Amine treating process for acid gas separation by using blends of amines and alkyloxyamines
A technology for acidic gases and mixtures, applied in separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, separation of dispersed particles, etc., can solve problems such as limited commercial utility, load capacity reduction of gas content, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
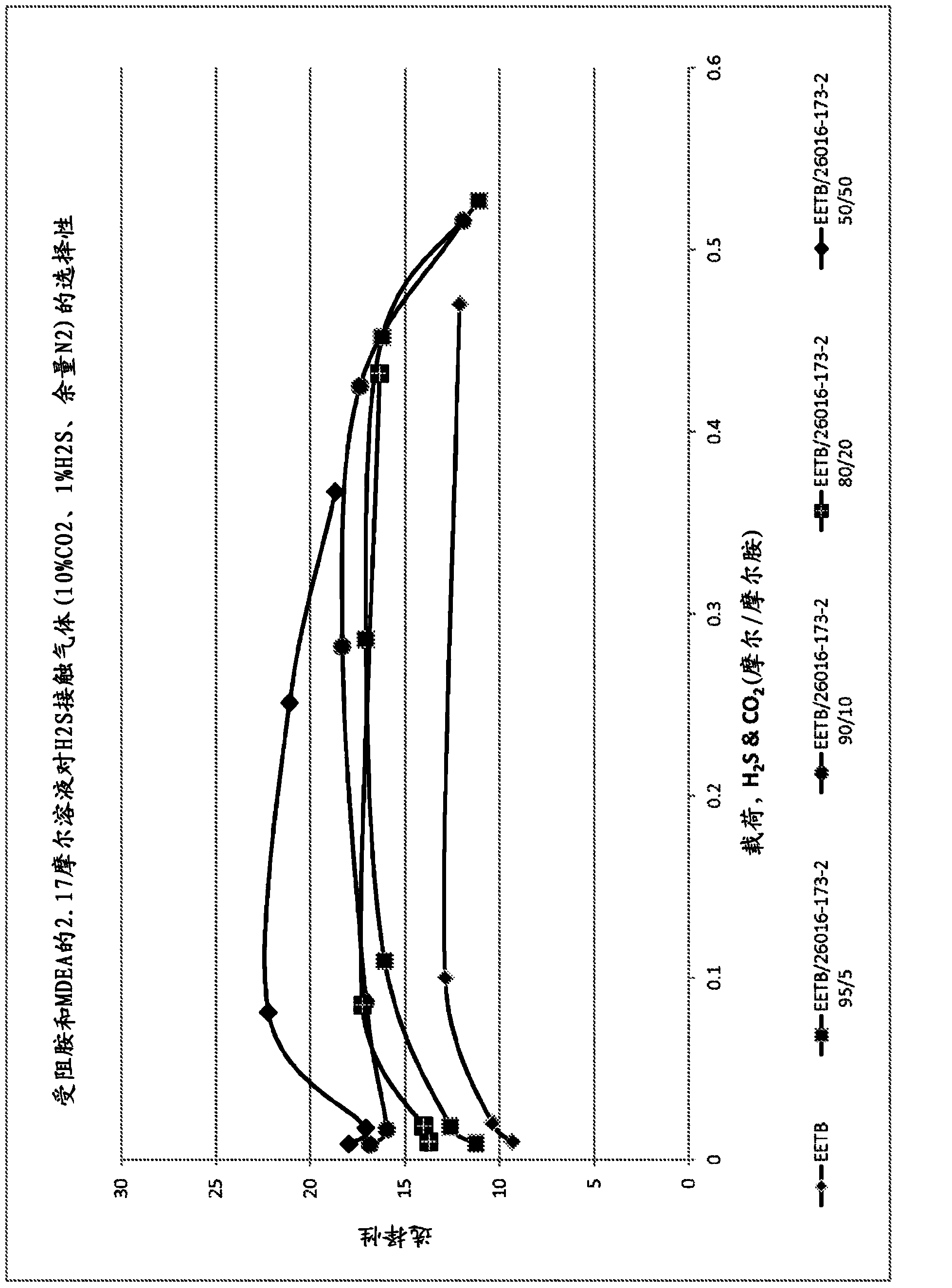
[0094] By containing 10%v / v CO at 40°C (absorbent and gas), 138kPag (20psig) 2 , 1%H 2 S, margin N 2 The gas mixture was bubbled through a stirred 2.17 mole aqueous amine mixture at a gas flow rate of 600 mL / min to test two ether amines in various ratios: tert-butylaminoethoxyethanol (EETB) and methoxy-triethylene glycol -Absorption characteristics of a mixture of tert-butylamine (MEEETB, tert-butylamino-ethoxyethoxyethyl methyl ether). The five gas ratios tested are (EETB / MEEETB): 100 / 0; 95:5; 90 / 10; 80 / 20 and 50:50.
