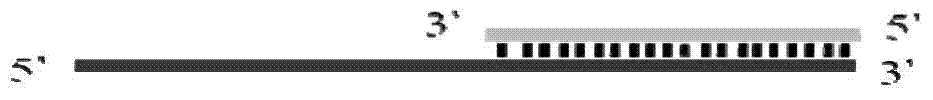
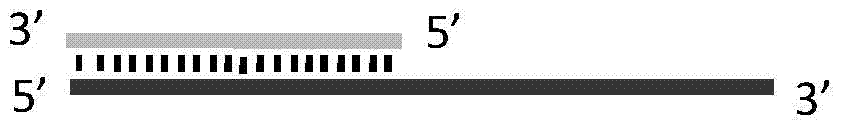
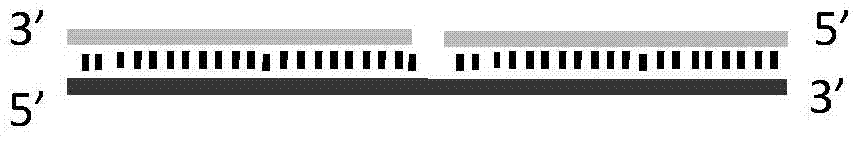
Method for implementing targeted cleavage on arbitrary nucleic acid
An endonuclease and nucleic acid technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of severe non-specific cleavage and cytotoxicity, and achieve the effect of strong versatility and good innovation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1
[0049] Gene A encoding the recognition domain was amplified according to the PCR method described below. The pET24a(+)-FEN1 plasmid template (SEQ ID NO.9), 0.025U / μL Primestar enzyme, 5mM Mg 2+ , 0.2 μM oligonucleotide primers (5'-TATACATATGGGTGCGGATATTGGTGA-3', which is SEQ ID No.10 and 5'-TATAGAATTCGAACCACCTCTCAAGCGT-3', which is SEQ ID No.11), and 0.2 mM dNTPs were added to the reaction solution respectively. Using a thermal cycler, the reaction solution was heat-treated at 94°C for 3 minutes, and then cycled 30 times with the program of "94°C for 30s, 60°C for 30s, and 72°C for 100s". The PCR amplification product was purified using a PCR purification kit. Attach instructions for purification and elute with 30 μL ultrapure water. After agarose electrophoresis analysis, the results were as follows: Figure 8 As shown, the lane M is the λ-EcoT14 I digest DNA Marker, and the lane 1 is the amplified band of the PCR product. Compared with the Marker, the ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Embodiment 2
[0051] Utilize Nde I and EcoR I enzyme-linked enzyme reaction, insert the amplified product A in Example 1 into the plasmid pET28a(+)-His-3N (i.e., SEQ ID NO.12, wherein the 1069th to 1716bp are encoding connecting peptides and the sequence of the cleavage functional domain) (whole gene synthesis of Shanghai Jierui Bioengineering Co., Ltd.) constitutes the recombinant plasmid pET28a(+)-His-A3N, and the structure of the recombinant plasmid is as follows Figure 9 shown. Transformed into the host strain ArcticExpress for preservation (purchased from China Microbial Strain Resource Bank). The strains were inoculated in 5 mL LB (containing 30 μg / mL kanamycin) liquid medium, shaken at 200 r / min at 37 °C overnight, and the plasmid was extracted by conventional methods. The extracted plasmid was treated with restriction endonucleases Xba I and Xho I, and the correctness of the plasmid was verified by agarose gel electrophoresis. The results are shown in Fig...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Embodiment 3
[0053] Using the Escherichia coli recombinant protein expression system, express the recombinant structure recognition endonuclease according to the following method. First, the recombinant plasmid prepared by the above method is transformed into the host strain ArcticExpress by a common method. The resulting transformant was inoculated into 5 mL of LB medium containing kanamycin, and incubated at 37° C. in a shaking culture until OD600 reached 0.6. The resulting culture was inoculated into 100 mL of LB medium containing kanamycin at 1%, and further incubated at 37°C with shaking until the OD600 reached 0.6. Next, isopropyl-β-thiogalactopyranoside was added to the culture at a final concentration of 0.1 mM, thereby inducing expression of the desired protein, and induced by shaking culture at 25° C. for 16 hours. Collect the cells induced to express, sonicate the bacteria, and centrifuge. Since the recombinant protein contains a histidine tag, the super...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com