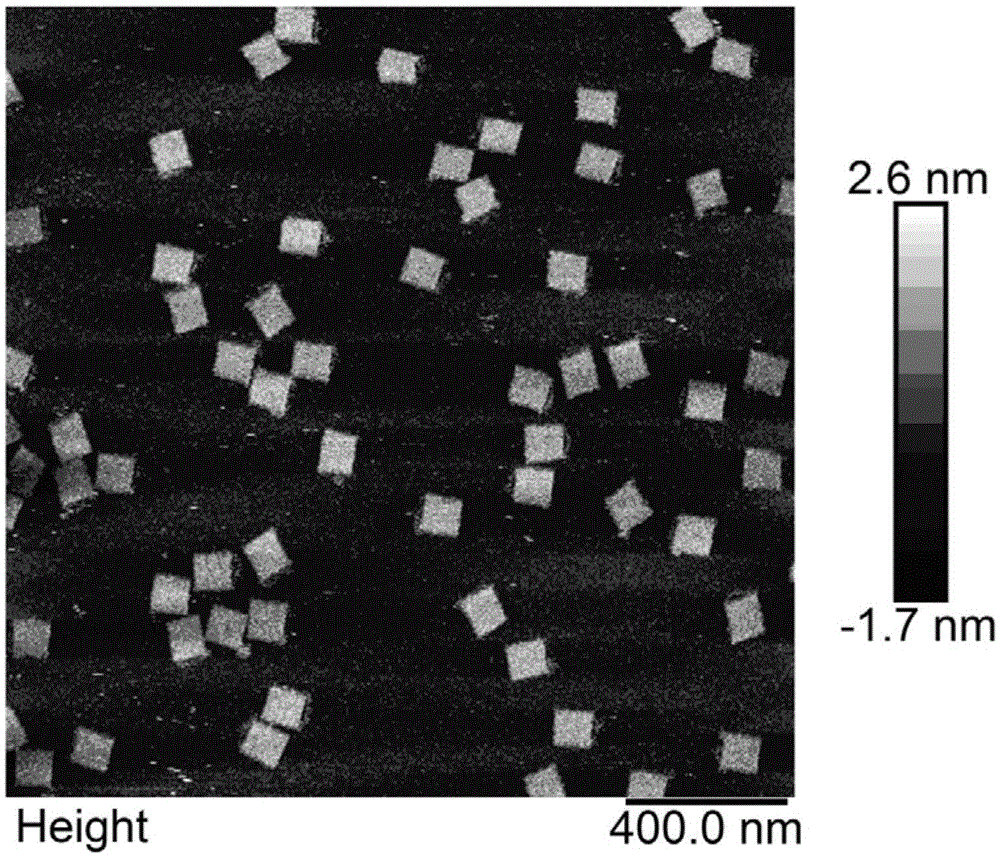
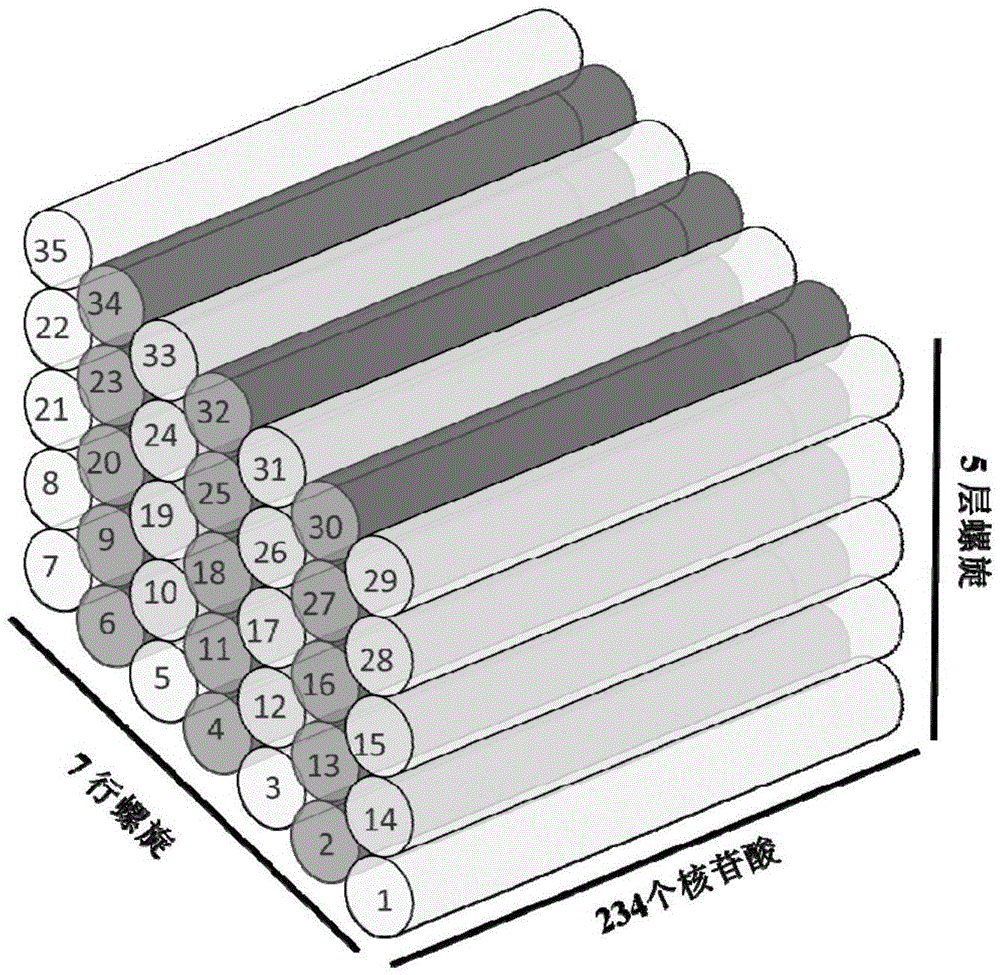
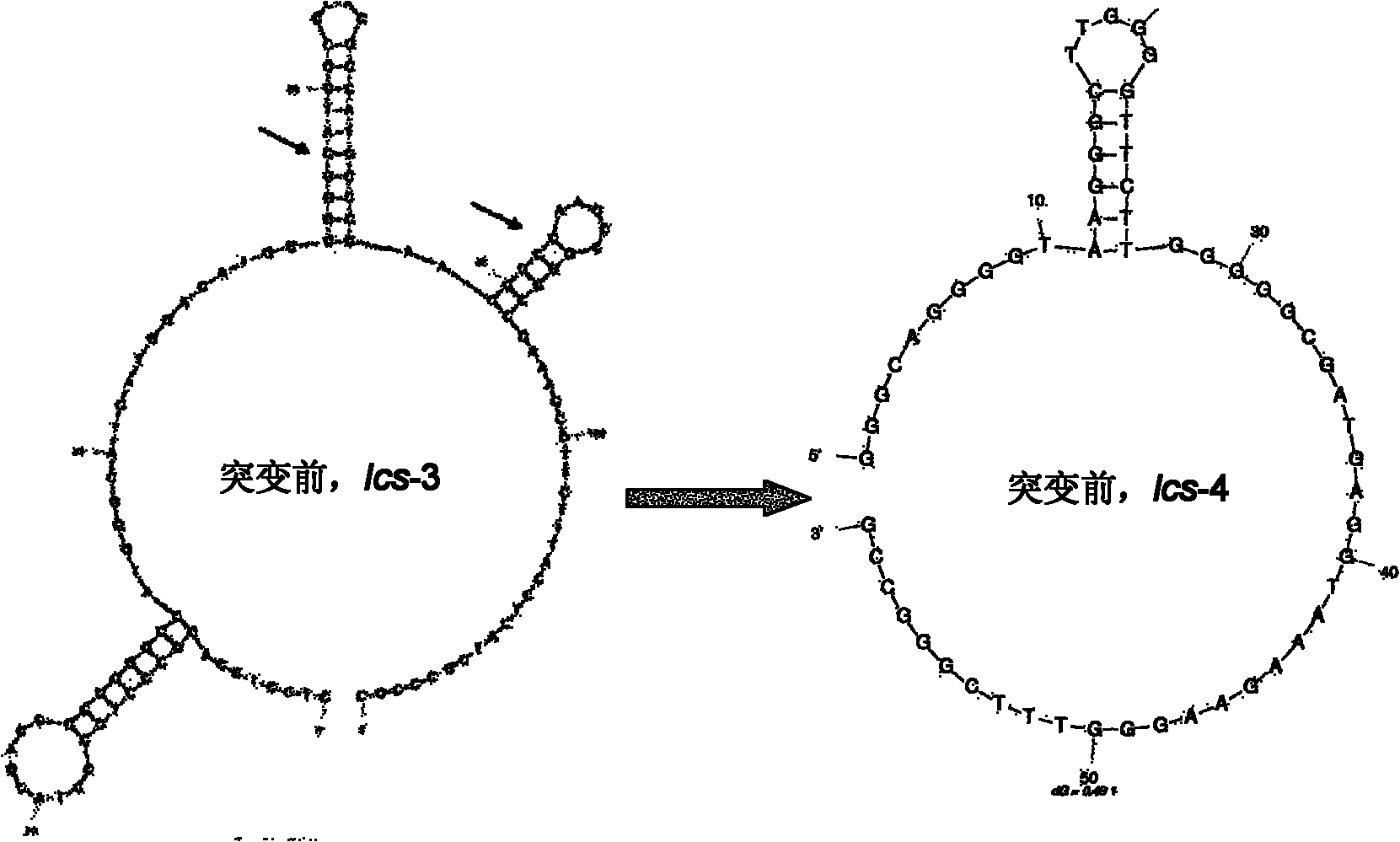
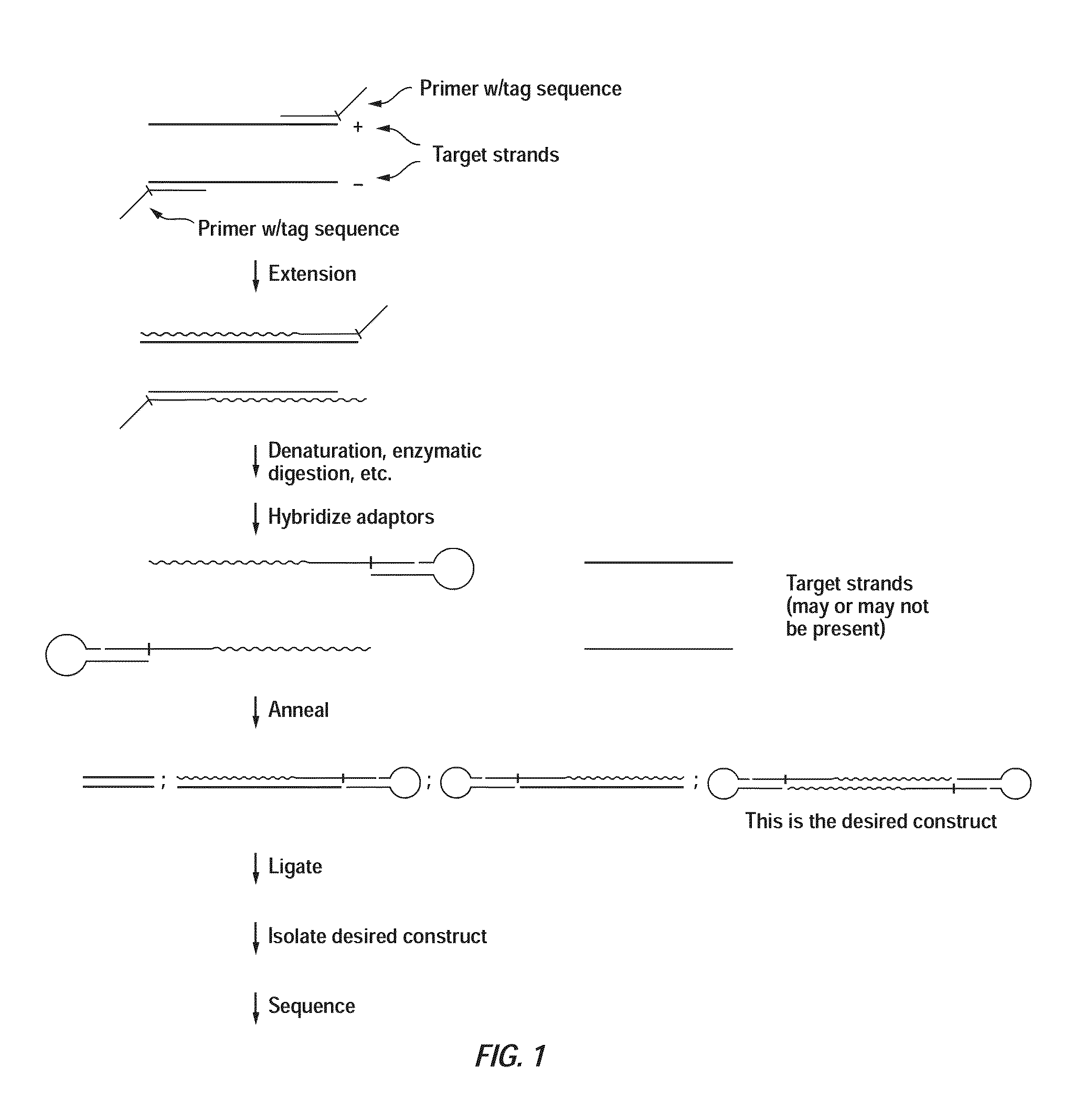
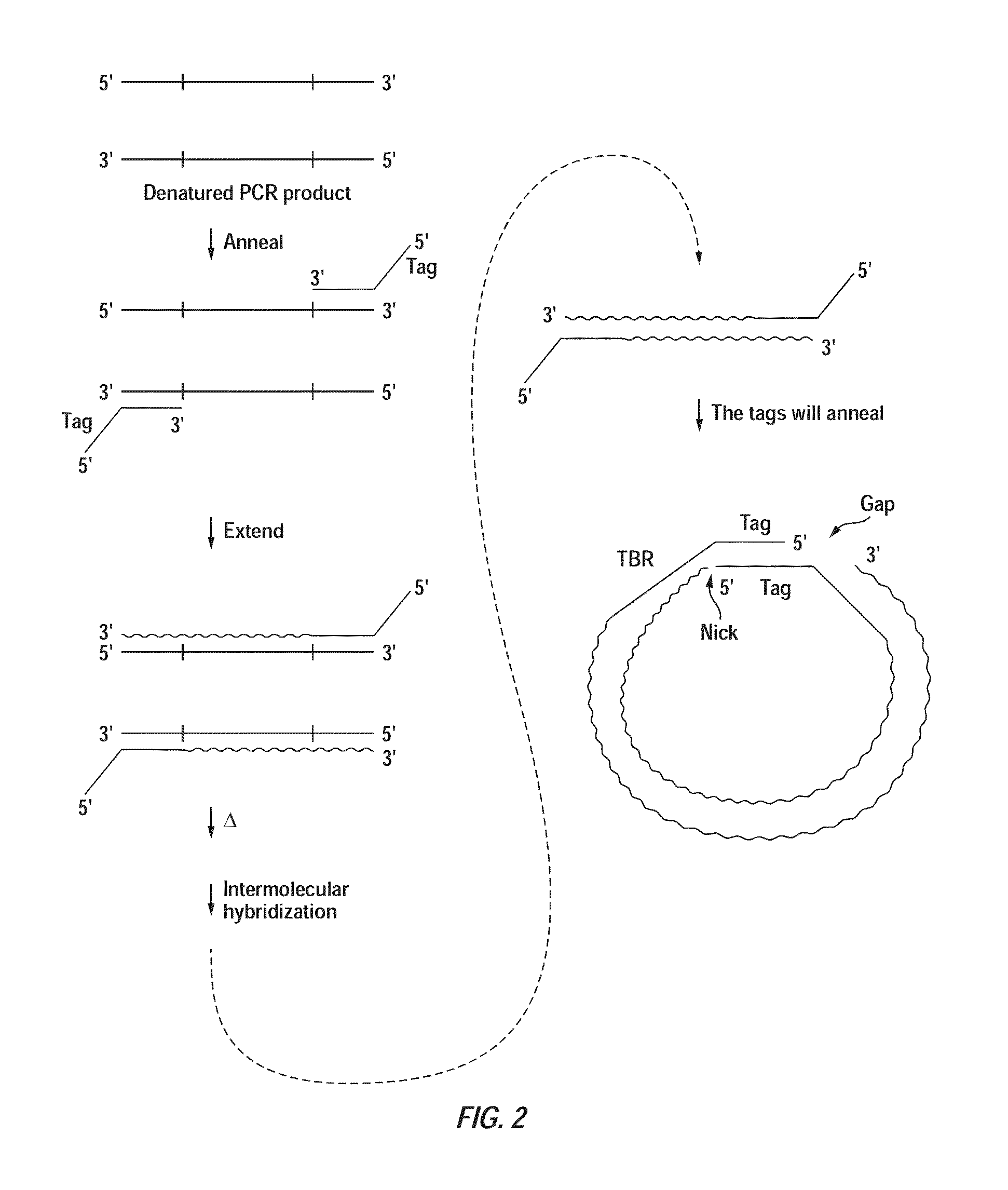
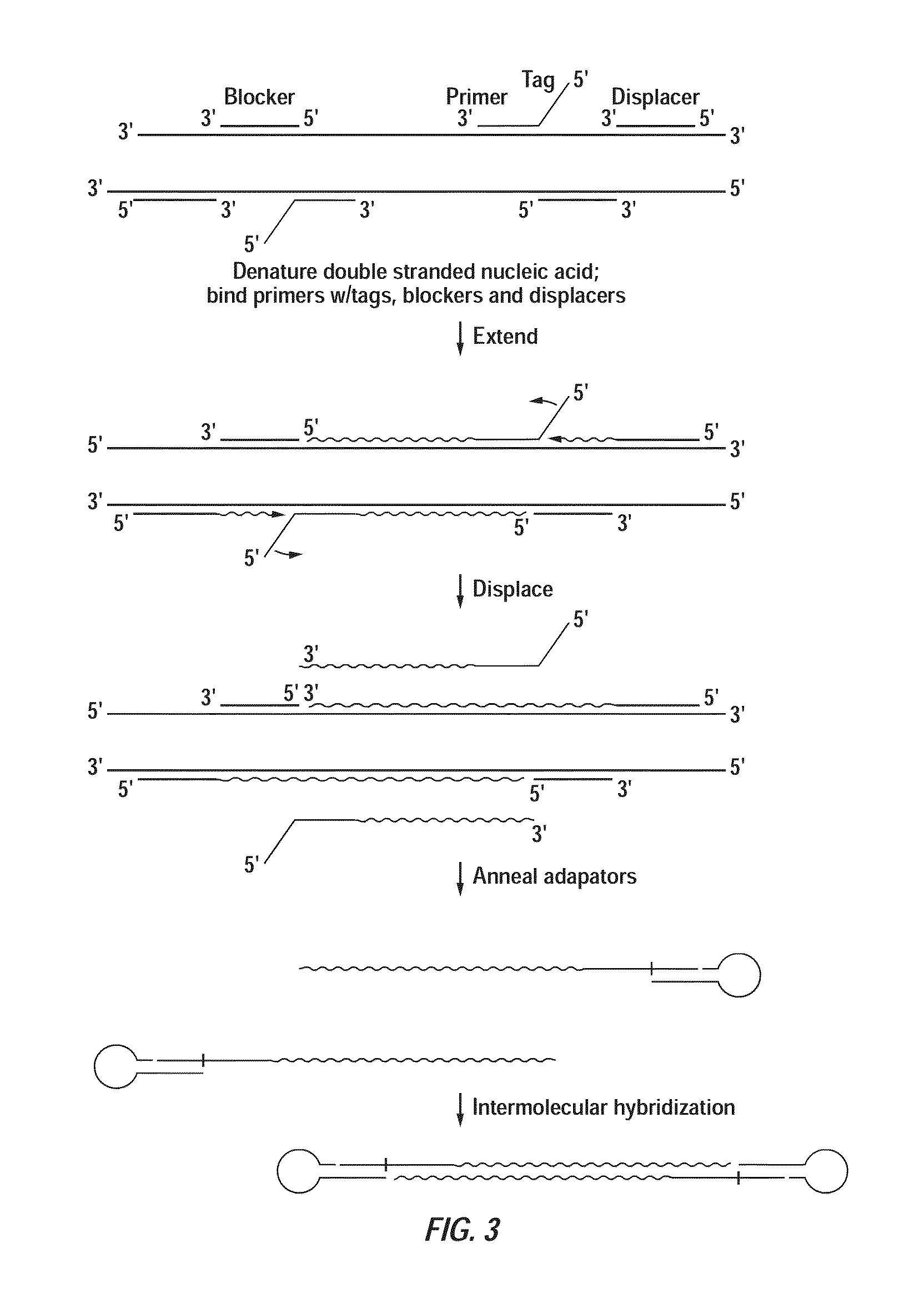
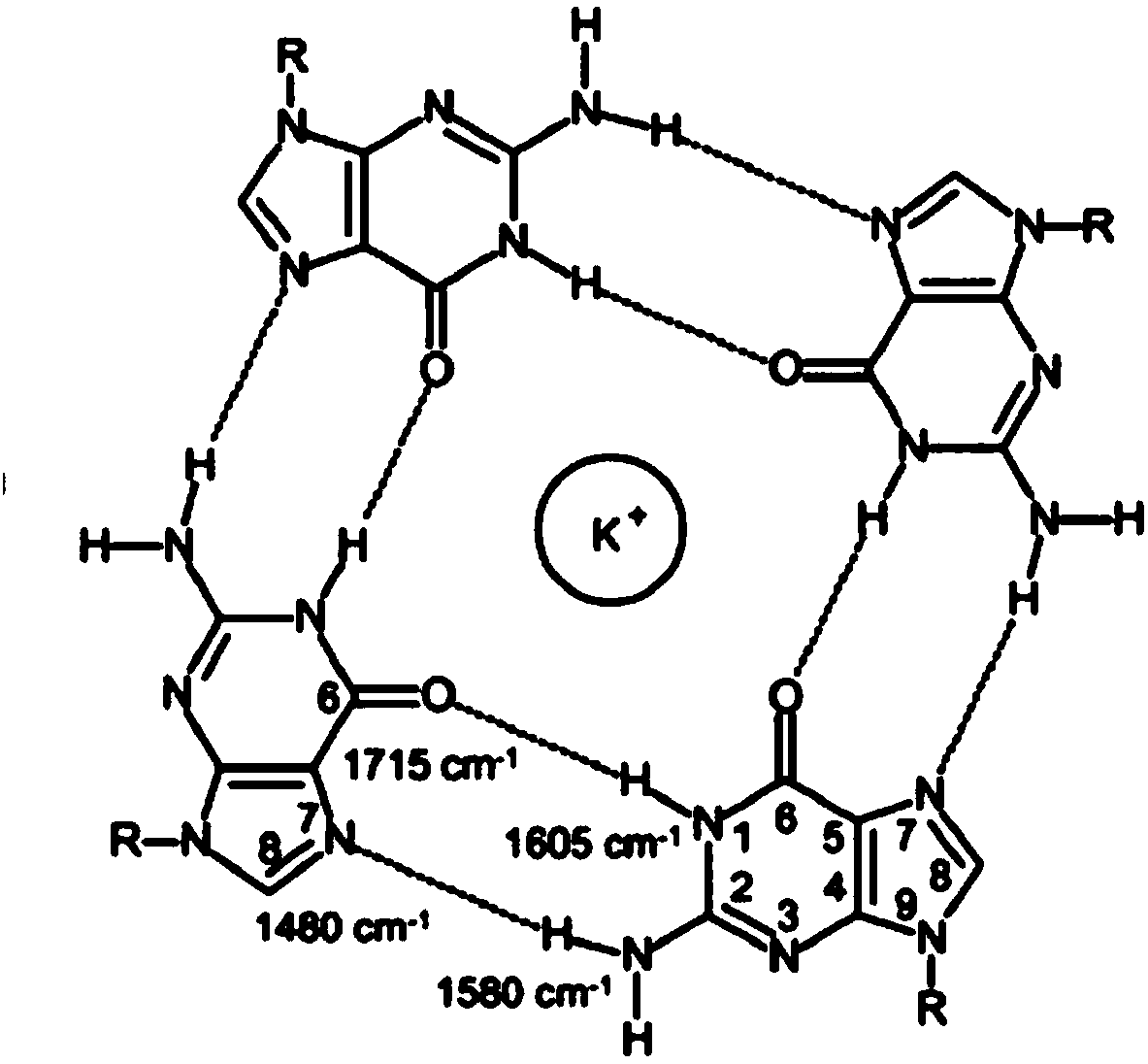
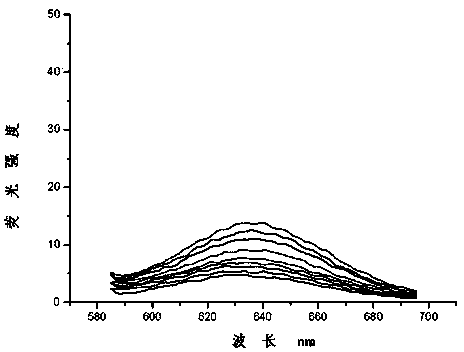
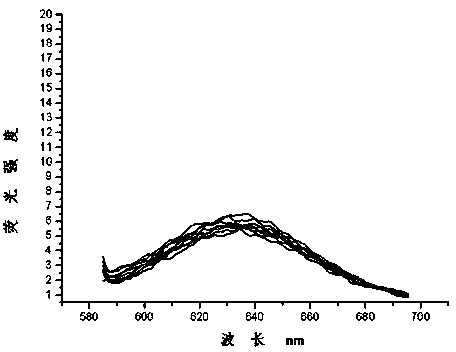
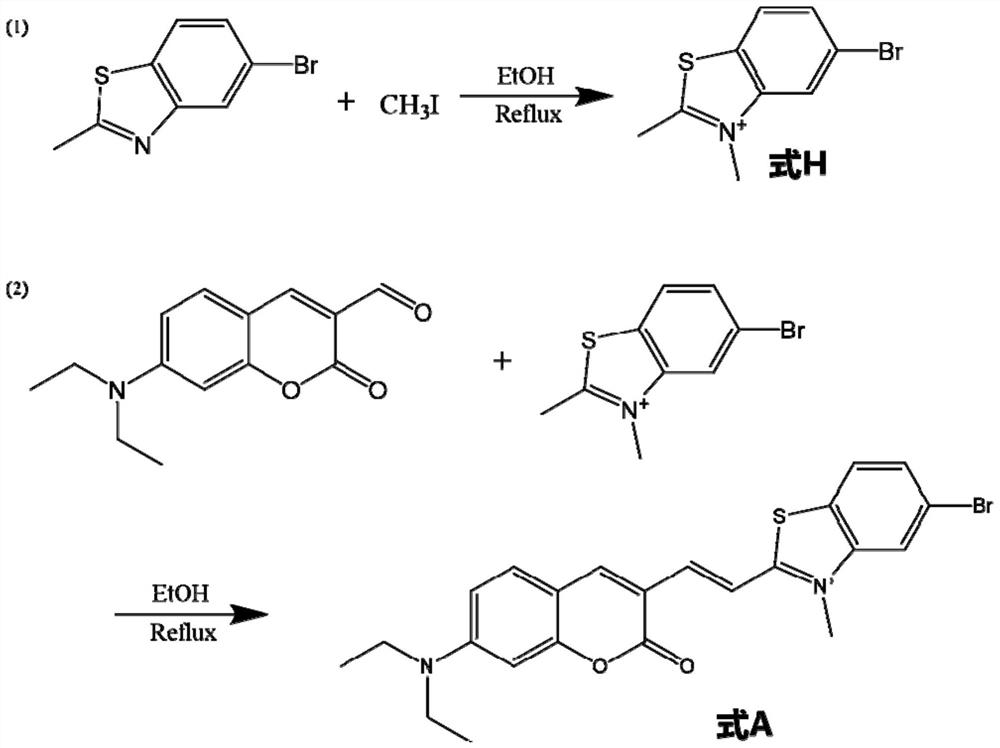
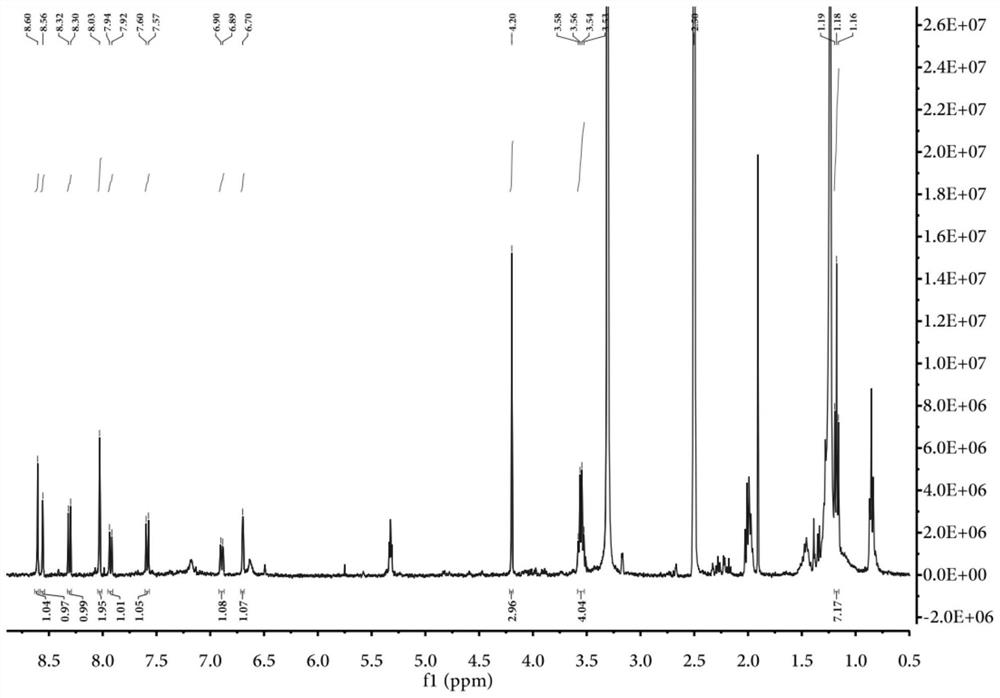
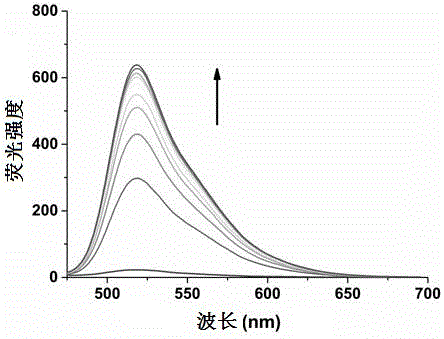
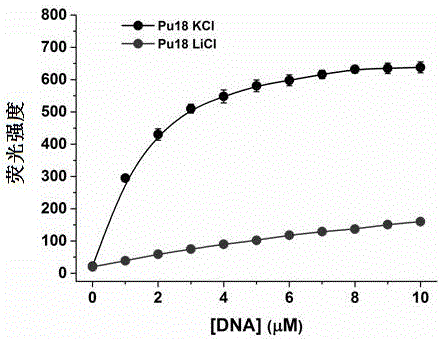
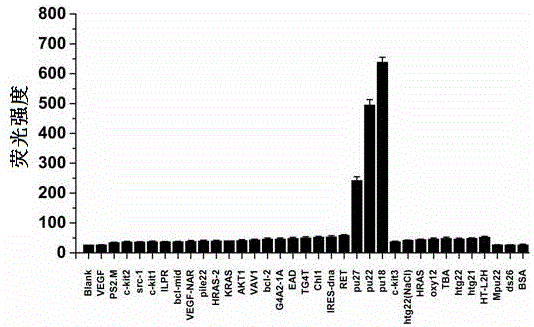
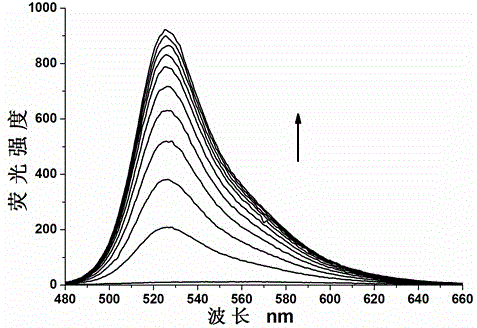
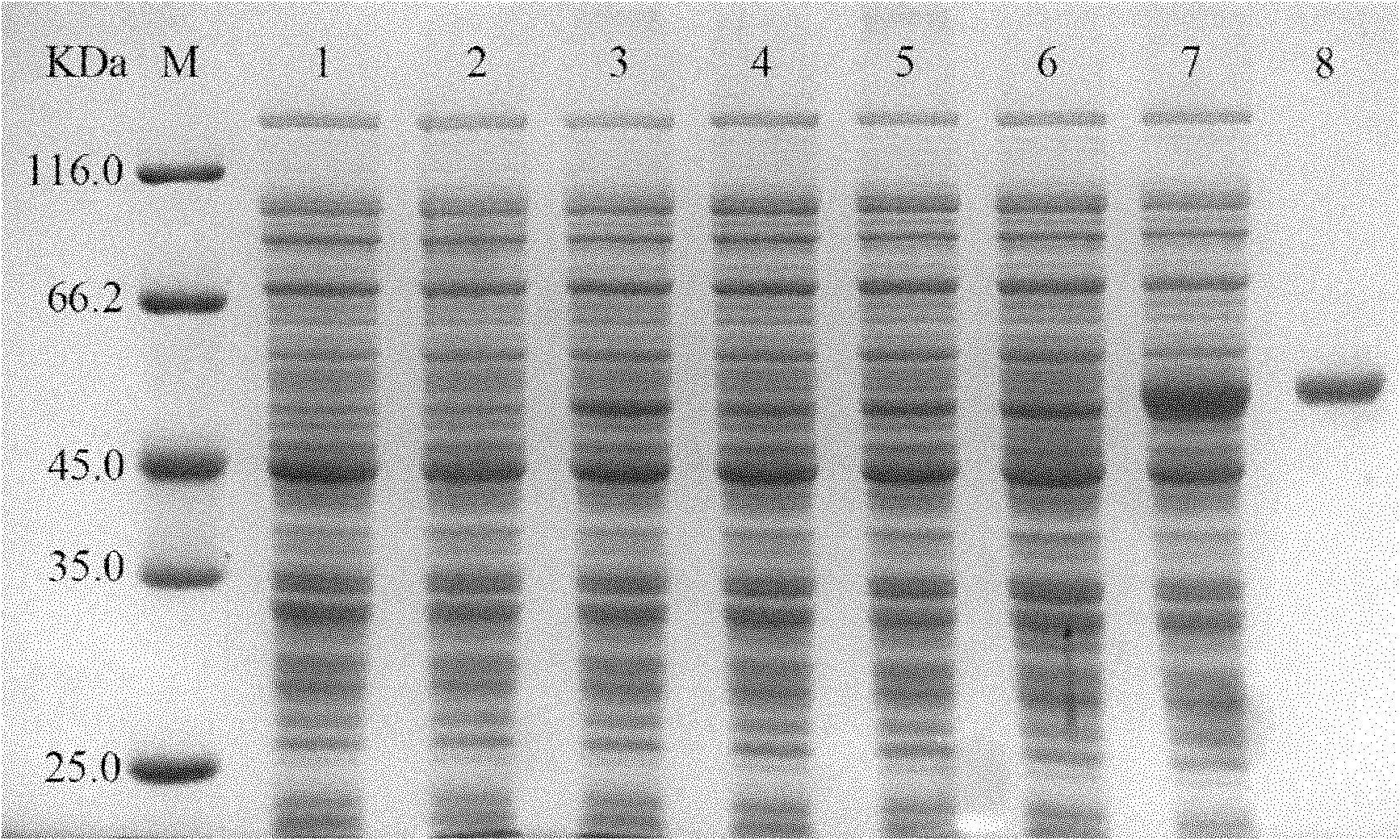Patents
Literature
30 results about "Nucleic acid secondary structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
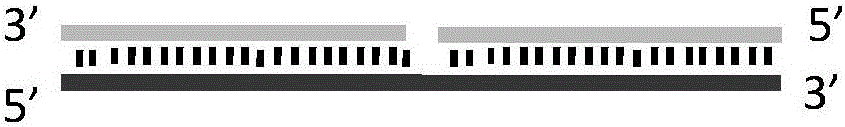
Nucleic acid secondary structure is the basepairing interactions within a single nucleic acid polymer or between two polymers. It can be represented as a list of bases which are paired in a nucleic acid molecule. The secondary structures of biological DNA's and RNA's tend to be different: biological DNA mostly exists as fully base paired double helices, while biological RNA is single stranded and often forms complex and intricate base-pairing interactions due to its increased ability to form hydrogen bonds stemming from the extra hydroxyl group in the ribose sugar.