[0095] The gas is introduced into the solvent solution under the dip tube, where the outlet is immersed just below the surface of the solvent (8mm). These parameters were found to provide stable and reproducible data on MDEA and other solutions. The test gas is saturated with water before entering the test unit. The variable speed paddle mixer circulates the solvent through the dip tube at a controlled rate. The unit operates at atmospheric pressure. The gas d...
Embodiment 2
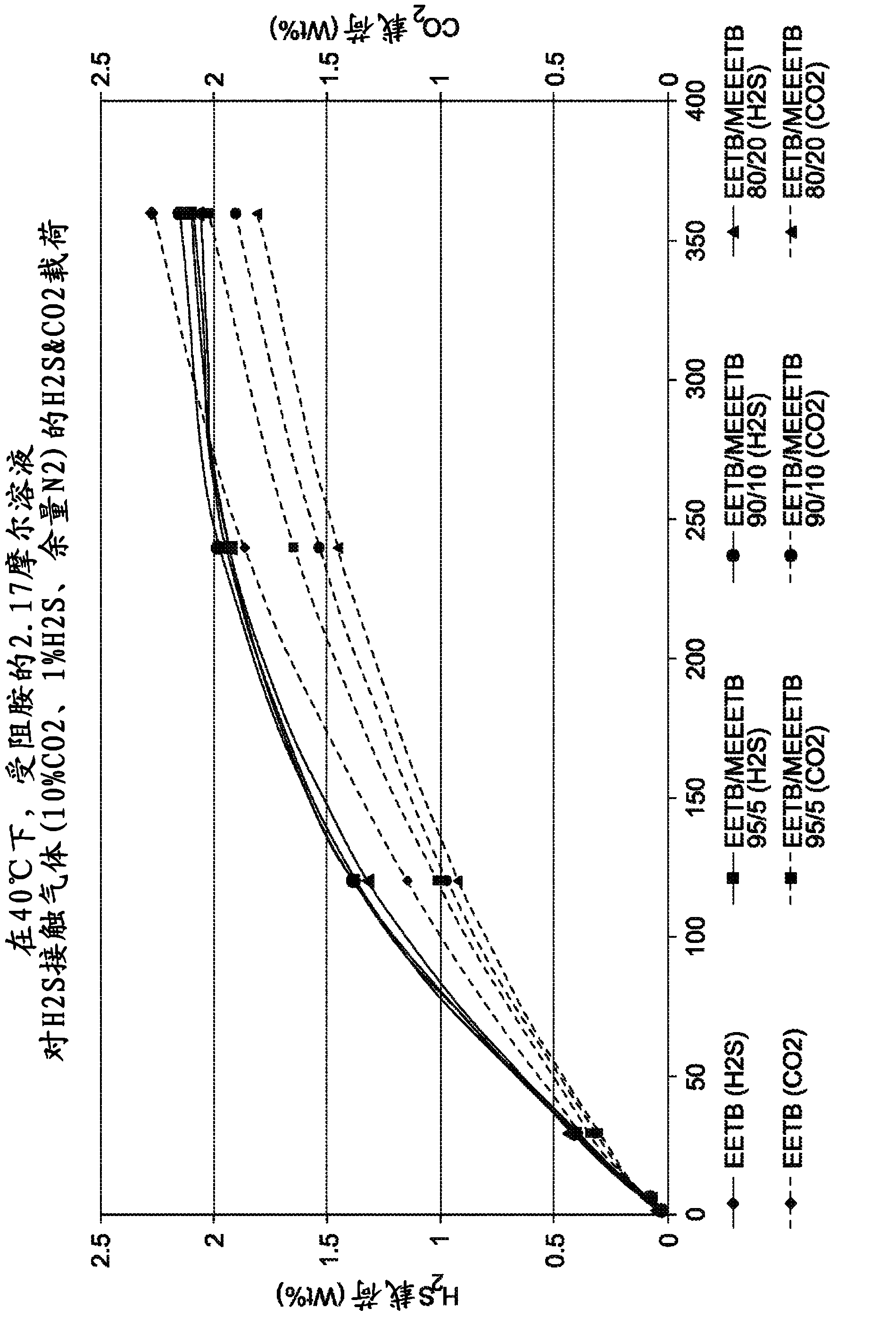
[0098] Other studies conducted in the same way with ether amines and ether amine mixtures show that the mixture has H 2 The potential advantages of S selectivity and load are shown in Table 1 below:
[0099] Table 1
[0100]
[0101] Bis-SE = Bis-(tert-butylamino)-diethylene glycol
[0102] TEGTB=Triethylene glycol-tert-butylamine
[0103] TEG(TB) 2 =Bis-(tert-butylamino)-triethylene glycol
[0104] Load = H 2 The molar amount of S / the molar amount of absorbent
[0105] Capacity = H absorbed by the solution 2 Molar amount of S / H after desorption from solution 2 S molar amount
[0106] Therefore, even if TEGTB and TEG(TB) 2 Compared with MEEETB (219.32), the mixture has a molecular weight disadvantage (weight-average molecular weight of 241.61), but results in the purchase of fewer moles of absorbent per unit weight and the increased H generated by the two reaction sites on the two amine groups 2 S selectivity and load, approximately twice that of MEEETB, make the use of the mixture attrac...
