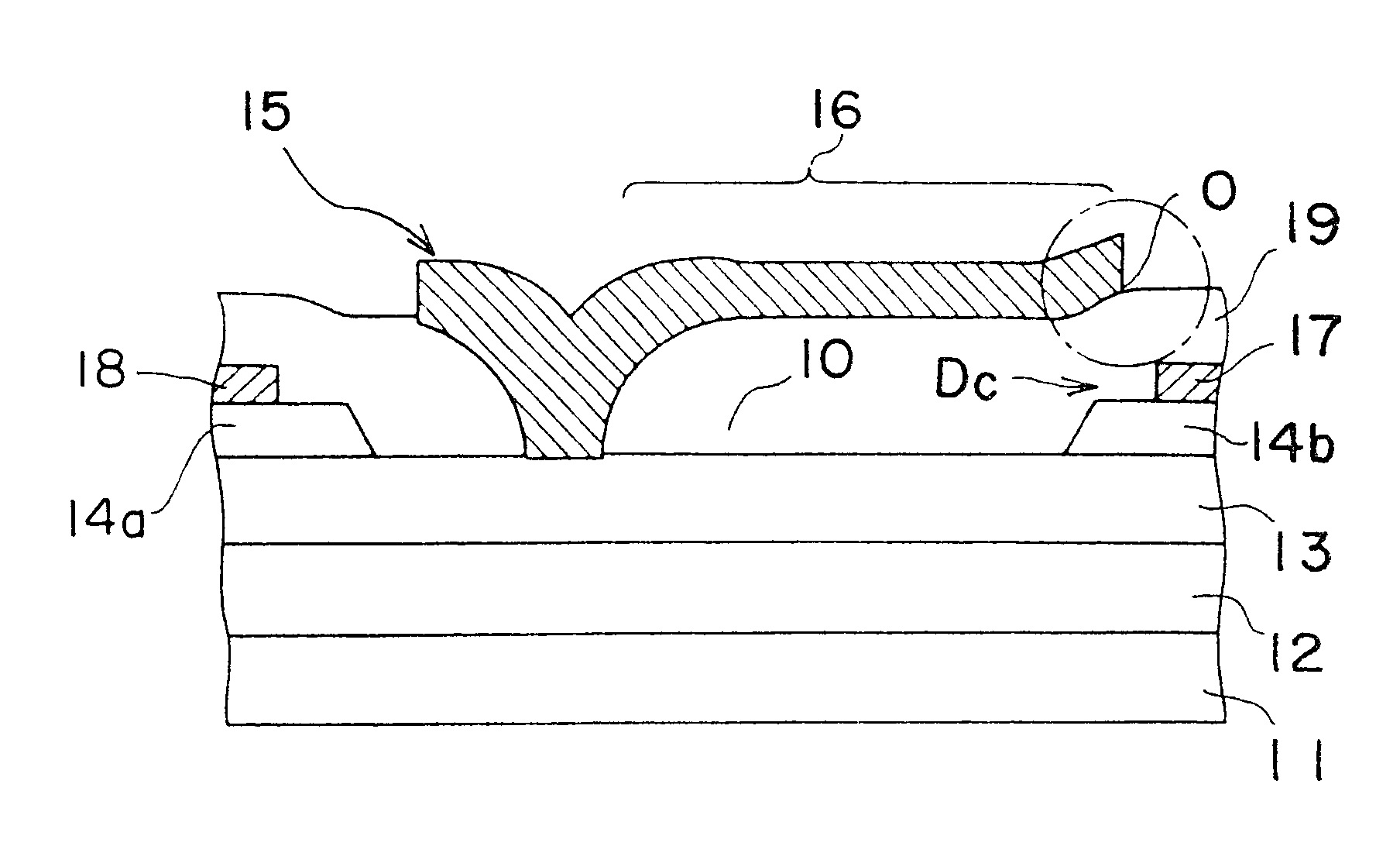
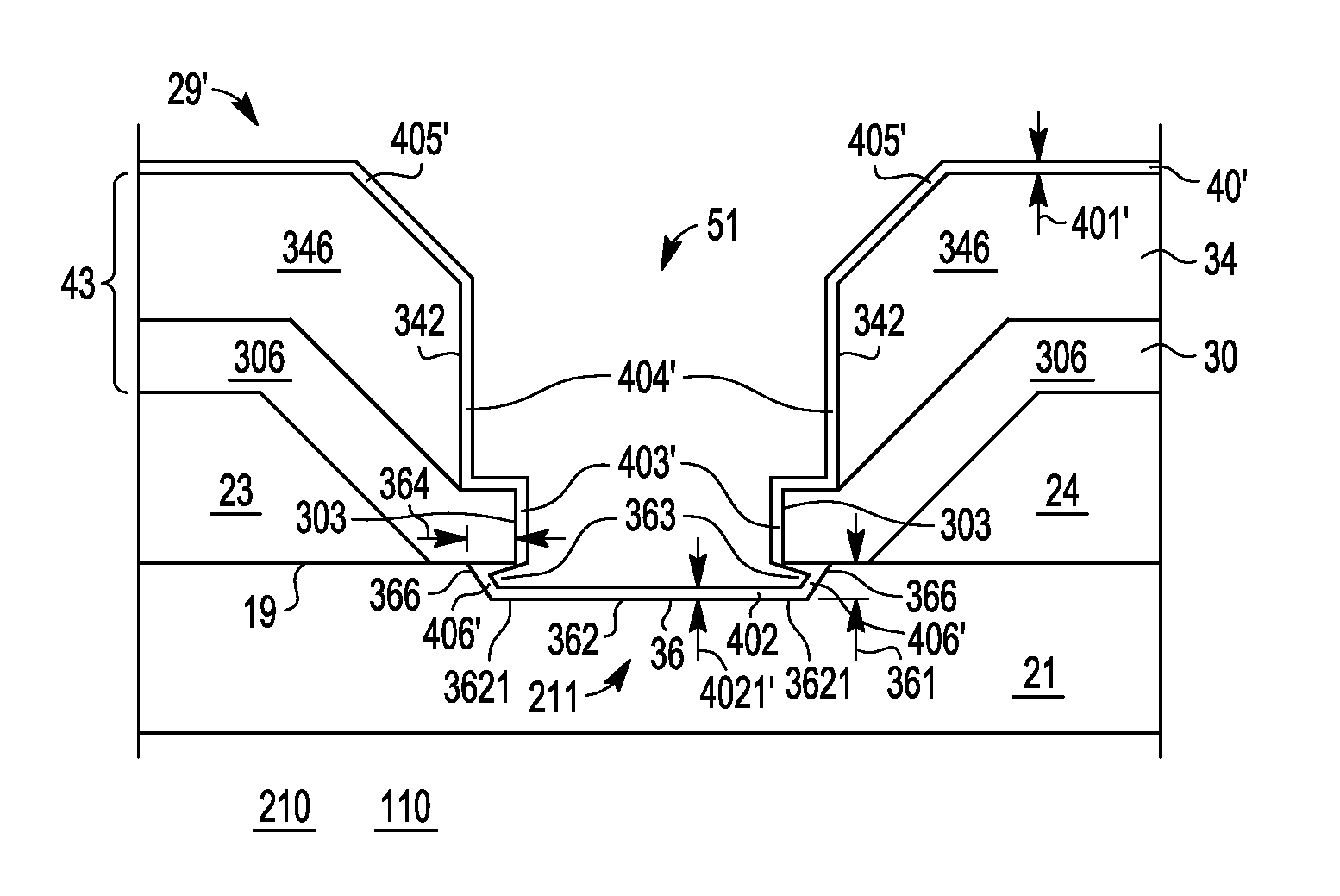
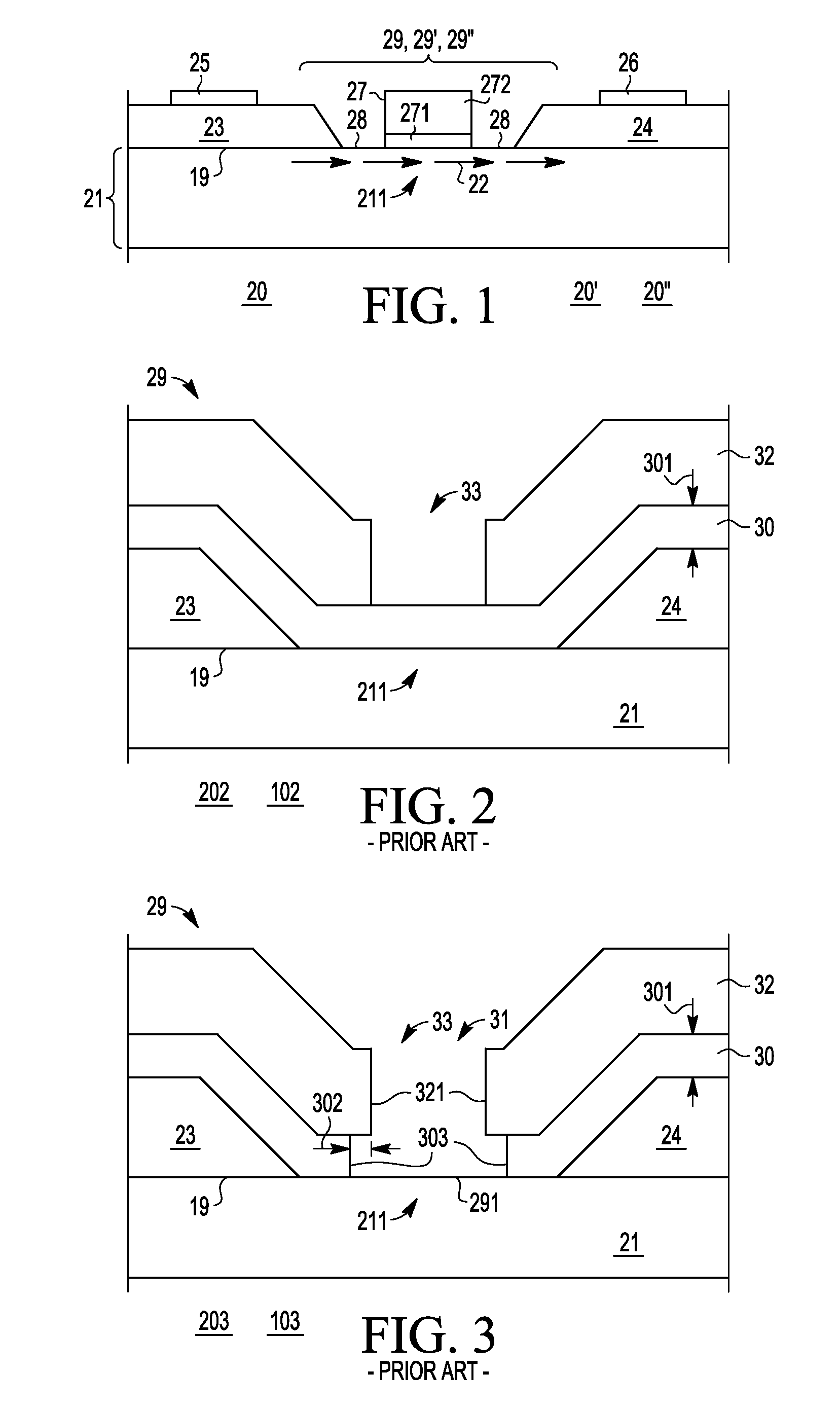
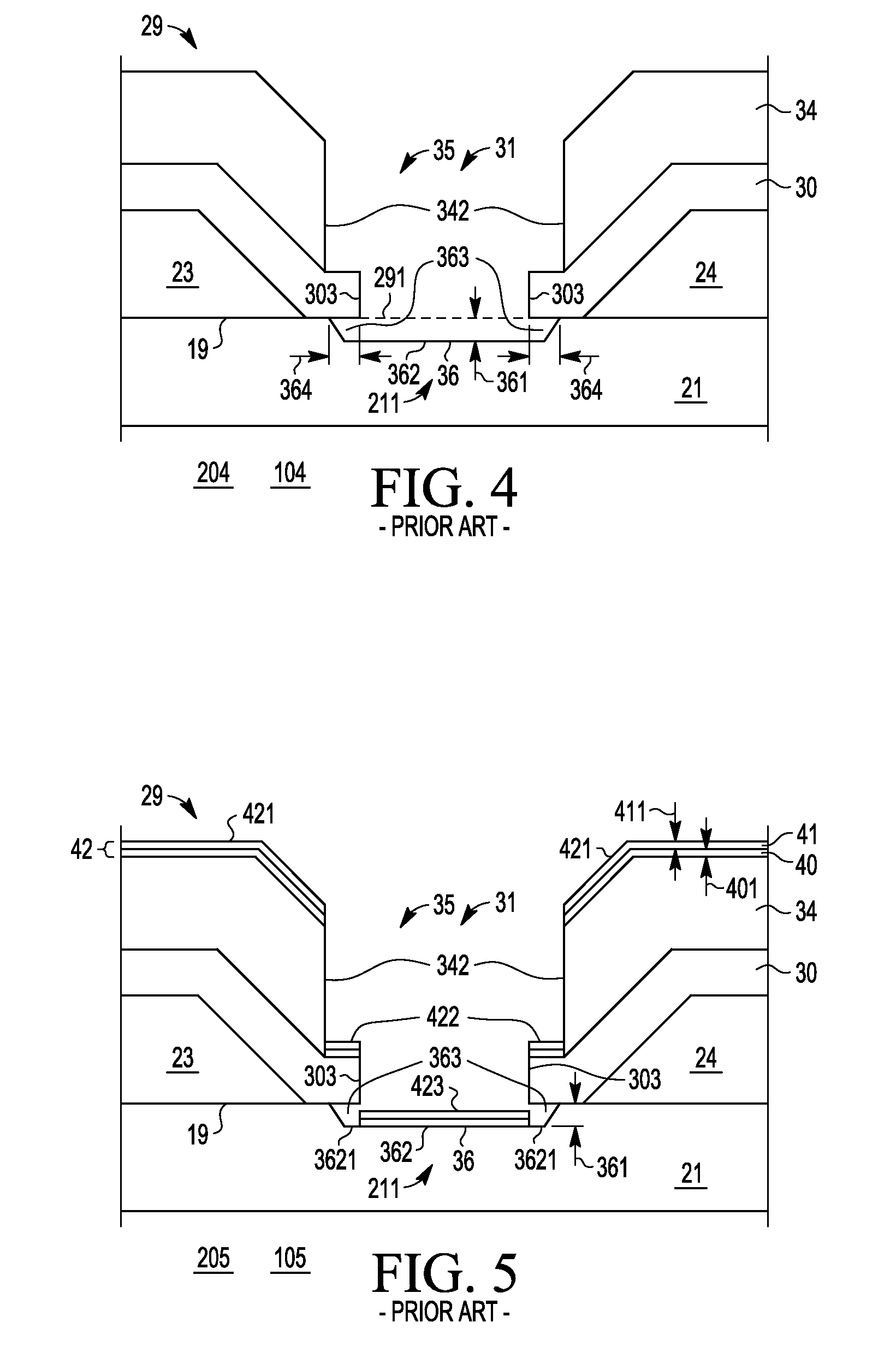
A Schottky gate (27′, 27″) of a metal-semiconductor FET (20′, 20″) is formed on a semiconductor comprising substrate (21) by, etching a gate recess (36) so as to expose a slightly depressed surface (362) of the substrate (21), the etching step also producing surface undercut cavities (363) extending laterally under the etch mask (43) from the gate recess (36), then conformally coating the slightly depressed surface (362) with a first Schottky forming conductor (40′) and substantially also coating inner surfaces (366) of the surface undercut cavities (363), and forming a Schottky contact to the semiconductor comprising substrate (21), adapted when biased to control current flow in a channel (22) extending between source (23) and drain (24) of the FET (20′, 20″) under the gate recess (36). In further embodiments, a conformal or non-conformal barrier layer conductor (41′, 41″) may be provided over the Schottky forming conductor (40′) and a thicker overlying gate conductor (442, 272) provided over the barrier layer conductor (41′, 41″).
