Sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnet without heavy rare earth and preparation method of sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnet
A non-weight rare earth and NdFeB technology is applied in the fields of magnetic objects, inorganic material magnetism, inductor/transformer/magnet manufacturing, etc. It can solve the problems of not giving full play to the performance advantages and achieve the effect of improving the magnetic performance of the product
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0038] A preparation method of a heavy rare earth-free sintered NdFeB magnet, comprising the following steps:
[0039] (1) The NdFeB rare earth permanent magnet material alloy is crushed by mechanical crushing or hydrogen crushing and jet milling to obtain NdFeB rare earth permanent magnet material alloy powder with an average particle size of 2.0-4.5 μm;
[0040] (2) Light rare earth element fine powder is obtained through various crushing processes to obtain light rare earth fine powder with an average particle size of 1-2.5 μm;
[0041] (3) adding the rare earth micropowder and nanometer metal into the NdFeB permanent magnet material alloy powder according to the weight ratio of 0.5%-3% and 0.05%-2% respectively, and mixing evenly;
[0042] (4) Pressing the mixed alloy powder into a blank in an orientation magnetic field with a magnetic field strength ≥ 1.4T;
[0043] (5) Put the formed blank into a vacuum sintering furnace for high-temperature sintering, the sintering tem...
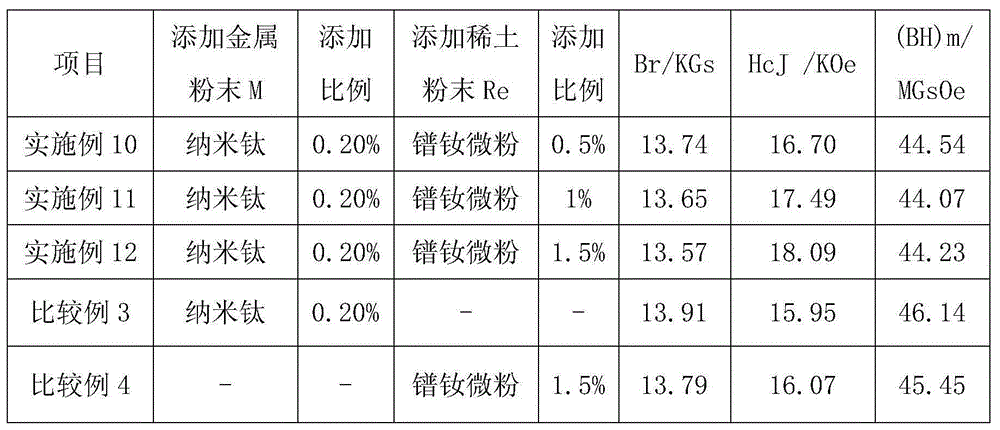
Embodiment 1
[0045] The composition is (Nd, Pr) 13.94 Fe 78.28 m 1.86 B 5.92 (at%) NdFeB permanent magnet material alloy, prepare according to the technical scheme of the present invention: carry out batching by above-mentioned composition and make NdFeB permanent magnet material alloy with quick-setting sheet technology; The rare earth NdFeB permanent magnet material alloy is crushed to obtain alloy powder with an average particle size of 3.1 μm.
[0046] Under the protection of nitrogen, the nano-titanium with an average particle size of 40nm and the prepared NdFeB permanent magnet material alloy are fully mixed, and the mixed powder is pressed into a 71.4×50×44.1 (mm) in an orientation magnetic field of ≥1.4T ) square blank, put the blank into a high vacuum sintering furnace, sinter at 1065°C for 4.5 hours, temper at 895°C for 2 hours and temper at 515°C for 4 hours to obtain a sintered magnet: take Φ10×10 (mm) Table sample 2 is only tested for magnetic properties.
Embodiment 1
[0047]Example 1: The addition percentage of nano-titanium is 0%, the magnetic performance test result of the gained sintered magnet: Br=(13.98-14.05) KGs, HcJ=(15.07-15.13) KOe, (BH)m=(46.81- 47.07) MGsOe.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com