Embodiment 3
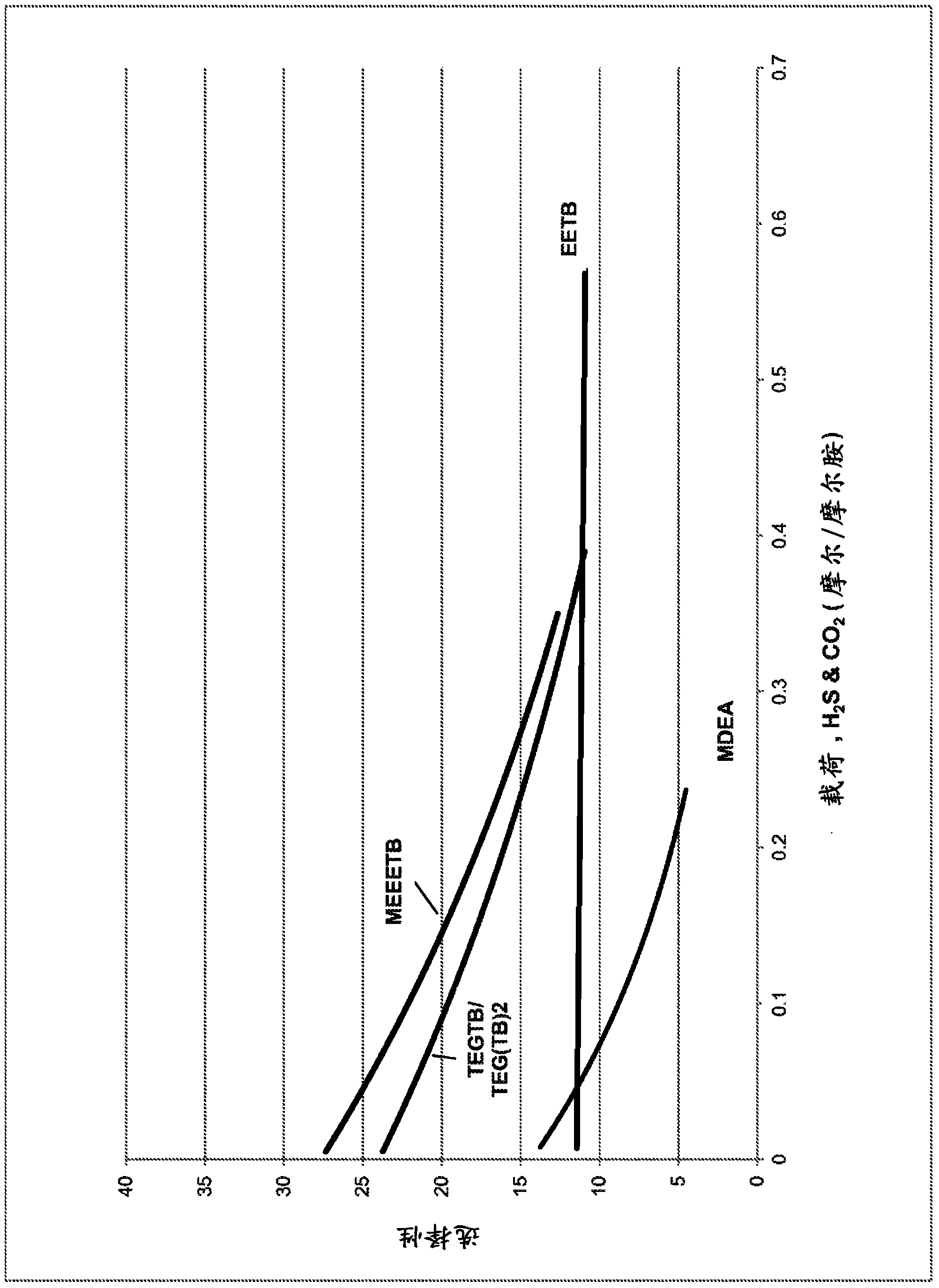
[0108] Use the same method to use MDEA, EETB, MEEETB and a mixture of TEGTB and TEG(TB)2 (57.8% / 35%, unreacted TEG as the balance) continue to evaluate to show H 2 The relationship between S selectivity and a wide range of loads. The results are shown in image 3 in. MDEA has approximately the same selectivity as EETB, but only at very low loads, after which the selectivity deteriorates sharply at a higher rate. EETB has the advantage of linear selectivity under all loads. MEEETB and TEG mixtures are significantly more selective than EETB at low to medium loadings, where MEETB has marginal advantages, but a given loading doubling is provided by the bis-(amino) derivatives in the mixture (see Example 2), the mixture has Compared with other materials, obvious selectivity advantages.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com