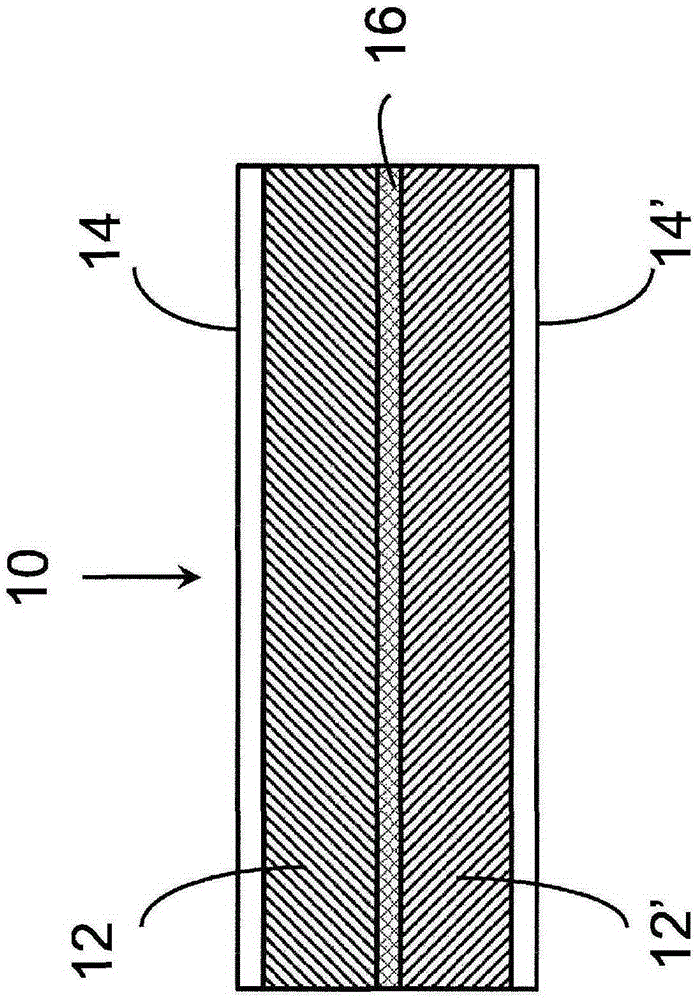
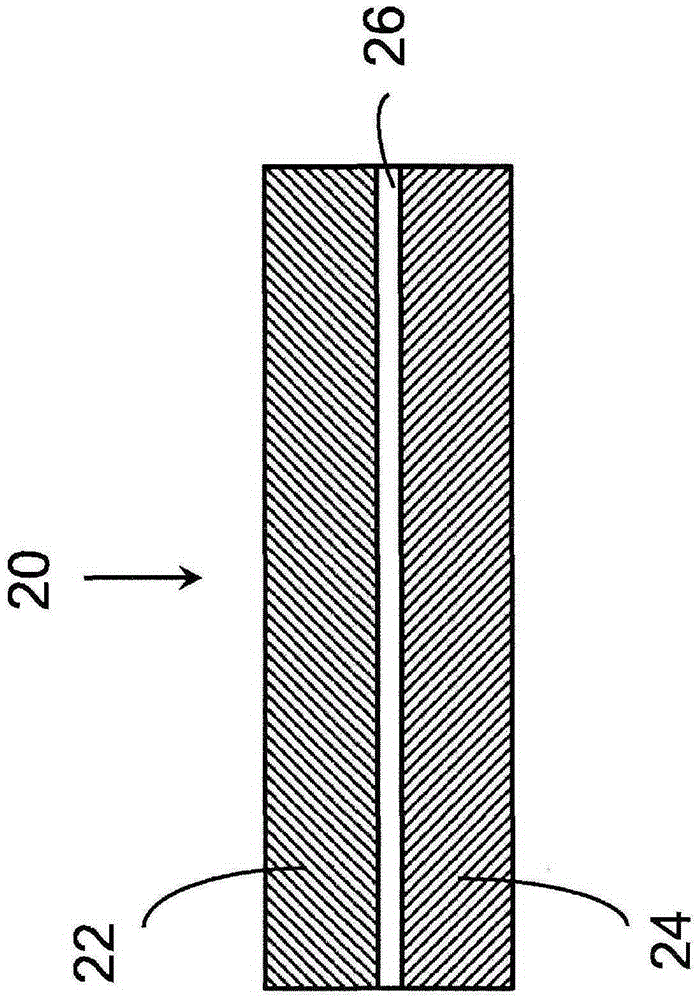
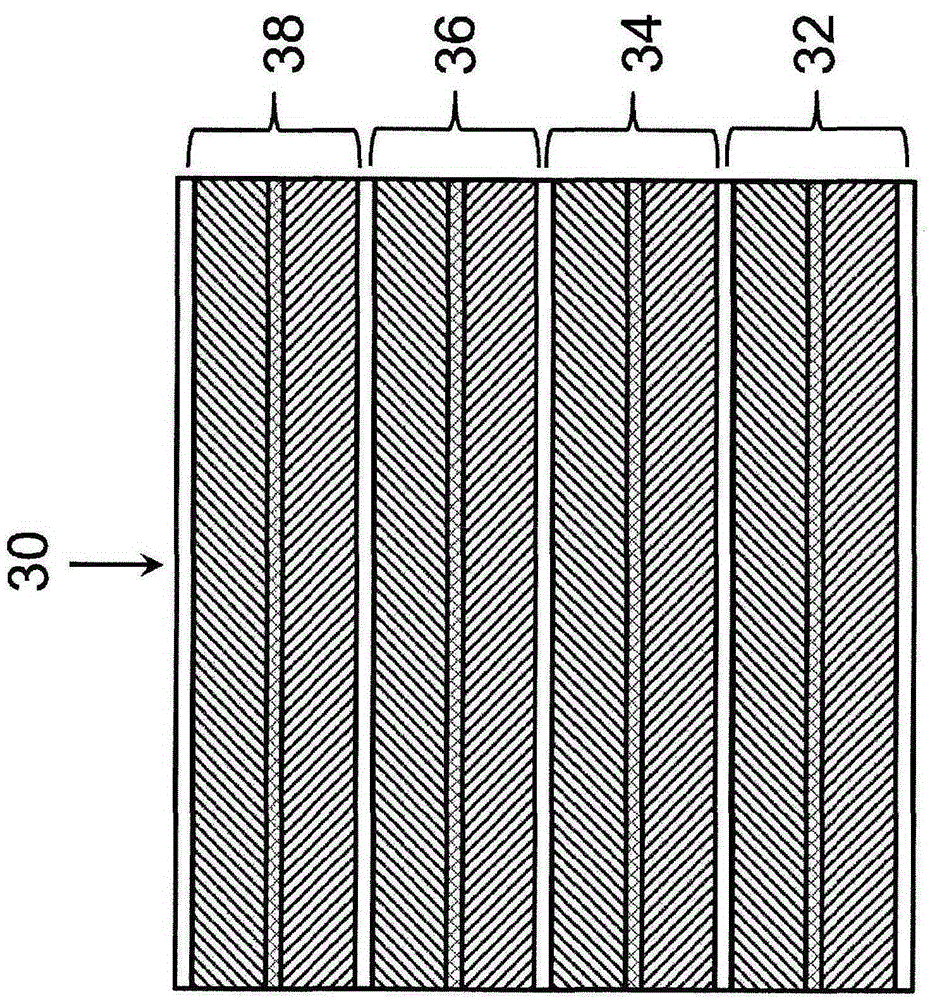
Methods of enhancing electrochemical double layer capacitor (EDLC) performance and EDLC devices formed therefrom
A double-layer capacitor, electrochemical technology, applied in the manufacture of hybrid/electric double-layer capacitors, protection/regulation of hybrid/electric double-layer capacitors, battery circuit devices, etc., can solve the problems of shortening the life of EDLC, shortening the life of EDLC, etc., to achieve The effect of increasing life and enhancing performance stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0362] Preparation of phosphonium ionic liquids. AgSO 3 CF 3 Fill a 50ml round bottom (Rb) flask and fit to a 3cm swivel frit. Evacuate the flask and place it in the glove box. In the glove box, di-n-propylethylmethylphosphonium iodide was added and the flask was reassembled, a vacuum line was connected, evacuated, and anhydrous THF was transferred thereto under reduced pressure. The flask can be warmed to room temperature and then to 40°C for 2 hours. This resulted in the formation of a pale green bead solid. The solid was removed by filtration. This produced a pearly, milky white solution. Volatile material was removed under high vacuum and heated using a 30°C hot water bath. This resulted in 0.470 g of white crystalline material. The material was subjected to thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and Figure 7 The results are shown in .
Embodiment 2
