Polyamide with sulfonic acid group
A technology of sulfonic acid groups and polyamides, applied in the field of polyamides, can solve the problems of lack of dyeing fastness of cationic dyes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
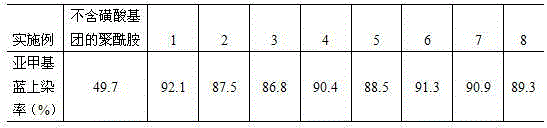
[0024] Add 2g of 5-sulfosalicylic acid, 2.1g of polyvinylpyrrolidone and a catalyst to 40g of polybutylene adipamide, heat to melt under a nitrogen atmosphere, gradually raise the temperature to 90°C, and react at a constant temperature for 2 hours. Then gradually raise the temperature to 260°C, and react at constant temperature for 3h. The polymer was decanted from the reaction vessel and soaked several times with sufficient distilled water to remove unreacted monomer. After drying in a vacuum drying oven for 24 hours, it was melt spun at a spinning speed of 600 m / min to obtain easily dyed fibers. The dyeing properties of the fibers are listed in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0026] Add 5g of 2-amino-5-sulfobenzoic acid, 0.9g of polyvinylpyrrolidone and a catalyst to 40g of polyhexamethylene dodecanediamide, heat it to melt under a nitrogen atmosphere, and gradually raise the temperature to 120°C. Constant temperature reaction 1h. Then gradually raise the temperature to 280° C., and react at constant temperature for 4 hours. The polymer was decanted from the reaction vessel and soaked several times with sufficient distilled water to remove unreacted monomer. After drying in a vacuum drying oven for 24 hours, it was melt spun at a spinning speed of 600 m / min to obtain easily dyed fibers. The dyeing properties of the fibers are listed in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0028] Add 2g of 5-sulfosalicylic acid, 1g of polyvinylpyrrolidone and a catalyst to 40g of 11-aminoundecanoic acid, add an appropriate amount of distilled water, and heat to 200°C for 3 hours at a constant temperature under a nitrogen atmosphere. Then the temperature was gradually increased to 270 °C, and the reaction was carried out at constant temperature for 6 h. The polymer was decanted from the reaction vessel and soaked several times with sufficient distilled water to remove unreacted monomer. After drying in a vacuum drying oven for 24 hours, it was melt spun at a spinning speed of 600 m / min to obtain easily dyed fibers. The dyeing properties of the fibers are listed in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com