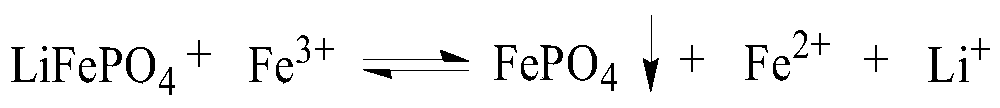Method for comprehensive recycling waste lithium iron phosphate battery cathode material
A technology of lithium iron phosphate battery and positive electrode material, applied in battery recycling, waste collector recycling, positive electrode and other directions, can solve the problems of complex process route, increase production cost, acid can not be recycled, etc., achieve wide source, reduce Cost recovery, high leaching efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
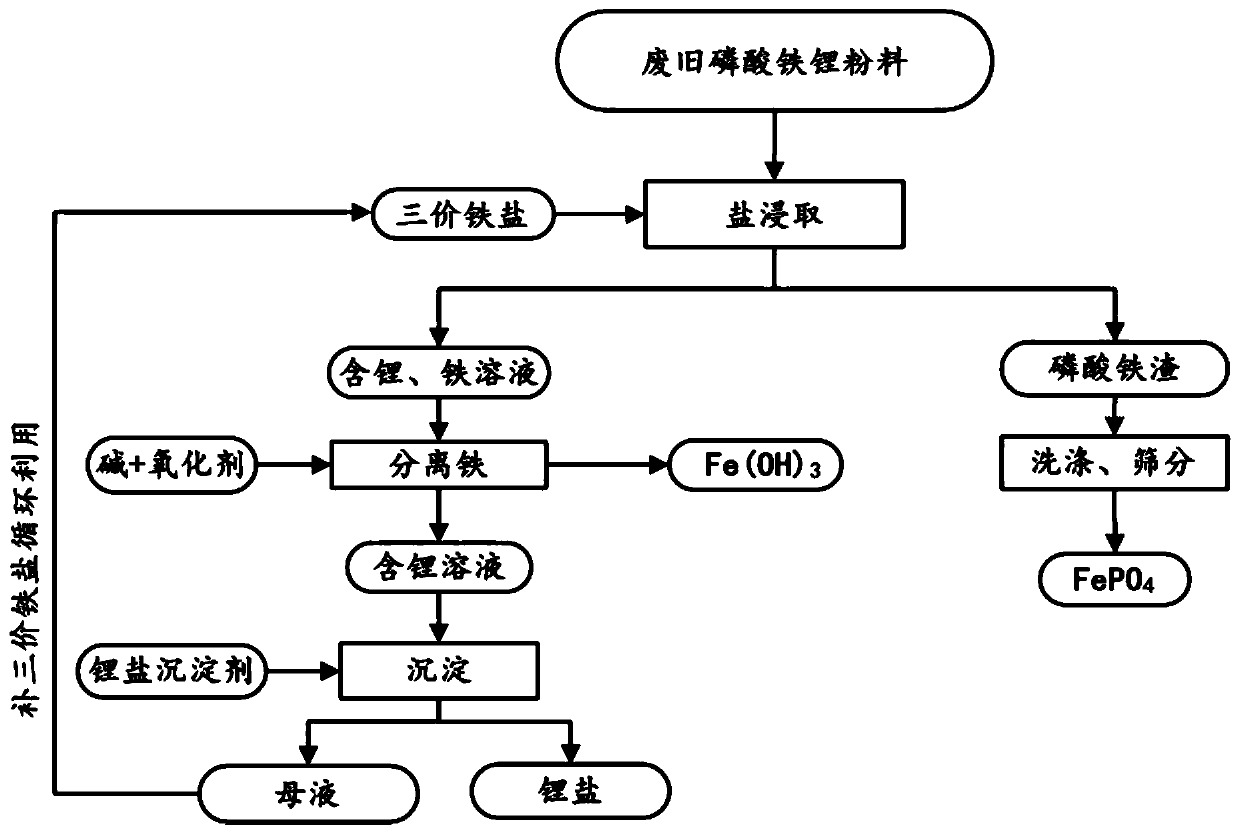
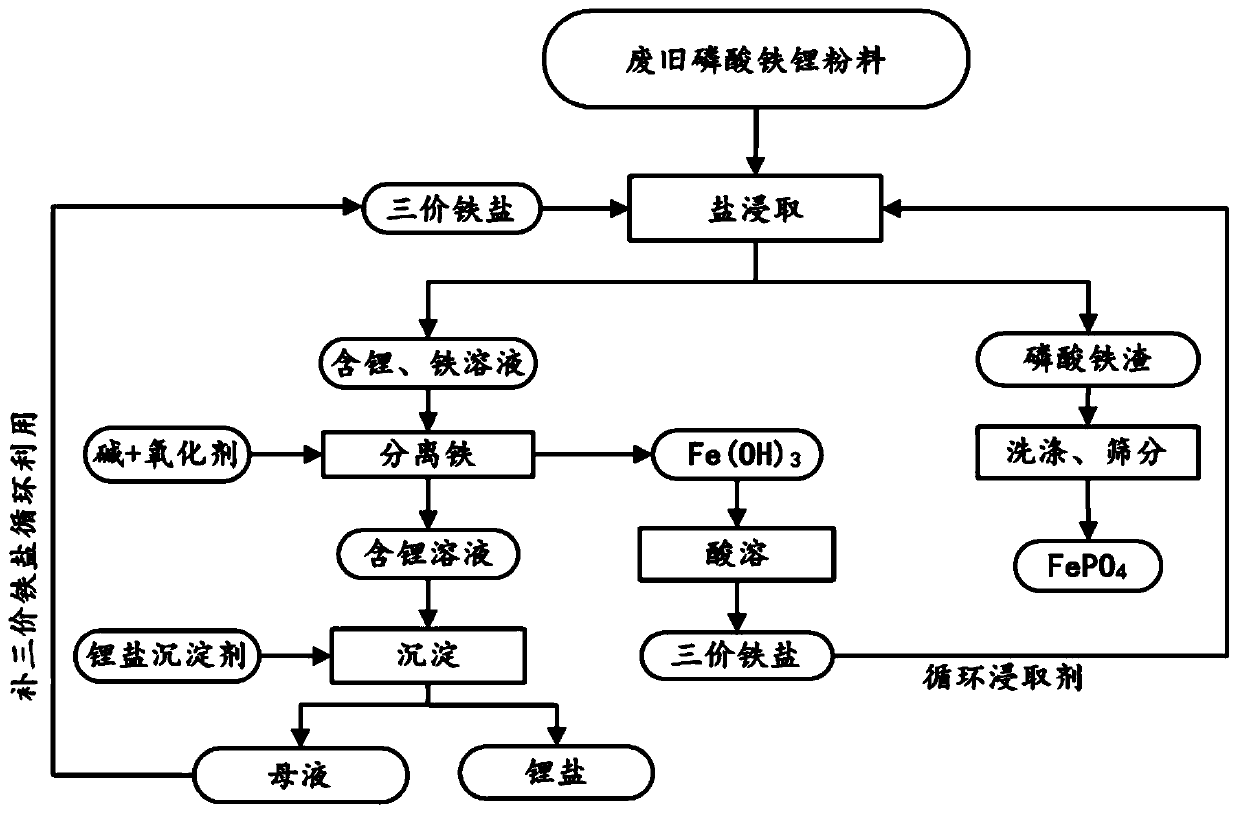
[0065] (1) 100g mass fraction of 93.27% lithium iron phosphate waste was pulverized and sieved, and then 1.875mol / L ferric sulfate solution was added for stirring reaction, wherein, 500g lithium iron phosphate waste was added to every liter of ferric sulfate solution, and the reaction temperature was 25°C. The reaction time is 23min, and a solution containing metal ions such as lithium and iron is obtained;
[0066] (2) filter step (1) gained solution, obtain ferric phosphate slag and lithium, iron solution;
[0067] (3) washing the ferric phosphate slag obtained in step (2) with water to obtain crude ferric phosphate;
[0068] (4) Add 5mol / L sodium hydroxide solution to the lithium-containing and iron-containing solution gained in step (2), and feed oxygen, filter after the reaction to obtain iron hydroxide slag and lithium-containing solution;
[0069] (5) in step (4) gained iron hydroxide slag, add in 2mol / L sulfuric acid solution, the iron salt solution that obtains can b...
Embodiment 2
[0072] (1) 100g mass fraction of 93.27% lithium iron phosphate waste was pulverized and sieved, and then 1.5mol / L iron sulfate solution was added to stir the reaction, wherein, 400g lithium iron phosphate waste was added to every liter of iron sulfate solution, and the reaction temperature was 70°C. The reaction time is 40min, and a solution containing metal ions such as lithium and iron is obtained;
