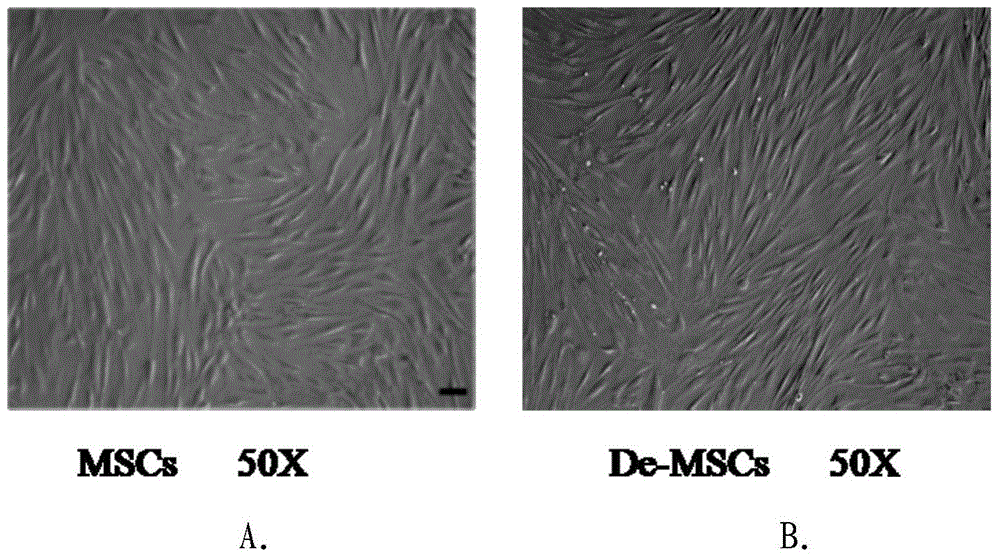
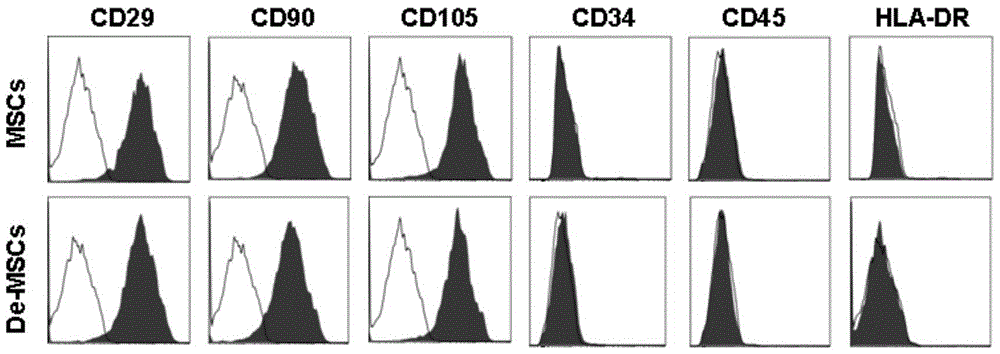
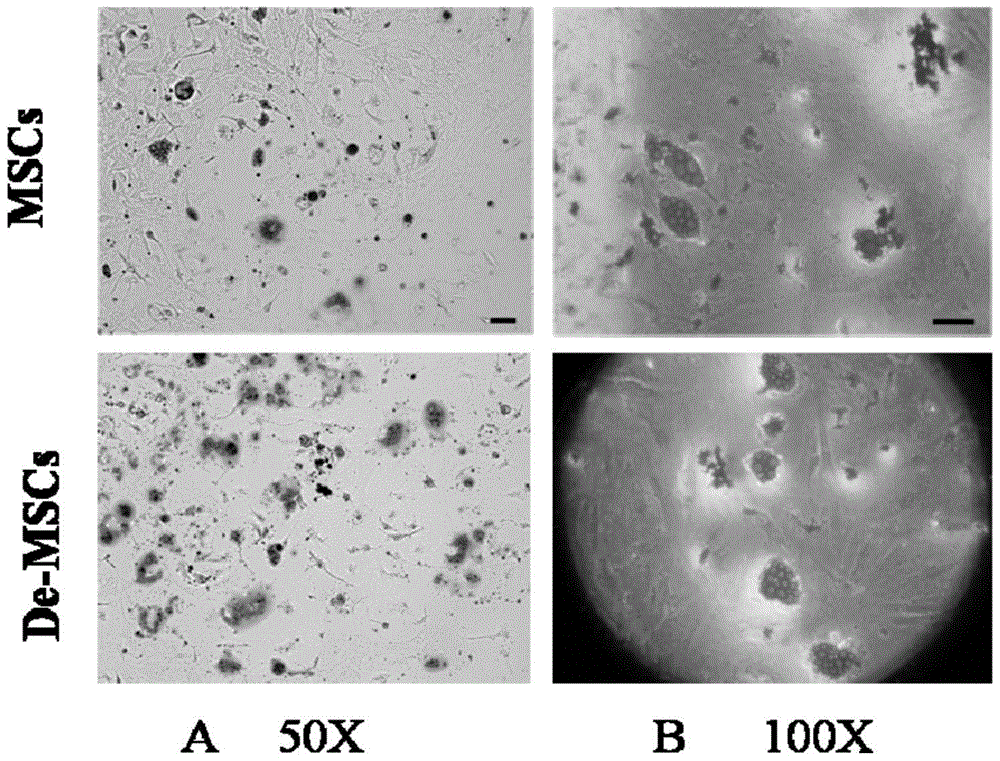
A method for culturing bone marrow dedifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells
A technology for bone marrow mesenchymal and stromal stem cells, which is applied in the field of culturing human bone marrow dedifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells, can solve the problems of long time period, complicated experimental process and high experimental cost, and achieves short experimental period, low experimental cost, Simple and convenient experimental operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Example 1: Induced and cultured osteogenic dedifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells and their biological characteristics analysis experiments
[0067] 1. Materials
[0068] 1.1 Reagents
[0069] 1640 complete medium: Hyclone (US); fetal bovine serum, trypsin, penicillin and streptomycin: Gibco (US); PBS: solarbio (US); DMSO, trypsin, dexamethasone, β-glycerol phosphate , 2-Phosphate-L-VitC, were purchased from Sigma Company (USA), all antibodies involved in the test were purchased from eBioscience Company (USA), cell culture dishes and 48, 96-well plates: Corning (USA), cck8 kit ( Dojindo Japan). The rest of the reagents were of domestic analytical grade.
[0070] 1.2. Instruments
[0071] CO 2 Incubator, Thermo (USA); ultra-clean workbench (Suzhou Purification Equipment Factory); biological safety cabinet (Beijing Wuzhou Technology Development Co., Ltd.); high-pressure steam sterilizer, constant temperature oven (Babajin Experimental Equipment Co., Ltd.); enzyme I...
Embodiment 2
[0096] Example 2: In vitro osteogenic potential analysis experiment of induced cultured dedifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells
[0097] 1. Materials
[0098] 1.1 Reagents
