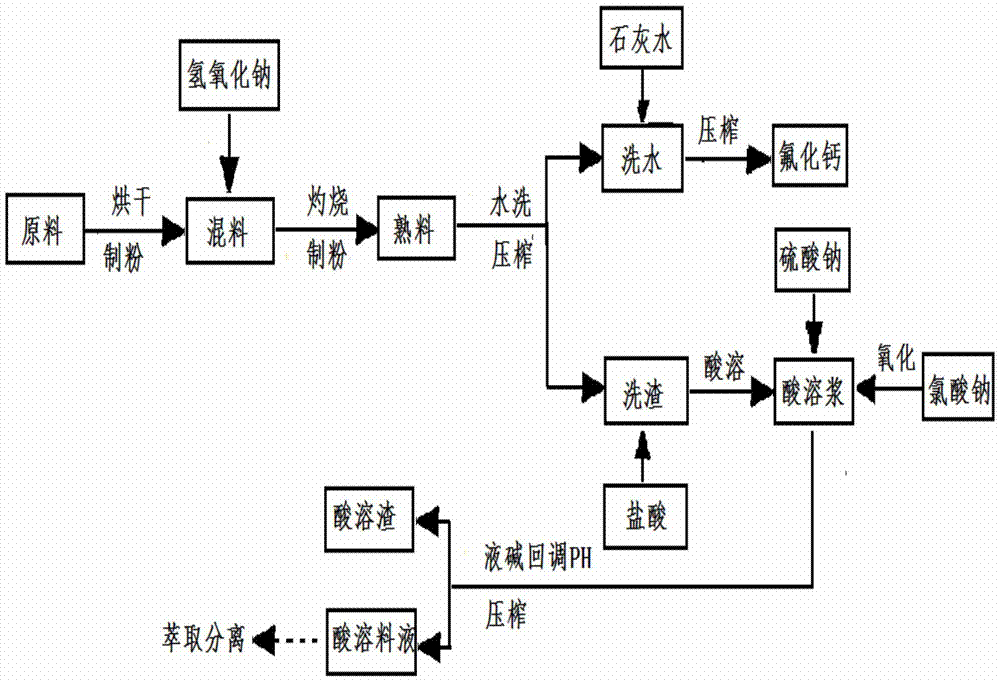
A process for decomposing fluorine-containing rare earth molten salt waste slag
A waste residue and rare earth technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of high extraction and separation cost, high roasting temperature, and large loss of pot, and achieve convenient extraction and separation, high primary acid dissolution rate, and low overall energy consumption. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
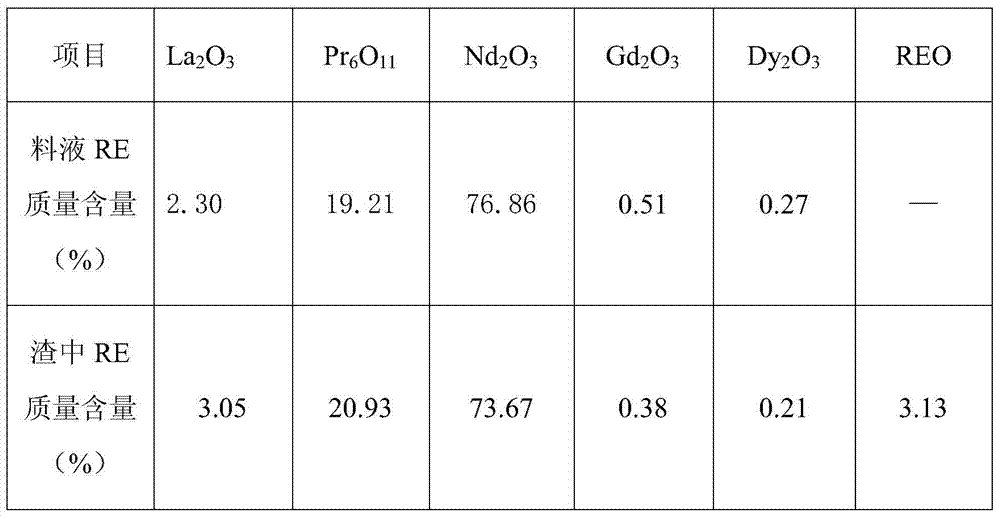
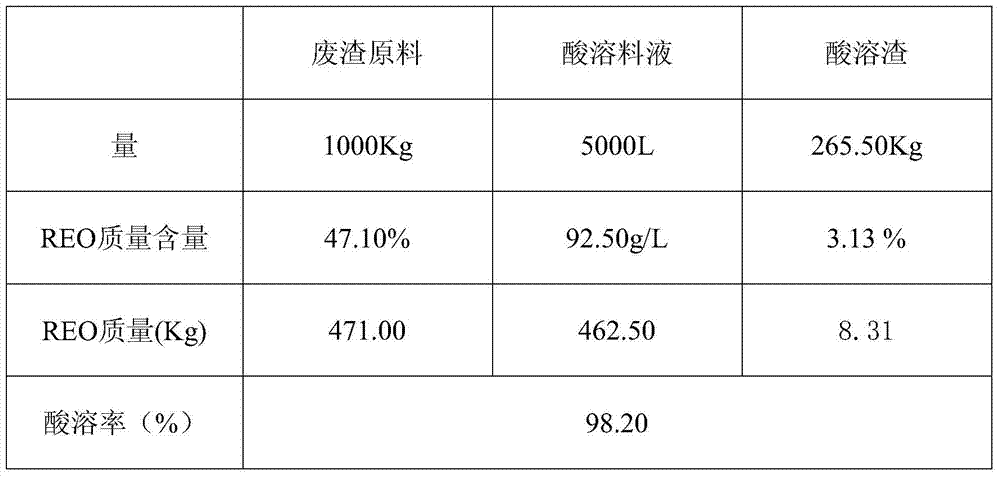
[0031] Example 1: 1000Kg of rare earth molten salt waste residue contains 471Kg of rare earth REO, the percentage content of a single rare earth and the test of non-rare earth content are shown in Table 1;
[0032] Table 1: Raw material distribution table
[0033] project La 2 o 3
CeO 2
PR 6 o 11
Nd 2 o 3
SM 2 o 3
Eu 2 o 3
Gd 2 o 3
Tb 4 o 7
Dy 2 o 3
quality(%) 2.94 0.07 19.18 76.84 0.07 <0.01
0.53 <0.01
0.22 project Ho 2 o 3
Er 2 o 3
T m 2 o 3
Yb 2 o 3
Lu 2 o 3
Y 2 o 3
REO Fe 2 o 3
F quality(%) 0.10 <0.01
<0.01
<0.01
<0.01
<0.01
47.10 7.58 16.57
[0034] Production steps:
[0035] (1) The molten salt waste slag raw material is crushed into a powder with a particle size of about 100 mesh by a Raymond machine;
[0036] (2) Roasting alkali conversion: mix the powder and caustic soda in step (...
Embodiment 2
[0046]Example 2: 850Kg of rare earth molten salt waste residue contains 360Kg of rare earth REO, the percentage content of a single rare earth and the test of non-rare earth content are shown in Table 4.
[0047] Table 4: Raw material distribution table
[0048]
[0049] Production steps:
[0050] (1) The molten salt waste slag raw material is crushed into a powder with a particle size of about 100 mesh by a Raymond machine;
[0051] (2) Roasting soda conversion: Mix the powder and caustic soda in step (1) evenly at a weight ratio of 1:0.7, put it in a bowl, and roast it in a push-pull kiln at 600°C for 4 hours. The blocky alkali melt obtained was pulverized in time to about 100 mesh with a Raymond machine;
[0052] (3) Washing of alkali-melted products: Add the alkali-melted product and water to the washing bucket at a weight ratio of 1:10, stir for 1 hour, and squeeze to obtain washing slag. Repeat 2 times until the washing water pH=9 to obtain the washing residue.
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com