A method of using biomass extraction products as additives in coal blending and coking
A technology of coal blending coking and biomass, which is applied in coke ovens, petroleum industry and other directions, can solve the problems of high cost and inability to further improve the effect of coal blending and coking, and achieve the effects of improving coke quality, increasing strength, and ensuring optimization effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
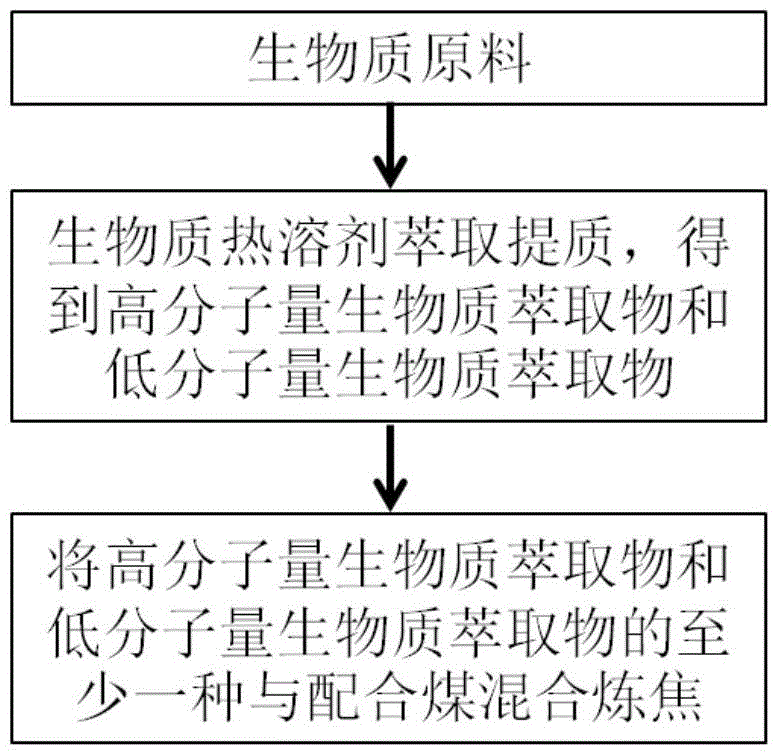
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Taking rice straw as an example, the experiment carried out hot solvent extraction and separation of rice straw in a specially designed reactor at 300°C. The solvent used was 1-methylnaphthalene, and the mass ratio of rice straw to solvent was 1:15. The diameter is 212um ~ 2mm. Raise the temperature to 300°C at a rate of 5°C / min and keep it for 90 minutes, then start in-situ thermal filtration to separate the extract and extraction residue, then filter at room temperature and distill under reduced pressure to obtain solid extracts: high molecular weight extract and low molecular weight extracts. The carbon-based yield (dry ash-free basis) of the low-molecular-weight extract was 23.10%, and the ash content of 0.06% was far lower than 9.98% of the original rice straw. Add 1% (mass percentage) of the low-molecular-weight extract of the extraction product to the Masteel blending coal (Masteel blending coal is a typical steelmaking coal blending, and the proportion of each ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Taking fir tree sawdust as an example, the experiment carried out hot solvent treatment on fir sawdust in a specially designed reactor at 350°C. The solvent used was 1-methylnaphthalene, and the mass ratio of sawdust to solvent was 1:15. The diameter is 212um ~ 2mm. Raise the temperature to 350°C at a rate of 5°C / min, keep it for 0min, and start in-situ thermal filtration to separate the extract and extraction residue, and then filter at room temperature and distill under reduced pressure to obtain solid extraction products: high molecular weight extract and low molecular weight extracts. The carbon-based yield (dry ash-free basis) of the high molecular weight extract was 39.85% with zero ash content. Add 1% (mass percentage) of the high molecular weight extract of the extraction product to the blended coal of Masteel, and then carry out crucible coking on the blended coal with and without the high molecular weight extract respectively. Compared with the coke made wit...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Taking rice straw as an example, the experiment carried out hot solvent extraction and separation of rice straw in a specially designed reactor at 350°C. The solvent used was 1-methylnaphthalene, and the mass ratio of rice straw to solvent was 1:15. The diameter is 212um ~ 2mm. Raise the temperature to 350°C at a rate of 5°C / min and keep it for 90 minutes, then start in-situ thermal filtration to separate the extract and extraction residue, then filter at room temperature and distill under reduced pressure to obtain solid extracts: high molecular weight extract and low molecular weight extracts. The carbon-based yield (dry ash-free basis) of the low-molecular-weight extract was 33.48%, and the ash content of 0.45% was far lower than 9.98% of the original rice straw. Add 1% (mass percentage) of the low molecular weight extract of the extraction product to the blended coal of Masteel, and then carry out crucible coking on the blended coal with and without the low molecul...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com