Owner:NXP USA INC
A HEMT gate leakage current separating structure and method based on capacitor structure
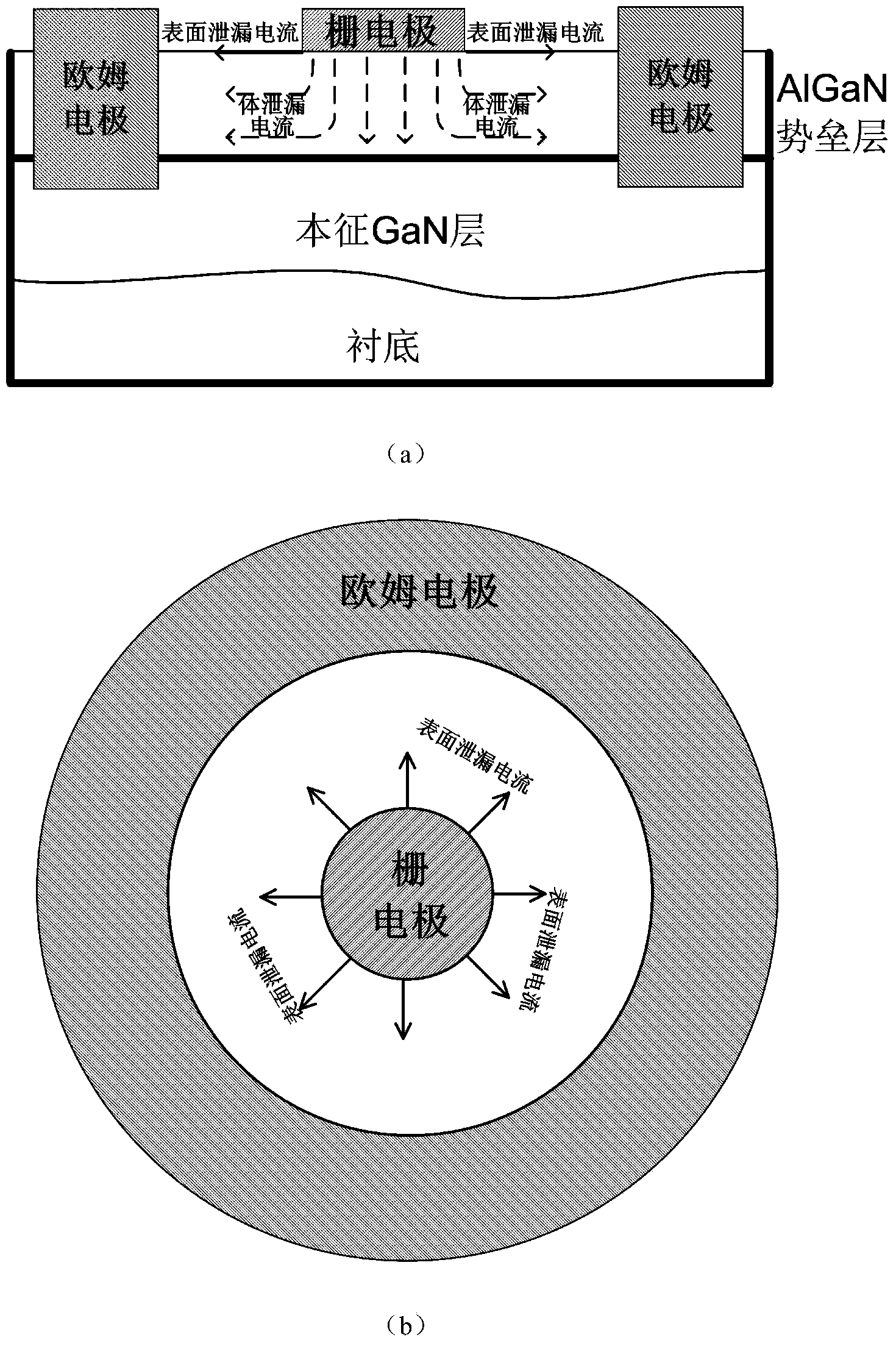
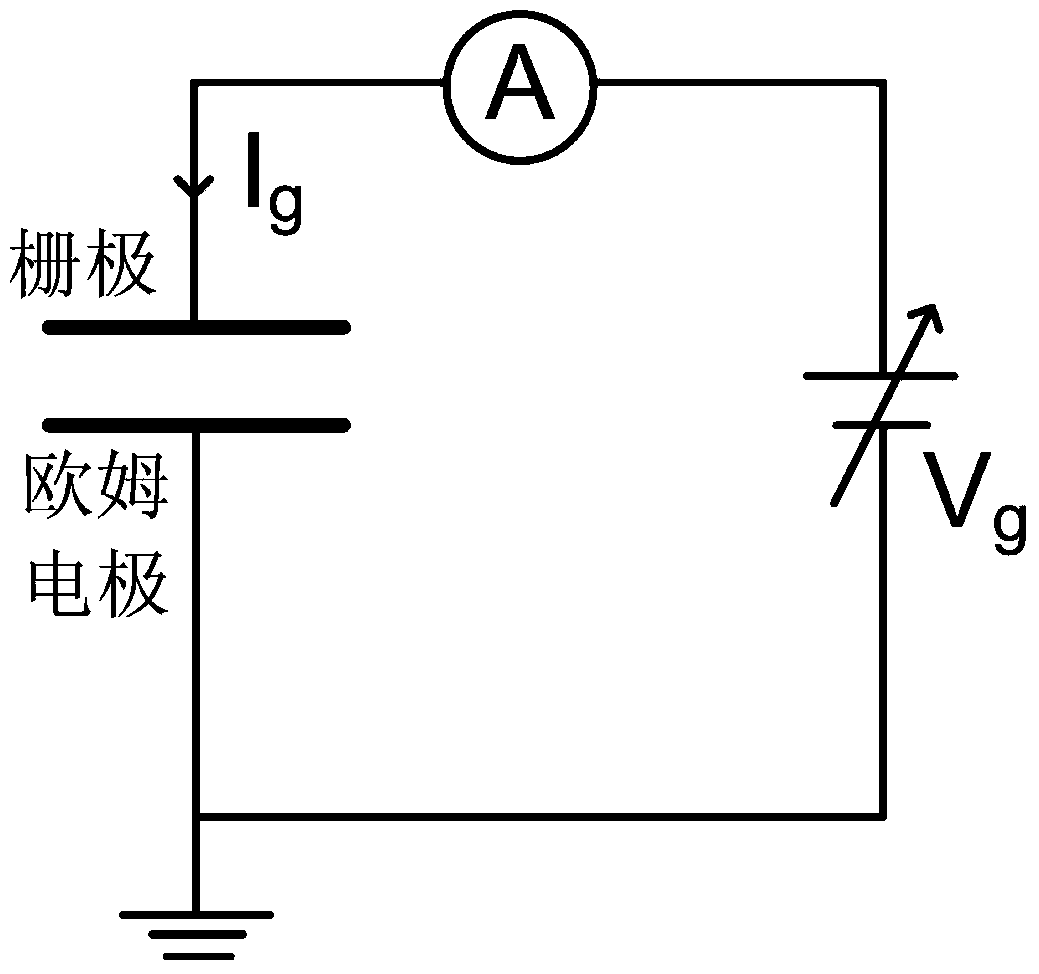
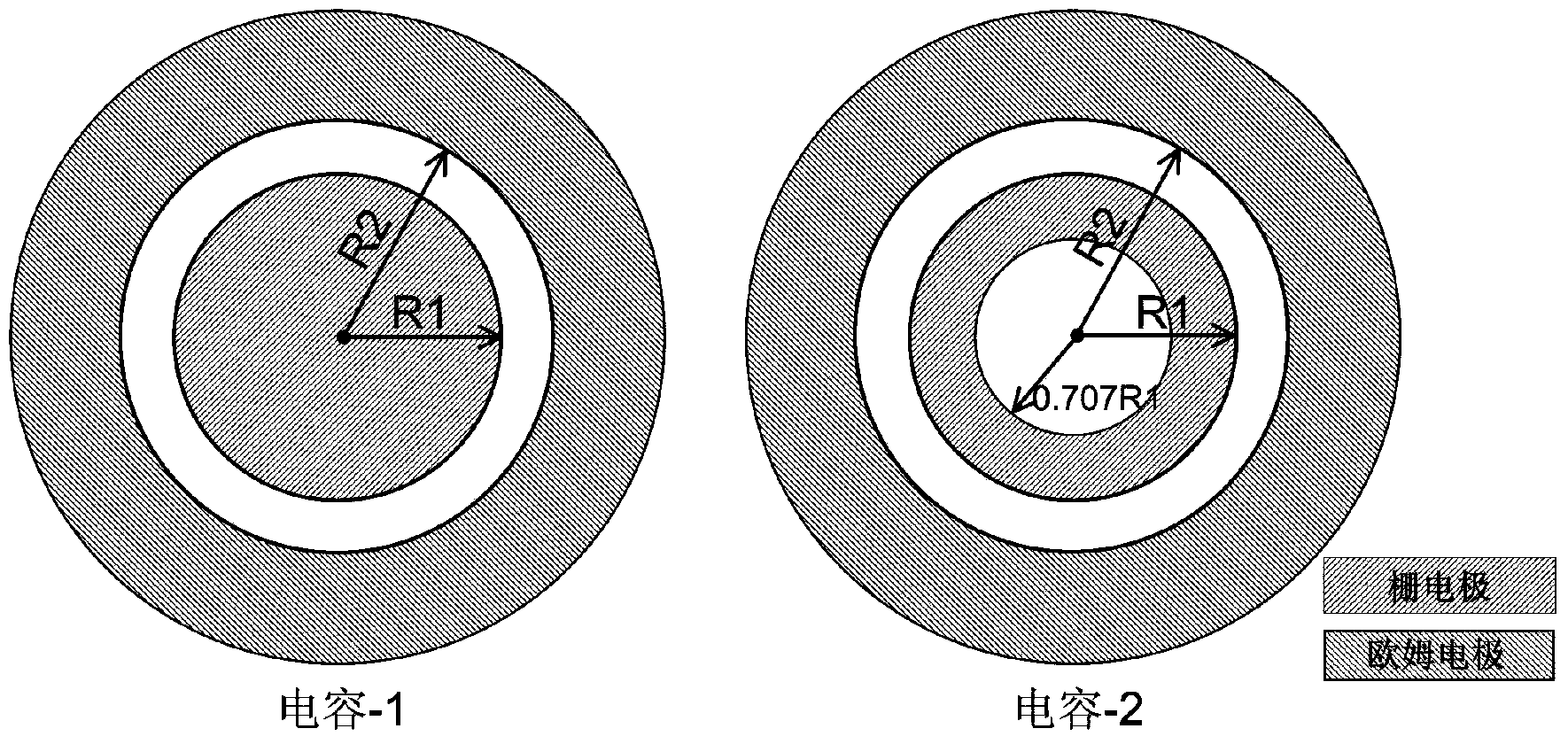
ActiveCN103646968ASimple structureSimple methodCurrent/voltage measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsProcess optimizationGate leakage current
The invention discloses a HEMT gate leakage current separating structure and method based on capacitor structure. The HEMT grid leakage current separating structure comprises two annular schottky gate capacitors with different areas. Each capacitor is configured in dual-end structure and comprises a gate electrode and an ohmic electrode. The radius of the gate electrode of the first capacitor is R1. The Schottky gate of the second capacitor is annular. The radius of the outer ring of the Schottky gate of the second capacitor is R1 while the radius of the inner ring of the Schottky gate of the second capacitor is 0.707R1. The two Schottky capacitors have same distance between the gate electrode and the Ohmic electrode, wherein the distance is equal to R2-R1. The method comprises using a conventional semiconductor parameter testing device to perform an electrical test on the two capacitors so as to achieve quantified separation of body leakage current and surface leakage current in the gate leakage current of a HEMT device. The HEMT gate leakage current separating structure and method have characteristics of simpleness and reliable results and can be widely used in material growth, device process optimization, and subsequent reliability assessment of the HEMT device.