Probe based on target triggering and supportive of secondary amplification and application thereof
A probe and target technology, applied in the field of molecular bioinformatics, can solve problems such as the inability to detect trace DNA sensitivity, and achieve the effects of wide dynamic detection range, enhanced signal, and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1: Probe design based on target-triggered secondary amplifiable probes
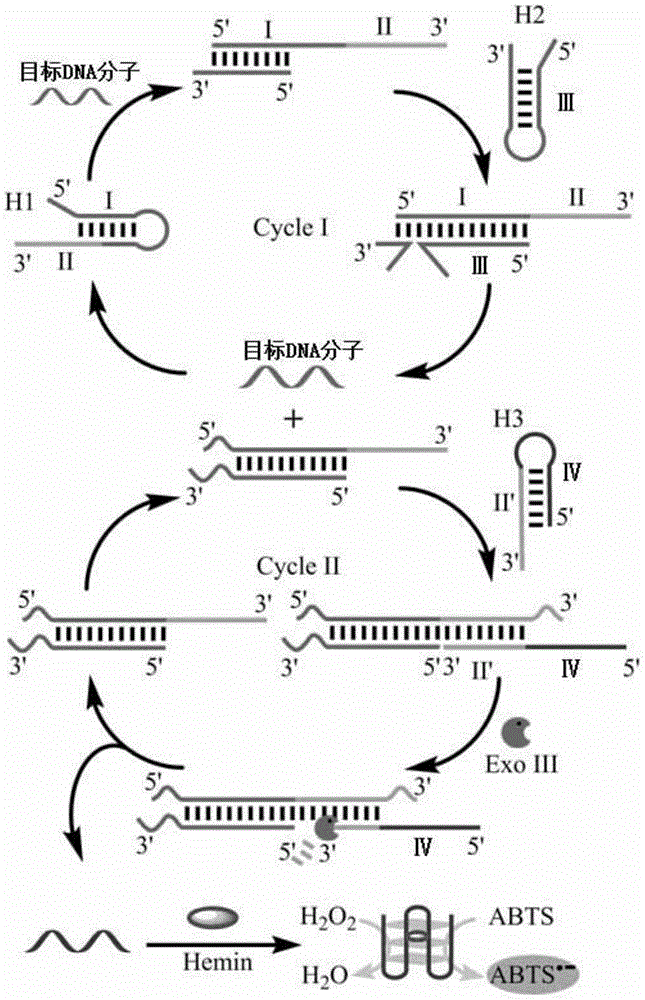
[0049] In this embodiment, the target-triggered secondary amplifiable probe includes: a first hairpin H1, a second hairpin H2 and a third hairpin H3, and the sequences of each are shown in Table 1. The target DNA to be detected has the following sequence: 5'-CAATATGTAGATCTAGTCACGCTA-3'.
[0050] Table 1 Probe sequences that can be amplified twice based on target triggering
[0051]
[0052] The first hairpin H1 includes: a recognition region I that recognizes target DNA and a first stem region II that partially hybridizes with the recognition region I to form a hairpin structure;
[0053] The second hairpin H2 includes: base complementary region III hybridized with the recognition region I part of the first hairpin;
[0054] The third hairpin H3 comprises: a second stem region II' hybridizable to a portion of the first stem region II of the first hairpin and a G-quadruplex region IV. ...
Embodiment 2
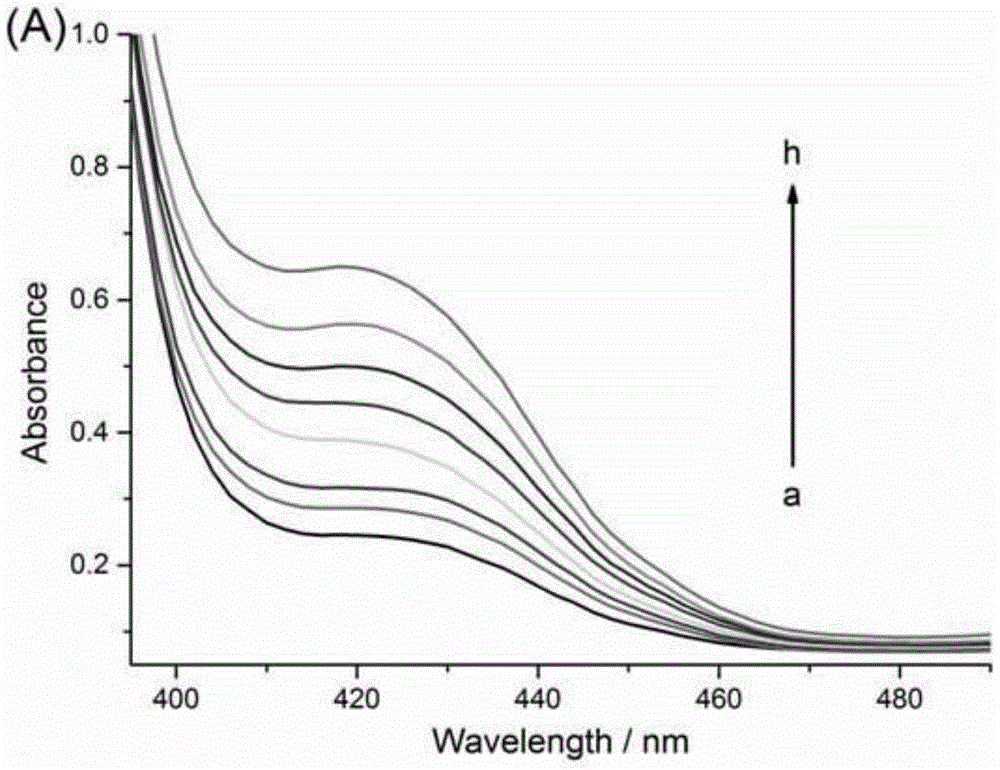
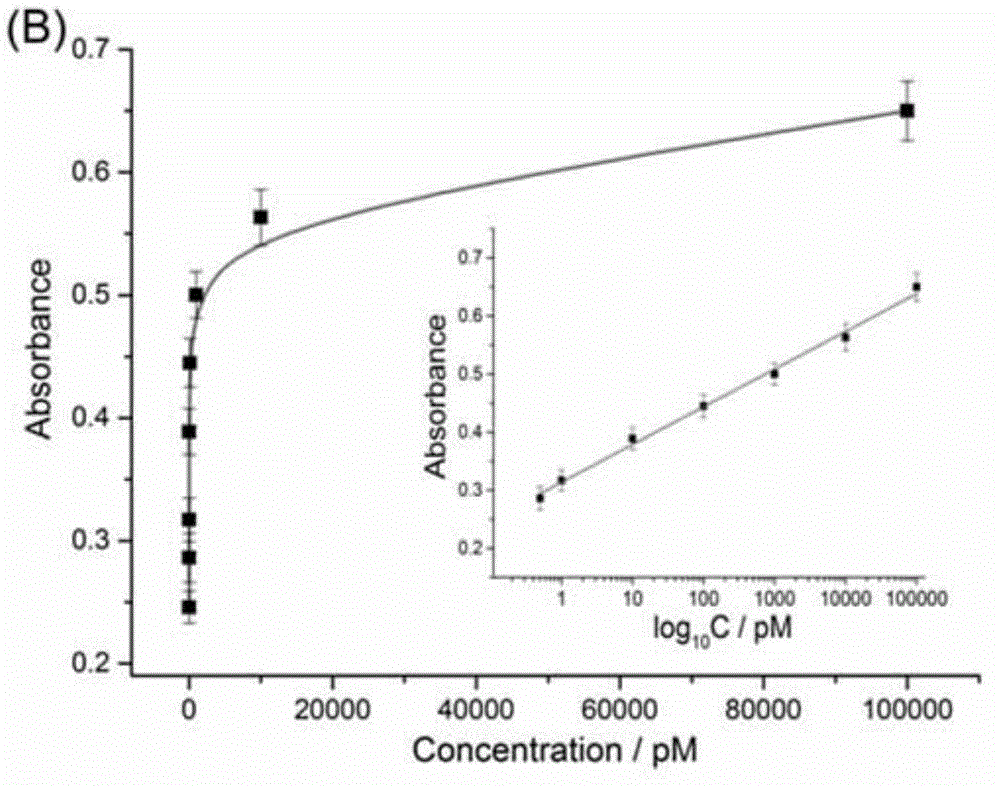
[0067] Example 2: Detection of target DNA at different concentrations based on target-triggered secondary amplifiable probes
