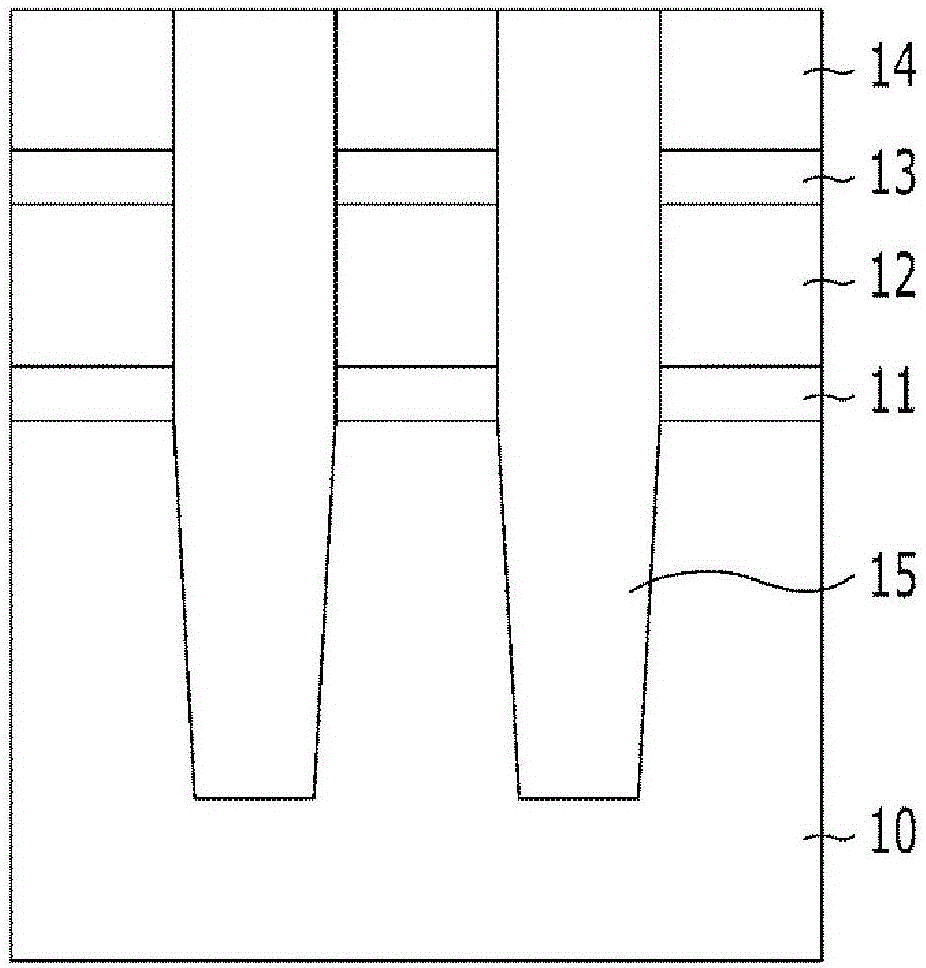
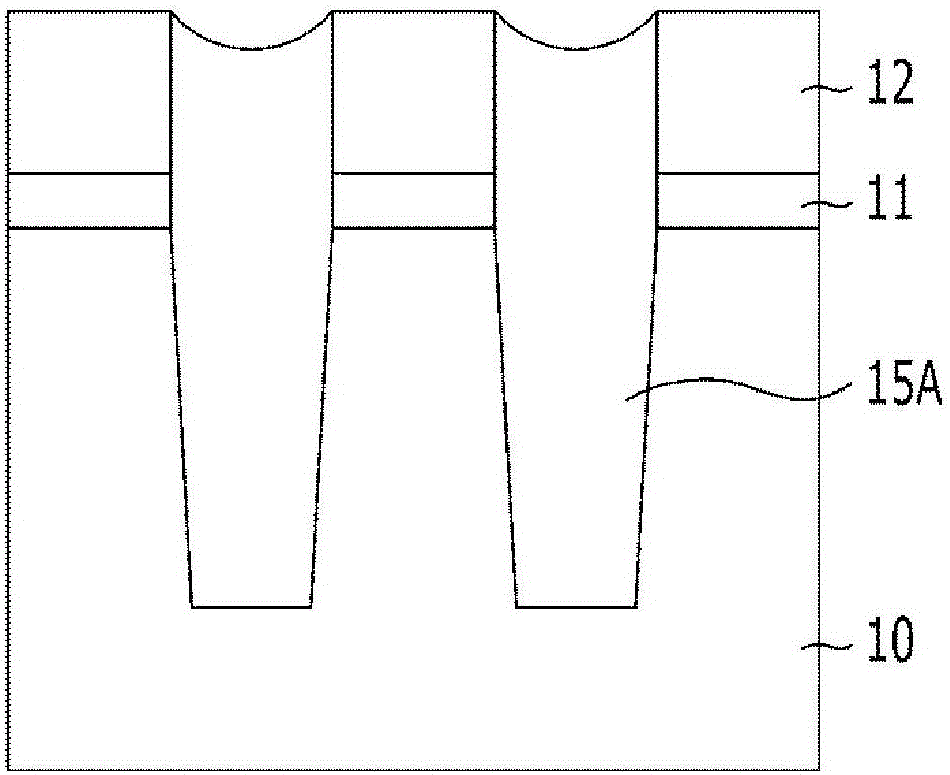
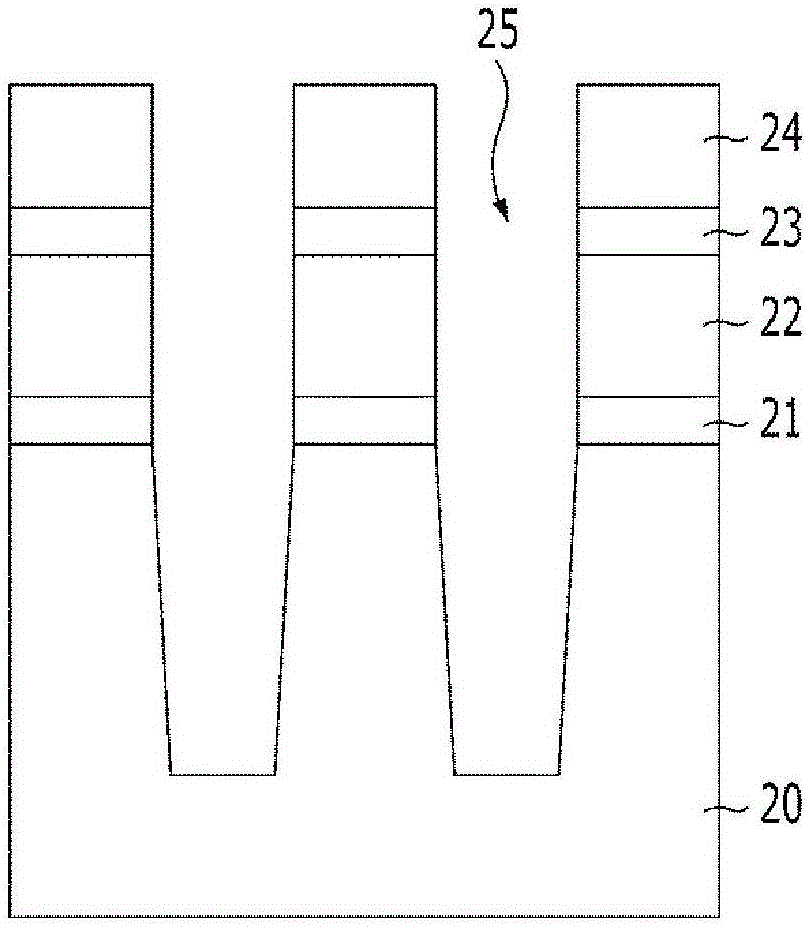
Composition for etching
A composition and compound technology, applied in the direction of surface etching compositions, semiconductor devices, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems affecting substrates, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach A
[0255] [First Embodiment A: Preparation of Etching Composition]
[0256] In the first embodiment A, an etching composition may be produced by mixing at least one silane inorganic acid salt and phosphoric acid in a predetermined weight ratio as shown in Table 1A below. As the first mineral acid, an 85% aqueous solution was used.
[0257] Table 1A
[0258]
[0259] 1)1 st IA: First Inorganic Acid
[0260] 2) 2 nd IA: Second Inorganic Acid
[0261] 3) PA: phosphoric acid
[0262] Figure 5 is an image showing nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) data of a silane mineral acid salt produced according to the first embodiment A.
[0263] refer to Figure 5 , an image showing at least one silane inorganic acid salt in an etching composition according to at least one embodiment. That is, with R 1 is methyl and R 2 to R 4 The compound represented by the chemical formula A1 which is chlorine reacts with phosphoric acid (for example, the second inorganic acid). Thus, at least ...
experiment Embodiment A1
[0264] [Experimental Example A1: Measurement of Selectivity of Etching Composition]
