Building method and application of STCH gene knock-out animal model
A gene knockout and animal model technology, applied in the field of genes, can solve the problems of lack of carboxy-terminal peptide binding domain, lack of
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] STCH gene knockout animal model construction method, STCH conditional gene knockout mouse is through the strategy of gene targeting, inserting LoxP sites in the same direction at both ends of exon 2 of STCH gene, when the mouse is introduced into Cre recombinase In some cases, Cre recombinase recognizes the LoxP site and excises the sequence between the LoxP sites to achieve the purpose of conditionally deleting the STCH gene in specific cells. Include the following steps:
[0060] 1) Cultivate CJ7 embryonic stem cells derived from 129SV / J strain male mice on mouse embryonic fibroblast trophoblasts, and collect STCH gene knockout embryonic stem cells that are mutated by targeting vectors targeting exon 2 of the STCH gene ,
[0061] 2) Preparation of mouse donor blastocysts,
[0062] 3) Inject STCH knockout embryonic stem cells into the mouse donor blastocyst,
[0063] 4) Transplantation of blastocyst-formed embryos containing STCH-knockout embryonic stem cells into t...
Embodiment 2
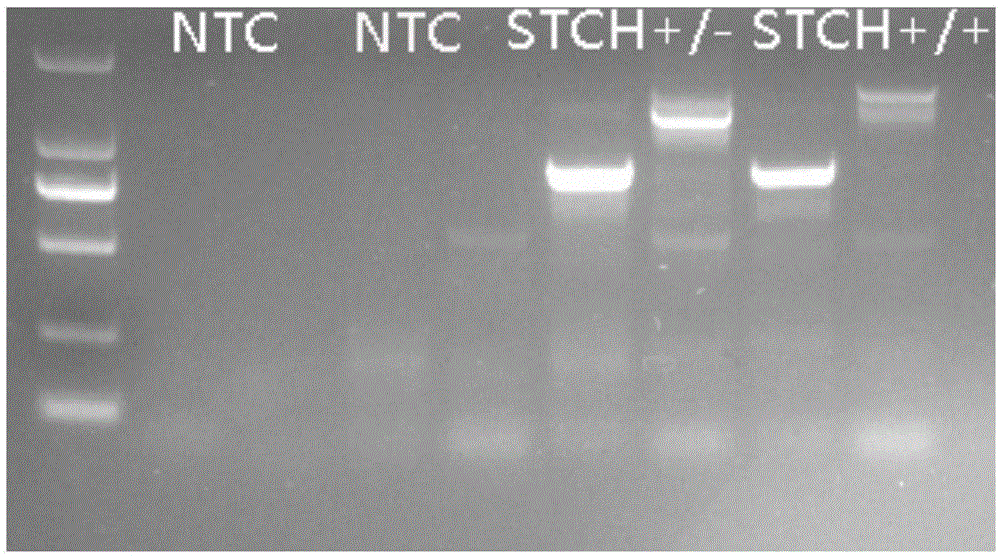
[0088] The phenotypes of the STCH+ / - mice (ie STCH gene heterozygous knockout mice) prepared in Example 1 were identified. STCH+ / - mice (ie STCH gene heterozygous knockout mice) were produced by the method in Example 1; STCH- / - mice (ie STCH gene homozygous knockout mice) were embryonic lethal. STCH+ / + mice: normal control mice.
[0089] 1. Detection of the genotype of newborn mice by PCR (using routine operation means)
[0090] Primer sequences, PAGE purification (Table 1).
