Corrosion-resistant zirconium-tin-niobium alloy for nuclear reactor core and preparation method thereof
A nuclear reactor, corrosion-resistant technology, applied in the field of zirconium alloy materials, to achieve excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties, improve corrosion properties, improve corrosion resistance and tensile properties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
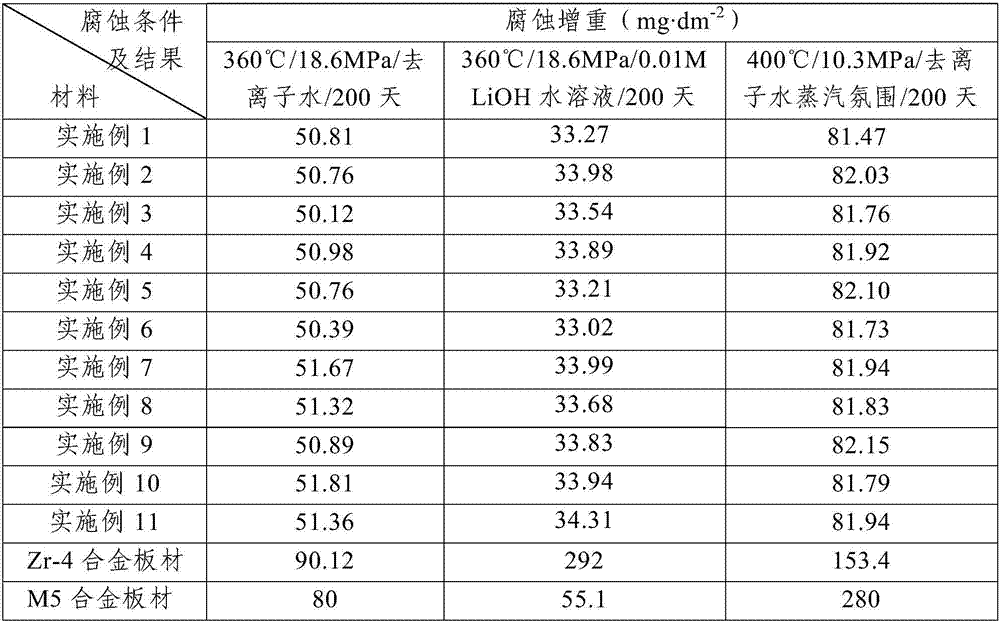
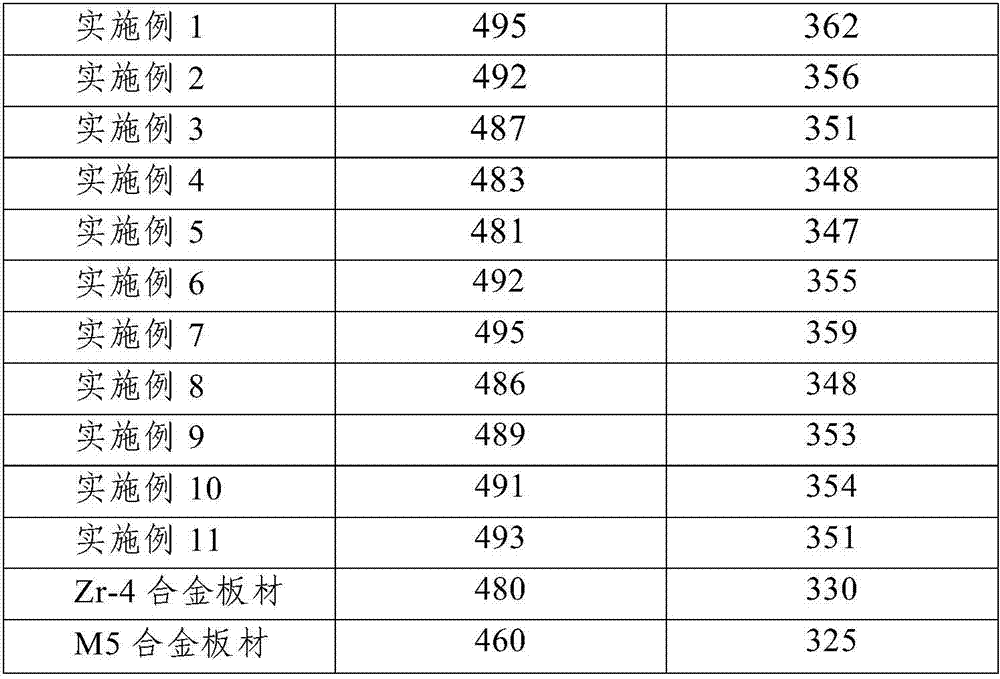
[0031] The corrosion-resistant zirconium-tin-niobium alloy for the nuclear reactor core of this embodiment is composed of the following mass percentages: Sn 1.2%, Nb 0.3%, Fe 0.4%, Cr 0.2%, Cu 0.1%, Mg 0.05%, O 1200ppm, the remainder The amount is Zr and unavoidable impurities.