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
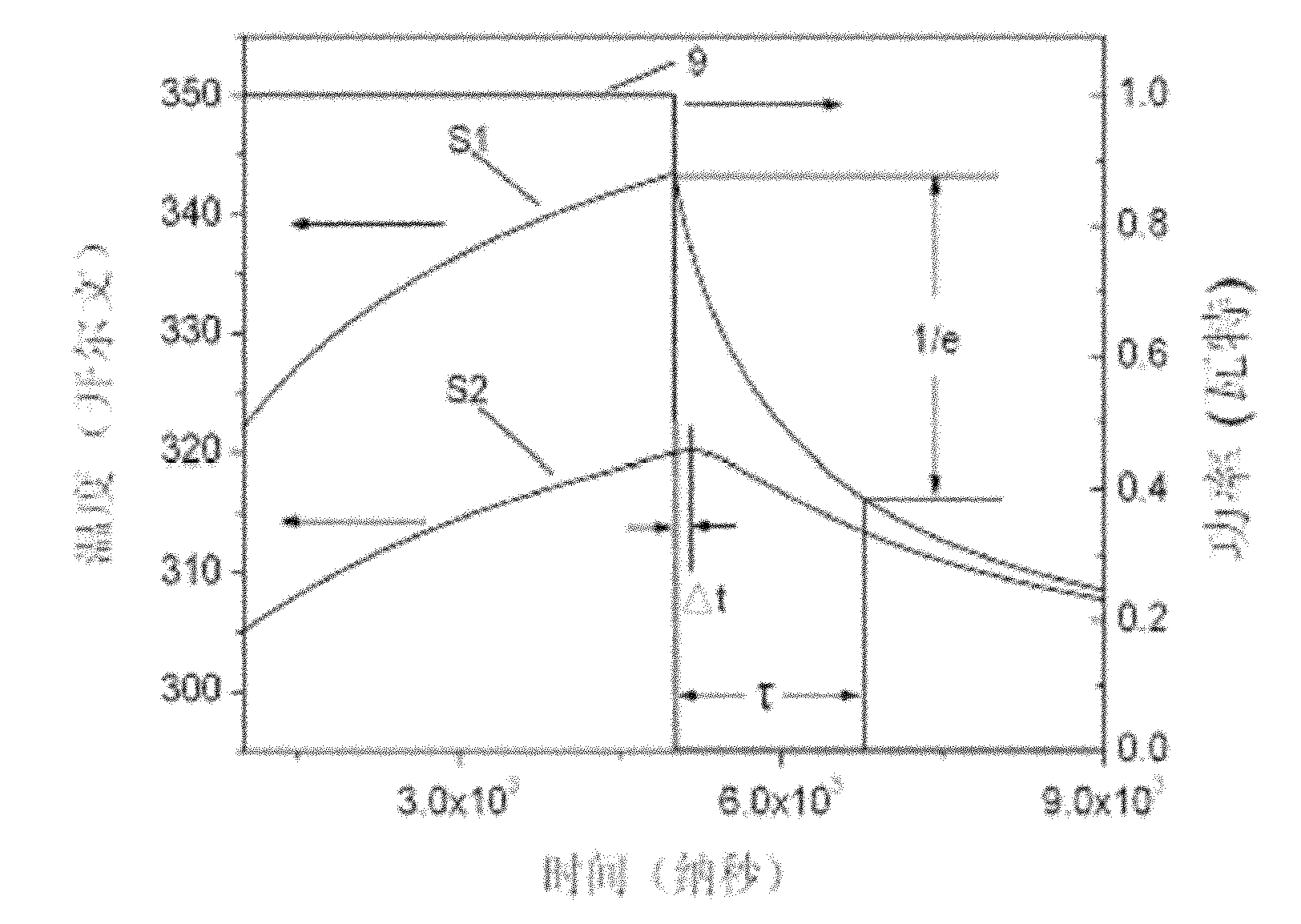
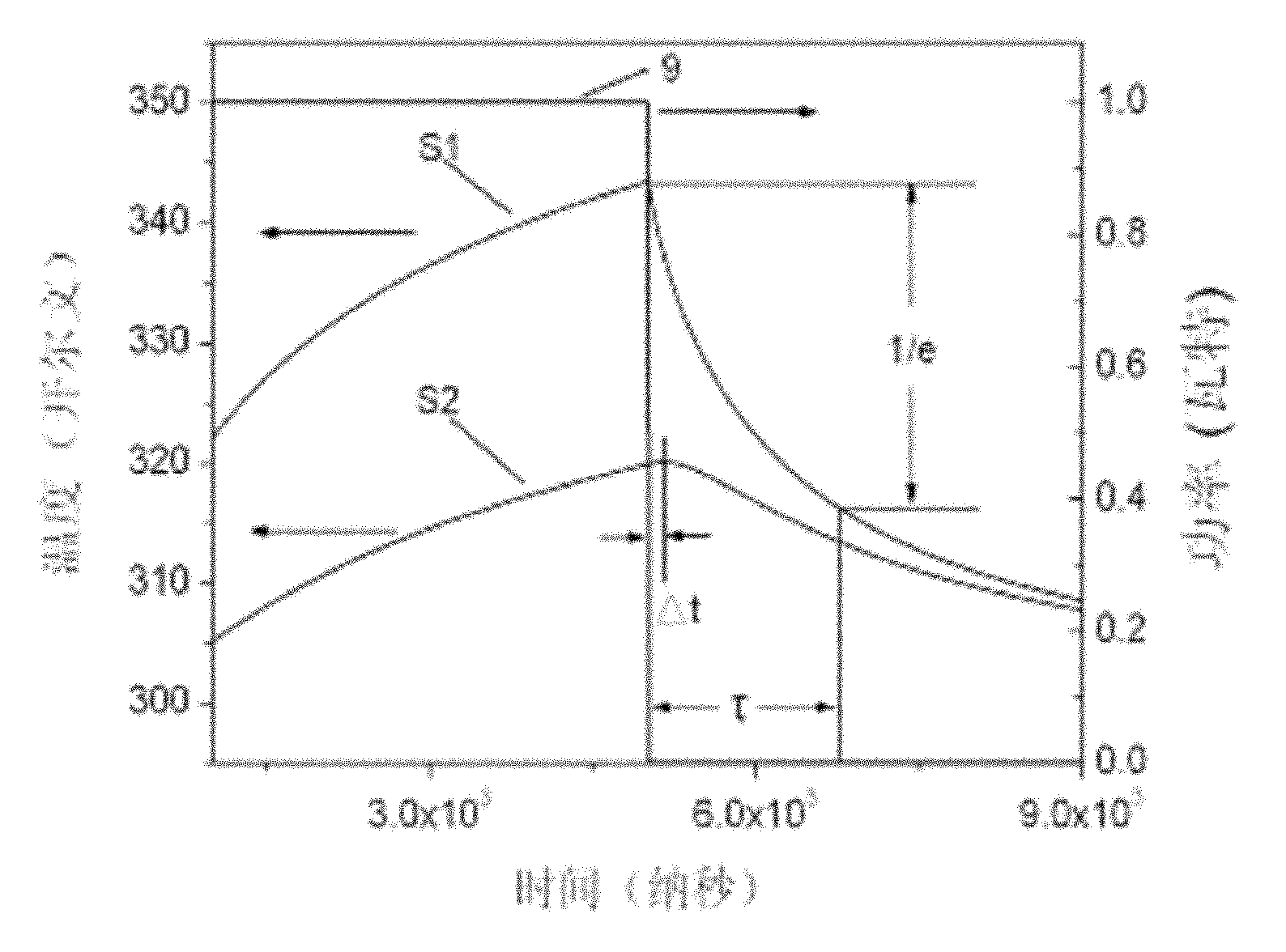
Method for measuring heat conduction parameter in thin layer material of active area of semiconductor device
The invention discloses a method for measuring a heat conduction parameter in a thin layer material of an active area of a semiconductor device, and relates to the field of semiconductor device test. In the prior art, the active area simultaneously plays the roles of a heating area and a temperature detection area, and the conduction speed of heat in a thin layer cannot be measured. A test chip prepared by adopting the method separates a heat source area and a temperature sensitive detection area on space. Heating and measurement processes can be simultaneously performed, so time delay does not exist, and the measured heat time constant of an actual device structure reaches nanosecond level (based on the speed of a high-speed analog / digital (A / D) acquisition card). The method can fulfill the purpose of testing the heat conduction parameter of the thin layer of the actual active area of the device such as a Schottky gate structure-based device such as a GaN high electron mobility transistor (GaN HEMT) or the like, and can also be used for measuring the heat conduction parameter of a specific film material.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