Closed nucleic acid structures
ActiveUS20140329282A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid structureNucleic acid secondary structure
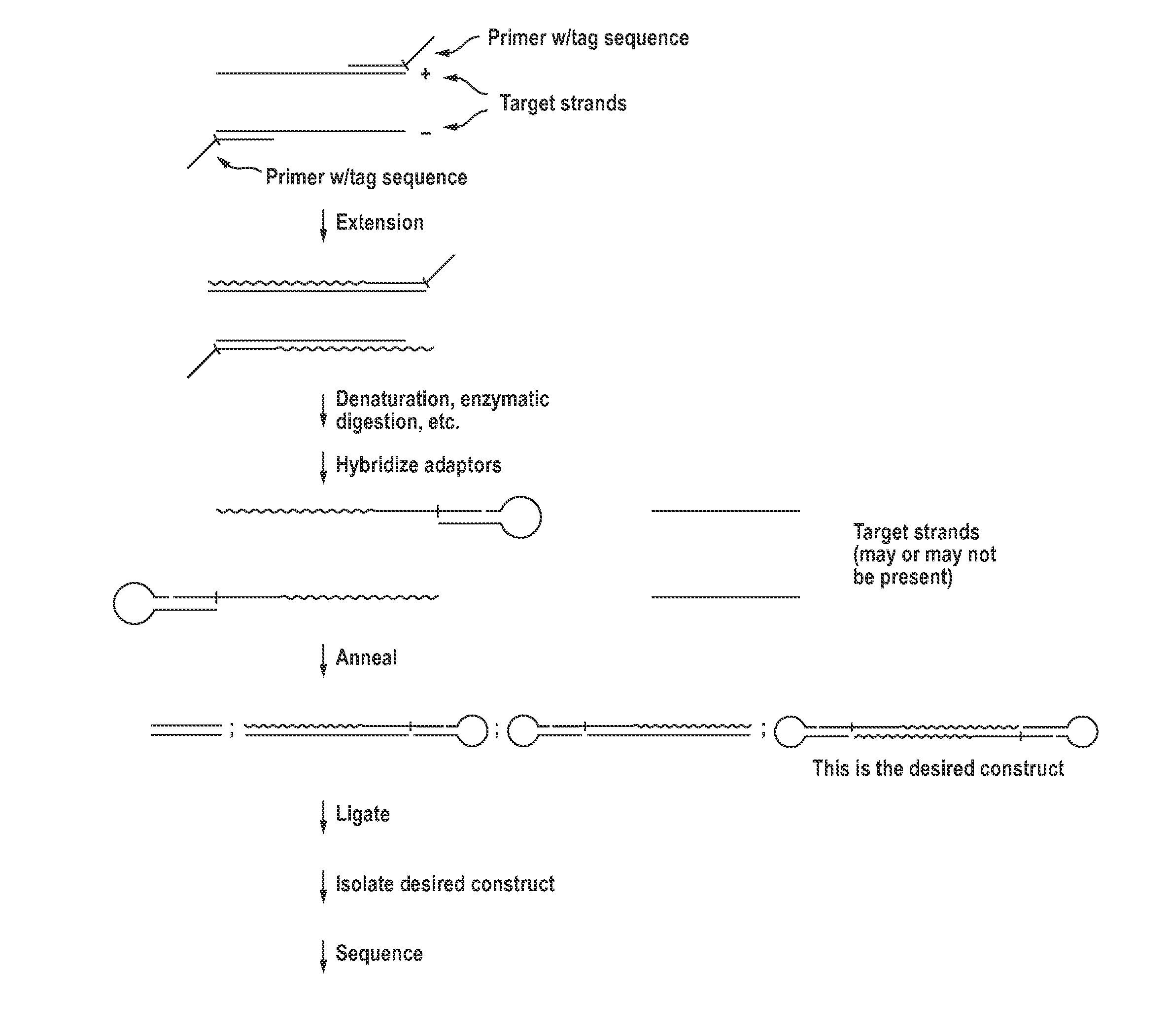
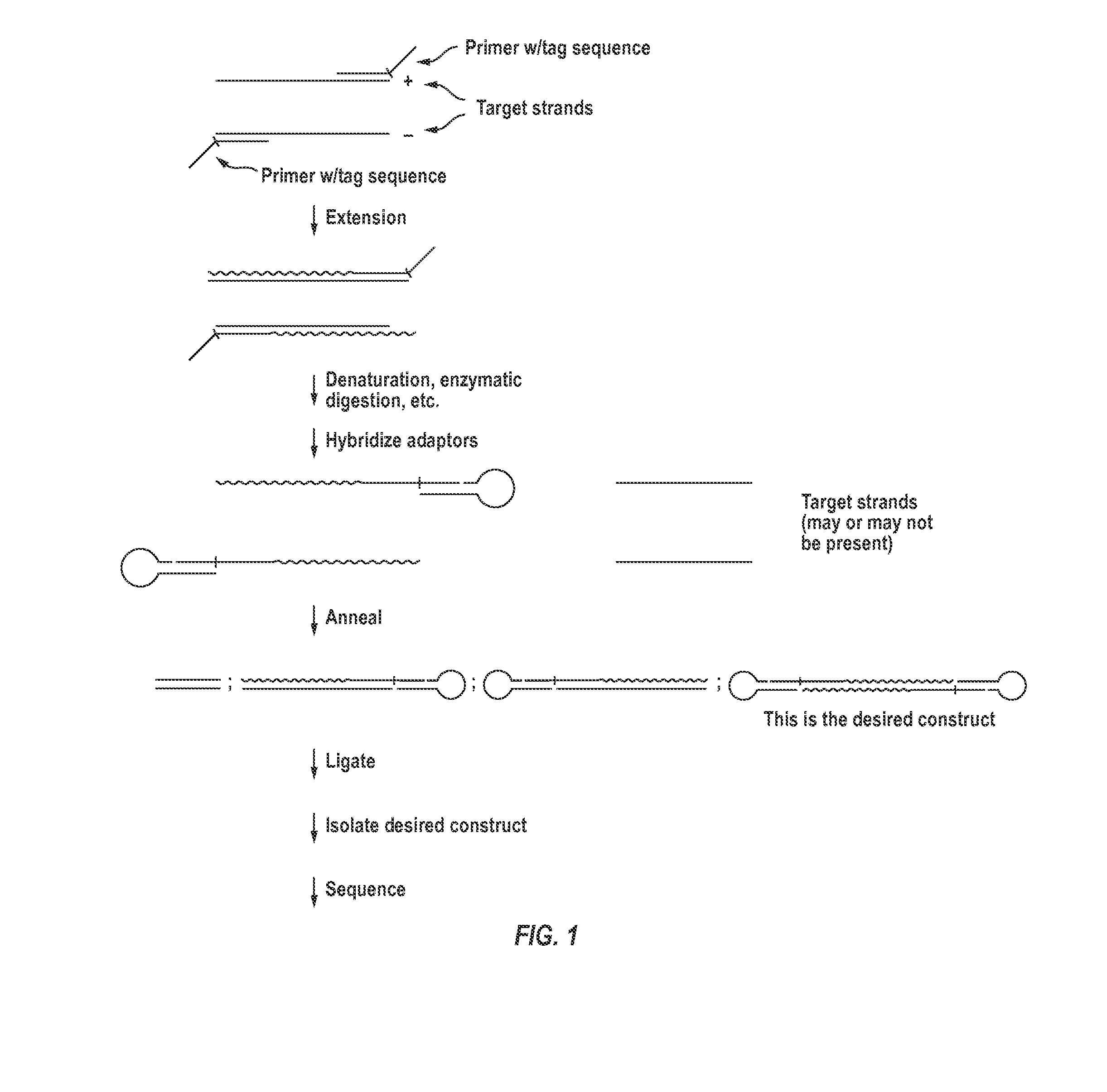
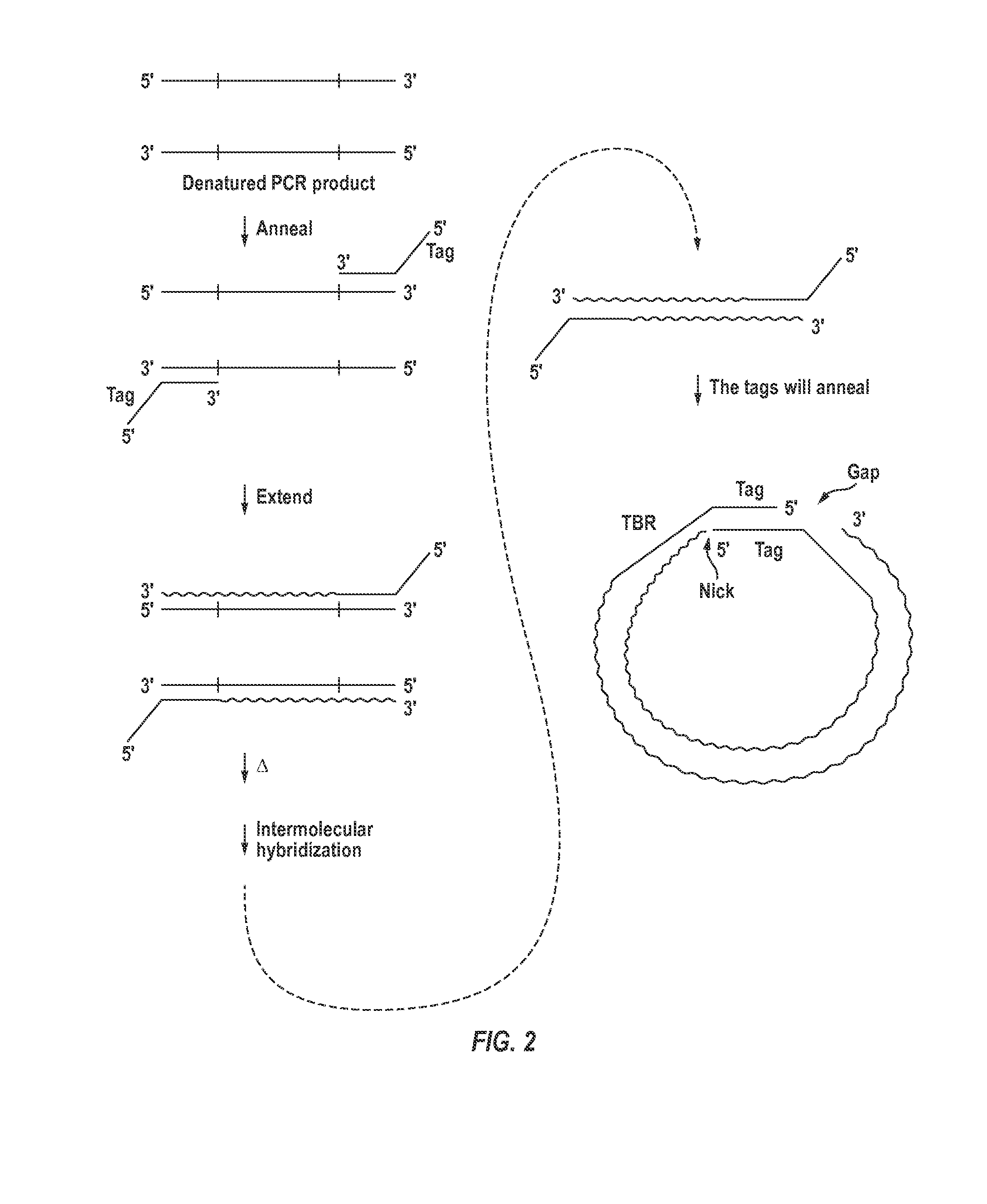
The invention provides compositions and methods for making closed nucleic acid structures in which one or both strands are continuous. The closed nucleic acid structures can be used as sequencing templates among other applications.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Protein synthesis efficiency enhancing RNA element
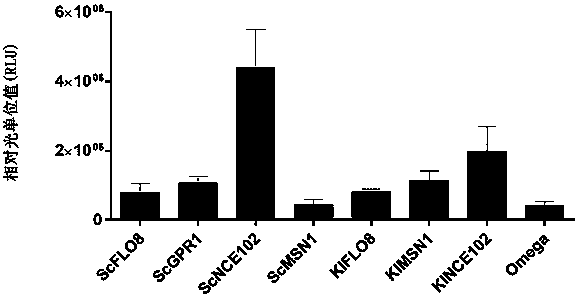
The invention provides a protein synthesis efficiency enhancing RNA element and particularly discloses a nucleic acid structure formed by coding sequences of optional promoters, yeast-derived IRES enhancers (such as ScGPR1, ScFLO8, ScNCE102, ScMSN1, KlFLO8, KlNCE102 and KlMSN1) and heterologous proteins. By application of the nucleic acid structure to a yeast in-vitro protein synthesis system, thesynthesized luciferase activity RLU (relative light unit) is extremely high.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
Nucleic acid nano structure for carrying antitumor drugs, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104368004AGuaranteed antitumor activityImprove targetingNanomedicinePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsNano structuringWhole body
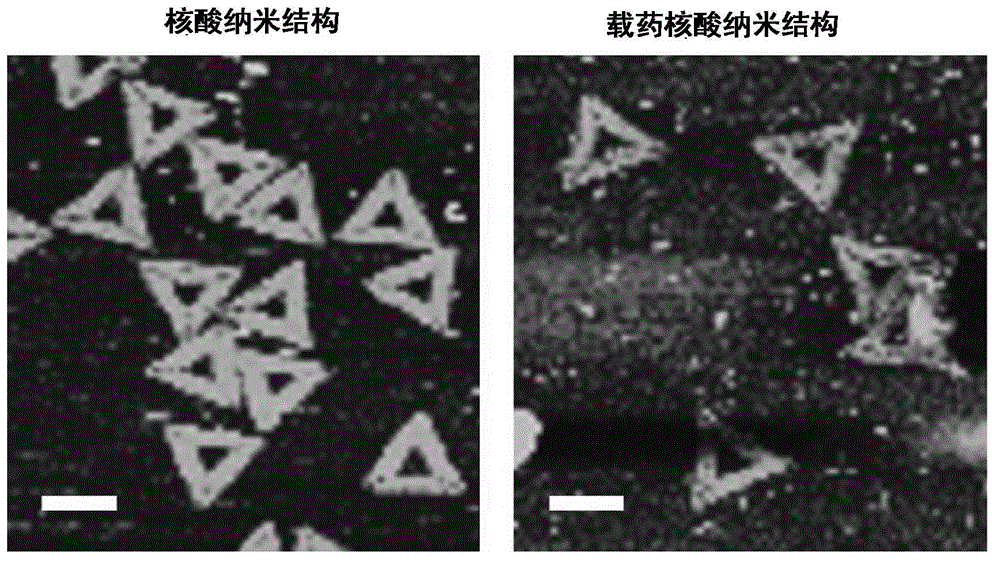
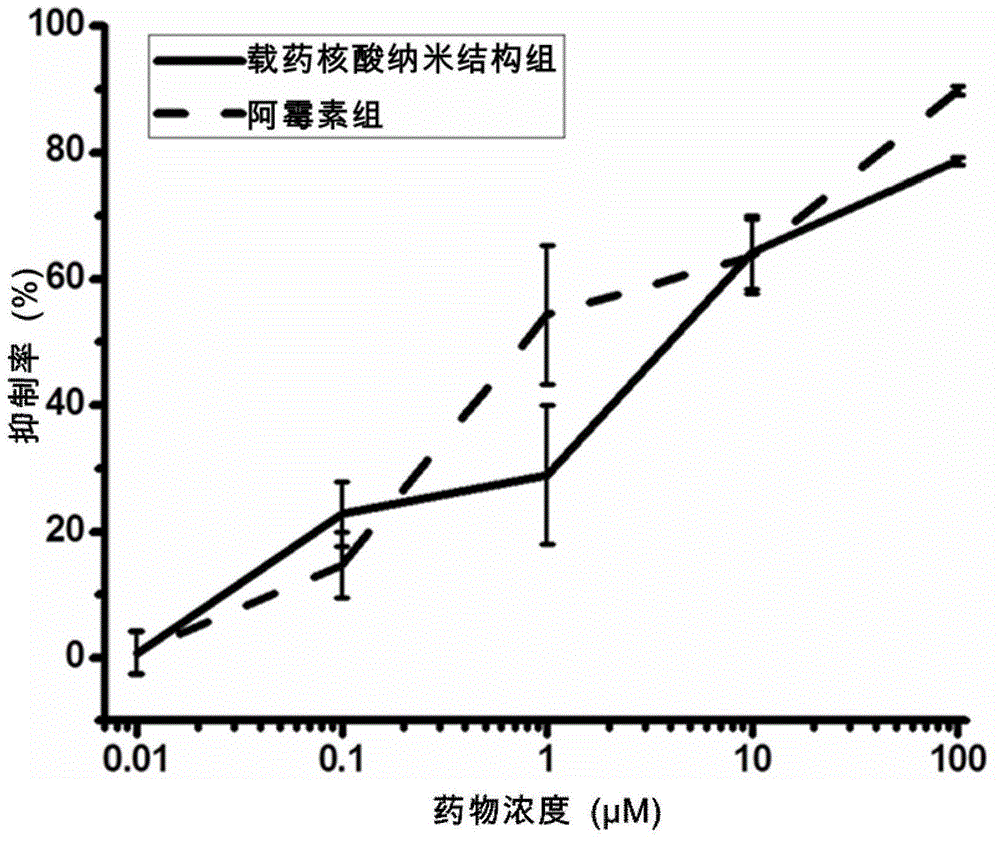
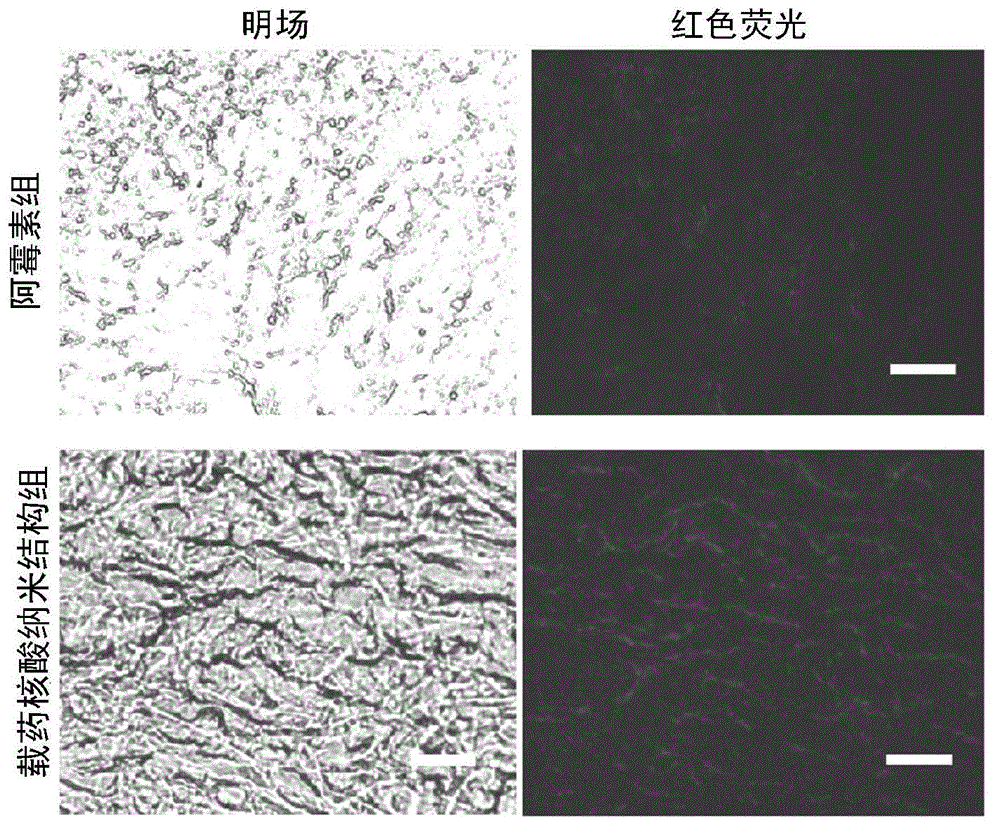
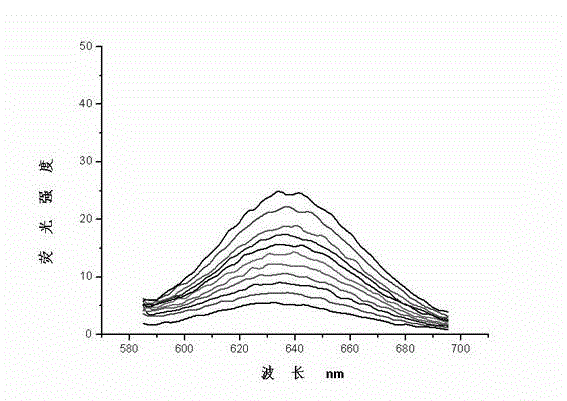
The invention discloses a nucleic acid nano structure for carrying antitumor drugs, a preparation method and applications thereof. The nucleic acid nano structure is a random two-dimensional and / or three-dimensional nano structure constructed through a DNA origami technology. The nucleic acid nano structure is obtained through self-assembly between a scaffold chain and a staple chain for auxiliary