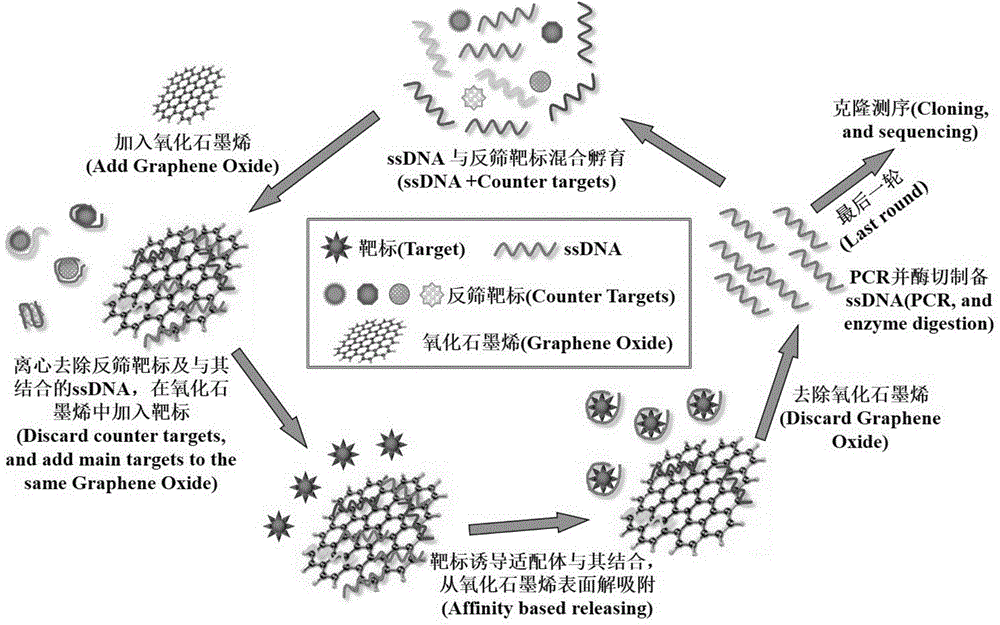
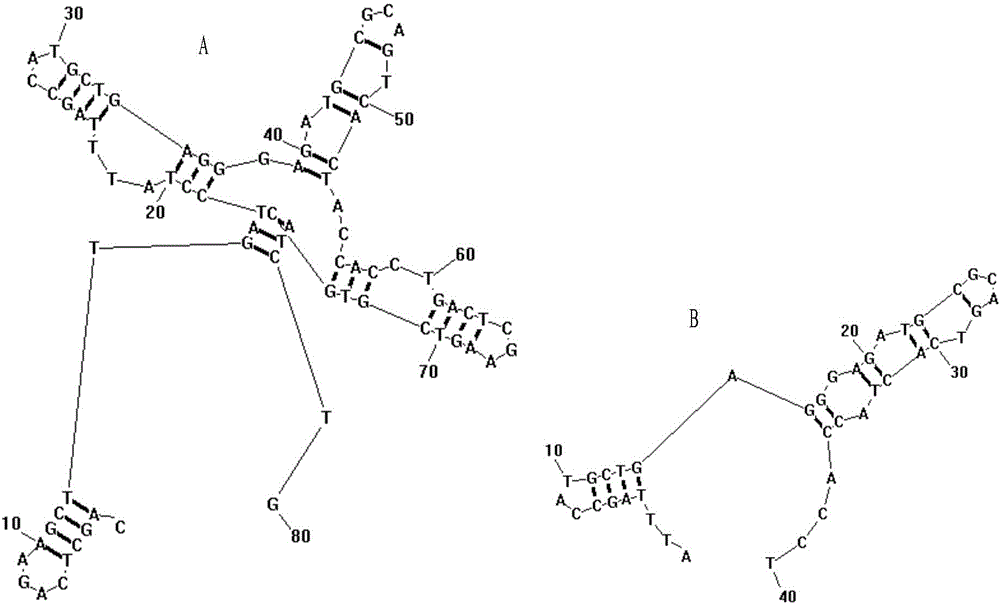
Group of nucleic acid aptamers for specifically recognizing okadaic acid
A technology of okadaic acid and nucleic acid aptamer, applied in recombinant DNA technology, DNA/RNA fragments, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problem of poor repeatability and stability of antibodies, tedious and time-consuming process, and harsh storage conditions and other problems, to achieve the effect of easy chemical modification, good stability and small difference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] 1. Synthesis of random ssDNA library and primers
[0021] A random ssDNA library with a length of 80nt was constructed, consisting of 20nt primer regions at both ends and a 40nt random region in the middle, with the sequence: 5'-CAGCTCAGAAGCTTGATCCT-N 40 -GACTCGAAGTCGTGCATCTG-3'(N 40 represents 40 random nucleotides), synthesized by Integrated DNA Technologies, USA.
[0022] Upstream primer: 5'-CAGCTCAGAAGCTTGATCCT-3'
[0023] Downstream primer: 5'-CAGATGCACGACTTCGAGTC-3'
[0024] Downstream primer for 5' phosphorylation: 5'-P-CAGATGCACGACTTCGAGTC-3'
[0025] Primers were synthesized by Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
[0026] The random ssDNA library and primers were prepared with 1×TE buffer (pH 7.4) into a 100 μM stock solution and stored at -20°C for later use.
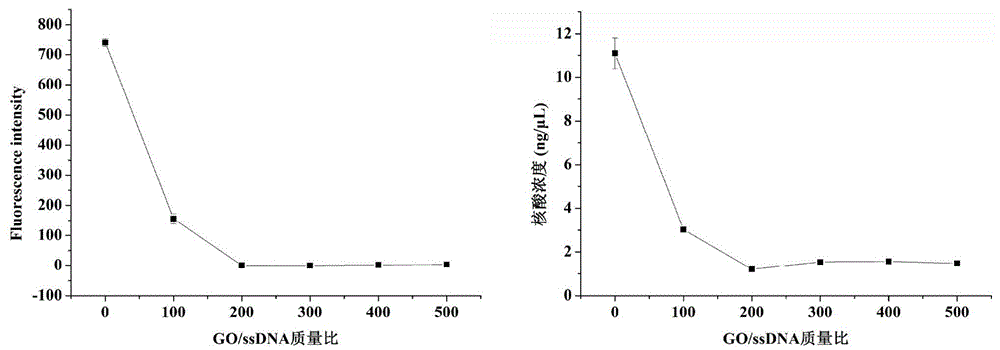
[0027] 2. Determination of the optimal amount of graphene oxide to adsorb ssDNA
[0028] Take six 2mL centrifuge tubes, add 8 μL of 10 μM carboxyfluorescein-labeled 80nt ssDNA, the mass is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com