Method for knocking out human papillomavirus e6e7 gene by zinc finger nuclease
A technology of human papillomavirus and zinc finger nuclease, which is applied in the fields of genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, botany equipment and methods, etc., and can solve problems such as limitation of drug delivery methods and poor stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0025] Example 1. Construction of ZFN16-603 expression vector
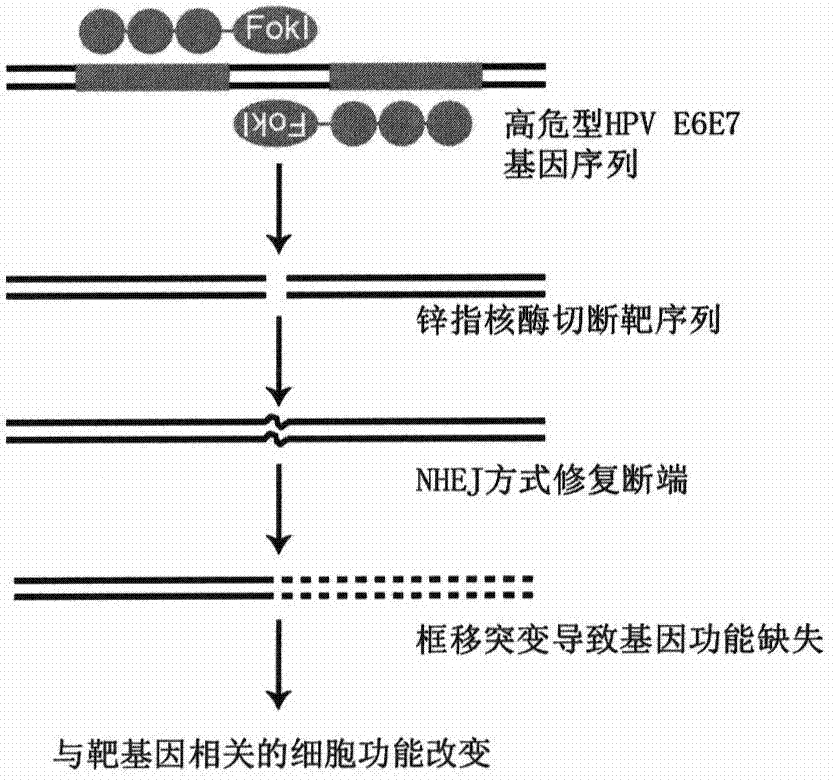
[0026] The E6E7 oncogene sequence information of HPV16 was obtained from the NCBI website, and the sequence was imported into the online design tool ZiFiT (http: / / zifit.partners.org / ZiFiT / ) to complete the design. The ZFNs pair targeting base 603 was selected and named ZFN16-603. The targeted DNA sequence is:
[0027] ZFN16-603: CAG AGG AGG AGG ATGAAA TAG ATG GTC CAG
[0028] The underlined part is the zinc finger protein binding sequence, and the middle part is the cleavage site of FokI endonuclease. The corresponding ZFNs expression vectors were named ZFN16-603F and ZFN16-603R, respectively.
[0029] For the construction method of zinc finger ribozyme expression vector, refer to Wright, D A et al., Nature Protocol, (2006) 1: 1637-1652, and the vector used for construction is pcDNA3.1+ (Invitrogen, USA, catalog number: V790-20).
