Vanadium and tungsten recovered from scrap selective catalytic reduction catalyst
A catalyst and selective technology, applied in the field of recovery of vanadium and tungsten, can solve the problems of reduced recovery, cumbersome operation steps, pollution of the environment, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] "Pre-processing steps"
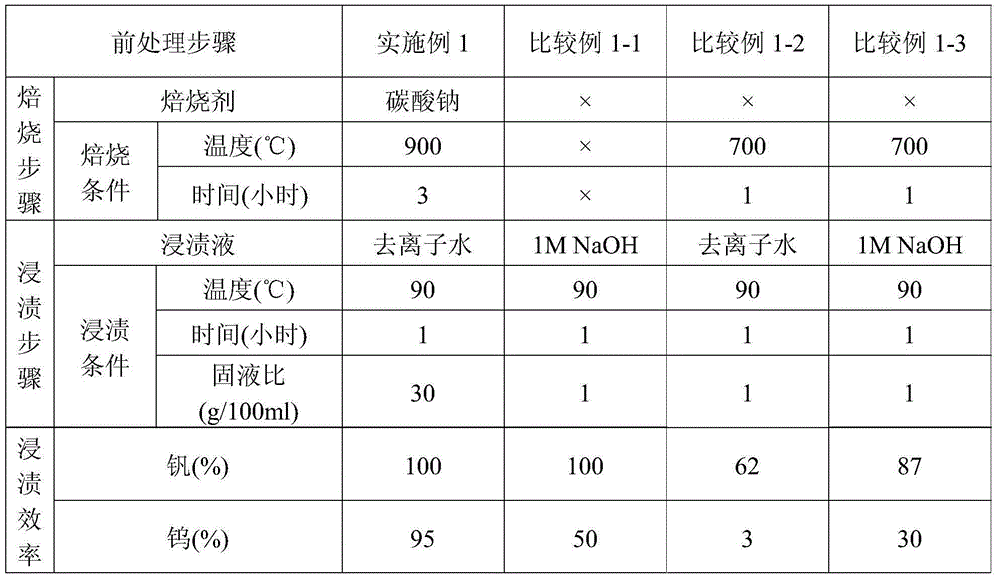
[0070] [Roasting step]: Take the waste selective catalytic reduction catalyst (hereinafter referred to as waste SCR catalyst, manufacturer model: SINOx@Argillon Plate type SCR Catalyst), the waste SCR catalyst contains vanadium source (vanadium oxide V 2 o 5 ) and tungsten source (tungsten oxide WO 3 ), grinding the waste SCR catalyst to below 140 mesh to form the waste SCR catalyst powder, and mixing the sintering agent (sodium carbonate) with the waste SCR catalyst powder to form a mixture (the weight ratio of the waste SCR catalyst powder to sodium carbonate =10:7), then the mixture was roasted at 900°C for 3 hours to form a roasted spent SCR catalyst, the vanadium source and the tungsten source reacted with the roasting agent to form vanadium salt (Na 2 VO 3 ) and tungsten salt (Na 2 WO 4 ).
[0071] [Impregnation step]: impregnating the waste SCR catalyst through roasting treatment in deionized water to dissolve the vanadium salt (Na ...
Embodiment 2-1
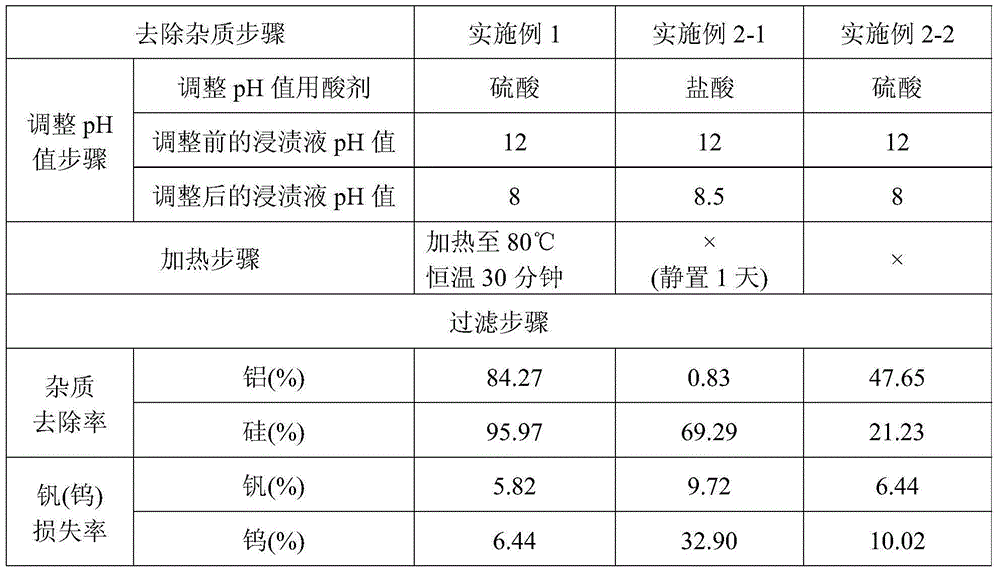
[0081] [Example 2-1] Step of removing impurities
[0082] After adjusting the pH value of the impregnation solution of Example 1 to 8.5 with hydrochloric acid (concentration: 37%), let it stand for one day, and filter to remove the mixture of impurities [comprising: Al(OH) 3 , SiO nH 2 O and aluminosilicates] to form a purified impregnating solution (containing vanadium salt V 3 o 9 3- And tungsten salt WO 4 2- ). In this precipitation separation step, the removal rate of aluminum was 0.83%, the removal rate of silicon was 69.29%, the loss rate of vanadium was 9.72%, and the loss rate of tungsten was 32.90%.
Embodiment 2-2
[0083] [Example 2-2] Impurity removal step
[0084] After adjusting the pH value of the impregnation solution of Example 1 to 8 with sulfuric acid (concentration: 98%), filter to remove the mixture of impurities [comprising: Al(OH) 3 , SiO nH 2 O and aluminosilicates] to form a purified impregnating solution (containing vanadium salt V 3 o 9 3- And tungsten salt WO 4 2- ). In this precipitation separation step, the removal rate of aluminum was 47.65%, the removal rate of silicon was 21.23%, the loss rate of vanadium was 6.44%, and the loss rate of tungsten was 10.02%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com