[0073] (2) filter step (1) gained solution, obtain ferric phosphate slag and lithium, iron solution;
[0074] (3) washing the ferric phosphate slag obtained in step (2) with water to obtain crude ferric phosphate;
[0075] (4) Add 4mol / L potassium hydroxide solution to the lithium-containing and iron-containing solution gained in step (2), and feed oxygen, filter after the reaction to obtain iron hydroxide slag and lithium-containing solution;
[0076] (5) adding in the 1.5mol / L sulfuric acid solution in the iron hydroxide slag gained in step (4), the iron salt solution obtaine...
Embodiment 3
[0079] (1) 100g mass fraction of 93.27% lithium iron phosphate waste was pulverized and sieved, and then 0.12mol / L iron sulfate solution was added to stir the reaction. Wherein, 40g lithium iron phosphate waste was added to every liter of iron sulfate solution, and the reaction temperature was 25°C. The reaction time is 30min, and a solution containing metal ions such as lithium and iron is obtained;
[0080] (2) filter step (1) gained solution, obtain ferric phosphate slag and lithium, iron solution;
[0081] (3) washing the ferric phosphate slag obtained in step (2) with water to obtain crude ferric phosphate;
[0082] (4) adding 2mol / L sodium hydroxide solution to the lithium-containing and iron-containing solution obtained in step (2), and feeding oxygen, and filtering after the reaction to obtain iron hydroxide slag and lithium-containing solution;
[0083] (5) adding in the 1mol / L sulfuric acid solution in the iron hydroxide slag gained in step (4), the iron salt soluti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com