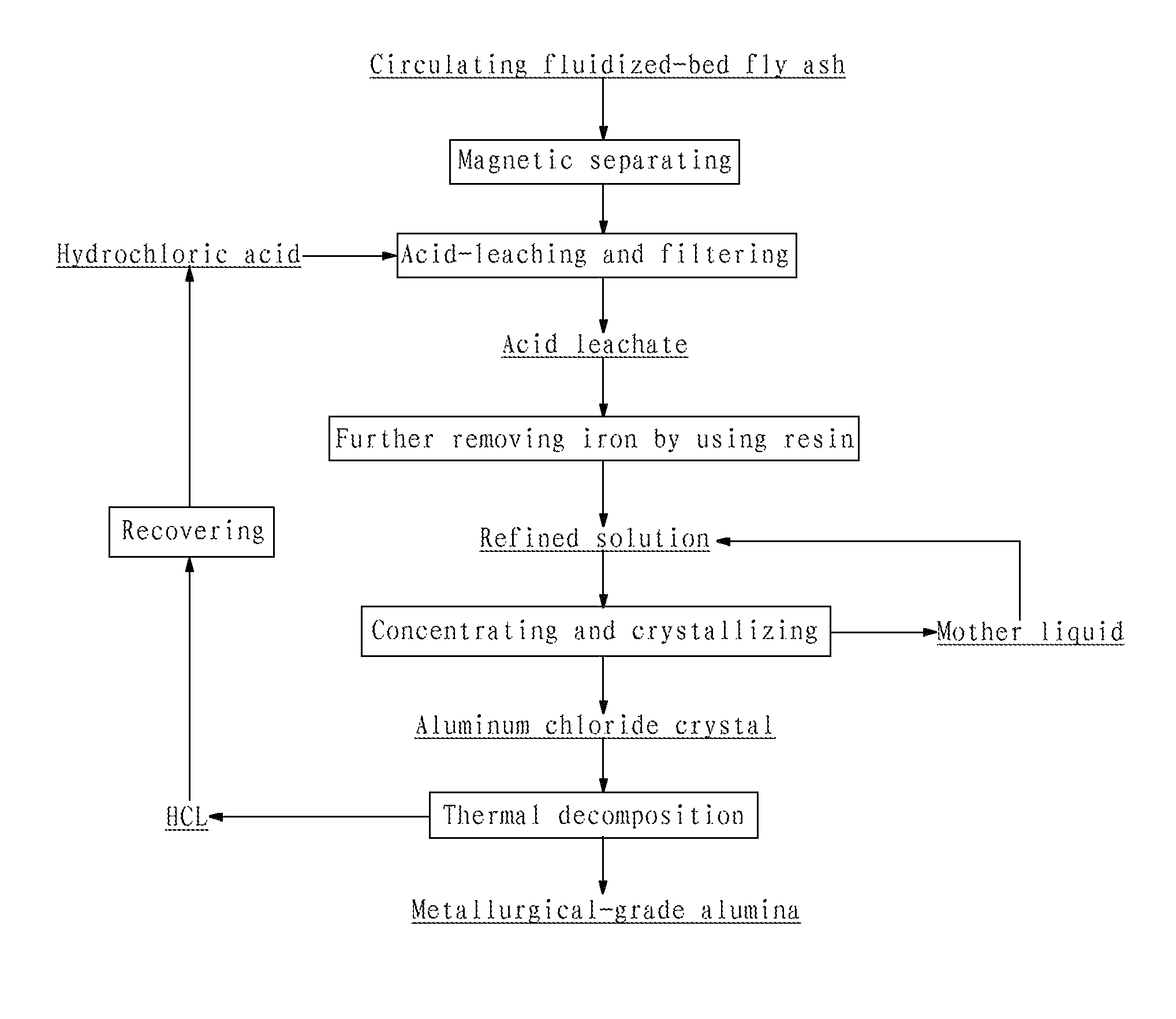
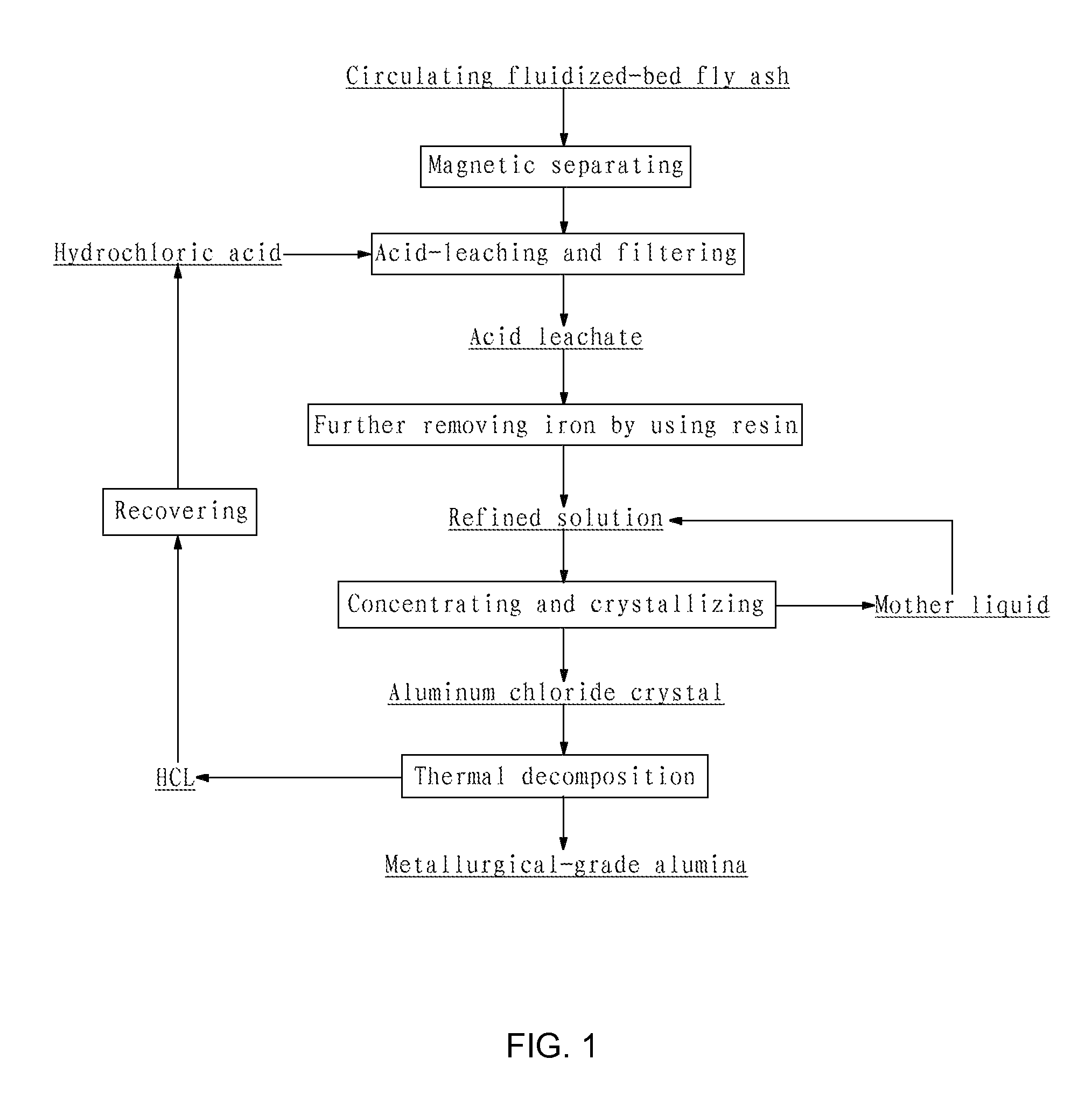
Method for preparing metallurgical-grade alumina by using fluidized bed fly ash
a technology of fly ash and metallurgical grade, which is applied in the direction of inorganic chemistry, solid separation, aluminum oxide/hydroxide, etc., can solve the problems of occupying a large area of fly ash, affecting product quality, and seriously polluting the environment, so as to achieve stable product quality, low production cost, and simple method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
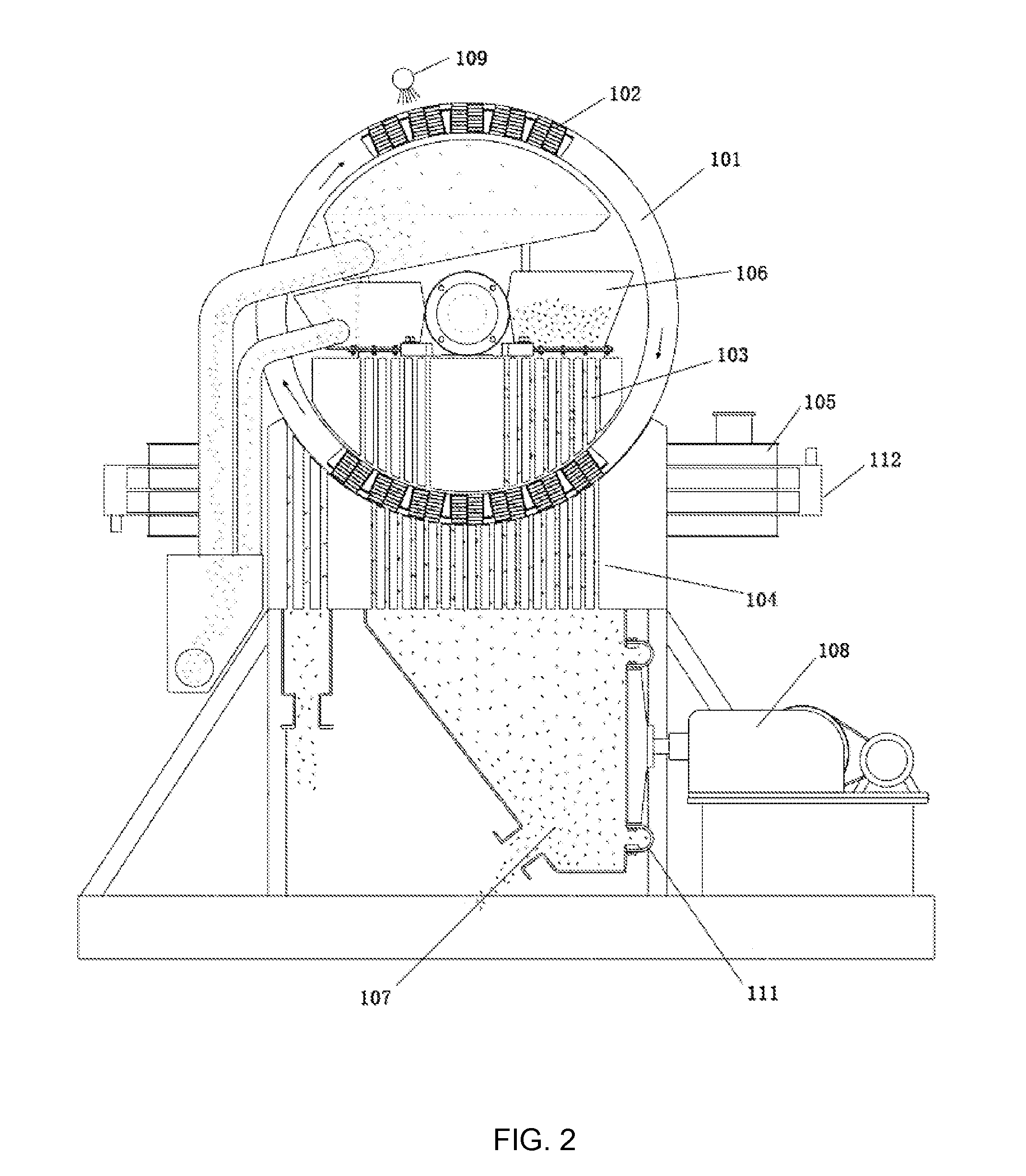
[0063](1) Crushing the circulating fluidized-bed fly ash to a size of 200 mesh, adding water into the crushed fly ash to prepare a slurry having a solid content of 33 wt %, removing iron contained in the slurry by wet magnetic separation using the vertical magnetic separator as illustrated in FIG. 2 for two times at a magnetic field strength of 15,000 Gs, such that the iron content of the fly ash was reduced to 0.76 wt %, and pressure-filtering the slurry by a plate-and-frame filter press to form a filter cake having a solid content of 37.5 wt %;