[0032] The method for preparing the described zirconium-tin-niobium alloy in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0033] Step 1. Using nuclear-grade sponge zirconium, copper scraps, and magnesium particles as raw materials, a Zr-Cu-Mg master alloy is prepared by melting in a vacuum induction furnace, and the mass percentage of Cu in the Zr-Cu-Mg master alloy is 50% %, the mass percentage of Mg is 25%, and the balance is Zr;
[0034] Step 2, using nuclear-grade sponge zirconium and niobium chips as raw materials, adopting a vacuum consumable electric arc furnace to melt three times to obtain a Zr-Nb master alloy, the mass percentage of Nb in the Zr-Nb master alloy is 60%, and the remaining...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The corrosion-resistant zirconium-tin-niobium alloy for the nuclear reactor core of this embodiment is composed of the following mass percentages: Sn1.1%, Nb 0.15%, Fe 0.3%, Cr 0.1%, Cu 0.2%, Mg 0.12%, O 1100ppm, remainder The amount is Zr and unavoidable impurities.
[0040] The method for preparing the described zirconium-tin-niobium alloy in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0041] Step 1. Using nuclear-grade sponge zirconium, copper scraps, and magnesium particles as raw materials, a Zr-Cu-Mg master alloy is prepared by melting in a vacuum induction furnace, and the mass percentage of Cu in the Zr-Cu-Mg master alloy is 20 %, the mass percentage of Mg is 12%, and the balance is Zr;
[0042] Step 2, using nuclear-grade sponge zirconium and niobium chips as raw materials, adopting vacuum consumable electric arc furnace melting three times to prepare a Zr-Nb master alloy, the mass percentage of Nb in the Zr-Nb master alloy is 50%, and the remaining The ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] The corrosion-resistant zirconium-tin-niobium alloy for the nuclear reactor core of this embodiment is composed of the following mass percentages: Sn 1.0%, Nb 0.4%, Fe 0.2%, Cr 0.25%, Cu 0.05%, Mg 0.05%, O 1000ppm, the remainder The amount is Zr and unavoidable impurities.
[0048] The method for preparing the described zirconium-tin-niobium alloy in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0049] Step 1. Using nuclear-grade sponge zirconium, copper scraps, and magnesium particles as raw materials, a Zr-Cu-Mg master alloy is prepared by melting in a vacuum induction furnace, and the mass percentage of Cu in the Zr-Cu-Mg master alloy is 40 %, the mass percentage of Mg is 40%, and the balance is Zr;
[0050] Step 2, using nuclear-grade sponge zirconium and niobium chips as raw materials, adopting vacuum consumable electric arc furnace melting three times to prepare a Zr-Nb master alloy, the mass percentage of Nb in the Zr-Nb master alloy is 40%, and the remaining...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| corrosion | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com