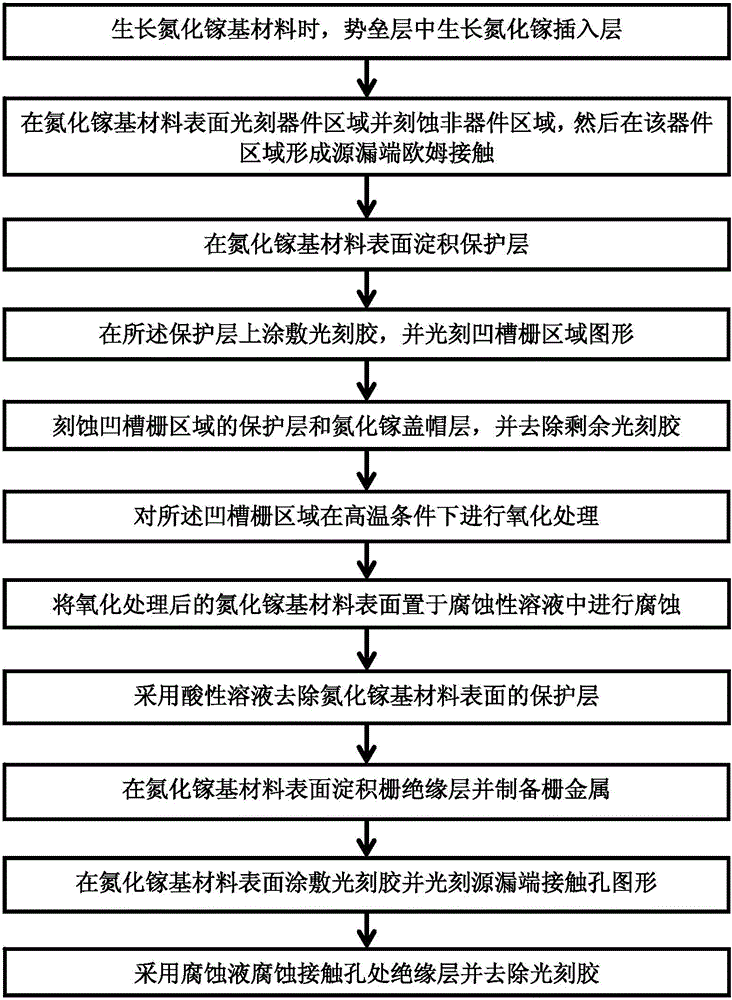
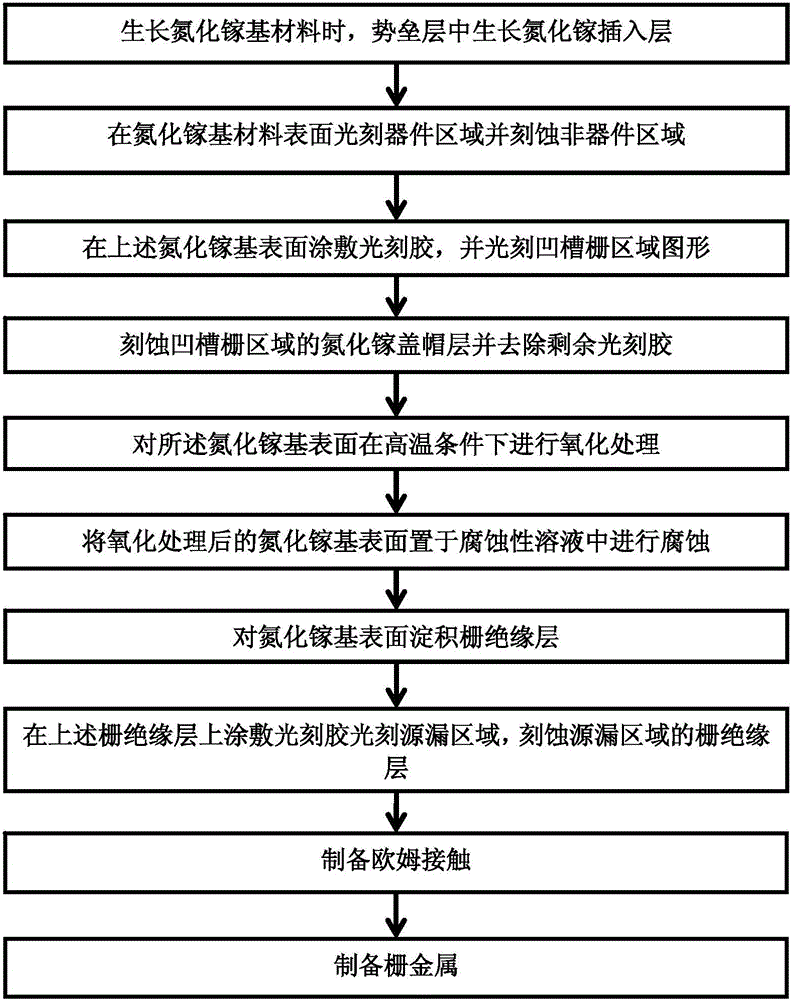
GaN-based enhanced device with gallium nitride insertion layer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106298904APerformance maximizationReduce the impactSemiconductor devicesOperabilityGallium nitride
The invention discloses a GaN-based enhanced device with a gallium nitride insertion layer and a preparation method thereof. Since a gallium nitride layer is inserted into a barrier layer, in the preparation of a groove gate structure, corrosion can be stopped at the gallium nitride insertion layer automatically, so that different depths of groove corrosion effects can be realized through different insertion positions of the gallium nitride layer in the barrier layer, and control and adjustment of Schottky gate and MOS structure gate threshold voltage can be finished based on the structure above; the left barrier layer in proper thickness under the gallium nitride insertion layer can protect the trenches during groove corrosion effectively to prevent degradation of device performance; and the GaN-based enhanced device and the preparation method thereof have higher operability and repeatability, and facilitate industrial production.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
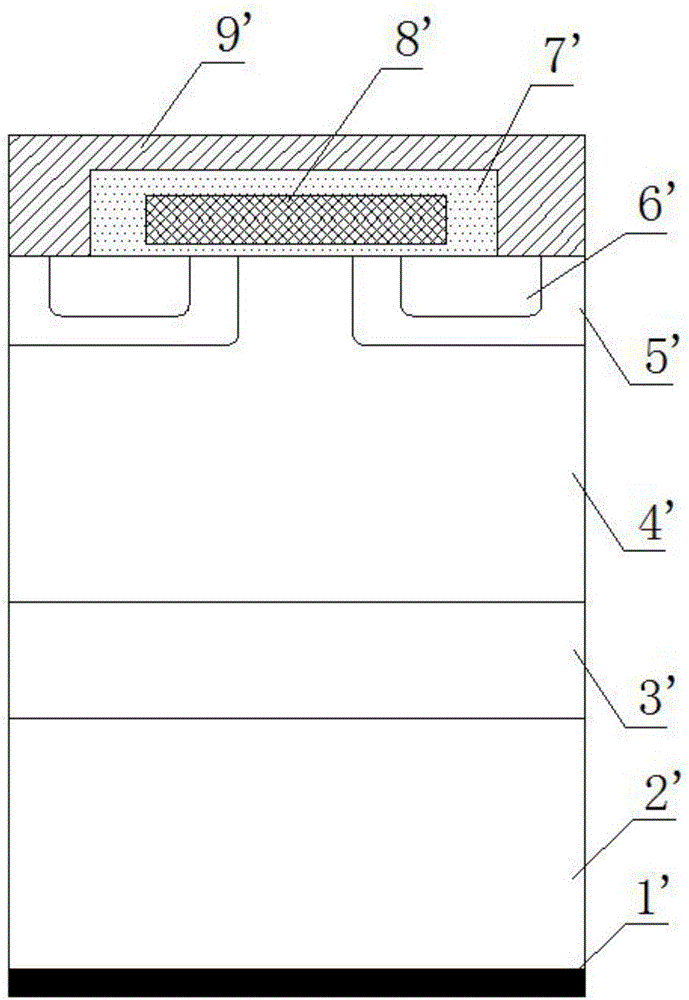