[0030] After the construction is completed, it is confirmed th...
example 2
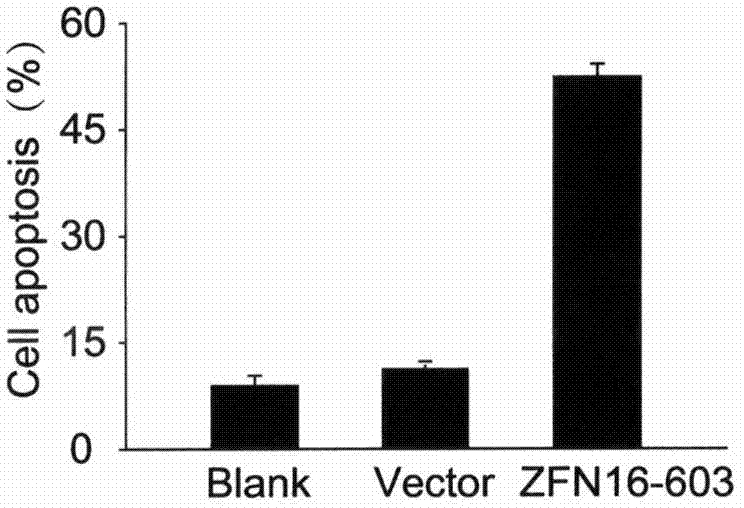
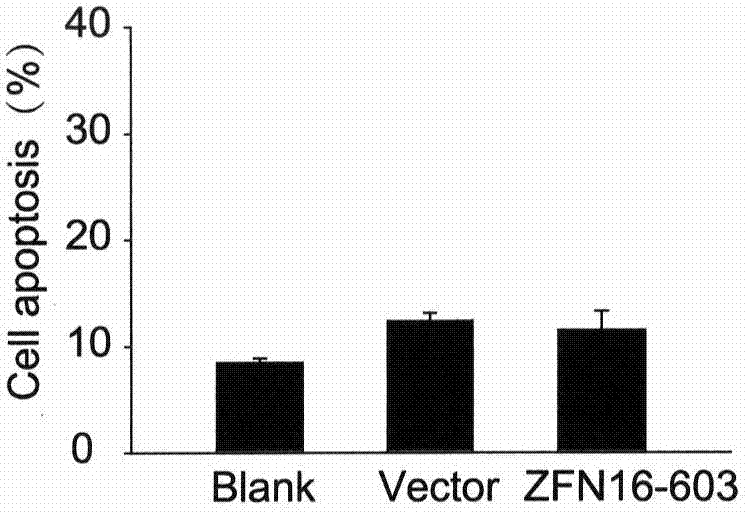
[0031] Example 2. ZFN16-603 induces apoptosis
[0032] ZFN16-603 targeting HPV16E6E7 is transfected into cells and expressed zinc finger ribozyme can quickly recognize and bind to the target sequence, and then play a cutting role, making it generate DSB at the target site, DSB activates the cell to use easily The wrong NHEJ repair mechanism is repaired; the base insertion or deletion caused by the repair causes the frame shift mutation of the codon, and finally the expression of the HPV16E6E7 protein is inhibited. The E6E7 protein can enhance the proliferation ability of cervical cancer cells and escape apoptosis through a series of mechanisms. After the expression of E6E7 protein is inhibited, the proliferation ability of the cells decreases and the apoptosis increases. On the other hand, ZFN16-603 can only specifically recognize and bind to the HPV16E6E7 sequence, but cannot recognize the E6E7 sequence of other subtypes such as HPV18. Therefore, ZFN16-603 can only induce ap...
example 3
[0041] Example 3. Verification of cutting efficiency of ZFN16-603
[0042] Zinc finger ribozymes cut and form DSBs after functioning in cells, inducing cells to use the error-prone NHEJ repair method to repair. After the repair, the insertion or deletion of bases is caused at the target site, thereby causing frame-shift mutations and achieving the purpose of gene knockout. At this time, if the wrongly repaired base sequence is annealed and extended with the normal (wild-type) base sequence, a hybrid double strand can be formed, and the base sequence of this hybrid double strand will occur at the original site. Mismatches (corresponding to the base insertion or deletion after repair), and then treated with T7Endonuclease I (NewEngland Biolabs, Cat. No.: M0302S), which can recognize and cut such mismatched bases in the sequence, can indirectly reflect Cutting efficiency of ZFNs. Due to the limitation of transfection efficiency, the successfully transfected cells were effective...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com