[0099] 1640 medium: Hyclone (USA); fetal bovine serum, trypsin, penicillin and streptomycin: Gibco (USA); PBS: solarbio (USA); DMSO, trypsin, dexamethasone, β-glycerol phosphate, 2-Phosphate-L-VitC and Alizarin Red were purchased from Sigma (USA), all antibodies involved in the test were purchased from eBioscience (USA), cell culture dishes and 48, 96-well plates: Corning (USA), cck8 reagent Kit (Dojindo Japan), reverse transcription reagents and qPCR reagents were purchased from Takara Company (Japan), ALP kit (Nanjing Jitian Company). The rest of the reagents were of domestic analytical grade.
[0100] 1.2 Instruments
[0101] CO 2 Incubator, Thermo (USA); ultra-clean workbench: Suzhou Purification Equipment Factory; biological safety cabinet: Beijing Wuzhou Technology Development Co., Ltd.; high-pr...
Embodiment 3
[0154] Example 3: In vivo osteogenic potential analysis experiment of induced cultured dedifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells
[0155] 1. Materials
[0156] 1.1 Reagents
[0157] 1640 medium: Hyclone (USA); fetal bovine serum, trypsin, penicillin and streptomycin: Gibco (USA); PBS: solarbio (USA); DMSO, trypsin, dexamethasone, β-glycerol phosphate, 2-Phosphate-L-VitC was purchased from Sigma (USA); cell culture dishes and 48 and 96-well plates: Corning (USA); Trizol, reverse transcription reagents and qPCR reagents were purchased from Takara Company (Japan); ALP reagents Box (Nanjing Jitian Company); collagen module (gifted by Professor Dai Jianwu, Chinese Academy of Sciences); BCA protein quantification kit, RIPA lysate, PMSF: Beyond Institute of Biotechnology (Shanghai). The rest of the reagents were of domestic analytical grade.
[0158] 1.2 Instruments
[0159] CO 2 Cell incubator, Thermo (USA); paraffin slicer: Leica (Germany); ultra-clean bench: Suzhou Purification...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com