[0064](2) adding industrial hydrochloric acid having a concentration of 28 wt % into the filter cake to perform acid-leaching reaction, wherein the molar ratio of HCl contained in the hydrochloric acid to alumina contained in the fly ash was 5:1, the reaction temperature was 150° C., the reaction pressure was 1.0 MPa and the reaction time was 2 h, and then pressure-filtering and washing the discharged reaction product to yield a hydrochloric...
example 2
[0070]The operation conditions were the same as those of Example 1 except step (1). Step (1) is adjusted as follows:
[0071]Crushing the circulating fluidized-bed fly ash to a size of 300 mesh, adding water therein to prepare a slurry having a solid content of 25 wt %, removing iron from the slurry by wet magnetic separation using the vertical magnetic separator as illustrated in FIG. 2 for three times at a magnetic field strength of 10,000 Gs, such that the iron content of the fly ash was reduced to 0.81 wt %, and pressure-filtering the slurry by the plate-and-frame filter press to form a filter cake having a solid content of 32.0 wt %.
[0072]The chemical components of the obtained alumina product were measured and shown in Table 2.
example 3
[0073]The operation conditions were the same as those of Example 1 except step (1). Step (1) was adjusted as follows:
[0074]Crushing the circulating fluidized-bed fly ash to a size of 150 mesh, adding water therein to prepare a slurry having a solid content of 40 wt %, removing iron from the slurry by wet magnetic separation using the vertical magnetic separator as illustrated in FIG. 2 for two times at a magnetic field strength of 20,000 Gs, such that the iron content of the fly ash was reduced to 0.69 wt %, and pressure-filtering the slurry by the plate-and-frame filter press to form a filter cake having a solid content of 43.0 wt %.
[0075]The chemical components of the obtained alumina product were measured and shown in Table 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com