[0265] Using the etching composition of the present embodiment, the etching of the nitride layer and the oxide layer was performed at a process temperature of 157°C. The etching rate and selectivity of the nitride layer and the oxide layer were measured using an ellipsometer (NANOVIEW, SEMG-1000) of a film thickness measurement system. The measurement results are shown in Table A2 below. The etch rate was determined by etching each layer for about 300 seconds and measuring the difference between the thickness of each layer before etching and the layer thickness of each layer after etching. Therefore, the etching rate is obtained by dividing the thickness difference by the etching time (minutes). Etching selectivity is expressed as the ratio of the etching rate of the nitride layer to the etching rate of the oxide layer.
[0266] Table A2
[0267]
[0268] 1) ThO: thermal oxide layer
...
experiment Embodiment A2
[0276] [Experimental Example A2: Measurement of change with time]
[0277] The etching compositions produced in Examples A1 and A2 were mixed with phosphoric acid. Etching of the nitride layer and the oxide layer was performed using each mixture immediately after mixing (0 hour) and at 8 hours after mixing. The etch rate and selectivity of nitride and oxide layers were measured. In Comparative Example 4 (base PA), the etch speed and selectivity of the nitride layer and the oxide layer were evaluated using phosphoric acid in the same manner as in the above examples.
[0278] The evaluation was performed at a process temperature of 160°C. The etch rate was determined by etching each layer for about 300 seconds and measuring the difference between the thickness of each layer before etching and the layer thickness of each layer after etching. Therefore, the etching rate is obtained by dividing the thickness difference by the etching time (minutes). The etching selectivity is e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com