Tetra-allkylammonium ionic liquid for proton exchange membrane fuel cell
A proton exchange membrane and fuel cell technology, applied in solid electrolyte fuel cells, fuel cells, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as difficult electrolytes, high melting point of ionic liquids, and few applied researches
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
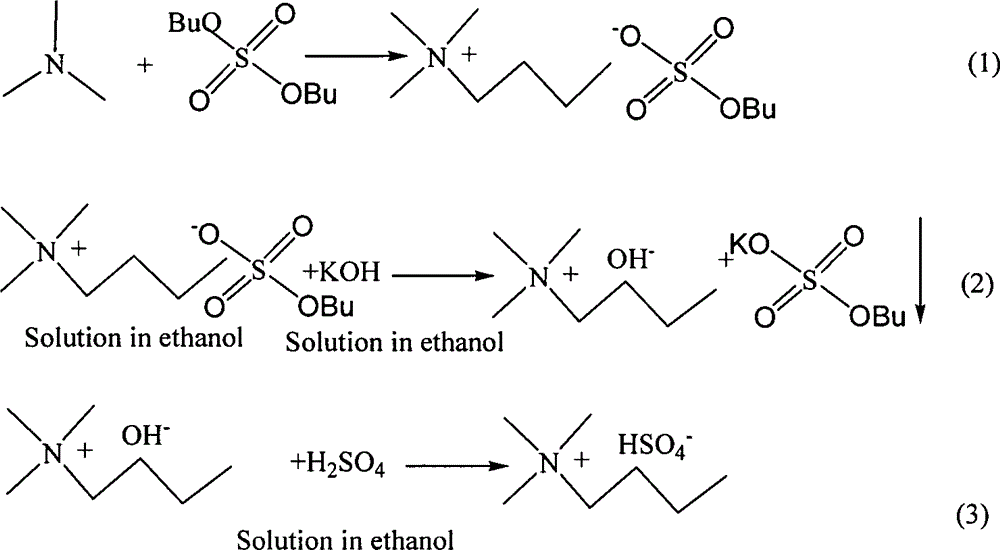
[0015] Embodiment one: N, N, N trimethyl-N-butyl bisulfate ([N1114]HSO 4 )synthesis
[0016] (1) Add 0.1 mol trimethylamine aqueous solution to a single-necked flask, then add 0.1 mol dibutyl sulfate, heat and stir in a 50°C water bath for about 12 hours after the addition, to obtain a colorless transparent ionic liquid aqueous solution.
[0017] (2) Dissolve the above liquid and 0.15mol KOH in ethanol respectively, then mix the two solutions, remove the resulting white precipitate, and collect the filtrate to obtain a colorless liquid.
[0018] (3) Add 0.15 moles of H to the solution 2 SO 4 , stirred evenly to obtain a colorless transparent liquid. The liquid was evaporated in a rotary evaporator to remove most of the water, ethanol and acetic acid produced to obtain a light yellow viscous liquid, which was dried in vacuum to obtain a viscous light yellow liquid, which was the product.
Embodiment 2
[0019] Embodiment two: N, N, N trimethyl-N-propyl bisulfate ([N1113]HSO 4 )synthesis
[0020] (1) Add 0.1 mol trimethylamine aqueous solution to a single-necked flask, then add 0.1 mol dipropyl sulfate, heat and stir in a 50°C water bath for about 12 hours after the addition, to obtain a colorless transparent ionic liquid aqueous solution.
[0021] (2) Dissolve the above liquid and 0.15mol KOH in ethanol respectively, then mix the two solutions, remove the resulting white precipitate, and collect the filtrate to obtain a colorless liquid.
[0022] (3) Add 0.15 moles of H to the solution 2 SO 4 , stirred evenly to obtain a colorless transparent liquid. The liquid was evaporated in a rotary evaporator to remove most of the water, ethanol and acetic acid produced to obtain a light yellow viscous liquid, which was dried in vacuum to obtain a viscous light yellow liquid, which was the product.
Embodiment 3
[0023] Embodiment three: N, N, N trimethyl-N-ethyl bisulfate ([N1112]HSO 4 )synthesis
[0024] (1) Add 0.1 mol trimethylamine aqueous solution to a single-necked flask, then add 0.1 mol diethyl sulfate, heat and stir in a 50°C water bath for about 12 hours after the addition, to obtain a colorless transparent ionic liquid aqueous solution.
[0025] (2) Dissolve the above liquid and 0.15mol KOH in ethanol respectively, then mix the two solutions, remove the resulting white precipitate, and collect the filtrate to obtain a colorless liquid.
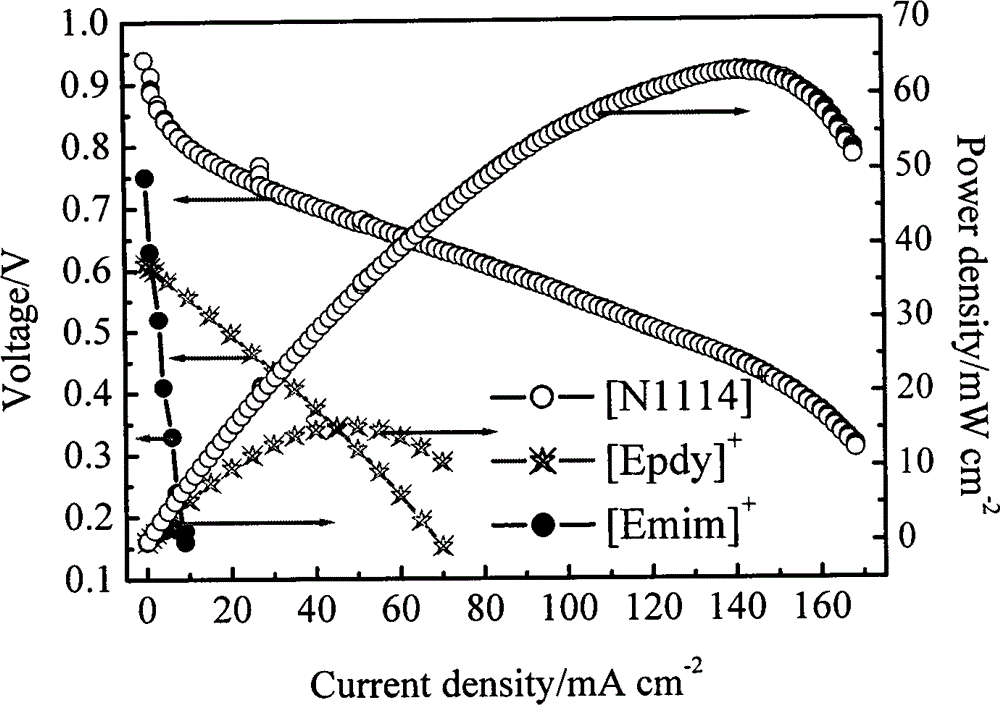
[0026] (3) Add 0.15 moles of H to the solution 2 SO 4, stirred evenly to obtain a colorless transparent liquid. Evaporate the liquid in a rotary evaporator to remove most of the water ethanol and the acetic acid produced to obtain a light yellow viscous liquid, dry it in vacuum and wash with ethanol to obtain a white solid, which is the product. Although this ionic liquid is not suitable as a PEMFC An electrolyte, but also a salt that c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com