Astaxanthin esterase production strain and application of strain in preparation of free astaxanthin
A technology of astaxanthin ester and astaxanthin, which is applied to astaxanthin esterase production strains and its application field in the preparation of free astaxanthin, can solve the problems of multiple by-products, waste, difficult products, etc., and achieve high efficiency The effect of preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the examples.
[0023] 1. Screening of strains degrading astaxanthin ester
[0024] The medium formula used in the present invention is as follows:
[0025] 1) Enrichment medium
[0026] NH 4 NO 3 0.1%, KH 2 PO 4 0.025%, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.025%, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.001%, cholesterol oleate 0.1%, tap water, pH 7.0, sterilized at 115°C for 30min.
[0027] 2) Screening plate solid medium (solid screening plate)
[0028] NH 4 NO 3 0.1%, KH 2 PO 4 0.025%, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.025%, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.001%, cholesterol oleate (1.0% Triton X-100 solubilization) 0.1%, agar 2%, tap water, pH 7.0, sterilized at 115°C for 30min.
[0029] 3) Fermentation medium
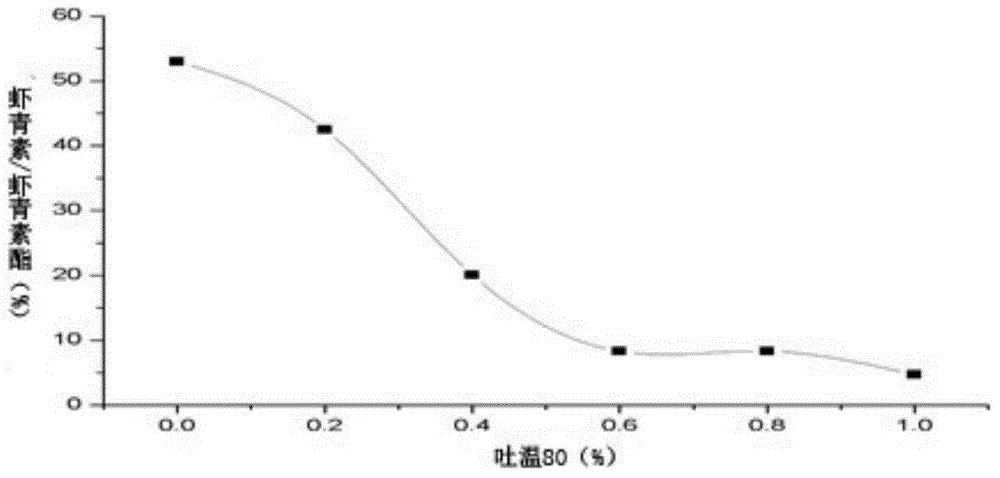
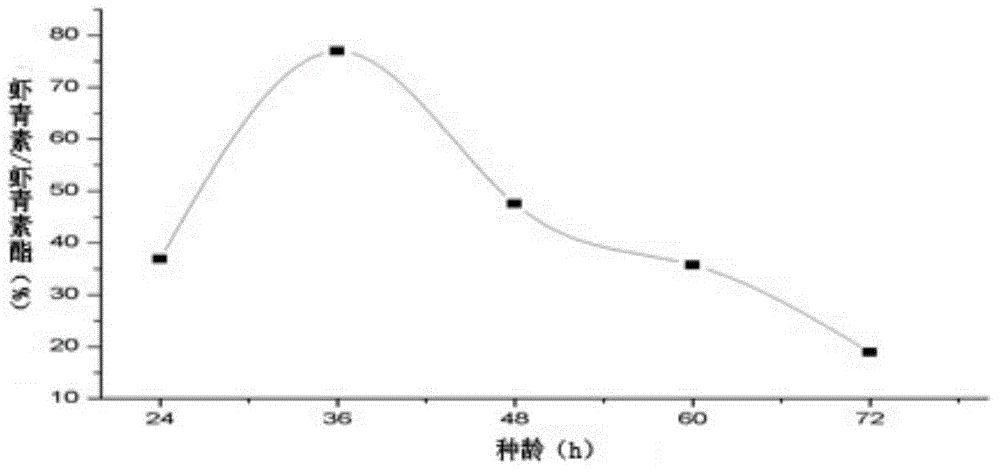
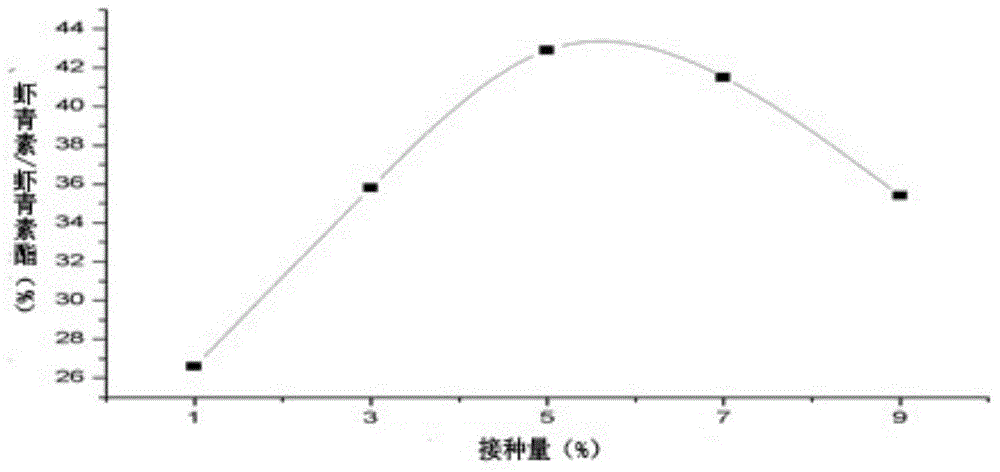
[0030] Haematococcus pluvialis oil fermentation medium: KH 2 PO 4 0.025%, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.025%, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.001%, beef extract 0.1%, peptone 1%, Haematococcus pluvialis oil (0.4% Tween80 solubilizing) 0.5%, tap water, pH 7...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com