[0068] Exonuclease III and hemin used in this example were purchased from Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (Tris), N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine -N'-2-ethanesulfonic acid (HEPES), 2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazole-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt (ABTS), hydrogen peroxide purchased from Aladdin reagents Company (Shanghai, China), there is no difference in the effect between the products of various commercially available models of the above materials. All solutions were prepared using redistilled water prepared by Milli-Q Purification System (Billerica, Massachusetts, USA).
[0069] The detection of the target DNA in embodiment 1 comprises the following steps:
[0070] First, take the solutions of the first hairpin, the second hairpin, and the third hairpin, heat them to 95° C., keep them for 5 minutes, then sl...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Embodiment 3: Signal amplification verification experiment based on target-triggered secondary amplifiable probes
[0077] In this example, the following solutions were prepared according to the method in Example 2, and numbered a, b, c, d in sequence:
[0078] Sample a: a solution in which the concentrations of the first hairpin H1, the second hairpin H2, and the third hairpin H3 are all 250 nM;
[0079] Sample b: a solution in which the concentrations of the first hairpin H1, the second hairpin H2, and the third hairpin H3 are all 250 nM, and the concentration of the exonuclease III is 2 U / uL;
[0080] Sample c: a solution in which the concentrations of the first hairpin H1, the second hairpin H2, and the third hairpin H3 are all 250 nM, and the concentration of the target DNA is 100 nM;
[0081] Sample d: a solution in which the concentrations of the first hairpin H1, the second hairpin H2, and the third hairpin H3 are all 250nM, the concentration of the exonuclease...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com