Working electrode biological reactant and application and electrode-type test strip thereof
A working electrode and biological reaction technology, applied in the field of electrochemical detection, can solve the problems of increasing detection cost and increasing operation difficulty, and achieve the effect of avoiding interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
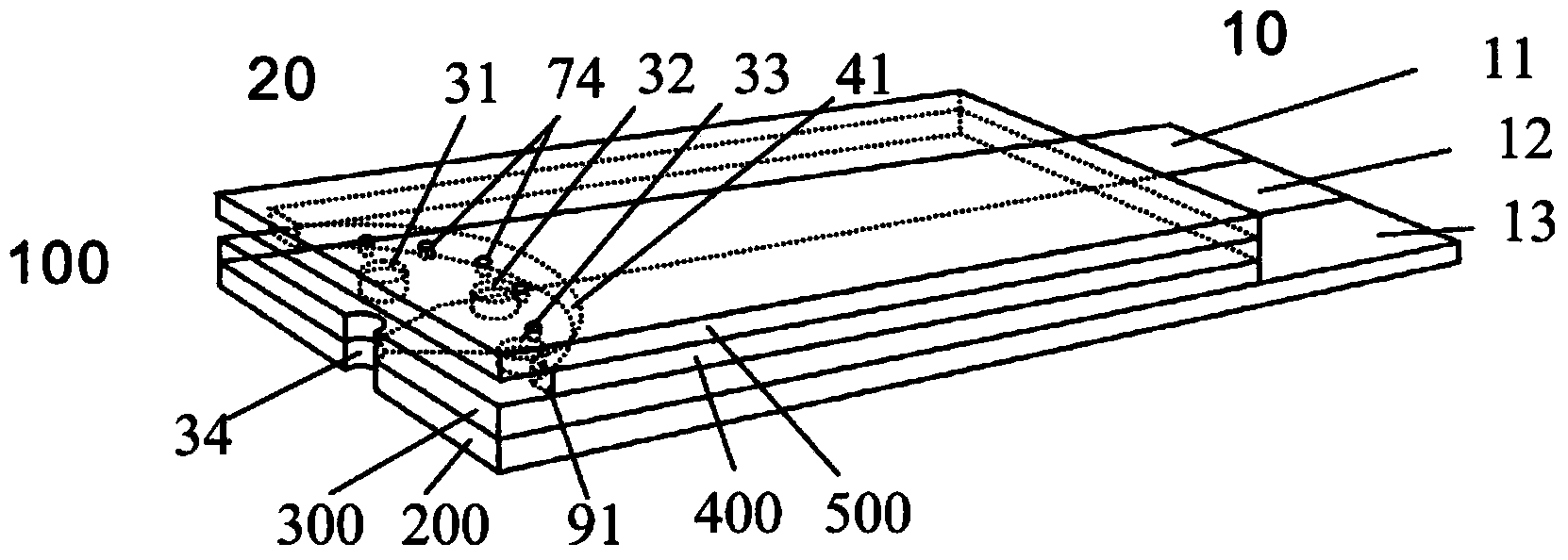
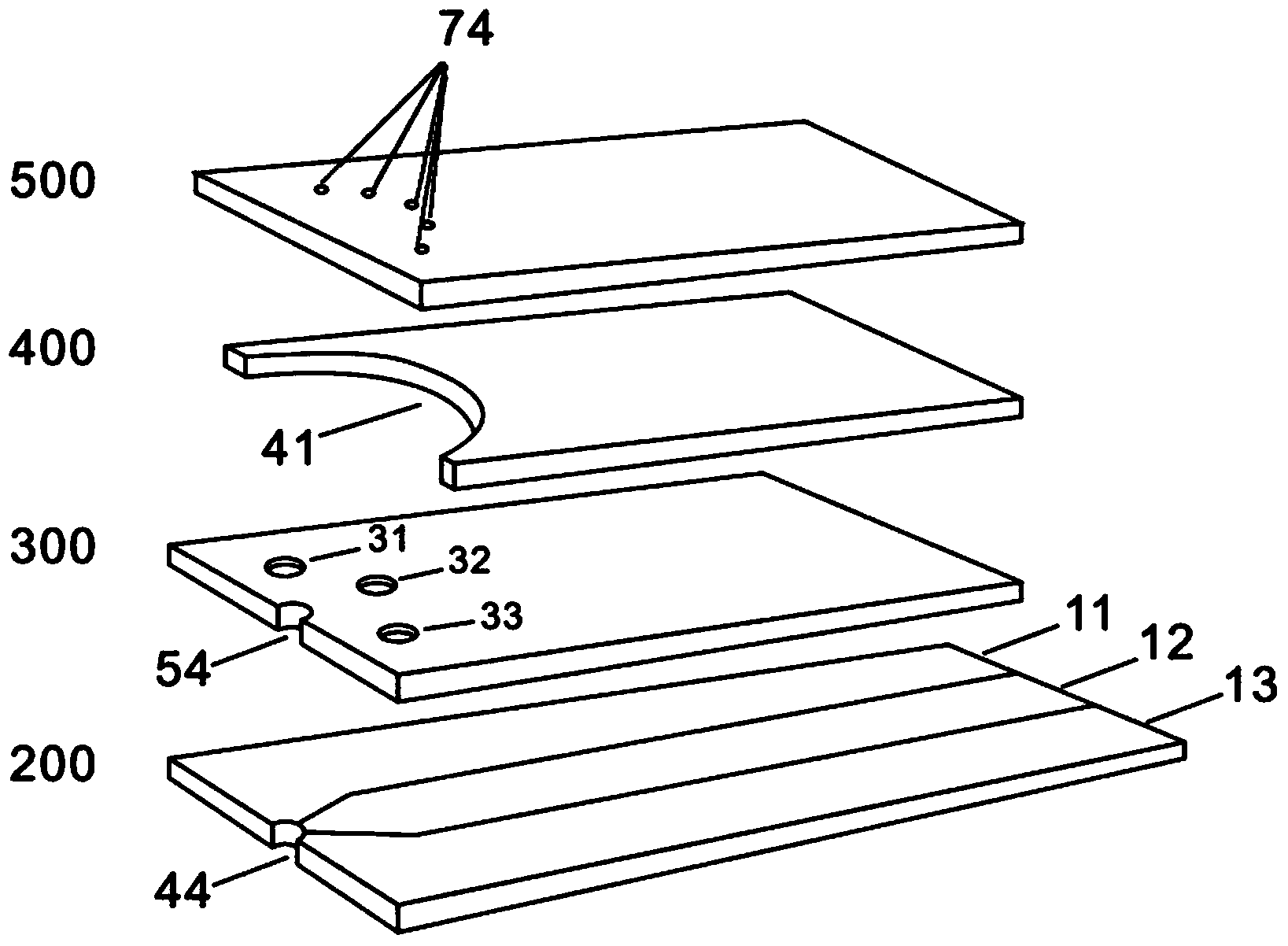
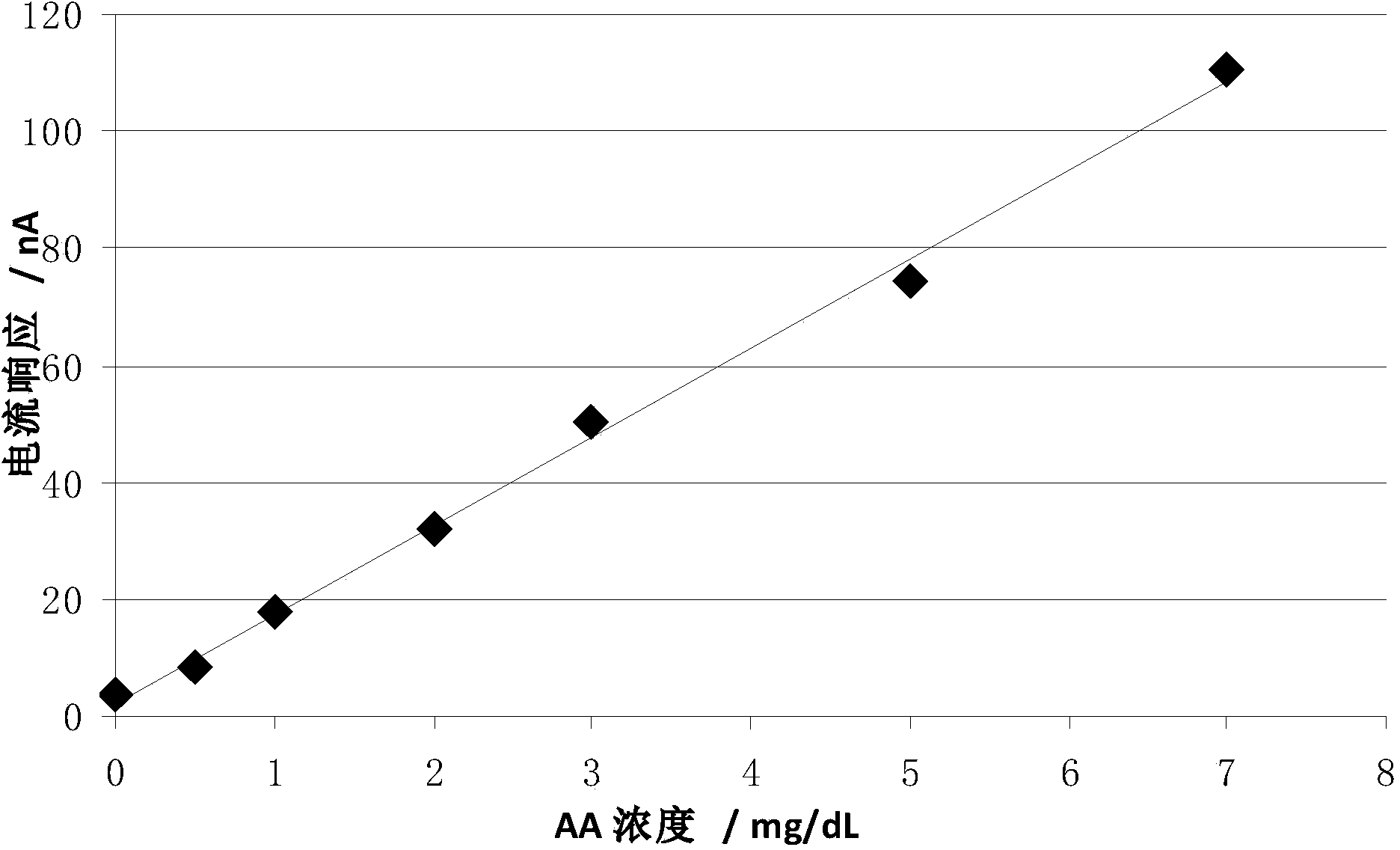
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Embodiment 1 The preparation of working electrode and reference electrode bioreaction membrane liquid
[0076] The formulation of the working electrode bioreaction membrane solution is shown in Table 1.
[0077] Table 1 The formula of the working electrode bioreaction membrane liquid
[0078]
[0079]
[0080] Take 80.85mL ultrapure water, add 8g methylcellulose, 5g lactose and 0.05g Triton-100, stir for 4 hours and dissolve completely. Then, 4 g of potassium ferrocyanide and 0.1 g of sodium sulfite were added, stirred and dissolved. Finally, 1 g of ascorbate oxidase (216 U / mg, purchased from Amano, Japan) and 1 g of peroxidase (254 U / mg, purchased from Japan Toyobo) were added, stirred and dissolved to obtain the working electrode bioreaction membrane solution.