[0091] Table 1 STCH gene sequence of mouse
[0092] Primer name
Primer sequence (5'-3')
KO P1
GGATGATCTGGACGAAGAGC
Common P2
GGGGGTAAGGTCTGGAATGT
STCH+ / + P3
AAAACGGGCATATCAGCATC
[0093] Electrophoresis band size: STCH+ / +: 904bp, STCH+ / -: 1372bp, CKO2000bp
[0094] The PCR kit was purchased from Takala (Code: D333)
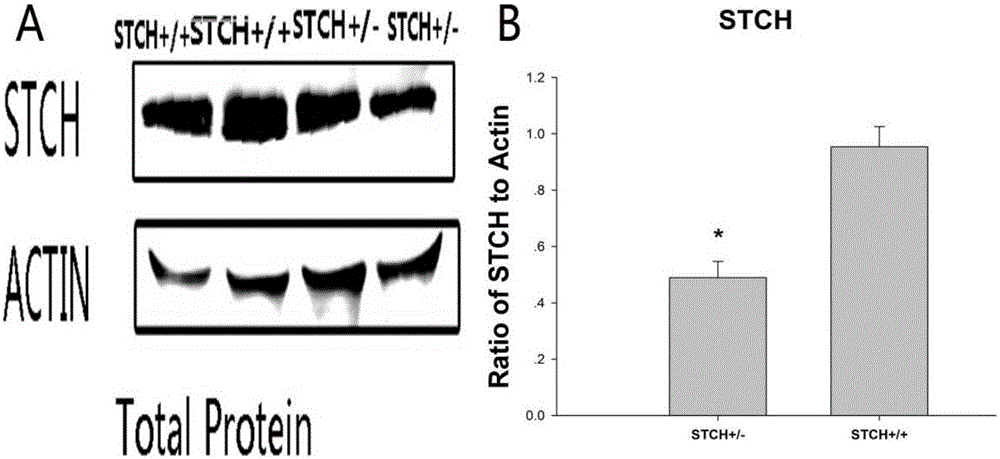
[0095] 2. Western Blot detection of STCH gene expression in STCH+ / - and normal mouse brains (using conventional methods)
[0096] G...
Embodiment 3
[0101] Behavioral test of STCH+ / + mice and STCH+ / - mice
[0102] Including the following experiments: rotarod behavior experiment, tail suspension behavior experiment, forced swimming behavior experiment, open field behavior experiment, water maze behavior experiment. The experimental method adopts conventional method or standard method.
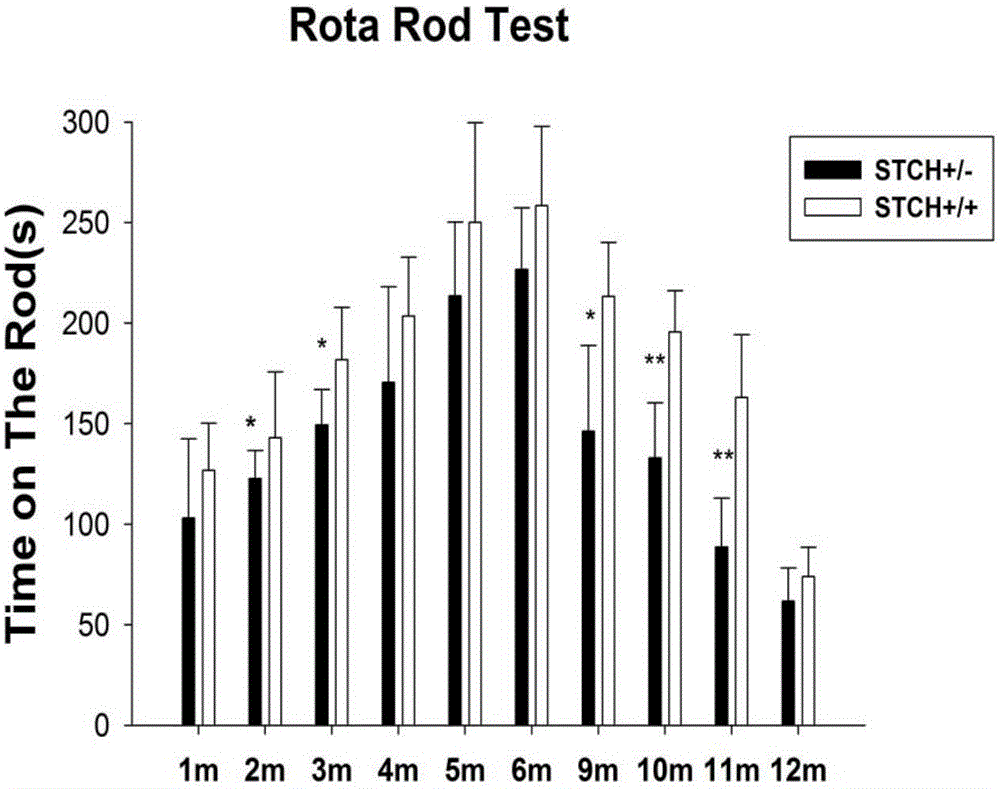
[0103] From image 3 According to the analysis of the results, the motor coordination ability of STCH+ / - mice was poorer than that of STCH+ / + mice at any age. And this significant difference began to appear when the age of the mice was two months, and then as the months increased, the motor coordination ability of the two groups of mice gradually increased and reached the peak at the age of six months, and then increased with the age of the mice. growth, the ability shows a gradual decline.
[0104] From Figure 4 According to the analysis of the results, the depression degree of STCH+ / - mice was significantly stronger than that of STCH+...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com