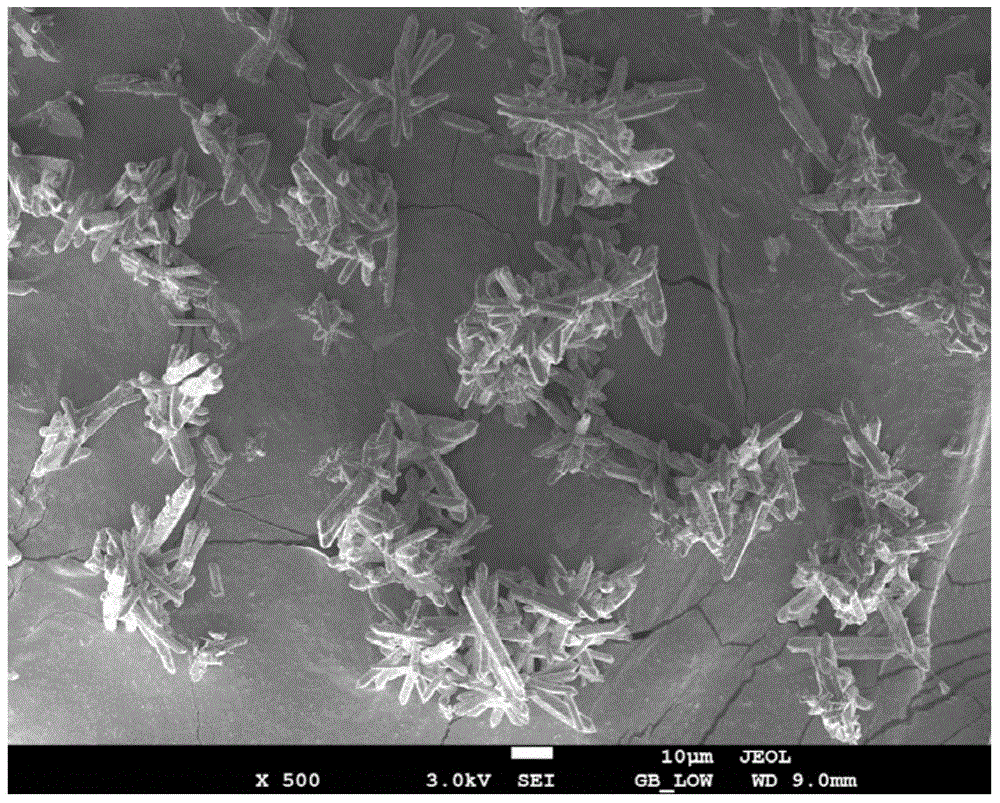
Method for recovering lead oxide from waste containing lead oxide
A technology containing lead oxide and lead oxide, applied in the field of lead oxide recovery, can solve the problems of large consumption of chemical raw materials, low purity, high recycling cost, etc., and achieve the effect of eliminating secondary pollution and shortening the process flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
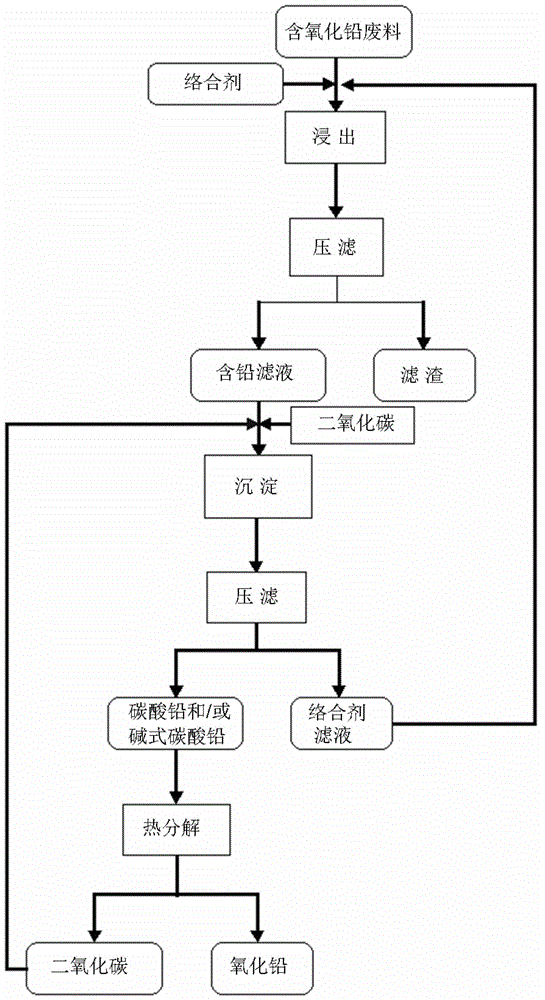
[0040] According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the precipitating agent is selected from one or more of carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide and sulfur trioxide, and the method for reclaiming lead oxide from waste containing lead oxide preferably also includes the step of ( 3) The gas obtained by the desalination and decomposition of the lead salt precipitation is recycled as the precipitant in step (2), which can meet the requirements of atomic economy reaction, thereby achieving zero consumption and zero emission, and has more industrial application prospects.
[0041] According to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, the precipitating agent is selected from one or more of ammonium sulfate, ammonium oxalate and ammonium carbonate, and the method for reclaiming lead oxide from waste containing lead oxide preferably also includes The ammonia solution formed by the ammonia gas generated by the reaction in step (2) is used in the desalination and ...
Embodiment 1
[0069] This embodiment is used to illustrate the method for reclaiming lead oxide from waste containing lead oxide provided by the present invention.
[0070] The lead oxide waste (930g) used in this example is lead-containing flue ash from Huitong Smelter. After analysis, it mainly contains PbO with a weight percentage of 69%, and the rest is a small amount of SnO 2 , CaSiO 3 、Al 2 o 3 and SiO 2and other insoluble impurities, the equivalent amount of PbO is 2.9mol.
[0071] The recovery process of lead oxide is as follows:
[0072] (1) Add the above lead oxide-containing waste to 10 liters of ethylenediaminediacetic acid aqueous solution with a temperature of 45°C and a concentration of 0.5mol / L, stir and react for 20 minutes, and then filter the reaction product to obtain lead-containing filtrate and filter residue.
[0073] (2) Heat the above-mentioned lead-containing filtrate to 70°C and feed 3.0mol sulfur dioxide, then keep the reaction temperature of 65°C for 12 min...
Embodiment 2
[0076] This embodiment is used to illustrate the method for reclaiming lead oxide from waste containing lead oxide provided by the present invention.
[0077] The lead oxide waste material used in this embodiment is lead-containing flue ash derived from gold and lead smelters. After analysis, it mainly contains 63% PbO and 8% PbSO by weight. 4 , the rest is a small amount of Al 2 o 3 and SiO 2 and other insoluble impurities.
[0078] Pretreatment process (pre-desalination treatment), as follows:
[0079] Since the main components of the lead oxide-containing waste are PbO and PbSO 4 , only the waste containing lead oxide needs to be pre-desalted. Take 1.6 kg of the above lead oxide-containing waste (equivalent to 4.942 mol of PbO) and put it into 0.5 liter of NaOH with a concentration of 2 mol / L for desalination reaction, control the reaction temperature at 60°C, stir and react for 10 minutes and then filter to obtain the pretreated lead-containing material .
[0080] T...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com