Gallium nitride device schottky contact system with composite metal barrier layer
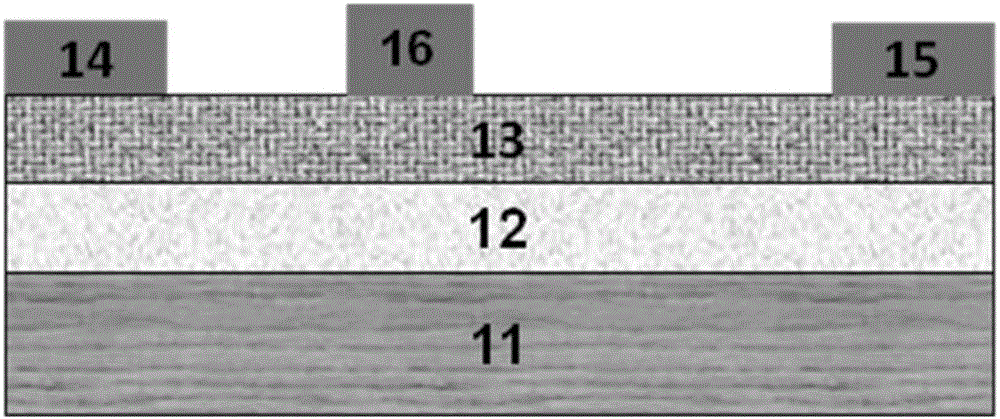
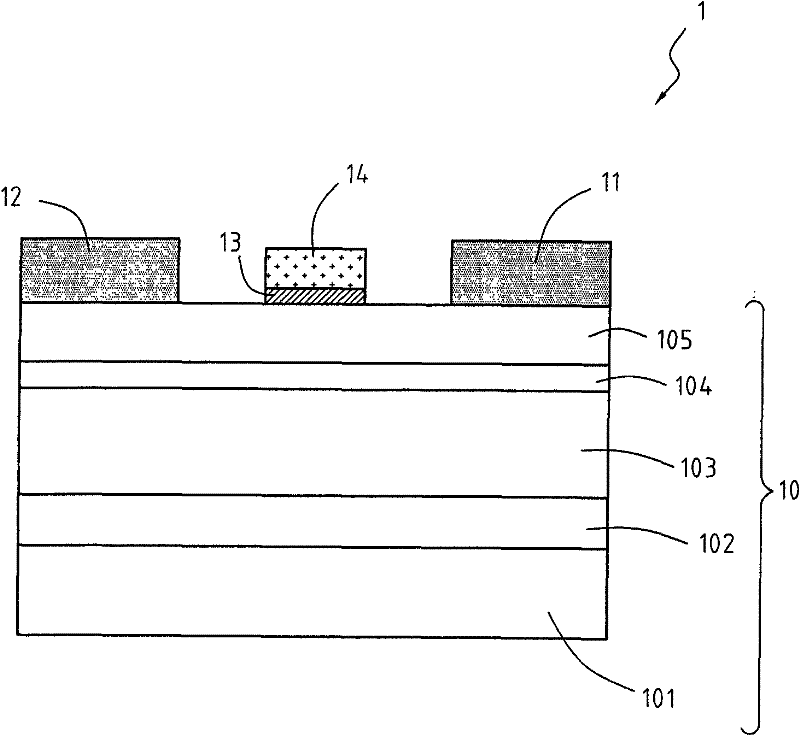
ActiveCN106684142APerformance impactSmall coefficient of thermal expansionSemiconductor devicesGallium nitrideSchottky gate
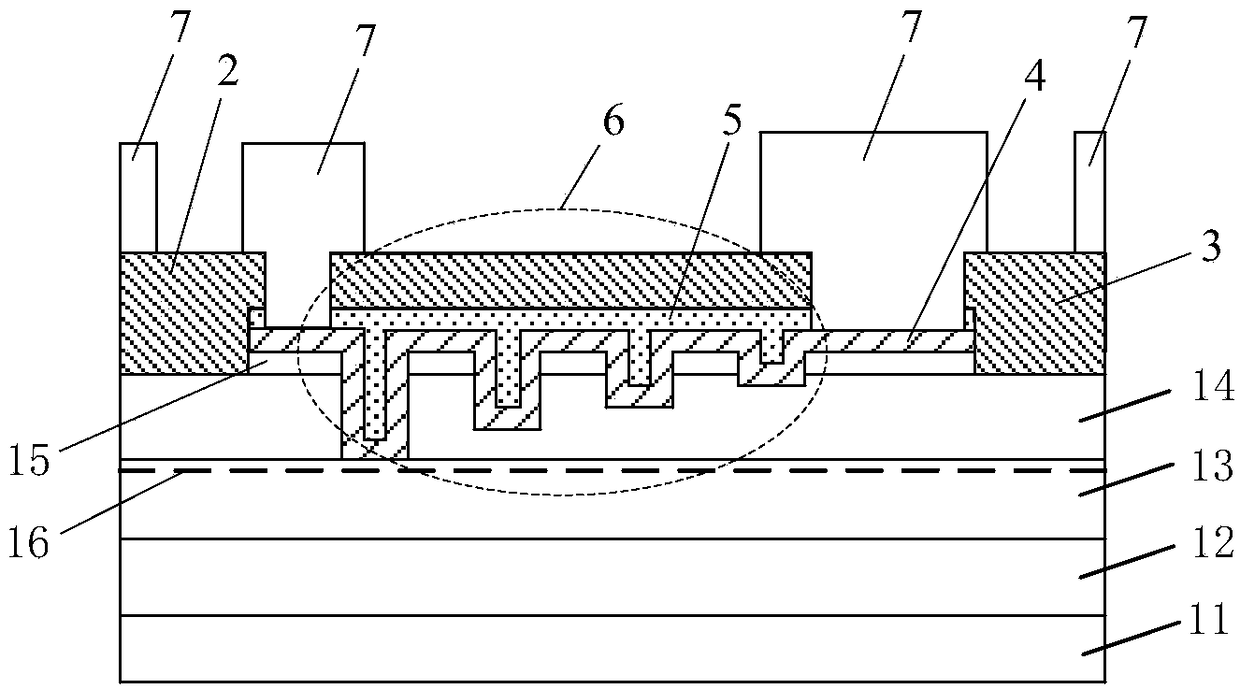
The invention relates to a gallium nitride device schottky contact system with a composite metal barrier layer. The structure of a gallium nitride device successively comprises a substrate 11, a GaN buffer layer 12 and an AlGaN barrier layer 13 from bottom to top; a source electrode 14 is arranged at one end of the upper part of the AlGaN barrier layer; a drain electrode 15 is arranged at the other end of the upper part of the AlGaN barrier layer 13; an AlGaN / GaN HEMT gate electrode 16 is arranged above the AlGaN barrier layer 13 positioned between the source electrode 14 and the drain electrode 15; the AlGaN / GaN HEMT gate electrode 16 is a gate electrode provided with a schottky contact structure; and the schottky contact structure comprises a composite metal layer provided with a Ni metal layer, a Mo metal layer, a Ti metal layer, a Pt metal layer and a Y metal layer. A multi-layered metal system of a schottky gate of the gallium nitride device and an epitaxial layer of the multi-layered metal system have excellent thermal matching property, and reliability of the gallium nitride device can be greatly improved.