folding, wherein the scaffold chain and the stable chain are hybridized according to the base paring principle. The provided nucleic acid nano structure taken as the carrier of antitumor drugs can guarantee the antitumor activity of the carried antitumor drugs, and further improves the targeting property of the antitumor drugs. Thus the antitumor drugs can be enriched in the tumor tissues, and the overall toxicity due to the non-specificity of the antitumor drugs is greatly reduced. Furthermore, the preparation method has the advantages of simple technology, low cost, convenience, and easy application.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA +1
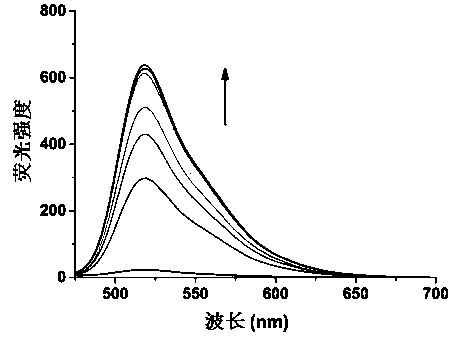
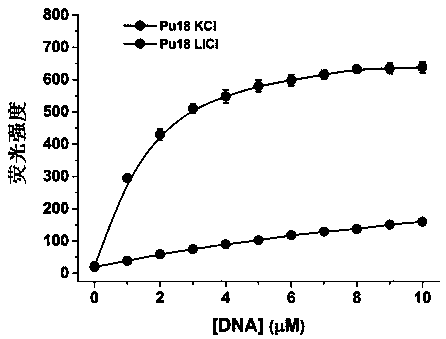
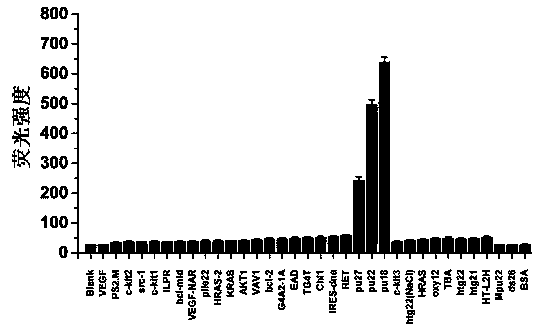
Dual-functional probe and preparation method and application in detection of G-quadruplex structure thereof
ActiveCN102719238AEasy to makeEasy to prepareOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementUv vis absorbanceA-DNA
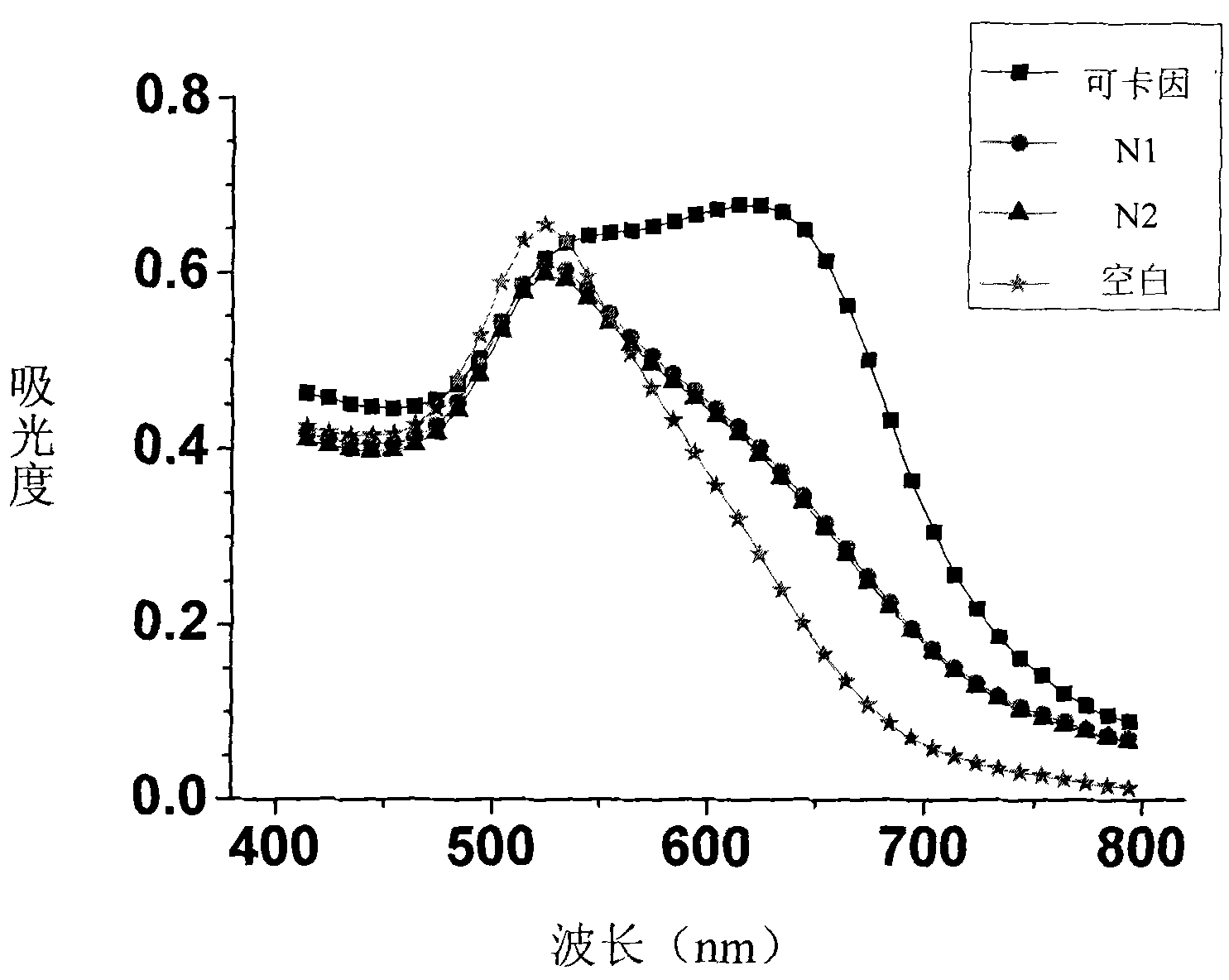
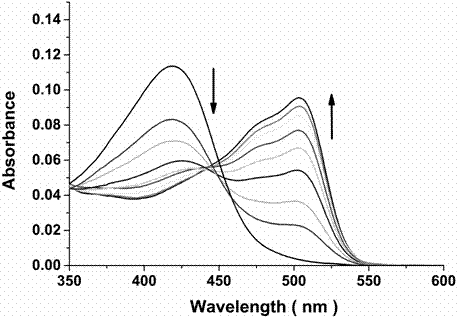
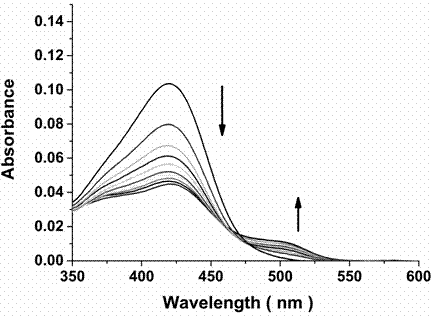
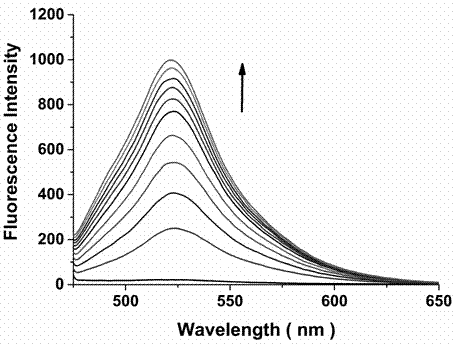
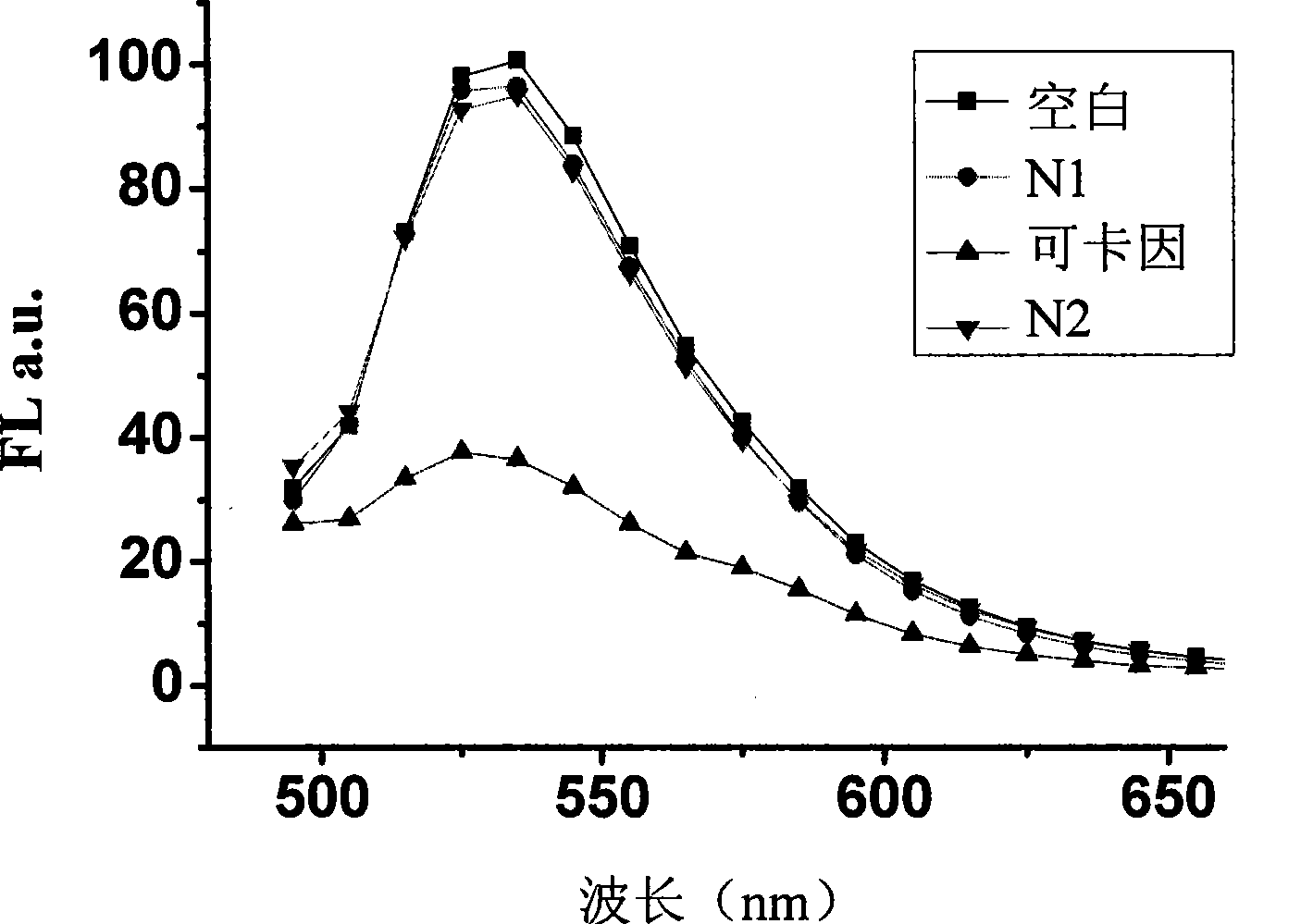
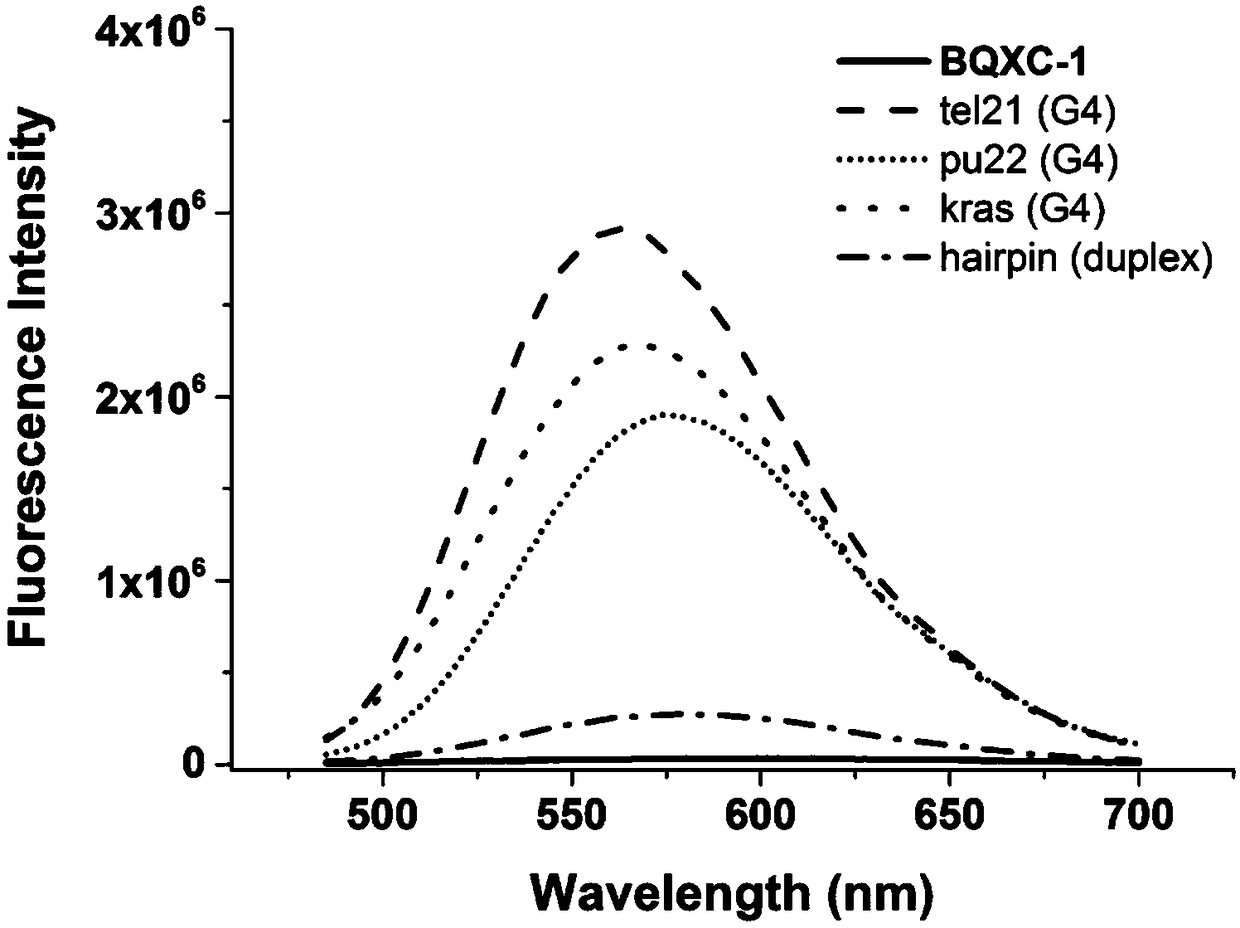
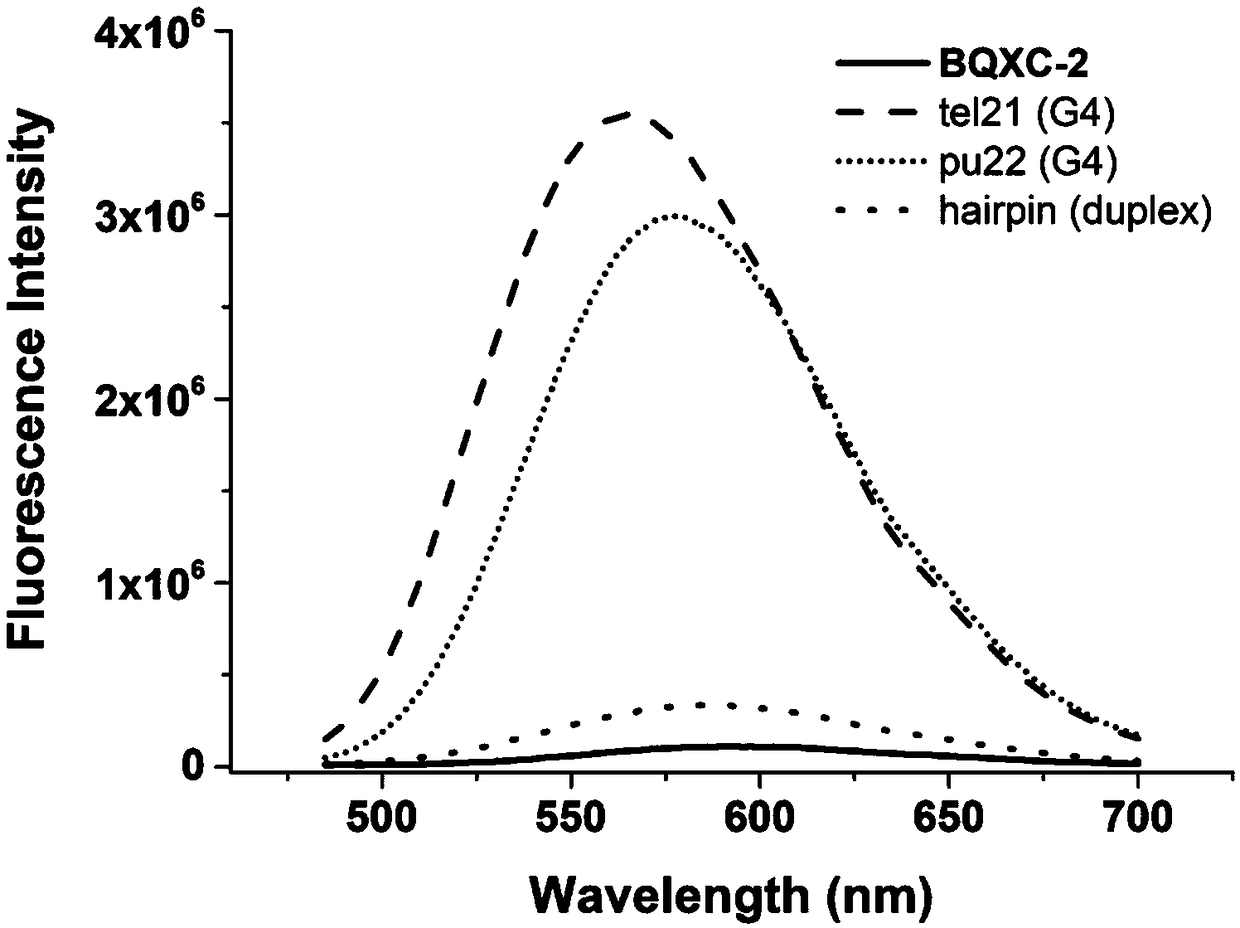
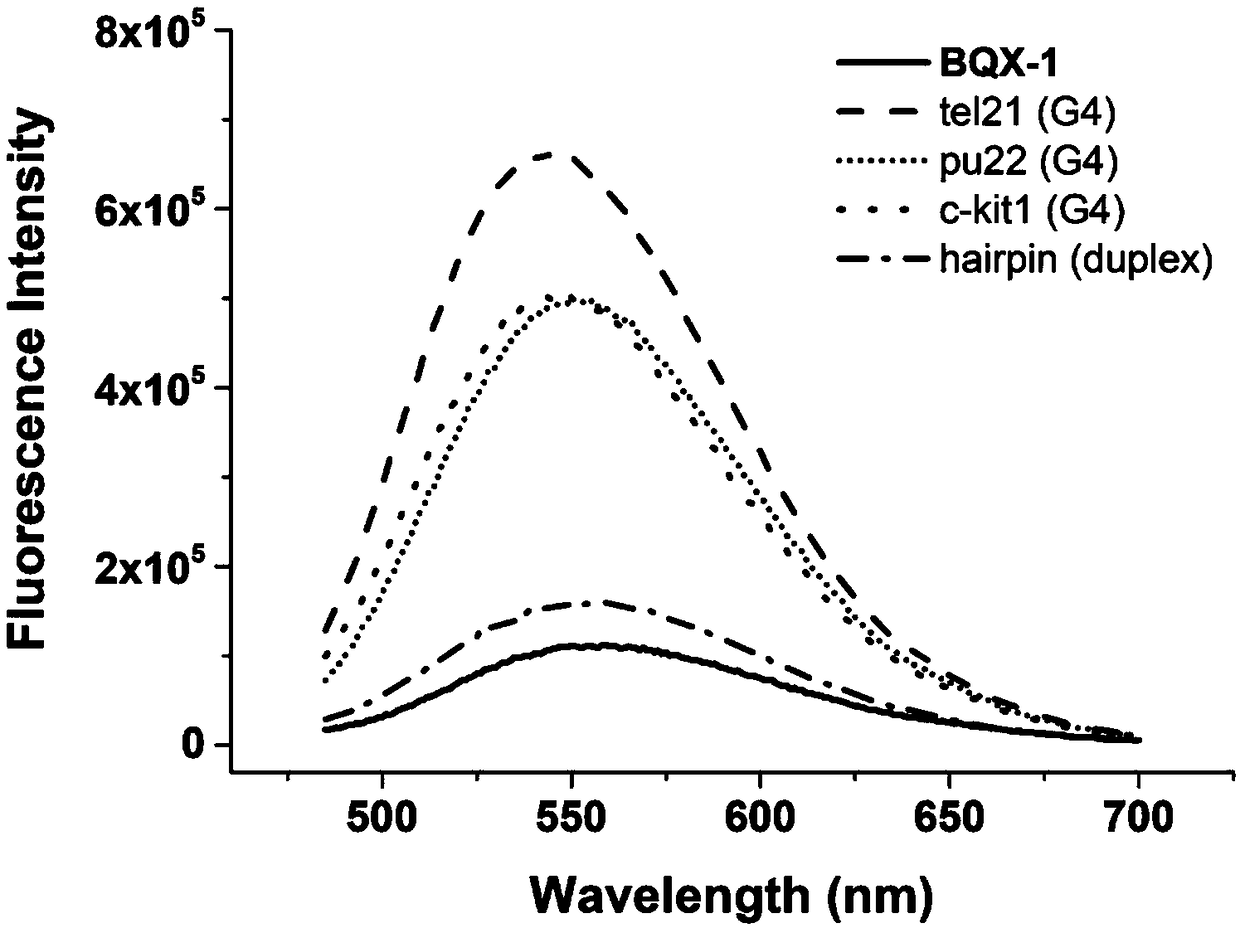
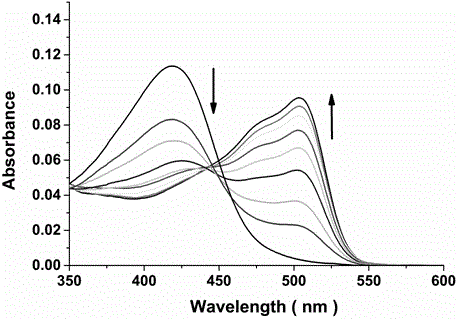
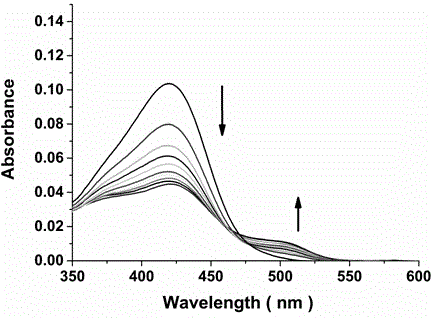
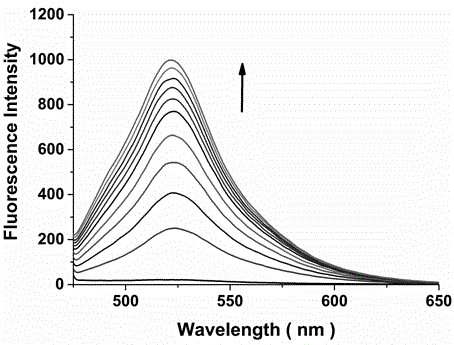
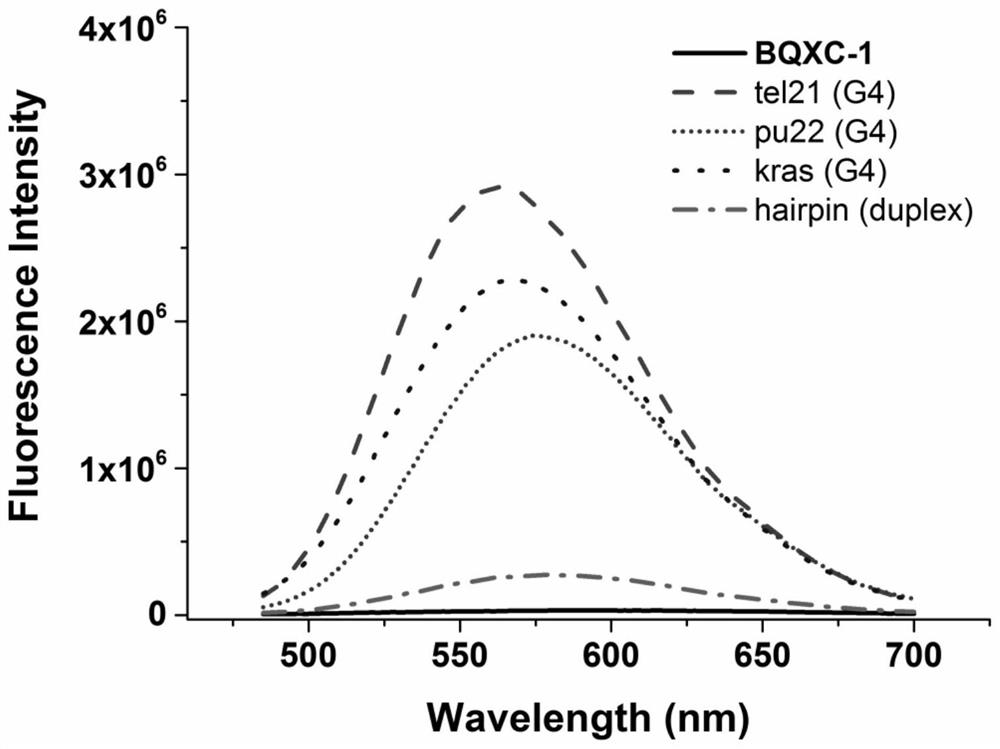
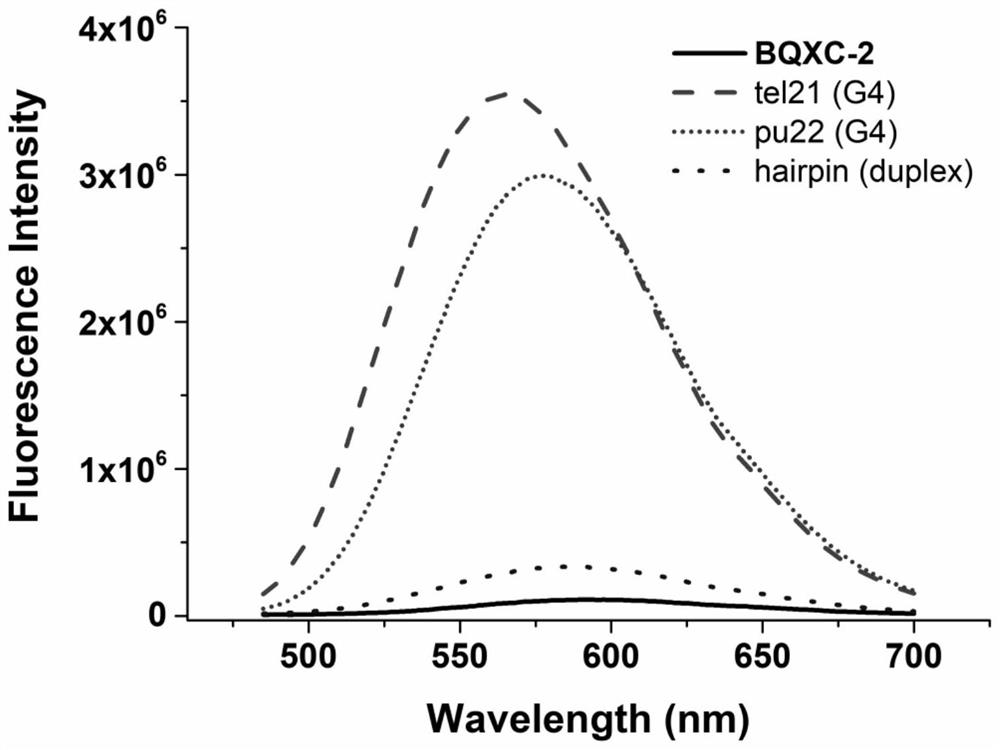
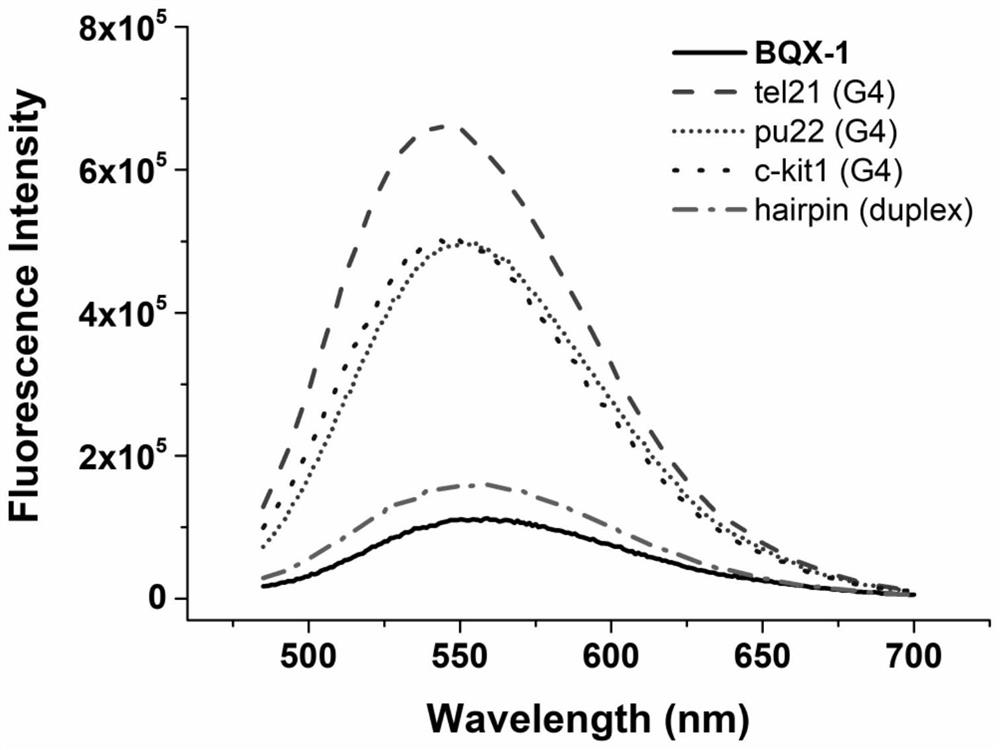
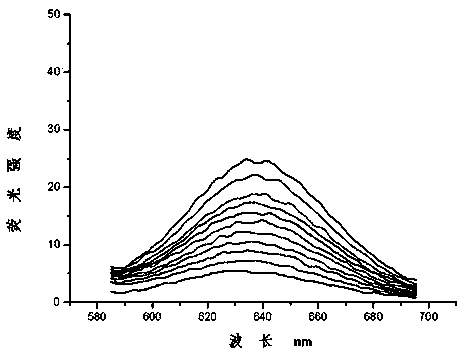
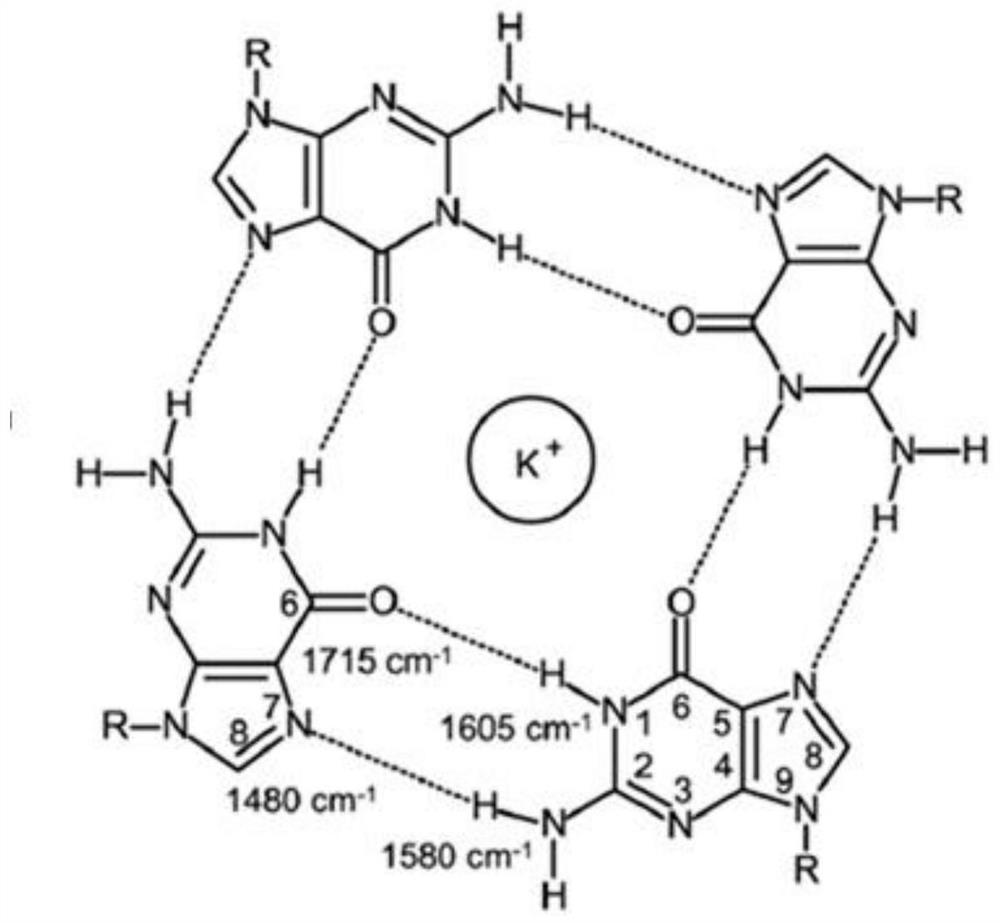
The invention discloses a dual-functional probe and a preparation method and application in detection of a G-quadruplex structure thereof. The probe is simple to prepare, readily available, and stable in structure, and can be used for the specific detection of G-quadruplex nucleic acid secondary structure, and fast detection of the