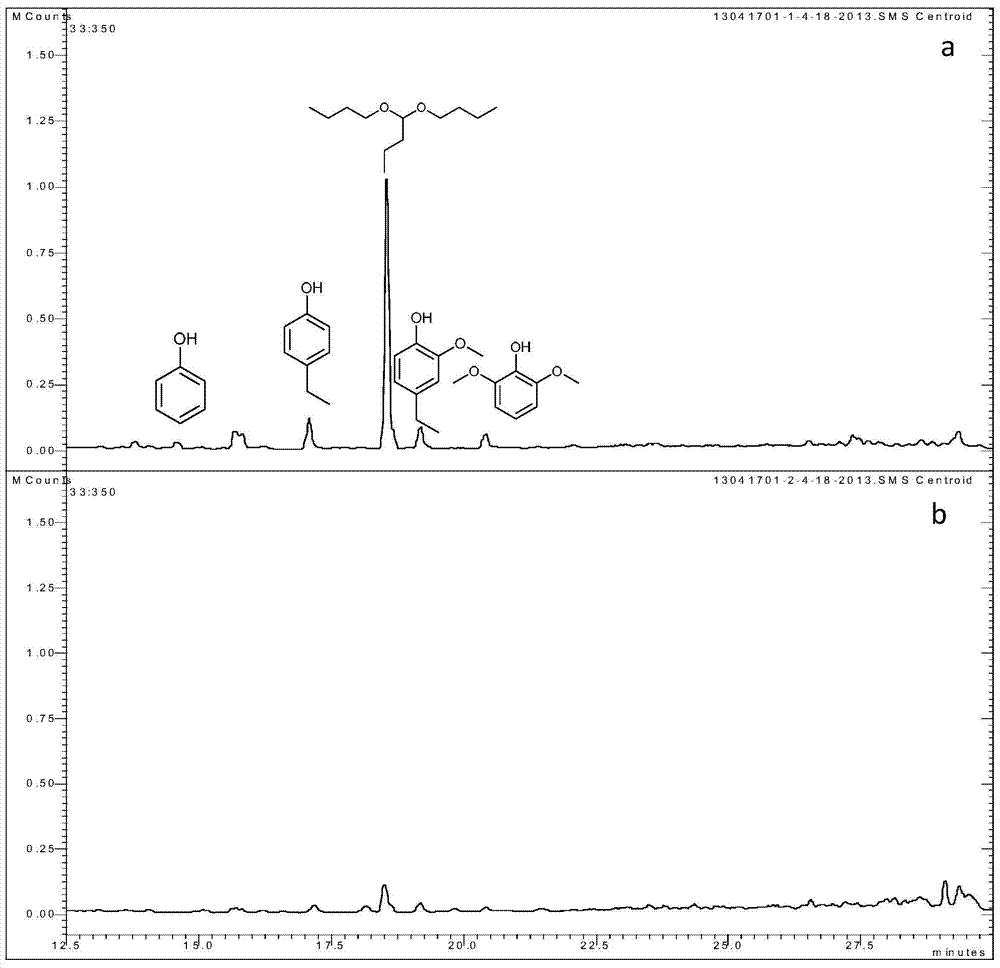
A microemulsion reactor for catalytic depolymerization of lignin
A technology for catalyzing depolymerization and lignin, which is applied in the field of lignin catalyzing depolymerization to prepare high value-added products, can solve the problems of difficulty in ionic liquids, unfavorable recycling, product separation, etc., and achieves easy recovery, extremely easy product separation, The effect of high liquefaction rate and selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] 1. Ionic liquid BSmimHSO 4 Preparation of:
[0030] (1) Weigh an equimolar amount of N-alkylimidazole and butane sultone to react at 50°C for 24h; after the reaction, wash with ether and dry under vacuum at 60°C to obtain a white solid inner salt; the N- The carbon chain length of the alkylimidazole is 1 to 6 carbon atoms;
[0031] (2) Weigh an equimolar amount of acid and the internal salt prepared above; add concentrated sulfuric acid dropwise to the internal salt while stirring, and react at 50° C. for 48 hours;
[0032] (3) After the reaction, wash with anhydrous ether and dry in vacuum at 80°C for 48 hours to obtain the ionic liquid BSmimHSO 4 .
[0033] 2. Preparation of bagasse lignin:
[0034] (1) Pretreatment of agricultural waste: After the bagasse is fully dried, it is pulverized to below 60 mesh by mechanical pulverization, and its soluble components and ash are washed with deionized water and fully dried for later use;
[0035] (2) Extraction of organo...
Embodiment 2
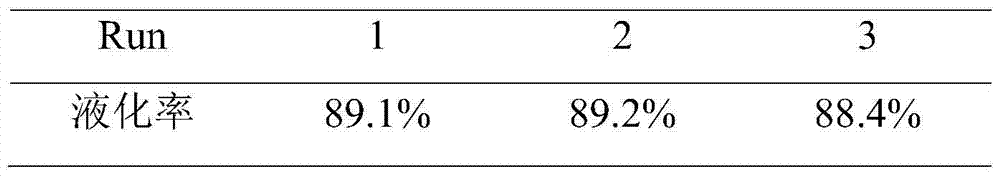
[0039] Accurately weigh 0.5g bagasse lignin, 20mL n-butanol, 20mL deionized water, 2mL n-hexane, 3.0mmol 1-(4-sulfonic acid butyl)-3-ethylimidazolium bisulfate (BSeimHSO 4 ) into a 100mL autoclave, and reacted at 250°C for 0.5h. After the reaction, the reaction liquid was separated by filtration to obtain a solid residue, which was dried in vacuum at 60° C. for 24 hours, and the calculated liquefaction rate was 87.9%. The n-butanol water was separated, the n-butanol phase was extracted three times with deionized water, and the volume was adjusted to 100 mL with n-butanol, and the yield of the main phenolic monomer was determined to be 20.14 mg / g by GC-MS.
Embodiment 3
[0041]Accurately weigh 0.5g bagasse lignin, 20mL n-butanol, 20mL deionized water, 2mL n-hexane, 3.0mmol 1-(4-sulfonic acid butyl)-3-propylimidazolium bisulfate (BSpimHSO 4 ) into a 100mL autoclave, and reacted at 250°C for 0.5h. After the reaction, the reaction solution was separated by filtration to obtain a solid residue, which was dried in vacuum at 60° C. for 24 hours, and the liquefaction rate was calculated to be 88.6%. The n-butanol water was separated, the n-butanol phase was extracted three times with deionized water, and the volume was adjusted to 100 mL with n-butanol, and the yield of the main phenolic monomer was determined to be 26.38 mg / g by GC-MS.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com