Owner:NO 55 INST CHINA ELECTRONIC SCI & TECHNOLOGYGROUP CO LTD
Schottky gate field effect transistor
InactiveUS6717192B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingContact layerSchottky gate
A Schottky gate FET including a gate electrode having a gate extension, a drain electrode and a drain contact layer overlying a semi-insulating substrate, wherein the gate extension overlies at least part of the drain electrode and the drain contact layer. The vertical overlapping between the gate extension and the drain contact region prevents the current reduction to make the circuit module mounting the Schottky gate FET non-usable.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Longitudinal-channel SiC Schottky gate bipolar transistor and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN106783987AReduce processing difficultyImprove featuresSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower flowJFET
The invention provides a longitudinal-channel SiC Schottky gate bipolar transistor. The longitudinal-channel SiC Schottky gate bipolar transistor comprises an N+ silicon carbide substrate, an emitter contact metal layer, a P+ buffer layer, a P- drift region, a P+ current collection region and a collector contact metal layer and also comprises at least two vertical grooves, wherein the emitter contact metal layer is formed on a surface of the N+ silicon carbide substrate, the P+ buffer layer is formed on the N+ silicon carbide substrate, the P- drift region is formed on the P+ buffer layer, the P+ current collection region is formed on the P- drift region, the collection contact metal layer is formed on the P+ current collection region, the at least two vertical grooves are formed in the P- drift region, and a Schottky gate metal layer is formed on each groove. In the device provided by the invention, an upper part structure of a traditional insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) device is substituted by employing a channel structure of a longitudinal-channel junction field-effect transistor (JFET) device on the P- drift region and taking Schottky contact metal as a device gate, and the width of a channel region of the device is 0.5-1.5 micrometers; and the device has the advantages of simple fabrication process, low cost, high device current grain and the like and can be used for a switching voltage-stabilization power supply, electric energy conversion, automobile electron, petroleum drilling equipment and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Semiconductor device and apparatus for communication system
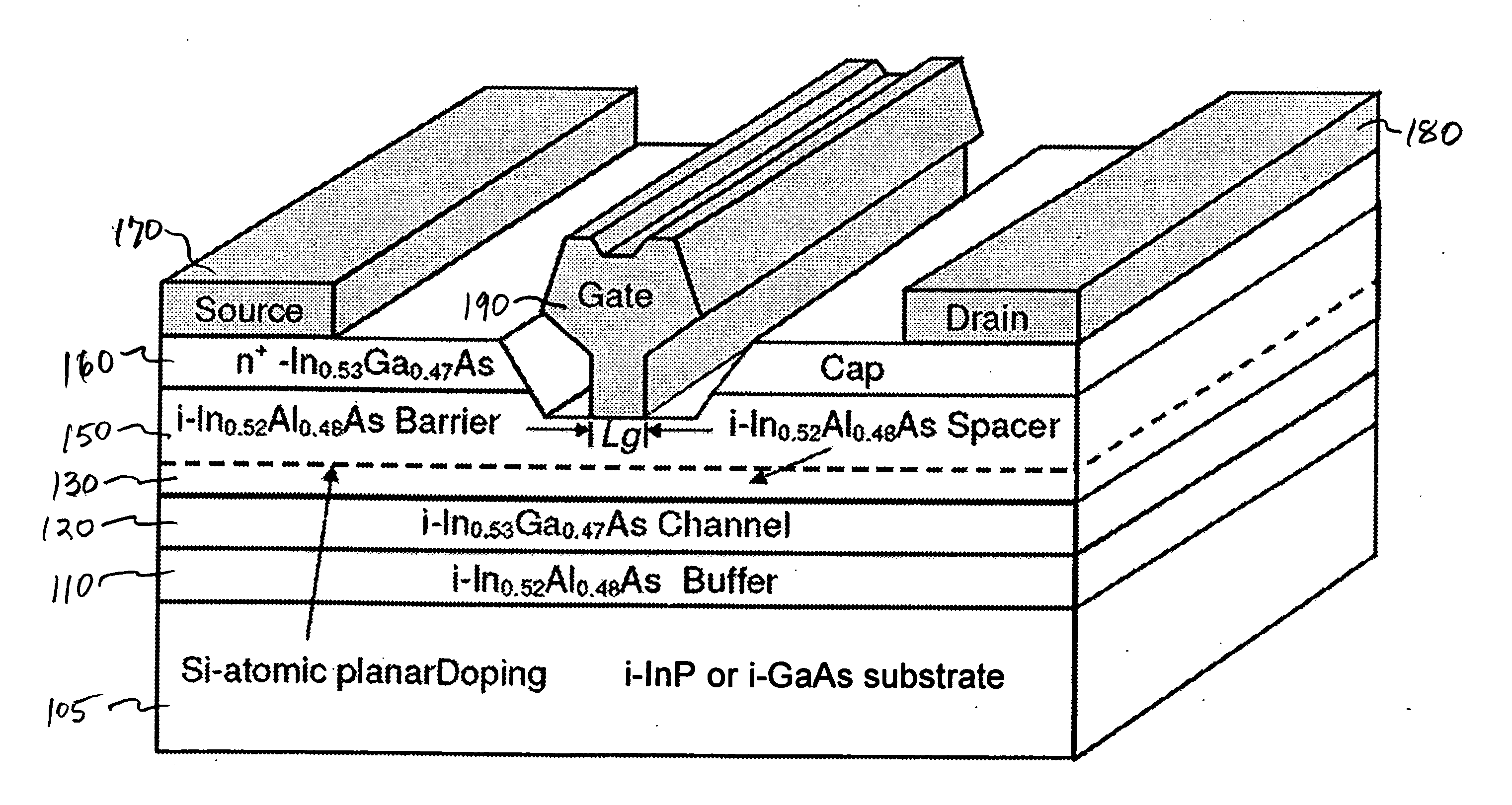
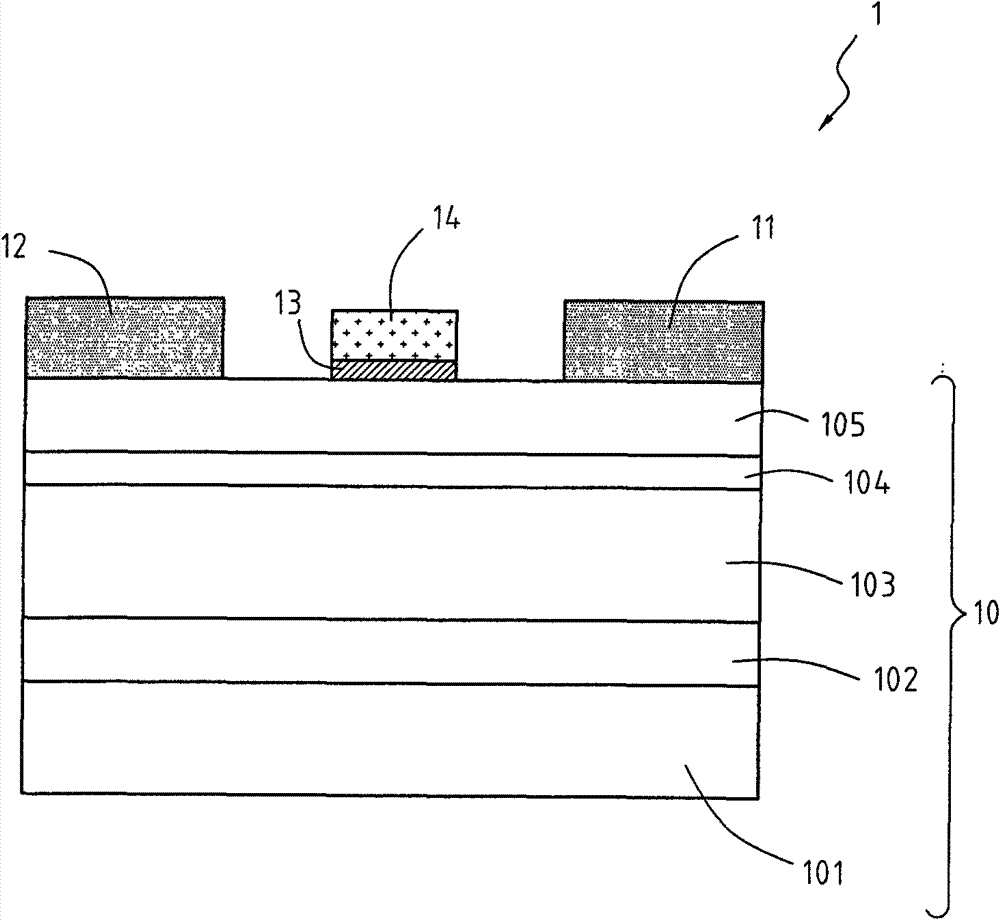
InactiveCN1476638AIncrease the amount of currentReduce setup costsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDelta dopingCommunications system
Provided is a semiconductor device of low power consumption and high breakdown voltage and equipment for a communication system using it by mitigating the tradeoff of breakdown voltage increase and resistance reduction. The solution: A HEMT has an InAlAs layer (202), an InGaAs layer (203), a multiple delta-doped InAlAs layer (204) composed of n-type doped layers (204a) and undoped layers (204b) which are alternately stacked, an InP layer (205), a Schottky gate electrode (210), a source electrode (209a), and a drain electrode (209b) on an InP substrate (201). When a current flows in a region (channel region) of the InGaAs layer (203) adjacent the interface between the InGaAs layer (203) and the multiple delta-doped InAlAs layer (204), a breakdown voltage in the OFF state can be increased, while resistance to the movement of carriers passing through the multiple delta-doped InAlAs layer (204) as a carrier supplying layer is reduced.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Gate-ballast structure RF AlGaN/GaN HEMTs device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109545760AImprove cooling effectRaise the barrier heightSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBallast resistorRadio frequency
The invention belongs to the technical field of a semiconductor and relates to a gate-ballast structure RF AlGaN / GaN HEMTs device and a preparation method thereof. The device includes a AlGaN / GaN substrate on SiC, a gate, a source and a drain, wherein the gate is a doped polysilicon, and square resistance is in a range of 20-40omega / sq. The doped polysilicon is taken as a gate, barrier potential height is high, a gate leakage is smaller compared with a conventional Ni / Au schottky gate, power consumption of a radio frequency power device is reduced, efficiency is improved, and the doped polysilicon has relatively low Rg and has the ballast resistor function. The device can be applied to a multi-finger gate device AlGaN / GaN HEMTs, through adjusting Lg length, the purpose of optimizing Wg length is achieved, heat radiation of the device is effectively improved, the device can be further applied to AlGaN / GaN HEMTs, and the polysilicon gate can be biased by wider Vgs swing.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Transistor assembly and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102290445AReduced surface state densityIncrease dependenceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectrical conductorEngineering
A transistor component and its manufacturing method, the component includes: a semiconductor substrate, a drain, a source, a gate metal seed layer formed on the semiconductor substrate, which has a gel-like substance layer And a plurality of metal seeds and a Schottky contact metal gate are formed on the gate metal seed layer. The method includes: step A: providing a semiconductor substrate; step B: forming a drain and a source on the semiconductor substrate; step C: defining a region of a gate metal seed layer on the semiconductor substrate; Step D: performing a sensitization and activation process to form the gate metal seed layer on the semiconductor substrate; and Step E: performing an electroless plating process to form a Schottky contact metal gate on the gate metal crystal above the seed layer.
Owner:刘文超
Schottky Gate Organic Field Effect Transistor and Fabrication Method of the Same
InactiveUS20070241325A1Increase speedEasy to makeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingContact formationSchottky barrier