secondary structure of a DNA sample in a solution according to an ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrum, a fluorescence spectrophotometer, or direct visual inspection of naked eyes. The method for detecting the G-quadruplex nucleic acid secondary structure by the probe has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, excellent and fast selectivity, and visibility by naked eyes, and overcomes the defects of high cost and equipment requirement, relatively complex technical operation and the like of other detection methods.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Colorimetric detection method based on nanometer-gold and nucleic acid structure and kit thereof
InactiveCN101832936ALow costVersatilityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsNucleic acid structure
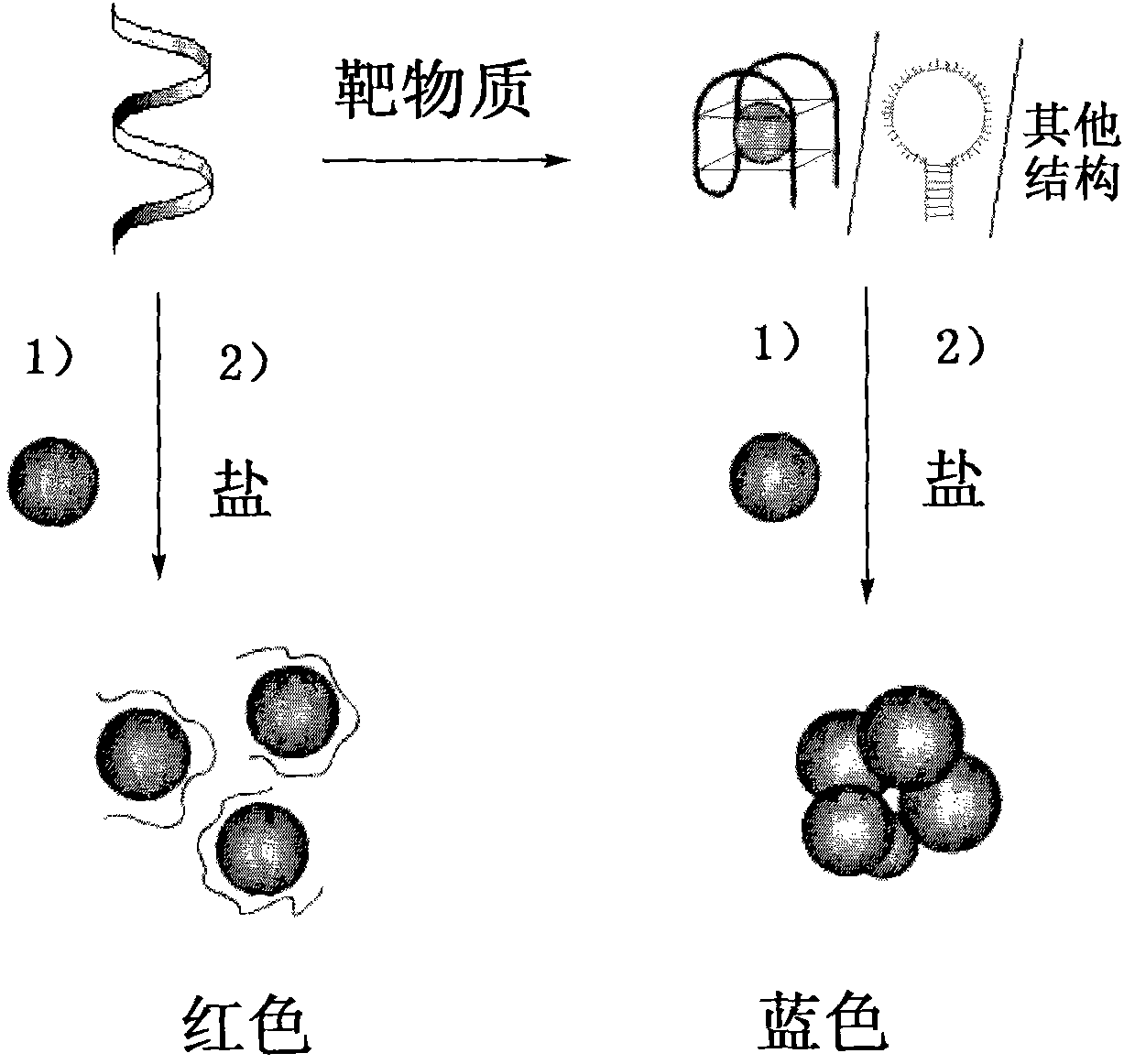
The invention discloses a colorimetric detection method based on a nanometer-gold and nucleic acid structure and a kit thereof. The colorimetric detection method comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing specific DNA which can be specifically combined with the target molecules with a solution to be detected for reaction; (2) mixing the reaction solution which is obtained in the step (1) with a nanometer-gold solution of which the number of moles is 0.01 to 1 time that of the specific DNA for reaction; and (3) adding a high-salt solution with the reaction concentration between 10 and 600 mM, and observing color change of the solution. In the operation process of the invention, DNA is not needed to be marked, expensive equipment is not needed need, and the existence of the target molecules can be determined only by observing the color change of the nanometer-gold solution. Therefore, the invention is simple, convenient and fast, has low cost, high specificity and high sensitive detection of any target molecules, is especially suitable for open-air analysis and high-throughput screening, and has wide application range.