[0081] The formulation of the reference electrode bioreaction membrane solution is shown in Table 2.
[0082] Table 2 The formula of the reference electrode bioreaction membrane liquid
[0083]
...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Embodiment 2 Preparation of working electrode and reference electrode bioreaction membrane liquid
[0086] The formulation of the working electrode bioreaction membrane solution is shown in Table 3.
[0087] Table 3 The formula of the working electrode bioreaction membrane liquid
[0088]
[0089]
[0090] Take 94.22mL ultrapure water, add 1g methylcellulose, 1g lactose and 0.03g Triton-100, stir for 4 hours and dissolve completely. Then, 0.5 g of potassium ferrocyanide and 0.5 g of sodium sulfite were added, stirred and dissolved. Finally, 0.25 g of ascorbate oxidase (216 U / mg, purchased from Amano, Japan) and 2.5 g of peroxidase (254 U / mg, purchased from Japan Toyobo) were added, stirred and dissolved to obtain the working electrode bioreaction membrane liquid.
[0091] The formulation of the reference electrode bioreaction membrane solution is shown in Table 4.
[0092] Table 4 The formula of reference electrode bioreaction membrane liquid
[0093]
[00...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Embodiment 3 Preparation of working electrode and reference electrode bioreaction membrane liquid
[0096] The formulation of the working electrode bioreaction membrane solution is shown in Table 5.
[0097] Table 5 The formula of the working electrode bioreaction membrane liquid
[0098]
[0099]
[0100] Take 68.15mL ultrapure water, add 10g methylcellulose, 10g lactose and 0.1g Triton-100, stir for 4 hours and dissolve completely. Then, 8 g of potassium ferrocyanide and 1 g of sodium sulfite were added and stirred to dissolve. Finally, 2.5 g of ascorbate oxidase (216 U / mg, purchased from Amano, Japan) and 0.25 g of peroxidase (254 U / mg, purchased from Japan Toyobo) were added, stirred and dissolved to obtain the working electrode bioreaction membrane liquid.
[0101] The formula of the reference electrode bioreaction membrane solution is shown in Table 6.
[0102] Table 6 The formula of reference electrode bioreaction membrane liquid
[0103]
[0104] Ta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com