A Schottky gate field effect transistor with high speed and simple structure is provided. The Schottky gate field effect transistor includes: a source, a channel and a drain formed by one organic conductive material, in which the source, channel and drain are formed in a continuous structure within an organic conductor; a gate electrode functioning as a metal gate on one surface of the organic conductor; a Schottky barrier formed by contact between the gate electrode and the organic conductor, in which the region overlapping with the Schottky contact is the channel region.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF YAMANASHI
P-channel schottky gate silicon carbide electrostatic induction thyristor and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN106098767ALower impedancePrevent punch-throughThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceOhmic contact
The invention discloses a P-channel schottky gate silicon carbide electrostatic induction thyristor and a manufacturing method thereof and aims at reducing the on-resistance of a device and improving the power characteristic. According to the technical scheme adopted by the structure, the P-channel schottky gate silicon carbide electrostatic induction thyristor comprises an N-type ohmic contact electrode, an N-type SiC substrate, a P-type SiC buffer layer, a P-type SiC drift layer and a P-type current enhancement layer which are sequentially arranged from bottom to top, wherein a plurality of steps are formed by etching the P-type current enhancement layer; grooves are arranged between the adjacent steps; the top part of each step is provided with a P-type SiC ohmic contact layer; the upper part of each P-type SiC ohmic contact layer is provided with a P-type ohmic contact electrode; the shape of each P-type ohmic contact electrode is the same as that of the corresponding P-type SiC ohmic contact layer; schottky electrodes are arranged in the grooves and are in contact with the side surfaces of the steps and the bottom parts of the grooves; each of the N-type ohmic contact electrode and the P-type ohmic contact electrode comprises an Ni layer and a Pt layer which are sequentially deposited; and each schottky electrode comprises an Ni layer, a Cr layer and an Au layer, or a Ti layer, the Cr layer and the Au layer, or a Pt layer, the Cr layer and the Au layer, which are sequentially deposited.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Field effect transistor gate process and structure
InactiveUS8319310B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorSchottky gate
Owner:NXP USA INC
Transistor assembly and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102290445BReduced surface state densityIncrease dependenceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectrical conductorEngineering
A transistor component and its manufacturing method, the component includes: a semiconductor substrate, a drain, a source, a gate metal seed layer formed on the semiconductor substrate, which has a trihydroxychloride The tin layer, multiple metal crystals and a Schottky contact metal gate are formed on the gate metal seed layer. The method includes: step A: providing a semiconductor substrate; step B: forming a drain and a source on the semiconductor substrate; step C: defining a region of a gate metal seed layer on the semiconductor substrate; Step D: performing a sensitization and activation process to form the gate metal seed layer on the semiconductor substrate; and Step E: performing an electroless plating process to form a Schottky contact metal gate on the gate metal crystal above the seed layer.
Owner:刘文超
Gallium nitride normally-off device with mixed gate electrode structure and preparation method of gallium nitride normally-off device
PendingCN113838930AIncrease the switching frequencyRaise the threshold voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricEngineering
The invention discloses a gallium nitride normally-off device with a mixed gate electrode structure and a preparation method of the gallium nitride normally-off device. The gallium nitride normally-off device comprises a buffer layer, a GaN channel layer, an AlGaN layer and a P-GaN cap layer which are sequentially arranged on a substrate layer, two ohmic electrodes which are arranged on the AlGaN layer, gate dielectric layers which are arranged on the P-GaN cap layer and on the two sides of the P-GaN cap layer, a passivation layer which is arranged on the AlGaN layer between the ohmic electrode and the gate dielectric layer on the two sides of the P-GaN cap layer, and a gate electrode which is arranged on the gate dielectric layer and filled in the groove of the gate dielectric layer. The gate electrode on the gate dielectric layer on the P-GaN cap layer and the gate electrodes filled in the plurality of grooves form a mixed gate structure of an MIS gate electrode structure and a Schottky gate electrode structure; and the gate electrodes on the gate dielectric layers on the two sides of the P-GaN cap layer and the gate dielectric layers on the two sides of the P-GaN cap layer form a field plate structure. The threshold voltage of the gate electrode of the device is improved, the switching frequency of the device is improved, and meanwhile the long-term reliability of the gate electrode of the device is improved.
Owner:宁波铼微半导体有限公司
InAs/AlSb HEMT and MOS-HEMT device manufacturing methods
ActiveCN107195548AReduced series resistanceImprove leakageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOhmic contactEpitaxial material
The invention discloses InAs / AlSb HEMT and MOS-HEMT device manufacturing methods, mainly to reduce on-state resistance of a device and solve the problem of gate current leakage. The InAs / AlSb HEMT device manufacturing method comprises the following process steps of: 1) epitaxial material growth, 2) mesa isolation, 3) ohmic contact manufacturing, 4) schottky gate contact manufacturing, 5) Pad deposition and 6) passivation. The InAs / AlSb MOS-HEMT device manufacturing method comprises the following process steps of: 1) epitaxial material growth, 2) mesa isolation, 3) ohmic contact manufacturing, 4) insulated gate manufacturing, 5) Pad deposition and 6) passivation. A gate slot etching step is saved, the gate current leakage is reduced, and the on-state resistance of the device is also reduced.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com