Owner:苏州市长三角系统生物交叉科学研究院有限公司
Nucleic acid nano structure as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107488661AImprove stabilityAnchor size largeMicrobiological testing/measurementTransportation and packagingNano structuringDNA origami
The invention provides a nucleic acid nano structure as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The nucleic acid nano structure is a hexagonal DNA nano structure formed by assembling six triangular DNA paper folding structures constructed by a DNA paper folding technology, and particularly a hexagonal DNA nano structure formed by self-assembling in a mode of carrying out hybridization on scaffold chains and staple chains as well as capturing chains and then respectively carrying out hybridization on connection chains and scaffold chains of six triangular DNA paper folding structures. The nucleic acid nano structure is high in stability, two 80nm gold triangular prisms can be anchored, a prepared golden bow structure can generate a strong electromagnetic field, and single molecule Raman detection is implemented.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Bifunctional probe, its preparation method, and its application in detection of orthographic parallel conformation G-quadruplex
InactiveCN104710977AEasy to makeRaw materials are easy to getOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSpecific detectionStructural formula
The invention provides a bifunctional probe. The concrete structural formula of the probe is shown in the specification. In the formula, R1 is F or an N-methylpiperazinyl group, R2 is F or an N-methylpiperazinyl group, and R1 and R2 cannot simultaneously be F; and R3 is a methoxy group, a diethylamino group, a dimethylamino group, an N-methylpiperazinyl group, F or H. The probe has the advantages of simple preparation steps, easily available raw materials and stable structure, can be used for the specific detection of the orthographic parallel conformation G-quadruplex nucleic acid secondary structure, can rapidly detect the orthographic parallel conformation G-quadruplex nucleic acid secondary structure in a nucleic acid sample through an ultraviolet spectrophotometer, a fluorospectrophotometer or an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay instrument, and even naked eye observation under sunlight or an ultraviolet lamp, and overcomes the disadvantages of difficult distinguishing of many different conformations of G-quadruplex nucleic acid, high price, high device requirements and complex technical operation of other detection methods.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Nucleic acid structure of which interchain exchange is achieved by support DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and synthesis method thereof
PendingCN105602949AHigh yieldSimple designDNA preparationDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA origamiNucleic acid structure
The invention discloses a nucleic acid structure of which the interchain exchange is achieved by a support DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). The nucleic acid structure is a two-dimensional or three-dimensional nucleic acid structure with controllable size and shape, which is formed by achieving interchain exchange by the support DNA. The nucleic acid structure comprises a set of parallel double helices connected by interchain exchange and a single-chain DNA segment, wherein the double helices are formed by carrying out folding and interchain exchange by the support DNA, carrying out specific matching with a plurality of short-chain DNAs and carrying out annealing reaction; and the single-chain DNA is the part of the support DNA which does not form the double helices. The invention provides the multiple nucleic acid structures and synthesis methods thereof. The nucleic acid structure is a variant technique based on DNA paper folding. The invention aims to form the nucleic acid structure with controllable size, shape, complexity and modification by achieving interchain exchange by using the support DNA. The nucleic acid structure is completed by the support DNA / short-chain DNA self-assembly process, and has the advantages of higher yield and simple design; and the predicated two-dimensional and three-dimensional structures can be simultaneously synthesized.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
Method for realizing over expression of thermostable laccase gene through location transformation
InactiveCN102061290AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses a method for realizing over expression of the thermostable laccase gene through location transformation. Thermostable laccase produced from thermus thermophilus bacteria has great application potential in the industrial processes of pulp bleaching, textile decoloring, biomass hydrolysate detoxifying and the like, but the thermostable laccase gene has low expression level and can not become an enzyme source. In the invention, a carrier in a pHsh series is firstly applied to carrying out cloning, in-situ mutagenesis and induced expression on the laccase gene. By carryingout case analysis and multiple explorative site-directed mutagenesis on a special sequence of the thermostable laccase gene, the invention has the effects of reducing rare codons in the gene, lowering the GC base content and weakening formation of a nucleic acid secondary structure and the like, thereby enhancing the expression level of the gene in escherichia coli by 317 times compared with a natural gene.
Owner:SHINE E BIOTECH CO LTD
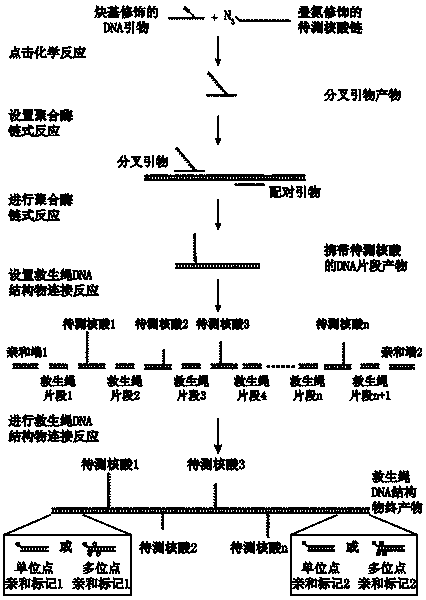
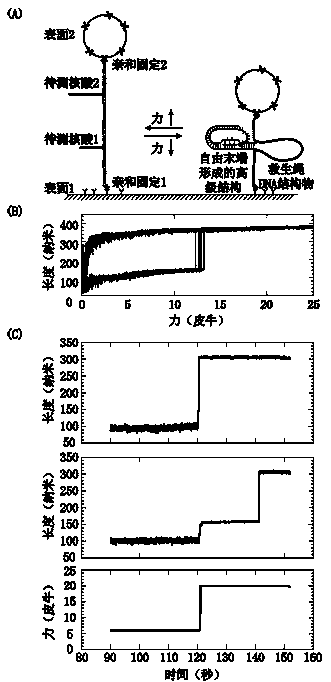
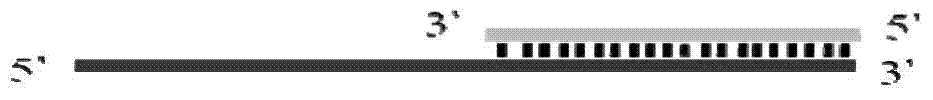
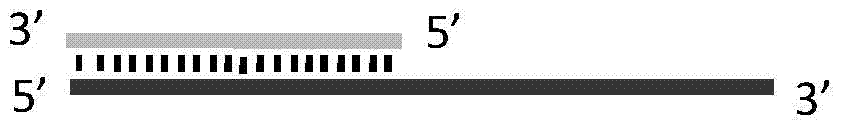
Method for detecting nucleic acid terminal structure based on single-molecule force spectroscopy
ActiveCN109852667AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBiological macromoleculeNucleic acid secondary structure
The invention relates to a method for detecting a nucleic acid terminal structure based on a single-molecule force spectroscopy, in particular to a single-molecule force spectroscopy method for detecting the higher structure of a free terminal of nucleic acid, and belongs to the field of mechanical precise measurement of the higher structure of biomacromolecule. The method comprises the steps of firstly through a combination reaction, anchoring a nucleic acid chain to be detected, carrying modified groups, on a DNA single-chain primer to generate a bifurcate primer; then through a polymerase chain reaction, preparing DNA carrying the nucleic acid chain to be detected, and a relieving rope DNA fragment; then through enzyme-cut and connection, generating a DNA structure substance carrying aplurality of relieving ropes having nucleic acid to be detected, and fixing the DNA structure substance between two surfaces; and finally, detecting the dynamic changes of the higher structure formedat the free terminal of the nucleic acid to be detected with the single-molecule force spectroscopy. The relieving rope DNA designed by the invention is mainly used for repeated, active, precise and real-time measurement of the higher structure at the terminal of the nucleic acid, and the application range of the single-molecule force spectroscopy is enlarged.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for implementing targeted cleavage on arbitrary nucleic acid
ActiveCN104745570AAchieve targeted cleavageImprove general performanceHydrolasesDNA preparationGlycineNucleic acid structure
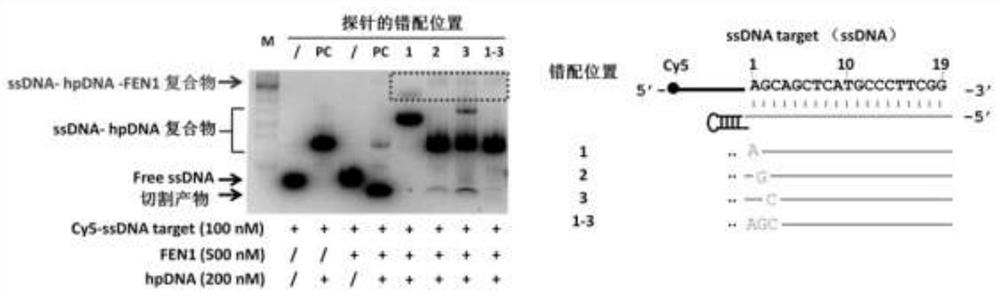
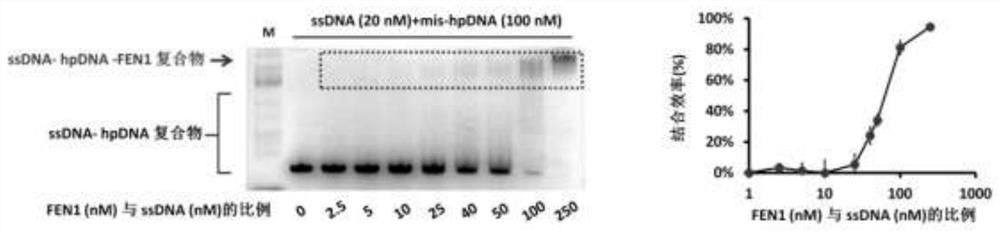
The invention relates to a method for implementing targeted cleavage on arbitrary nucleic acid; a structural identification endonuclease is constructed and expressed for establishing the method. The method comprises the concrete steps: selecting a cleavage position of a target nucleic acid, and designing a nucleic acid probe complementary with target nucleic acid; adding into a reaction system, making the probe hybridized with a substrate, and forming a secondary structure which can be identified by the structural identification endonuclease; and adding the enzyme, and carrying out a cleavage reaction. The nucleic acid structure which can be identified includes a nucleic acid intrusive structure and the like; an endonuclease identification functional domain is composed of a peptide fragment which can identify a nucleic acid secondary-structure enzyme and can be selected from E.coliMuts and the like; the cleavage functional domain is selected from a cleavage function of an IIS type endonuclease; a connection fragment between the identification functional domain and the cleavage functional domain of the endonuclease is mainly composed of serine and glycine; and the method breaks through the limit of a sequence of a nucleic acid substrate, so that the method can realize effective targeted cleavage of nucleic acids with different sequences.
Owner:NANJING GENERAL HOSPITAL NANJING MILLITARY COMMAND P L A
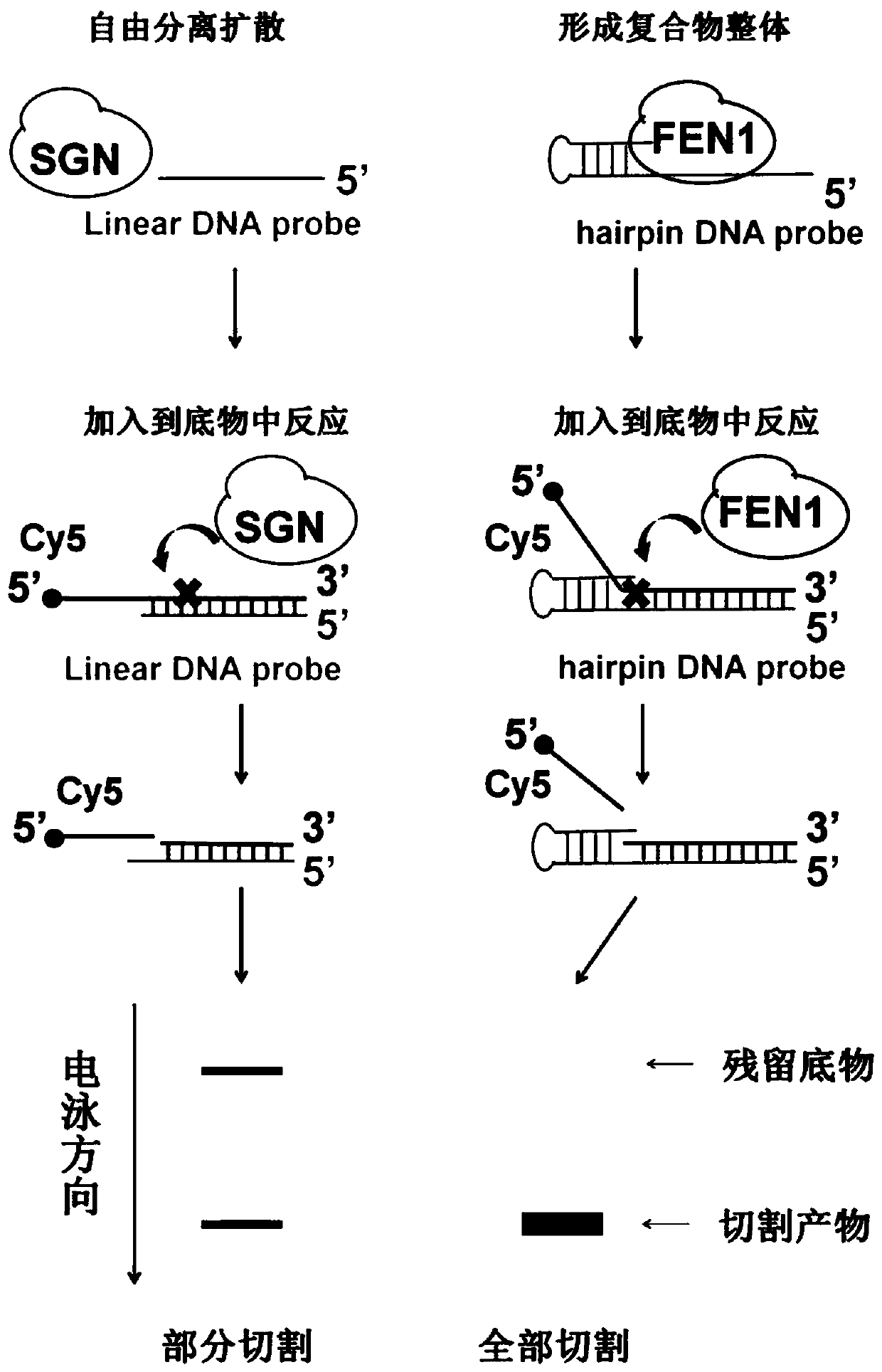
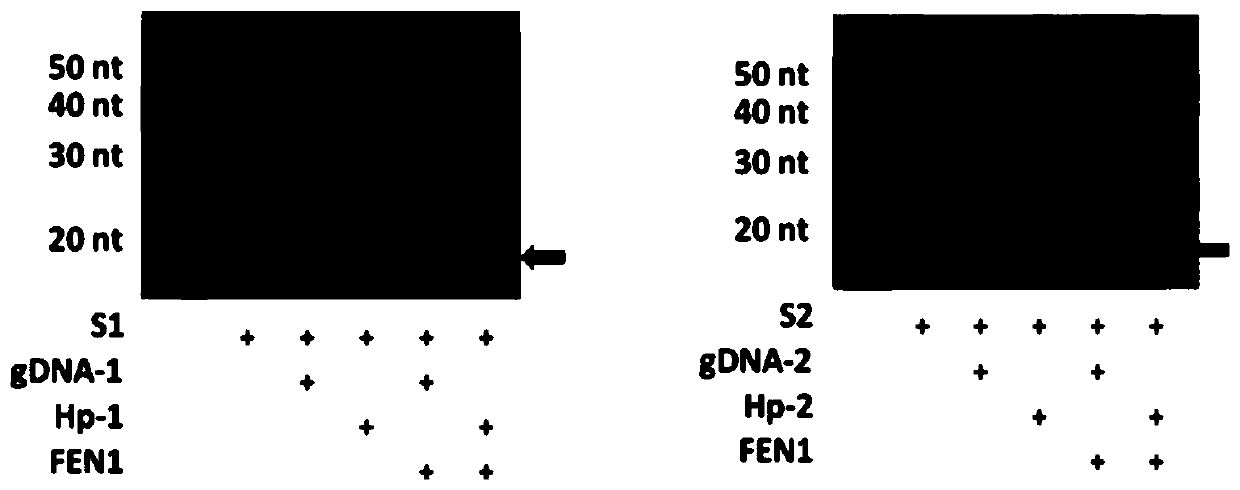
Random nucleic acid editing composition and method
ActiveCN111172164AImprove editing efficiencyWith identification functionHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAA-DNAMolecular recognition
The present invention discloses a random nucleic acid editing composition and method. The composition for targeted cleavage of random nucleic acids comprises two main components: a component A: an oligonucleotide probe consists of two parts, one part is complementary to a target substrate, and the other part has a secondary structure of nucleic acids; and a component B: an endonuclease molecule: the endonuclease molecule can recognize the secondary structure of the nucleic acids of the oligonucleotide probe to bind with the probe, and can also cleave a DNA or RNA substrate. The secondary hairpin structure (stem-loop structure) on the oligonucleotide probe can be directly recognized by the endonuclease molecule to form a complex molecule. Probability that the complex molecule collides withthe target substrate is greater than probability that two independently diffused molecules of the probe and the enzyme simultaneously collide with the target substrate, thereby improving gene editingefficiency.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
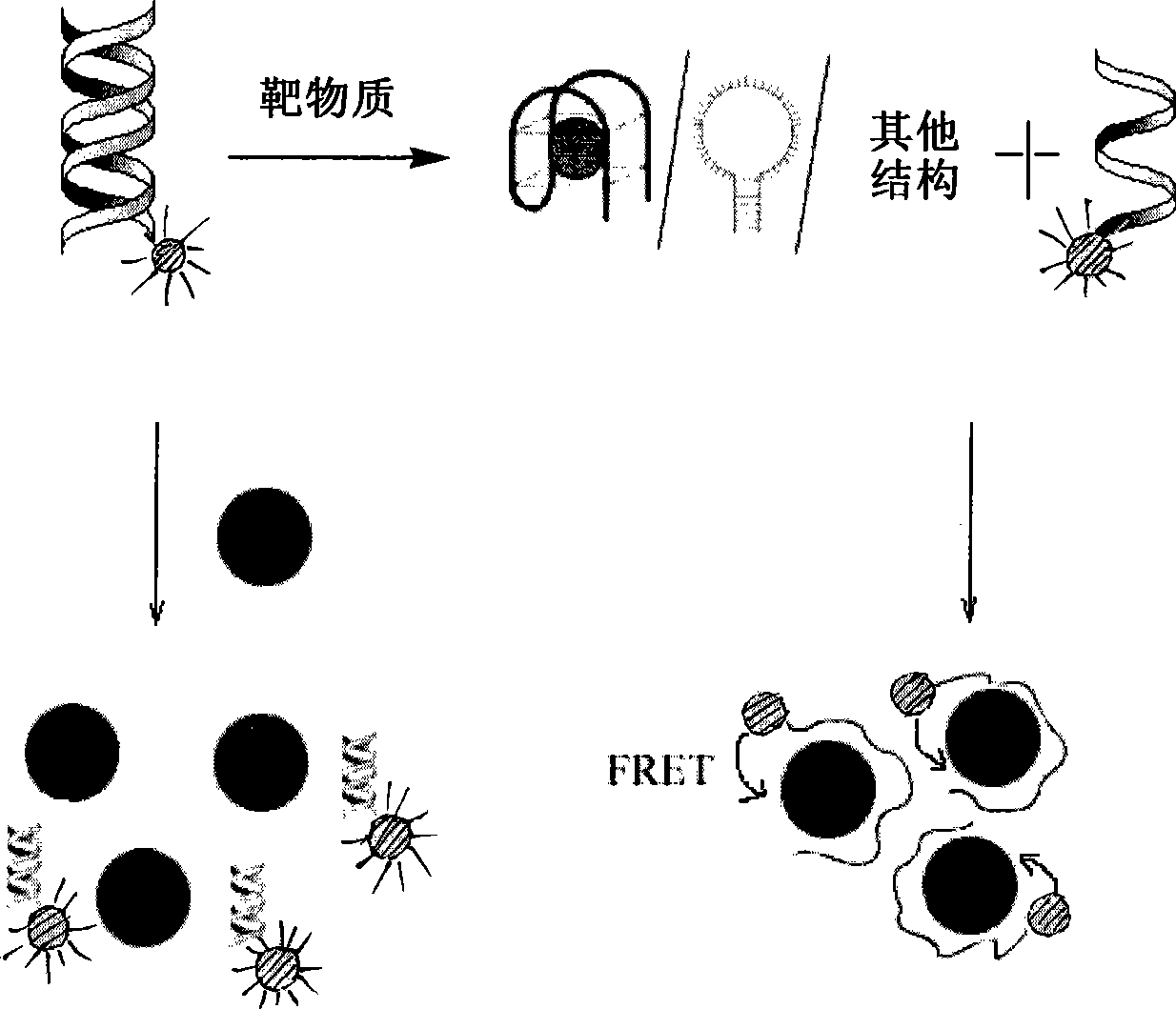
Target molecule detecting method based on nanometer aurum and nucleic acid structure
InactiveCN101424642BVersatilityAchieving Specific DetectionMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceNucleic acid structureComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention discloses a detection method of target molecules, which is based on manometer gold and a nucleic acid structure and comprises the sequential steps: (1), hybridizing specific DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) with cDNA (Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) in fluorescence labeling to form a double-stranded capture probe, wherein the specific DNA can be in specificity combination with the target molecules; (2), adding a solution to be detected for reaction; (3), adding a manometer gold solution for reaction and recording a fluorescence spectrum of the reaction solution. The detection method of the invention has commonality and wide range of application so that detection objects can be any target molecule. The invention can be utilized to conveniently realize the rapid, sensitive andselective detection of the target molecules.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of quinoxaline type fluorescent probe and application of quinoxaline type fluorescent probe in detection of G-quadruplex