[0364] Additional phosphonium ionic liquids were prepared. Di-n-propylethylmethylphosphonium iodide was charged to a 100 ml Rb flask in the glove box, then removed and dissolved in 50 ml DIH 2 O middle. AgO 2 CCF 3 Addition of this solution immediately produced a yellow, beaded precipitate. After stirring for 2 hours, AgI was removed by filtration and washed with 5 ml of DIH 2 O Wash the filter cake three times. The gravity water was removed on a rotary evaporator. This then yielded a clear low viscosity liquid which was dried under high vacuum with heating and stirring. This results in solidification of the material. Gentle warming of the white solid in a warm water bath yielded a liquid that appeared to be melting above room temperature. This experiment yielded 0.410 g of material. exist Figure 8A The reaction scheme is described in . Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and escape gas analysis (EGA) were performed on the material and in Figure 8B and Figure 8C T...
Embodiment 3
[0366] In this example, di-n-propylethylmethylphosphonium iodide was added to a 100 ml Rb flask in the glove box and then removed to a fume hood and dissolved in 70 ml MeOH. Next, add AgO 2 CCF 2 CF 2 CF 3 , a yellow colored slurry was produced immediately. After 3 hours of stirring the solids were removed by filtration, the bulk MeOH was removed by rotary evaporation and the remaining residue was dried under high vacuum. This produced a yellow gelatinous slurry material. When "melting" off via scraping of the flask, a "liquid" type crystal was observed to form at the rim of the Rb flask. This experiment yielded 0.618 g of material. The material was subjected to thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and Figure 9A The results are shown in . Evolved Gas Analysis (EGA) was also performed and at Figure 9B The results are shown in .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com