ActiveCN109232446ARadiation transition blockedEasy to pile upOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuinoxalineProtein secondary structure
The invention provides a preparation method of a quinoxaline type fluorescent probe and application of the quinoxaline type fluorescent probe in detection of a G-quadruplex. The structural formula ofthe quinoxaline type fluorescent probe is as shown in the specification. In the formula, R1 adopts at least one of N-methylpiperazinyl, morpholinyl and diethylamino, R2 adopts F and methyl, and R3 adopts at least one of F, methyl, N-methylpiperazinyl and triazolyl. Compared with the prior art, the probe provided by the invention has the following advantages: (1) the probe is simple in preparation,easily available, stable in structure and convenient to store; (2) the probe provided by the invention can specifically detect a G-quadruplex structure to distinguish the G-quadruplex structure fromother secondary structures, the secondary structure of a nucleic acid sample can be identified by using a simple fluorescence spectrophotometer or even can be observed with naked eyes without any instrument, the process is fast, the operation is simple and convenient, the cost is low, and field inspection can be realized; and (3) the probe has no obvious influence on the secondary structure of thenucleic acid to be detected, and can accurately detect the original structure of the nucleic acid.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Closed nucleic acid structures
ActiveUS9404147B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid structureNucleic acid secondary structure
The invention provides compositions and methods for making closed nucleic acid structures in which one or both strands are continuous. The closed nucleic acid structures can be used as sequencing templates among other applications.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
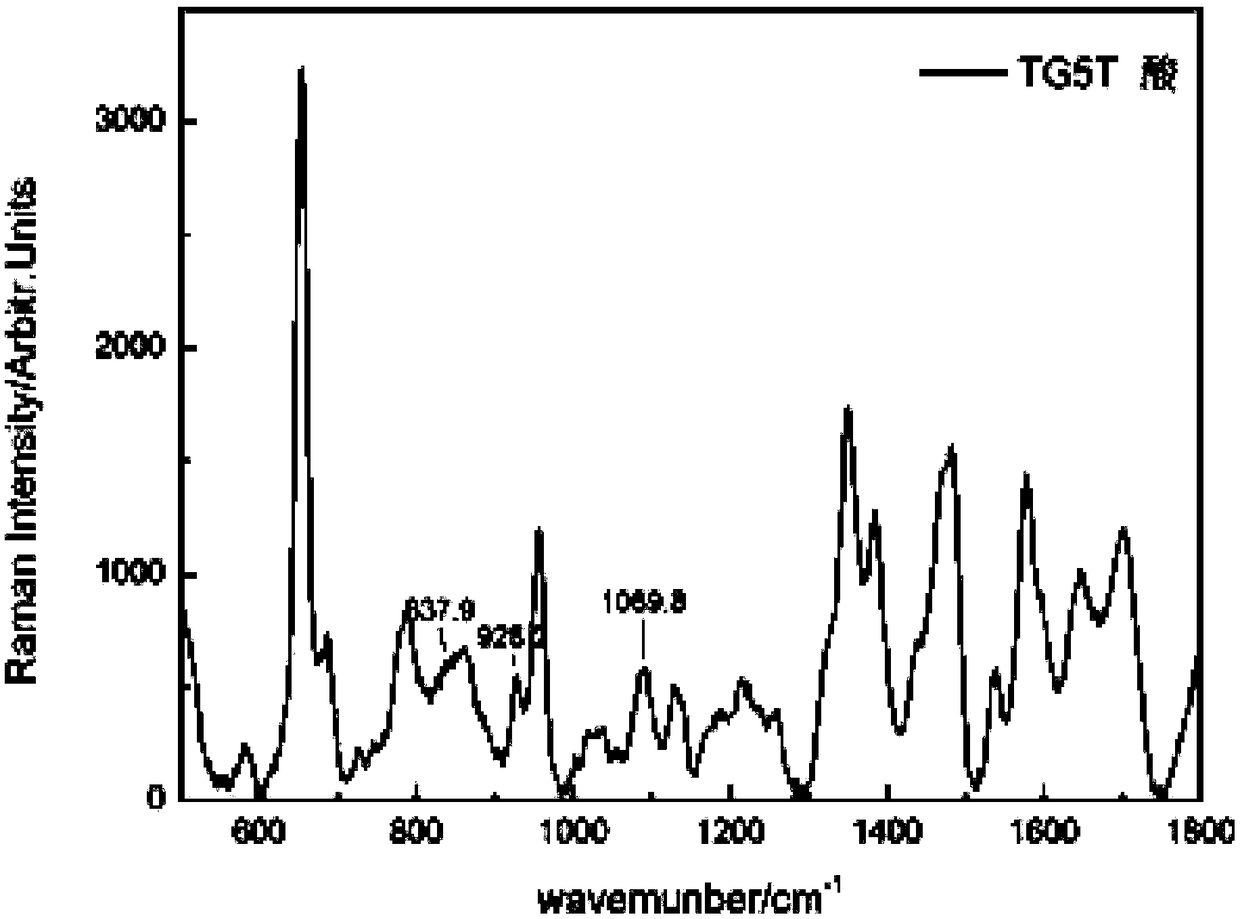
Nucleic acid structure detection method based on surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy
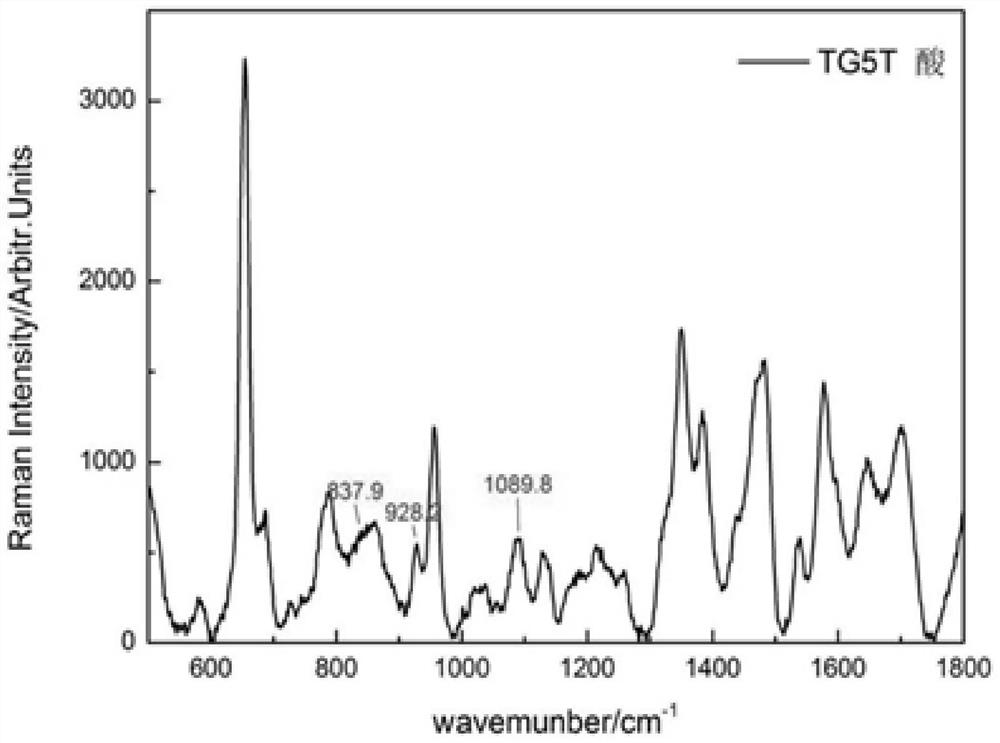
ActiveCN108444969AEfficient removalImprove accuracyRaman scatteringAluminum IonSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
The invention relates to a nucleic acid structure detection method based on surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. The nucleic acid structure detection method comprises: (1) preparing a silver nanoparticle sol modified and cleaned with iodine ions; and (2) adding a to-be-detected DNA sample to a centrifuge tube filled with the iodine ion modified silver nanoparticle, adding a buffer solution with the PH value of 3.0-5.0, adding an aluminum ion or titanium ion aggregating agent, and carrying out surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection. According to the present invention, the method effectively detect the secondary structure of nucleic acid, has the advantages of simpleness, rapidness and the like of SERS, and further has extremely high reproducibility and extremely high reliability; themethod overcomes the difficulty in the detection of the secondary structure of nucleic acid in the traditional SERS detection, has advantages of simple operation steps, rapidness, high sensitivity and good reproducibility, can obtain the signal with the extremely high signal-to-noise ratio, and achieves the high sensitivity detection on various nucleic acid secondary structures.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
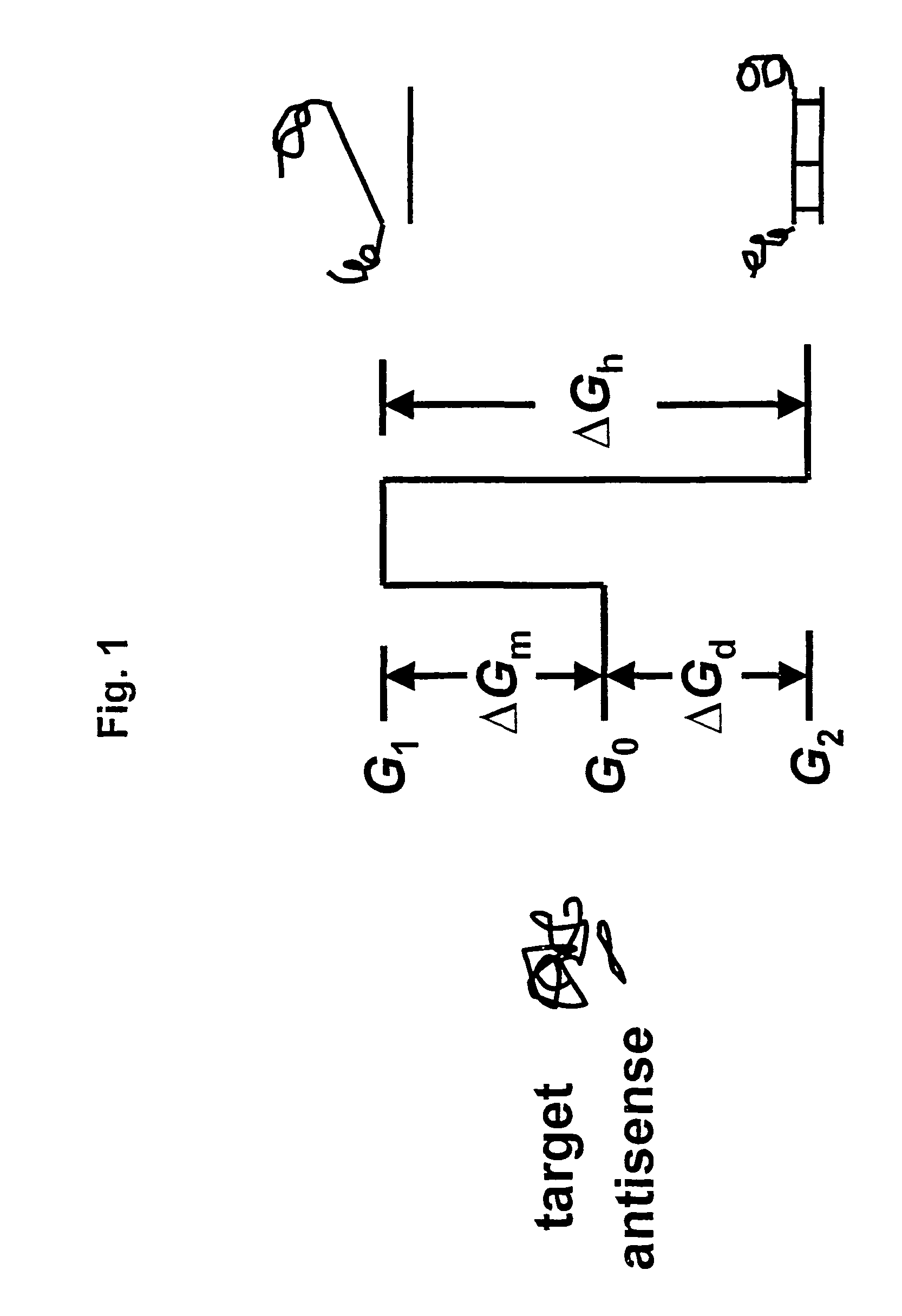
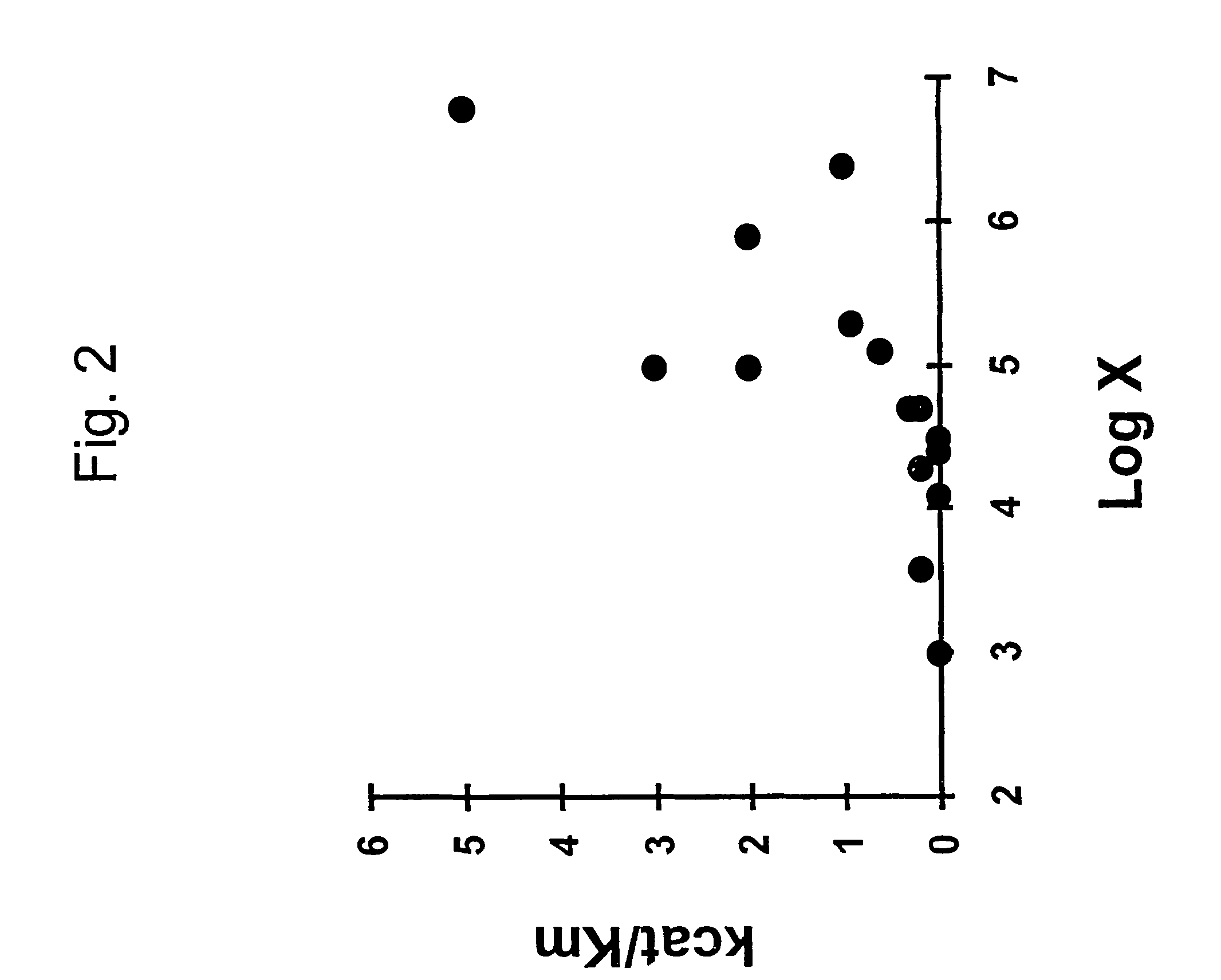
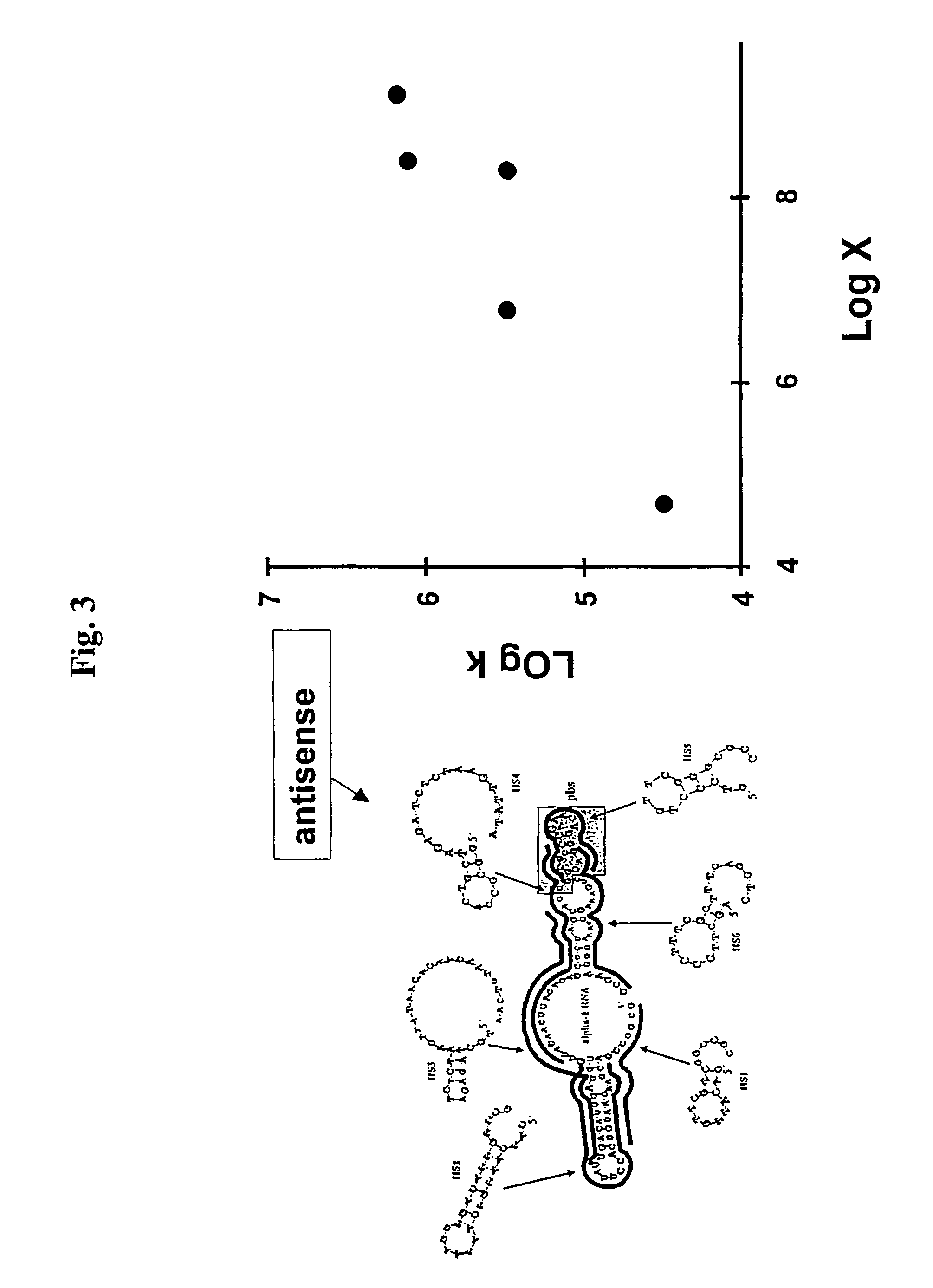
Selection of target sites for antisense attack of RNA
InactiveUS7313482B2Free energyCalculating a rate factor for hybridization to any target site is relatively straightforwardMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsRapid identificationSingle strand
Nucleic acid hybridization under steady-state conditions is described by a kinetic model in which the intermediate state is assumed to be locally single stranded. An expression was derived that relates nucleic acid secondary structure to the rate of oligonucleotide-RNA hybridization. The model allows the calculation of a rate factor that is proportional to the rate constant for hybridization between complementary nucleic acids and is generally applicable to any RNA molecule with potential utility for rapid identification of sites for antisense attack of mRNA.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
A polyaryl-substituted imidazole fluorescent probe and its preparation method and application in specific detection of g-quadruplexes
ActiveCN106749208BEasy to makeRaw materials are easy to getOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceSpecific detectionStructural formula
The invention discloses a polyaryl-substituted imidazole fluorescence probe. The structural formula of the polyaryl-substituted imidazole fluorescence probe is shown in the formula (I). The invention further discloses a preparation method of the polyaryl-substituted imidazole fluorescence probe and application of the polyaryl-substituted imidazole fluorescence probe in the specific detection of a G-quadruplex. The fluorescence probe is simple to prepare, stable in structure and can be applied to the specific detection of a wild c-MYC G-quadruplex nucleic acid secondary structure, the raw materials are easily available, the wild c-MYC G-quadruplex nucleic acid secondary structure in a solution can be rapidly detected by virtue of a fluorescence spectrometer, and the fluorescence probe has no fluorescent responsiveness to mutational c-MYC G-quadruplexes or other DNA secondary structures. The method for the specific detection of the wild c-MYC G-quadruplex nucleic acid secondary structure has the beneficial effects that the operation is simple and convenient, the sensitivity and the specificity are strong, and disadvantages of other detection methods that the cost is high, the equipment requirement is high, the technical operation is relatively complex, and the like can be overcome.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Helicase activity determination method based on double-stranded DNA and application of helicase activity determination method
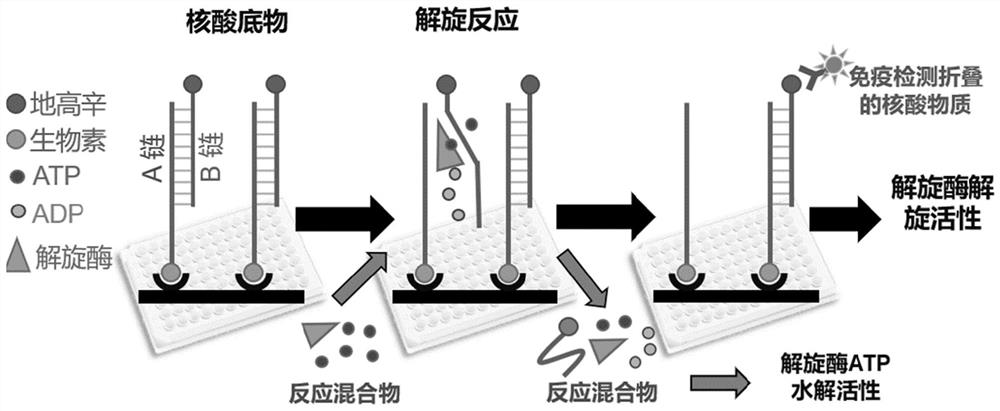
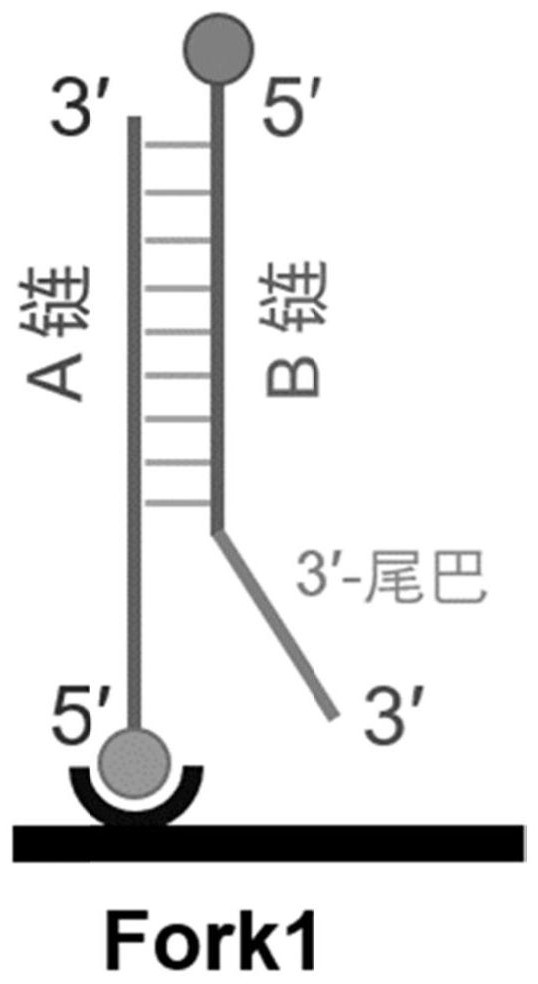
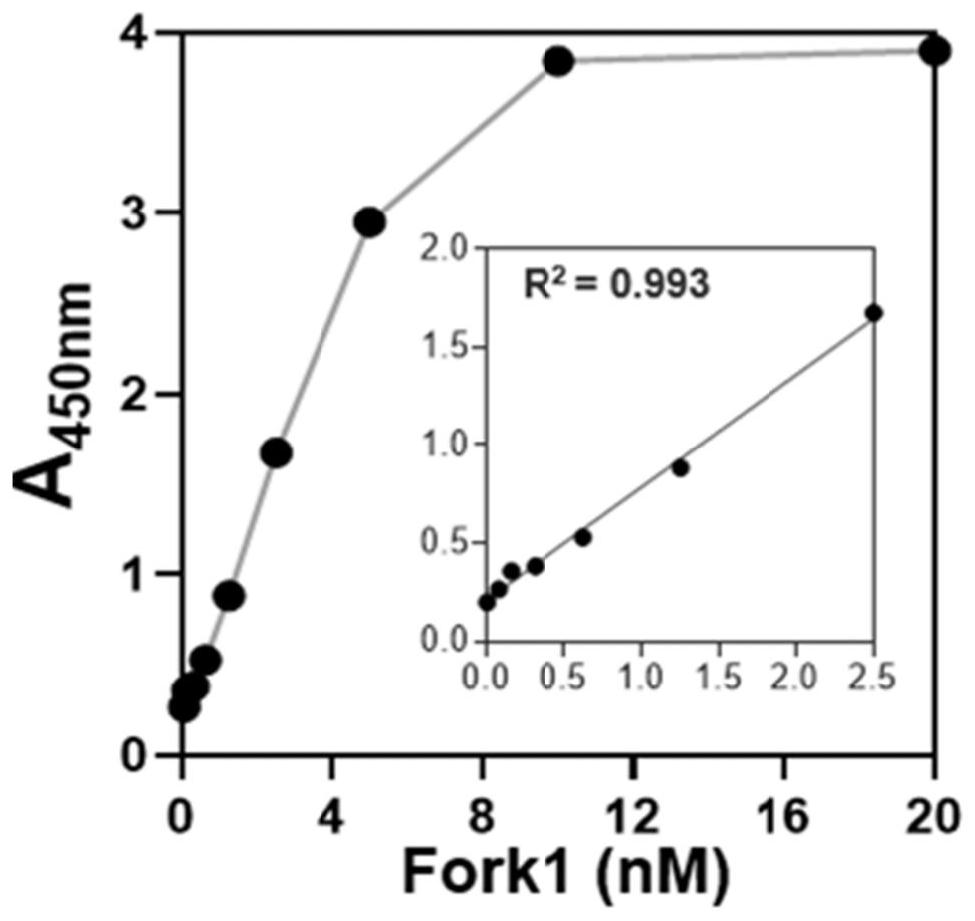
PendingCN114561442AAccurate activity quantification effectIncrease freedomMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisElectrophoresesSingle strand
The invention discloses a double-stranded DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)-based helicase activity determination method and application thereof. The method mainly realizes detection based on a nucleic acid secondary structure obtained by single-stranded hybridization of at least two DNAs. The tail end of at least one DNA single chain in the nucleic acid secondary structure is connected with a tail sequence, and the tail ends of any two different DNA single chains in the nucleic acid secondary structure are respectively connected with two substances or groups which are not interfered with each other and are specifically combined. Compared with other helicase detection methods, the detection method provided by the invention has a more accurate helicase activity quantitative effect, does not need tedious steps such as electrophoresis and membrane transfer, shortens the detection time by 3-4 hours, allows simultaneous detection of ATP consumption in the same solution system, and makes helicase activity evaluation more comprehensive.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
Composition and method for regulating any gene expression
PendingCN113637670AImprove general performanceWide applicabilityHydrolasesDNA/RNA fragmentationBase JProtein molecules
The invention discloses a composition and a method for regulating any gene expression. The composition comprises an oligonucleotide probe and a protein molecule; the oligonucleotide probe is composed of two parts, one part of the oligonucleotide probe is provided with a nucleic acid secondary structure, the other part of the oligonucleotide probe is basically complementary to a target substrate, and basic groups at certain specific positions are not complementary to the target substrate; the protein molecule can recognize the nucleic acid secondary structure of the oligonucleotide probe, so that the protein molecule is bound with the probe, is guided by the probe and is bound with the target substrate to form a 'target substrate-protein molecule-probe' ternary complex; based on the fact that the basic groups on the certain specific positions of the oligonucleotide probe are not complementary with the target substrate, the protein molecule only has a binding reaction with the target substrate, and a cleavage reaction does not occur. The composition not only acts on a DNA target, but also acts on an RNA target; the composition not only can work in prokaryotic cells, but also can work in eukaryotic cells; and the composition not only can up-regulate gene expression, but also can down-regulate gene expression.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Signal amplification
ActiveUS9862990B2Guaranteed detection effectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid structureBiology
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the use of enzymes composed of nucleic acid and / or protein enzymes to generate and amplify a signal indicative of the presence of a target. More particularly, the invention relates to compositions comprising nucleic acid structures that serve as partial or complete enzyme substrates and methods for using these structures to facilitate detection of targets.
Owner:SPEEDX
A bifunctional probe, its preparation method and its application in the detection of normal parallel conformation g-quadruplex
InactiveCN104710977BEasy to makeRaw materials are easy to getOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSpecific detectionStructural formula
The invention provides a bifunctional probe. The concrete structural formula of the probe is shown in the specification. In the formula, R1 is F or an N-methylpiperazinyl group, R2 is F or an N-methylpiperazinyl group, and R1 and R2 cannot simultaneously be F; and R3 is a methoxy group, a diethylamino group, a dimethylamino group, an N-methylpiperazinyl group, F or H. The probe has the advantages of simple preparation steps, easily available raw materials and stable structure, can be used for the specific detection of the orthographic parallel conformation G-quadruplex nucleic acid secondary structure, can rapidly detect the orthographic parallel conformation G-quadruplex nucleic acid secondary structure in a nucleic acid sample through an ultraviolet spectrophotometer, a fluorospectrophotometer or an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay instrument, and even naked eye observation under sunlight or an ultraviolet lamp, and overcomes the disadvantages of difficult distinguishing of many different conformations of G-quadruplex nucleic acid, high price, high device requirements and complex technical operation of other detection methods.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A kind of preparation method of quinoxaline fluorescent probe and its application in detecting g-quadruplex
ActiveCN109232446BEasy to makeEasy to prepareOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuinoxalineFluoProbes
The invention provides a preparation method of a quinoxaline fluorescent probe and its application in detecting G-quadruplexes. At least one of ethylamino, R2 adopts F, methyl, and R3 adopts at least one of F, methyl, N-methylpiperazinyl and triazolyl. Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the following advantages: (1) The probe is easy to prepare, easy to obtain, stable in structure and convenient for storage. (2) The probe provided by the present invention can specifically detect the G-quadruplex structure, realize the distinction between the G-quadruplex structure and other secondary structures, and use a simple fluorescence spectrometer, even without any instrument, to observe with the naked eye The secondary structure of the nucleic acid sample can be identified, which is fast, easy to operate, low in cost, and can realize on-site detection. (3) The probe has no obvious influence on the secondary structure of the nucleic acid to be detected, and can accurately detect the original structure of the nucleic acid.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Dual-functional probe and preparation method and application in detection of G-quadruplex structure thereof
ActiveCN102719238BEasy to makeEasy to prepareOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementUv vis absorbanceA-DNA
The invention discloses a bifunctional probe, its preparation method and its application in detecting the G-quadruplex structure. This type of probe is easy to prepare, easy to obtain, and has a stable structure. It can be used to specifically detect the secondary structure of G-quadruplex nucleic acid. It can be quickly detected by ultraviolet-visible absorption spectroscopy, fluorescence spectrophotometer, or directly by naked eye observation. The secondary structure of a DNA sample in solution is detected. This type of probe has the advantages of simple operation, good selectivity, quickness, and visible to the naked eye for the detection of the secondary structure of G-quadruplex nucleic acid, and overcomes the disadvantages of other detection methods such as expensive, high equipment requirements, and relatively complicated technical operations. .
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A semicyanine compound based on benzothiazole-linked heterocycle and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111217806BEasy to detectQuick checkOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceEthyl groupStructural formula
The invention discloses a semicyanine compound based on a benzothiazole biheterocycle, a preparation method and an application thereof. The structural formula of this type of compound is shown in formula I: the preparation method of this compound comprises the following steps: using the benzothiazole compound shown in formula II and haloalkane R b X is subjected to an alkylation reaction to obtain a substituted benzothiazole compound, which is then subjected to a Knoevenagel condensation reaction with N-ethylcarbazole-3-formaldehyde to obtain the product. The synthesis and preparation steps of the invention are simple and easy, the raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, the probe has a stable structure and high specificity, and can be used to specifically detect the secondary structure of G-quadruplex and double helix of nucleic acid. The method for detecting the secondary structure of nucleic acid by the probe has the advantages of low price, simple operation, good selectivity and quickness, and overcomes the disadvantages of high price, high equipment requirements and relatively complicated technical operation of other detection methods.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for realizing over expression of thermostable laccase gene through location transformation
InactiveCN102061290BIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses a method for realizing over expression of the thermostable laccase gene through location transformation. Thermostable laccase produced from thermus thermophilus bacteria has great application potential in the industrial processes of pulp bleaching, textile decoloring, biomass hydrolysate detoxifying and the like, but the thermostable laccase gene has low expression level and can not become an enzyme source. In the invention, a carrier in a pHsh series is firstly applied to carrying out cloning, in-situ mutagenesis and induced expression on the laccase gene. By carryingout case analysis and multiple explorative site-directed mutagenesis on a special sequence of the thermostable laccase gene, the invention has the effects of reducing rare codons in the gene, lowering the GC base content and weakening formation of a nucleic acid secondary structure and the like, thereby enhancing the expression level of the gene in escherichia coli by 317 times compared with a natural gene.
Owner:SHINE E BIOTECH CO LTD
A method for targeted cleavage of arbitrary nucleic acids
ActiveCN104745570BAchieve targeted cleavageImprove general performanceHydrolasesDNA preparationGlycineNucleic acid structure
The invention relates to a method for implementing targeted cleavage on arbitrary nucleic acid; a structural identification endonuclease is constructed and expressed for establishing the method. The method comprises the concrete steps: selecting a cleavage position of a target nucleic acid, and designing a nucleic acid probe complementary with target nucleic acid; adding into a reaction system, making the probe hybridized with a substrate, and forming a secondary structure which can be identified by the structural identification endonuclease; and adding the enzyme, and carrying out a cleavage reaction. The nucleic acid structure which can be identified includes a nucleic acid intrusive structure and the like; an endonuclease identification functional domain is composed of a peptide fragment which can identify a nucleic acid secondary-structure enzyme and can be selected from E.coliMuts and the like; the cleavage functional domain is selected from a cleavage function of an IIS type endonuclease; a connection fragment between the identification functional domain and the cleavage functional domain of the endonuclease is mainly composed of serine and glycine; and the method breaks through the limit of a sequence of a nucleic acid substrate, so that the method can realize effective targeted cleavage of nucleic acids with different sequences.
Owner:NANJING GENERAL HOSPITAL NANJING MILLITARY COMMAND P L A
A method for detection of nucleic acid structure based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
ActiveCN108444969BEfficient removalImprove accuracyRaman scatteringAluminum IonSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
The invention relates to a method for detecting nucleic acid structure based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, comprising the following steps: (1) preparing iodide ion-modified and cleaned silver nanoparticle sol; (2) preparing iodide ion-modified silver nanoparticle centrifuge tube Add the DNA sample to be detected, add a buffer solution with a pH value of 3.0-5.0, and then add aluminum ions or titanium ion aggregation agents to perform surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection. It effectively detects the secondary structure of nucleic acid, has the advantages of simplicity and speed of SERS, and has high reproducibility and reliability. This method overcomes the difficulty of detecting the secondary structure of nucleic acid in the traditional SERS detection, and has the advantages of simple, fast, high sensitivity and good reproducibility, and obtains a signal with a very high signal-to-noise ratio, realizing the detection of various High sensitivity detection of nucleic acid secondary structure.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Polyaryl-substituted imidazole fluorescence probe, preparation method thereof and application thereof in specific detection of G-quadruplex
ActiveCN106749208AEasy to makeRaw materials are easy to getOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceArylSpecific detection
The invention discloses a polyaryl-substituted imidazole fluorescence probe. The structural formula of the polyaryl-substituted imidazole fluorescence probe is shown in the formula (I). The invention further discloses a preparation method of the polyaryl-substituted imidazole fluorescence probe and application of the polyaryl-substituted imidazole fluorescence probe in the specific detection of a G-quadruplex. The fluorescence probe is simple to prepare, stable in structure and can be applied to the specific detection of a wild c-MYC G-quadruplex nucleic acid secondary structure, the raw materials are easily available, the wild c-MYC G-quadruplex nucleic acid secondary structure in a solution can be rapidly detected by virtue of a fluorescence spectrometer, and the fluorescence probe has no fluorescent responsiveness to mutational c-MYC G-quadruplexes or other DNA secondary structures. The method for the specific detection of the wild c-MYC G-quadruplex nucleic acid secondary structure has the beneficial effects that the operation is simple and convenient, the sensitivity and the specificity are strong, and disadvantages of other detection methods that the cost is high, the equipment requirement is high, the technical operation is relatively complex, and the like can be overcome.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A kind of fluorescent probe and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN104151301BEasy to makeEasy to prepareOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceA-DNAStructural formula
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe, as well as preparation method of the fluorescent probe, and applications of the fluorescent probe in detecting conformation of G-quadruplex nucleic acid. The specific structural formula is as shown in specification, wherein R1 in the formula is F or N-methylpiperazine, and R2 is N-methylpiperazine. The probe is simple to prepare and easily available, and stable in structure, and can be used for specifically detecting the secondary structure of the orthographically parallel conformed G-quadruplex nucleic acid, and the secondary structure of a DNA sample in a solution can be rapidly detected through a fluorospectro photometer. A method for detecting the secondary structure of the orthographically parallel conformed G-quadruplex nucleic acid through the probe has the advantages of being simple and convenient to operate, and good in selectivity, and the defects that other detection methods are difficult for various conformations of the G-quadruplex nucleic acid to distinguish, expensive in price, high in equipment requirement, relatively complicated in technical operations, and the like can be overcome.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com